The Circulatory System: Blood Outline Part 1
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Circulatory Functions (3)
Transportation: oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, waste, hormones and cells
Protection: immune cells, initiates clotting
Regulation: fluid balance, ECF pH stabilization, and temp control
Adults have how much blood?
4-6 liters of blood
Blood is a liquid connective tissue in cells + matrix what are these?
Matrix of blood: Plasma— clear, light yellow fluid
Cells: RBC, WBC, and platelets
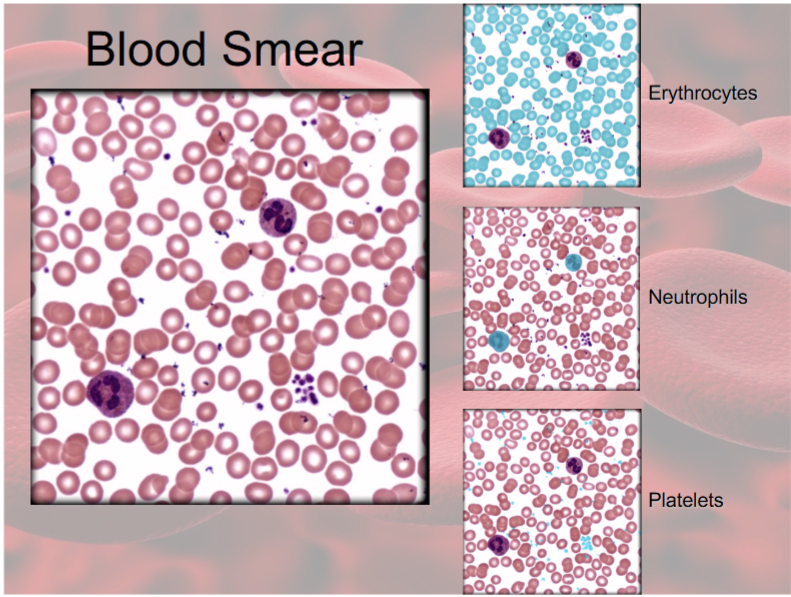
7 kinds of formed elements in blood
1) erythrocytes (RBCs)
2) Platelets
Leukocytes (WBCs)
Granulocytes
3) Neutrophils
4) Eosinophils
5) Basophils
Agranulocytes
6) Lymphocytes
7) Monocytes
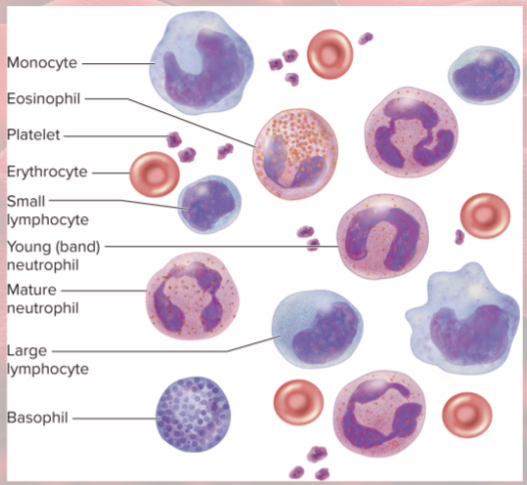
Hematocrit
% of volume of RBCs
anemia vs polycynemia
too few RBCs vs too many RBCs
Albumins (category of plasma protein) (abundance and what it does)
smallest and most abundant
contribute to viscosity & osmolarity; influence BP & flow
Globulins (alpha, beta, antibodies) (category of plasma protein)(abundance and what it does)
2nd most abundant plasma protein
transporters
provide immune system function
Fibrinogen (category of plasma protein) (abundance and what it does)
least abundant plasma protein
precursor of fibrin— help form blood clots
Blood plasma nitrogenous compounds
free amino acids
nitrogenous wastes (urea)
toxic end products of catabolism
removed by kidneys
Viscosity
resistance of fluid to flow, b/c of cohesion
thickness
honey is more viscous than water
Osmolarity of blood
total molarity of dissolved particles that cannot pass through BV wall
osmolarity of blood (too high vs too low)
blood absorbs too much water, BP increases
too much water stays in tissues (edema), BP drops
optimum osmolarity achieved by regulation of sodium, proteins, and RBCs
hypoproteinemia
deficiency of plasma proteins
starvation or lack of dietary protein
liver or kidney disease
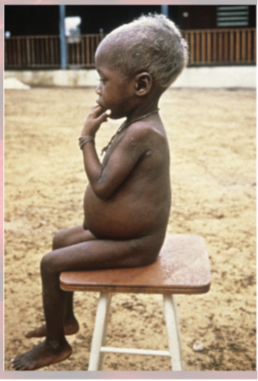
kwashiorkor
in children with severe protein deficiency
fed on cereals once weaned—swollen abdomen
Hemopoiesis
production of blood, especially formed elements
Hemopoietic tissues produce
blood cells
yolk sac produces stem cells for first blood cells
liver stops producing blood cells at birth
spleen continues lymphocyte production
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs, make RBCs and WBCs) and then…
colony-forming units (CFUs)— specialized stem cells; produce one class of formed element
blast=immature cell
cyte=mature cell
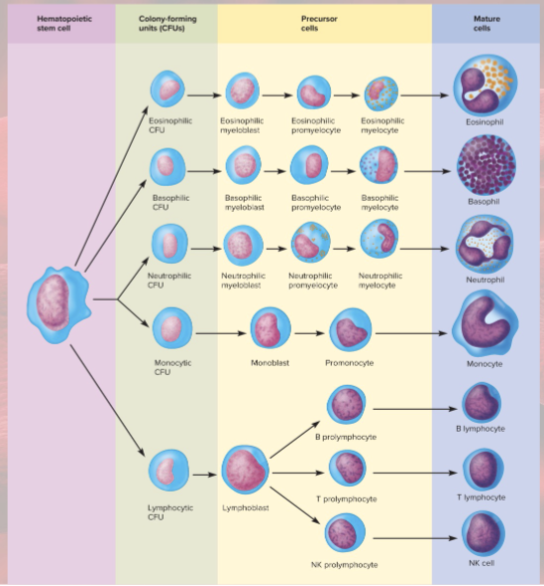
Myeloid vs lymphoid hemopoiesis
blood formation in bone marrow vs lymphatic organs
erythrocyte functions
carry oxygen from lungs to tissues
pick up carbon dioxide from tissues and bring to lungs
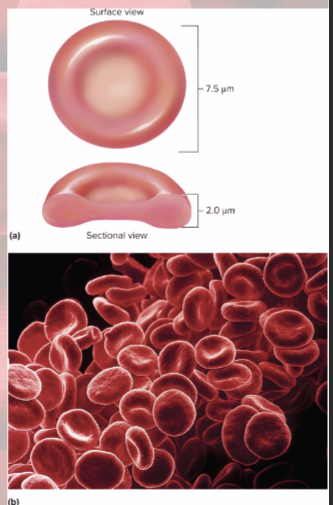
erythrocyte form
disc-shaped cell with thick rim
lose nearly all organelles during development
lack mitochondria and nucleus/DNA
cytoskeletal proteins (spectrin and actin) give membrane durability and resistance—helps it squeeze through small capillaries
erythrocyte gas transport
33% of cytoplasm is Hemoglobin (Hb)
oxygen delivery to tissues and carbon dioxide transport to lungs
carbonic anhydrase (CAH) in cytoplasm of erythrocyte
produces carbonic acid from CO2 and water
important for gas transport and pH balance
Hemoglobin anatomy
4 protein chains—globins
4 heme groups
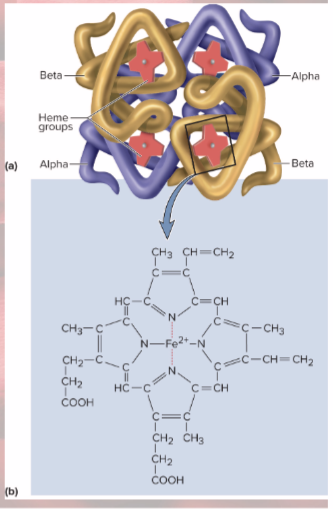
Heme groups
nonprotein moiety that binds oxygen to ferrous ion at center (this is why RBC can carry so much oxygen)
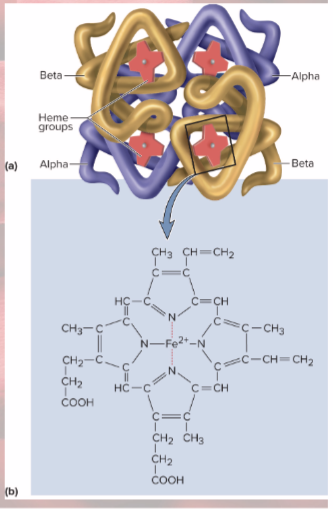
Globins
4 protein chains
2 alpha and 2 beta chains
fetal hemoglobin… likes it better than in an adult hemoglobin!
oxygen
how many erythrocytes in blood?
5 million per microliter
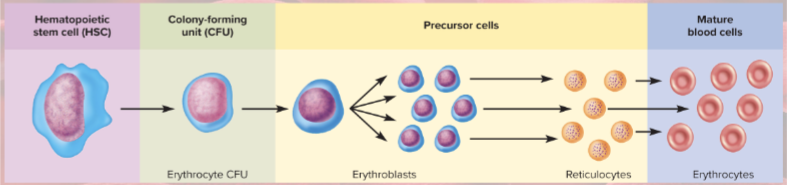
erythrocyte production process
First committed cell: erythrocyte CFU (erythropoietin (EPO) acts on CFUs to make RBCs)
Erythroblasts multiply and synthesize hemoglobin
Nucleus discarded to form reticulocyte (1% of RBCs)
Iron is a key nutritional requirement for
Hemoglobin!
lost daily through urine, feces, and bleeding
men 0.9 mg/day, women 1.7 mg/day
Vitamin B12 (meat and fish) and folic acid (leafy greens) good for
mitosis in erythropoiesis

Vitamin C (citrus fruits) and copper (mushrooms and oysters) good for
enzymes synthesizing hemoglobin

Erythrocyte negative feedback for when RBC count drops
causes kidney hypoxemia (low levels of oxygen)
kidney production of EPO stimulates bone marrow
RBC count increases
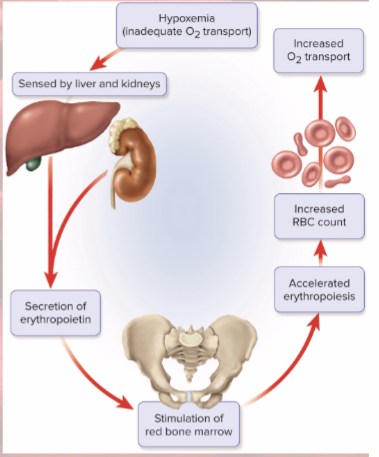
Stimuli for increasing erythropoiesis
low levels O2 (hypoxemia)
high altitude
increase in exercise
emphysema (lung disorder/ lack surface area in lungs)
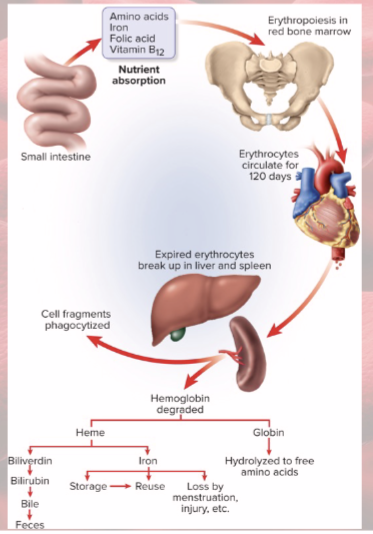
RBCs lyse in narrow channels in…
spleen
Macrophages in spleen: digest and separate heme from globin
Globins hydrolyzed into amino acids
Iron removed from heme
heme converted to biliverdin
biliverdin converted to bilirubin, released into blood
liver takes bilirubin and secretes into bile
bile concentrated in gall bladder: released into small intestines; bacteria create urobilinogen
Polycythemia def and dangers
excess RBCs
increased blood volume, BP, viscosity—risk of stroke, heart failure
Primary polycythemia (polycythemia vera)
cancer of erythropoietic cell line
Secondary polycythemia
dehydration, emphysema, high altitude, or physical conditioning
3 causes of Anemia
1) Inadequate erythropoiesis or hemoglobin synthesis
2) Hemorrhagic anemias from bleeding
3) Hemolytic anemias from RBC destruction
pernicious anemia
inadequate vitamin B12
hypoplastic anemia
slowing of erythropoiesis
aplastic anemia
cessation of erythropoiesis
3 consequences of anemia
tissue hypoxia and necrosis (tissue death from disease)
short of breath; necrosis of vital organs
blood osmolarity reduced, producing tissue edema
blood viscosity low
heart races, BP drops
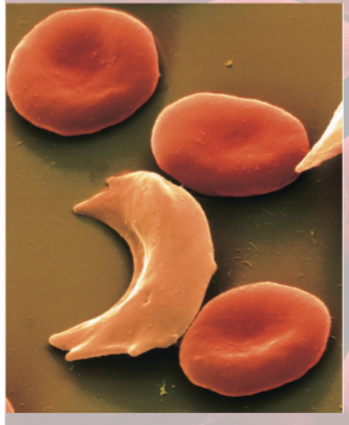
Sickle-Cell disease
Hereditary hemoglobin defects
Caused by recessive allele, modifies structure of hemoglobin
Hemoglobin does not bind oxygen well
clump together and can block blood vessels—intense pain
risks: kidney/heart failure, stroke, or paralysis