Arenes (Aromatic Chemistry)
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
How is benzene structured? (3 bullet points)
Cyclic, planar molecules with formula C6H6
Carbon has 4 valent electrons, each carbon is bonded to 2 other carbons and 1 hydrogen atom. Therefore the final lone electron is in a p-orbital which sticks out above and below the planar ring.
Lone electrons in the p-orbitals combine to form a delocalized ring of electrons.
(as a result all C-C bonds have same bond length of 139pm)
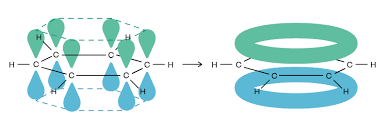
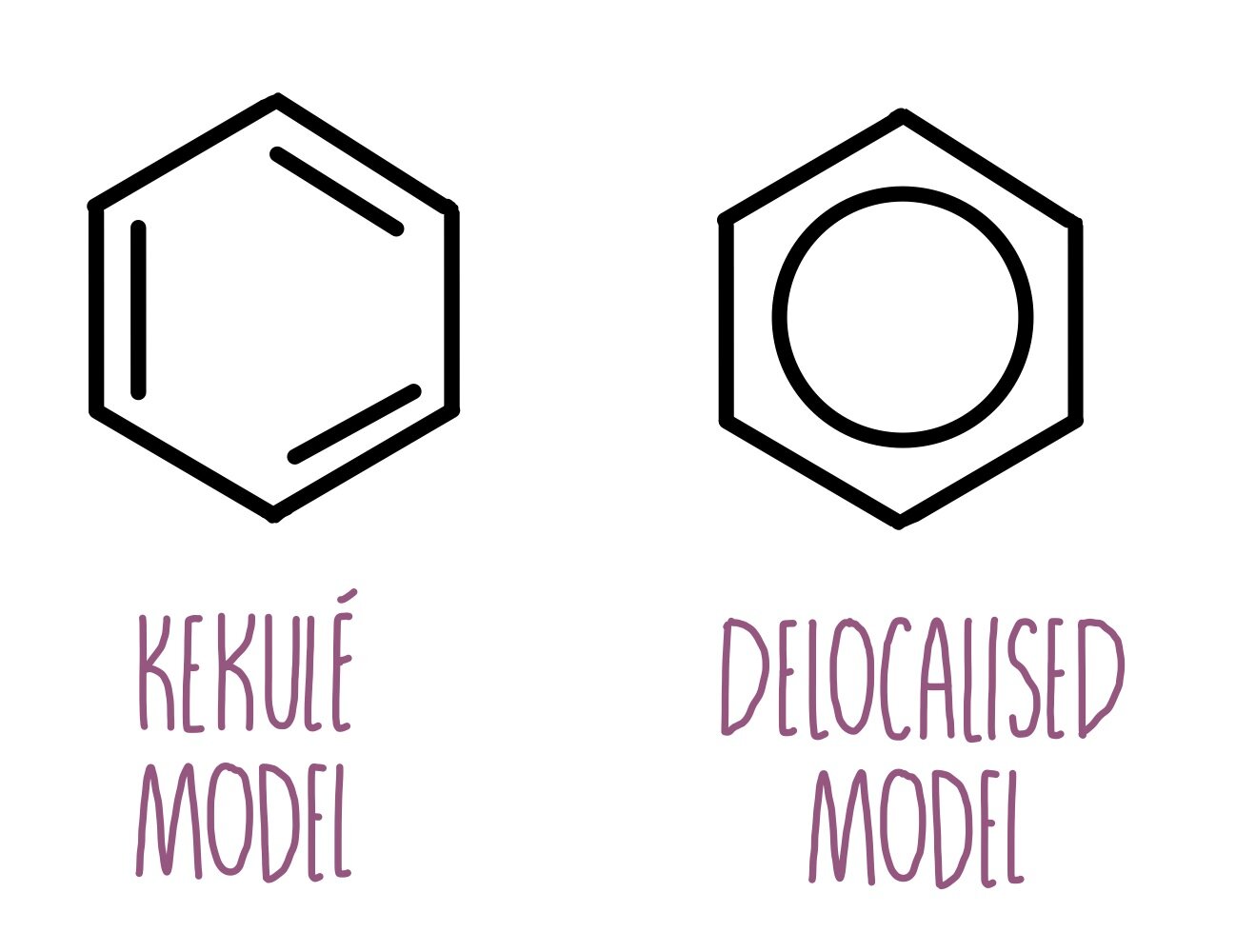
What is Kekule’s theoretical structure vs the current structure of Benzene?
Kekule (cyclohexa-1-3-5-triene)
shows benzene with alternating double bonds and single bonds.
Benzene
shows delocalised electron system
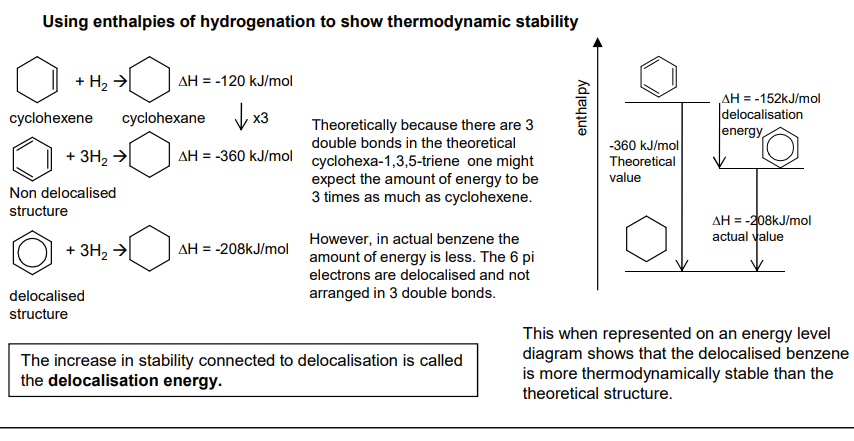
Compare the stability of benzene against Kekule's structure.
Measured by the hydrogenation of the structures (adding hydrogen)
Benzene is less exothermic (more endothermic) meaning it requires more energy to break bonds making it more stable
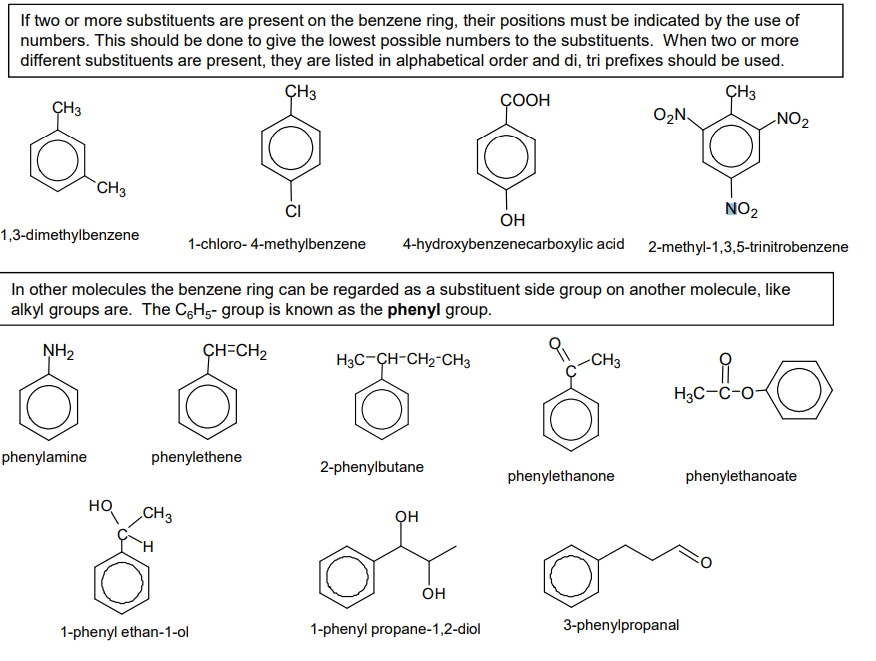
What are the two ways of naming benzenes?
with benzene at the end
or named as phenyl - when it becomes a side group
What reactions do benzenes undergo?
They undergo electrophilic SUBSTITUTION (replaces hydrogen or functional group), as electrophilic addition disrupts the stable ring of electrons
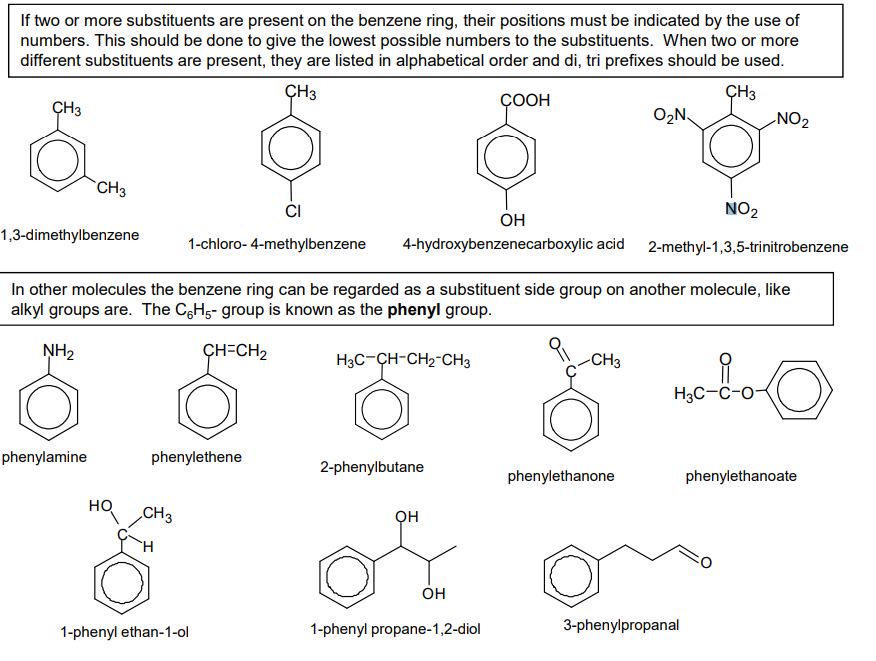
What is Friedel-Crafts acylation?
When an acyl group (RCO-) is added onto a benzene molecule to make it weaker and easy to modify.
To add this acyl group (electrophile) it has to have a very strong positive charge.
We use a halogen carrier to act as a catalyst (AlCl3) to produce a much stronger electrophile with a stronger positive charge.
R-C(O)-Cl + AlCl3 → RC+O + AlCl-4
Change: benzene → phenylketone
Reagents: acyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride catalyst
Conditions: heat under reflux (50 C)
H+ at the end reacts with AlCl4- to produce AlCl3 + HCl
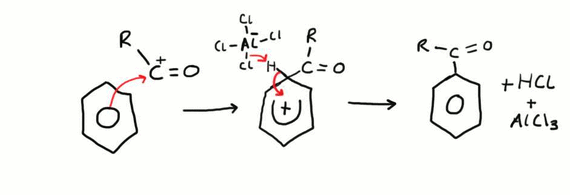
What is the nitration of benzene?
Reagents - concentrated nitric acid (HNO3) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
Conditions - A temp below 55 celcius to ensure a single NO2 substitution → submerge in ice bath
making the electrophile (NO2+)
HNO3 + H2SO4 → H2NO3+ + HSO4-
H2NO3+ → NO2+ + H2O
Overall equation
HNO3 + H2SO4 → HSO4- + NO2+ + H2O
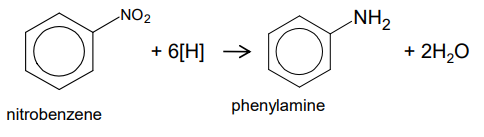
How do you reduce nitrobenzene to an aromatic AMINE?
Reagent - Sn (tin catalyst) and conc. HCl/ Fe and conc. HCl
Conditions - heating
Mechanism - reduction
As the reaction is carried out in HCl the ionic salt C6H5NH3+Cl- will be formed. Reacting this salt with NaOH will give phenylamine.