A level Chemistry AQA - Periodicity
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Trends across a period - atomic radius
Decreases
Why does atomic radius decrease across a period?
Nuclear charge increases so there is a stronger electrostatic attraction between the nucleus of elements across a period and their outer electrons, so the outer electrons are drawn in closer to the nucleus
Trends across Period 3 - melting points
melting points of P3 metals increase
melting point of silicon is very high
melting points of P, S, Cl, Ar are low
The melting point of S is greater that P
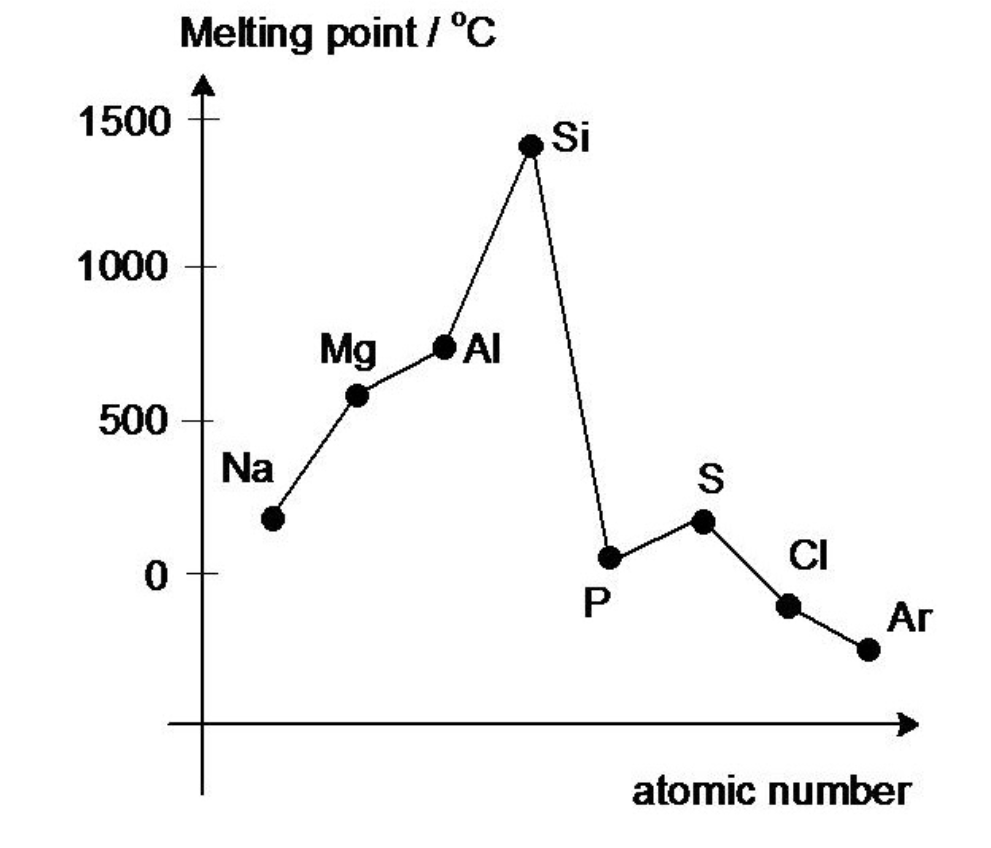
Why do the melting points of metals increase across P3?
The number of outer electrons increases
More delocalised electrons.
Greater electrostatic forces of attraction between the positive metal ions and the delocalised electrons.
Ionic radius from Na→Al decreases so charge density increases.
Why is the melting point of silicon very high?
Has a giant covalent lattice structure
A lot of energy is required to break the many strong covalent bonds
Why are the melting point of P, S, Cl, Ar low?
Are simple covalent molecules
Little energy is required to overcome the weak van der Waals forces between molecules
Why is the melting point of S greater than P?
S has more electrons per molecule than P or Cl2
Therefore S has stronger van der Waals forces of attraction between molecules
More energy is required to overcome those forces
Trends across a period - first ionisation energy
Increases
Why does first ionisation energy increase across a period?
Nuclear charge increases
Atomic radius decreases
Outer electron is closer to the nucleus
Shielding stays the same
Stronger electrostatic forces of attraction between nucleus and outer electron
More energy is required to lose outer electron
First IE in Group 3
Al (G3) has lower first ionisation energy than expected
Why does aluminium have a lower first IE than expected
Electron being added into 3p subshell
This subshell is further from the nucleus
First IE in Group 6
S has lower first IE than expected
Why does sulfur have a lower first IE than expected?
Pairing of electrons in the p-subshell
The electrons in the pair repel
Less energy required to remove one of the electrons
First IE in group 1
Have the lowest first IE in each period
Why do elements in G1 have the lowest first IE in each period?
Greatest atomic radius
Lowest nuclear charge
First IE in Group 0
Highest first IE in each period
Why do elements in G0 have highest first IE in each period?
smallest atomic radius
Highest nuclear charge