Mathematical Language, Set Operations, and Logic Fundamentals
1/201
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
202 Terms
What does the symbol ∈ represent in set theory?
It denotes that an object is an element of a set.
What does the symbol ∉ represent in set theory?
It denotes that an object is not an element of a set.
Who first formally used the term 'set'?
Georg Cantor, a German mathematician.
What is the union of two sets A and B?
The union, denoted by A ∪ B, is the set containing all elements found in A or in B or in both.
How is the union of sets represented in symbols?
A ∪ B = {x | x ∈ A or x ∈ B}.
What is an example of a union of sets?
If A = {1, 2, 4} and B = {3, 4, 5, 6}, then A ∪ B = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}.
What does it mean for set A to be a subset of set B?
A is a subset of B if every element of A is also an element of B, denoted A ⊆ B.
What is the notation for when A is not a subset of B?
A ⊈ B.
What is a Venn diagram?
A pictorial representation for sets and their fundamental operations.
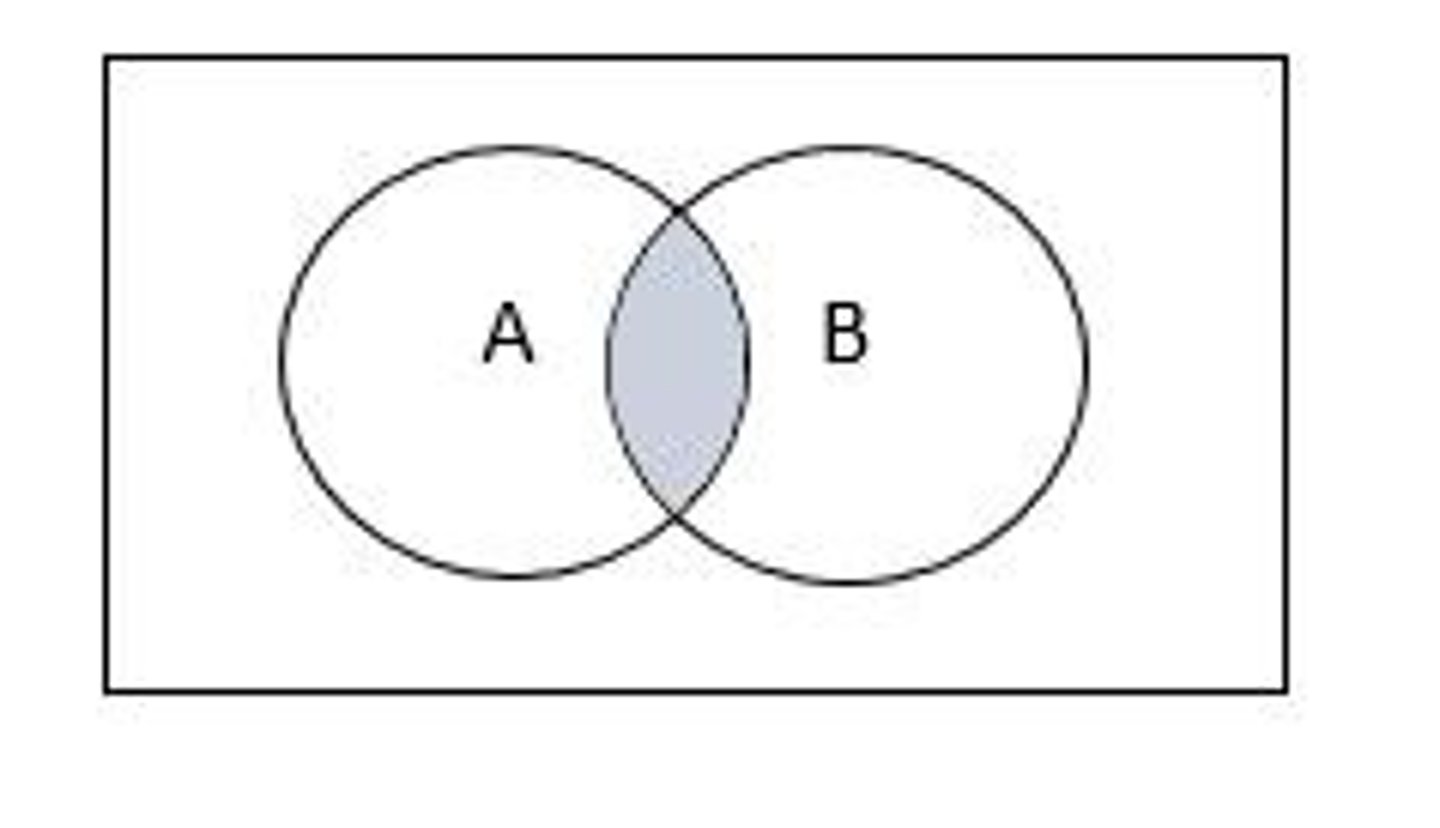
What does the shaded portion of a Venn diagram represent?
The union of sets.
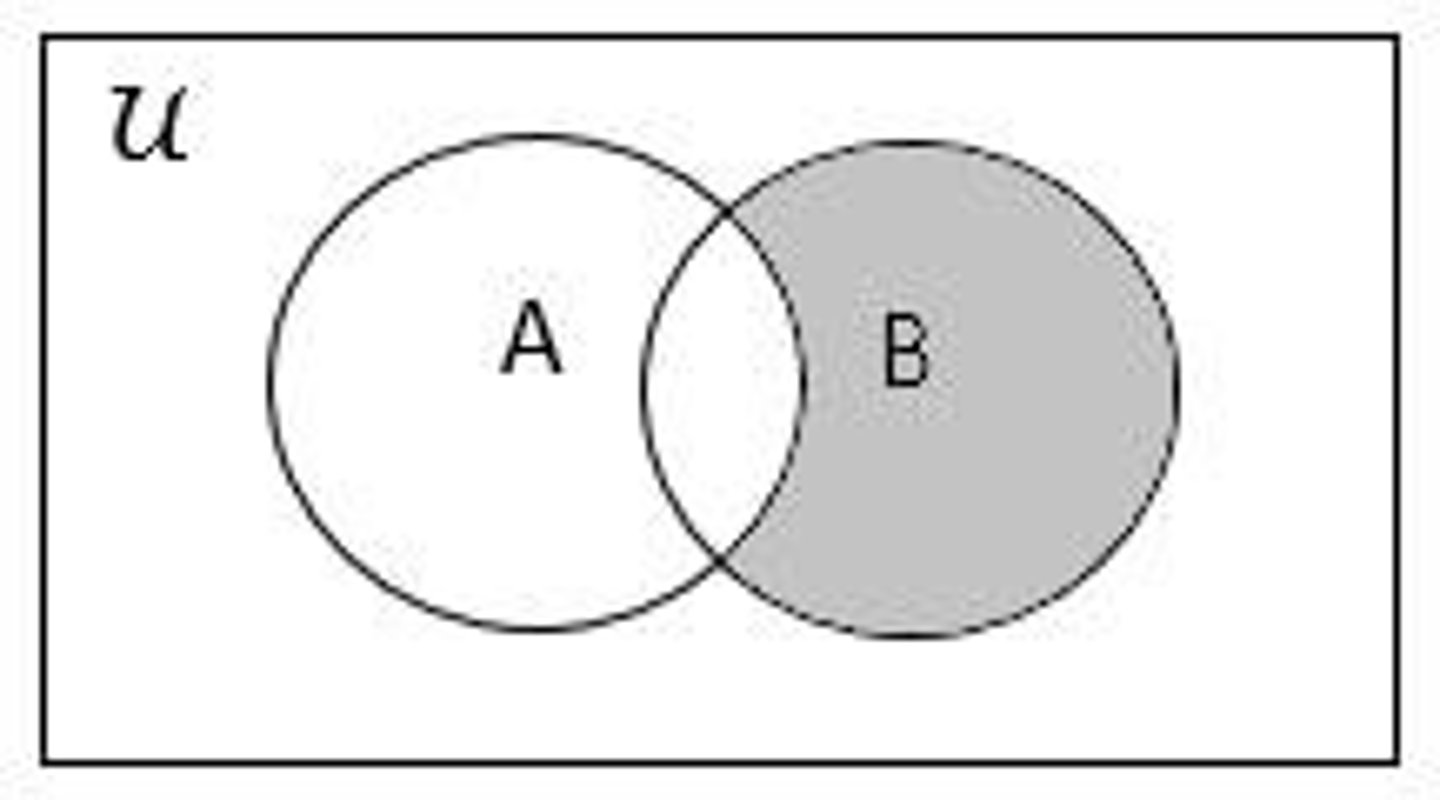
What is the first example of a set given in the notes?
Let S = {a, b, c}.
What is the set of the first 10 positive odd integers?
B = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19}.
What is an element in a set?
An object that belongs to a set.
What is the notation for the set containing elements common to both A and B?
The intersection of sets, denoted by A ∩ B.
What is the difference between a set and a list?
A set is a collection of distinct objects, while a list can contain duplicates and has a specific order.
What is a subset?
A set A is a subset of set B, written A ⊆ B, if every element of A is also an element of B.
What is a proper subset?
A set A is a proper subset of set B, written A ⊂ B, if A is a subset of B and there exists at least one element in B that is not in A.
What does A ⊈ C mean?
It means that A is not a subset of C, indicating at least one member of A is not in C.
What is the intersection of sets A and B?
The intersection of two sets A and B, denoted by A ∩ B, is the set of all elements common to both A and B.
What does it mean for two sets to be disjoint?
Two sets A and B are disjoint if A ∩ B = ∅, meaning they have no elements in common.
What is the complement of a set?
The complement of a set A, denoted A', is the set of elements in the universal set U that are not in A.
How do you denote the universal set?
The universal set is typically denoted by U and contains all elements being considered.
What is the union of sets A and B?
The union of sets A and B, denoted A ∪ B, is the set of all elements that are in A, in B, or in both.
What does A ∪ B ∪ C represent?
It represents the union of sets A, B, and C, including all unique elements from all three sets.
What is the notation for an empty set?
The empty set is denoted by ∅ or by using empty braces {}.
What is an example of a proper subset?
If A = {1, 2} and B = {1, 2, 3}, then A is a proper subset of B, written A ⊂ B.
What does A ∩ B = {4} indicate?
It indicates that the only element common to both sets A and B is 4.
What is the result of A ∩ B if A = {1, 2, 4} and B = {3, 4, 5, 6}?
A ∩ B = {4}.
What does A' represent when U = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9} and A = {1, 3, 5, 7}?
A' = {0, 2, 4, 6, 8}.
What is the relationship between the sets ℕ, ℤ, ℚ, ℝ, and ℂ?
ℕ ⊂ ℤ ⊂ ℚ ⊂ ℝ ⊂ ℂ, indicating that each set is a proper subset of the next.
What is the symbol for the null set?
The null set is represented by the symbol ∅.
What does the notation A' ∩ C' signify?
It signifies the intersection of the complements of sets A and C.
What is the result of A ∩ B if A = {nausea, night sweats} and B = {nausea, nervousness}?
A ∩ B = {nausea}.
What does A ∪ B = {nausea, night sweats, nervousness, dry mouth, swollen feet, weight gain, blurry vision, fever, trouble sleeping} represent?
It represents the union of sets A and B, listing all unique side effects.
What is the significance of the notation (A ∩ B)'?
It represents the complement of the intersection of sets A and B.
What does the notation B' ∪ (A ∩ C') indicate?
It indicates the union of the complement of B and the intersection of A with the complement of C.
What is the definition of equivalent sets?
Equivalent sets are sets that have the same number of elements.
How do you denote the set of all even numbers?
The set of all even numbers is denoted by 𝔼.
What is the definition of equal sets?
Equal sets are sets that contain exactly the same elements.
What does the notation A' = {x | x ∈ U and x ∉ A} mean?
It defines the complement of set A as all elements in the universal set U that are not in A.
What is the result of A ∩ B ∩ C if A = {nausea, night sweats} and B = {nausea, nervousness} and C = {dry mouth, nausea}?
A ∩ B ∩ C = {nausea}.
What is the intersection of the complements of sets A and C, denoted as A' ∩ C'?
{weight gain, trouble sleeping, motor mouth, darting eyes, uncontrollable falling down}
What is the result of the operation B' ∪ (A ∩ C')?
{night sweats, dry mouth, swollen feet, weight loss, eczema, motor mouth, darting eyes, uncontrollable falling down, nervousness}
What does the notation (A ∩ B)' ∩ C represent?
The intersection of the complement of the intersection of A and B with set C.
How is the set difference B - A defined?
The set of all elements of set B that are not in set A.
What is the result of the set difference A - B when A = {1, 2, 4} and B = {3, 4, 5, 6}?
{1, 2}
What does the cardinality of a set represent?
The number of distinct elements in the set.
If A = {a, b, c, d, e}, what is n(A)?
5
What is the cardinality of the set of all positive integers, ℤ+?
∞ (infinity)
What is the Cartesian product of two sets A and B?
The Cartesian product A x B is the set of all ordered pairs (a, b) where a is in A and b is in B.
How is the Cartesian product denoted?
It is denoted as A x B and read as 'A cross B'.
Given sets X = {1, 2} and Y = {3, 4}, what is X x Y?
X x Y = {(1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 3), (2, 4)}.
What is the result of B x A if A = {1, 2, 3} and B = {u, v}?
B x A = {(u, 1), (u, 2), (u, 3), (v, 1), (v, 2), (v, 3)}.
How many elements are in A x B if A has 3 elements and B has 2?
There are 6 elements in A x B, calculated as n(A) ∙ n(B).
What is a proposition?
A proposition is a declarative sentence that is either true or false but not both.
What symbols are used to denote the truth value of propositions?
T or 1 for true, and F or 0 for false.
What is an example of a proposition?
The main campus of Palawan State University is in Puerto Princesa City.
What is Goldbach's conjecture?
Every even integer greater than 4 is a sum of two odd primes; it is a proposition because it is either true or false.
What is the difference between a simple and a compound proposition?
A simple proposition conveys a single idea, while a compound proposition conveys more than one idea.
What is the negation symbol in logic?
The negation symbol is ~.
What does the conjunction symbol (∧) represent?
It represents 'and' in logical statements.
What does the disjunction symbol (∨) represent?
It represents 'or' in logical statements.
What does the implication symbol (→) indicate?
It indicates a conditional statement 'if...then...'.
What does the biconditional symbol (↔) mean?
It means 'if and only if' in logical statements.
How many elements are in Y x Y if Y = {a, b, c}?
Y x Y has 9 elements.
What is the result of Y x Z if Y = {a, b, c} and Z = {1, 2}?
Y x Z = {(a, 1), (a, 2), (b, 1), (b, 2), (c, 1), (c, 2)}.
What is the result of Z x Y?
Z x Y = {(1, a), (1, b), (1, c), (2, a), (2, b), (2, c)}.
What is the truth value of the proposition: 'Iran is a country in the Middle East'?
True.
What is the truth value of the statement: '5x + 1 = 2'?
Not a proposition (requires a value for x to determine truth).
What is the result of A ∪ B if A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} and B = {5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}?
A ∪ B = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}.
What does the notation A' represent?
A' represents the complement of set A.
What is the result of D - C' if D = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9} and C = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10}?
D - C' includes elements in D that are not in the complement of C.
What is the significance of the order of elements in a Cartesian product?
The first coordinate must come from the first set, and the second coordinate must come from the second set.
What is the negation of a proposition?
The negation of a proposition is the denial of the original idea, represented by the symbol '~' or '¬'.
How is the negation of the proposition '3 is a prime number' expressed?
The negation is '~f: 3 is not a prime number', which is false.
What is a unary operation in logic?
A unary operation is an operation that involves only one operand, such as negation.
What does the truth value table for negation indicate?
It shows that if the original proposition is true, the negation is false, and vice versa.
What is a conjunction in logic?
A conjunction is a compound proposition formed by joining two propositions with 'and', denoted by the symbol 'Λ'.
When is a conjunction true?
A conjunction is true only when both of its conjuncts are true.
What is the truth value of the conjunction 'p Λ q' if p is true and q is false?
The truth value is false.
What are some words that can be used interchangeably with 'and' in propositions?
But, however, whereas, furthermore, still, while, nevertheless, although, yet, despite, moreover.
What is a disjunction in logic?
A disjunction is a compound proposition formed by joining two propositions with 'or', denoted by the symbol 'v'.
When is a disjunction true?
A disjunction is true when at least one of the disjuncts is true.
What is the truth value of the disjunction 'p v q' if both p and q are false?
The truth value is false.
How can the statement 'Lee takes Information Technology or he does not take mathematics' be expressed symbolically?
It can be expressed as 'p v ∼q'.
What does the symbol '∼' represent in logic?
It represents negation, meaning 'not'.
What is the result of negating the proposition '2 is positive'?
The negation is 'It is not the case that 2 is positive', which is false.
What is the result of negating the proposition '5 is even'?
The negation is '5 is not even', which is true.
What is the truth value of the conjunction 'Prices are high and salaries are low' if prices are high (true) and salaries are low (false)?
The truth value is false.
What is the truth value of the disjunction 'You are good in Mathematics or you like poetry' if both statements are true?
The truth value is true.
What is the truth value of the statement 'Red is a primary color and orange is a secondary color' if both are true?
The truth value is true.
What is a compound proposition?
A compound proposition is formed by combining two or more propositions using logical connectives.
What does the truth table for conjunctions indicate?
It indicates that a conjunction is false if at least one conjunct is false.

What is the outcome of the compound proposition '(p ∧ q) ∧ ∼p' when p is true and q is false?
The outcome is false.
How many rows are in the truth table for a proposition with two operands?
There are 2^2 = 4 rows.
What is the significance of a truth table in logic?
A truth table lists all possible combinations of truth values for propositions and their resulting truth value.
What is the definition of a tautology?
A tautology is a proposition that is always true regardless of the truth values of its components.
What is a fallacy in logical terms?
A fallacy is a proposition that is always false.
What is a contingency in logic?
A contingency is a proposition that can be either true or false depending on the truth values of its components.
What is the truth value of the compound proposition ∼p ∨ ∼(q ∧ r) when p is false, q is true, and r is false?
True