AQA GCSE Chemistry - Using Resources
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
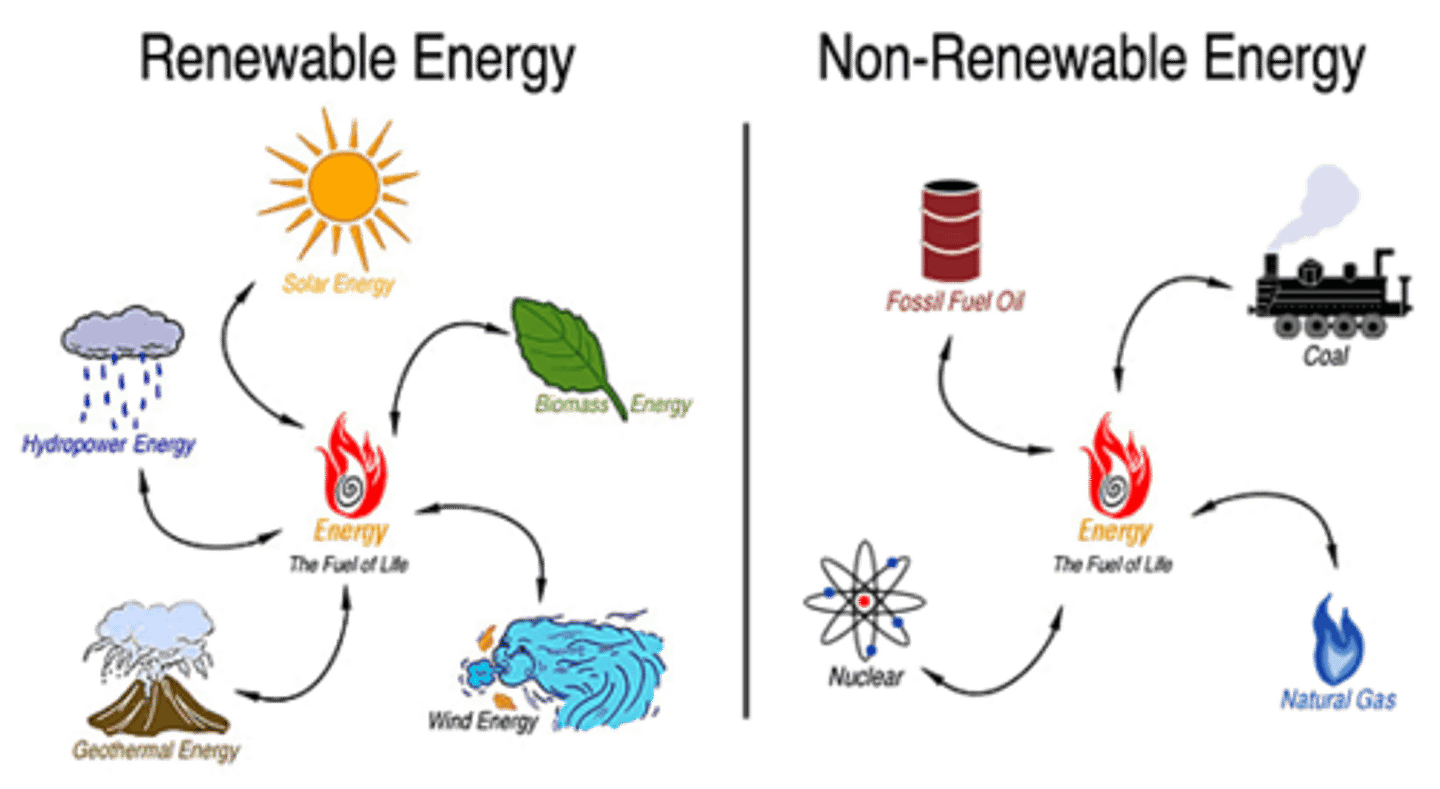
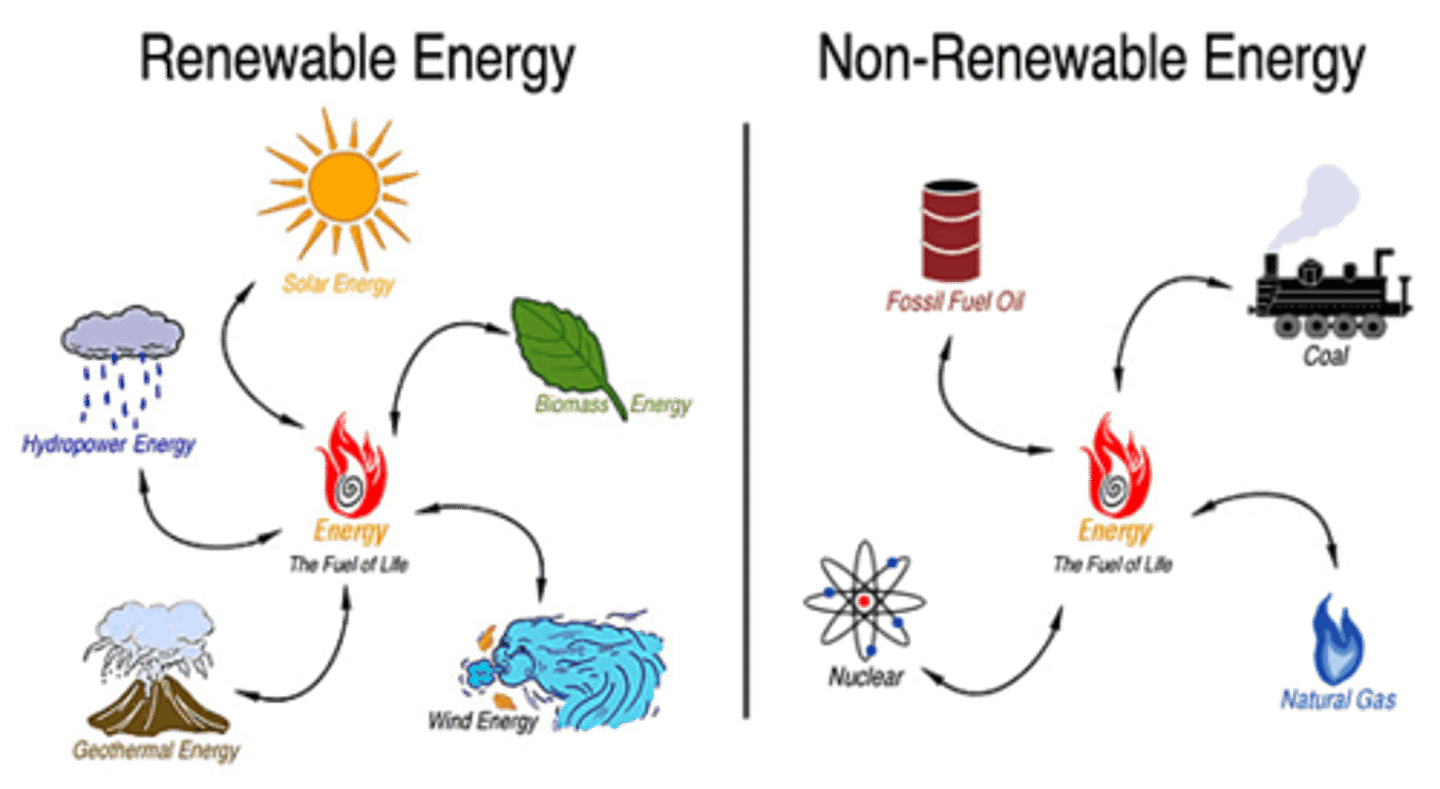
Finite
A resource we use faster that it can be replaced

Renewable
A resource which can be replaced faster than we use it up
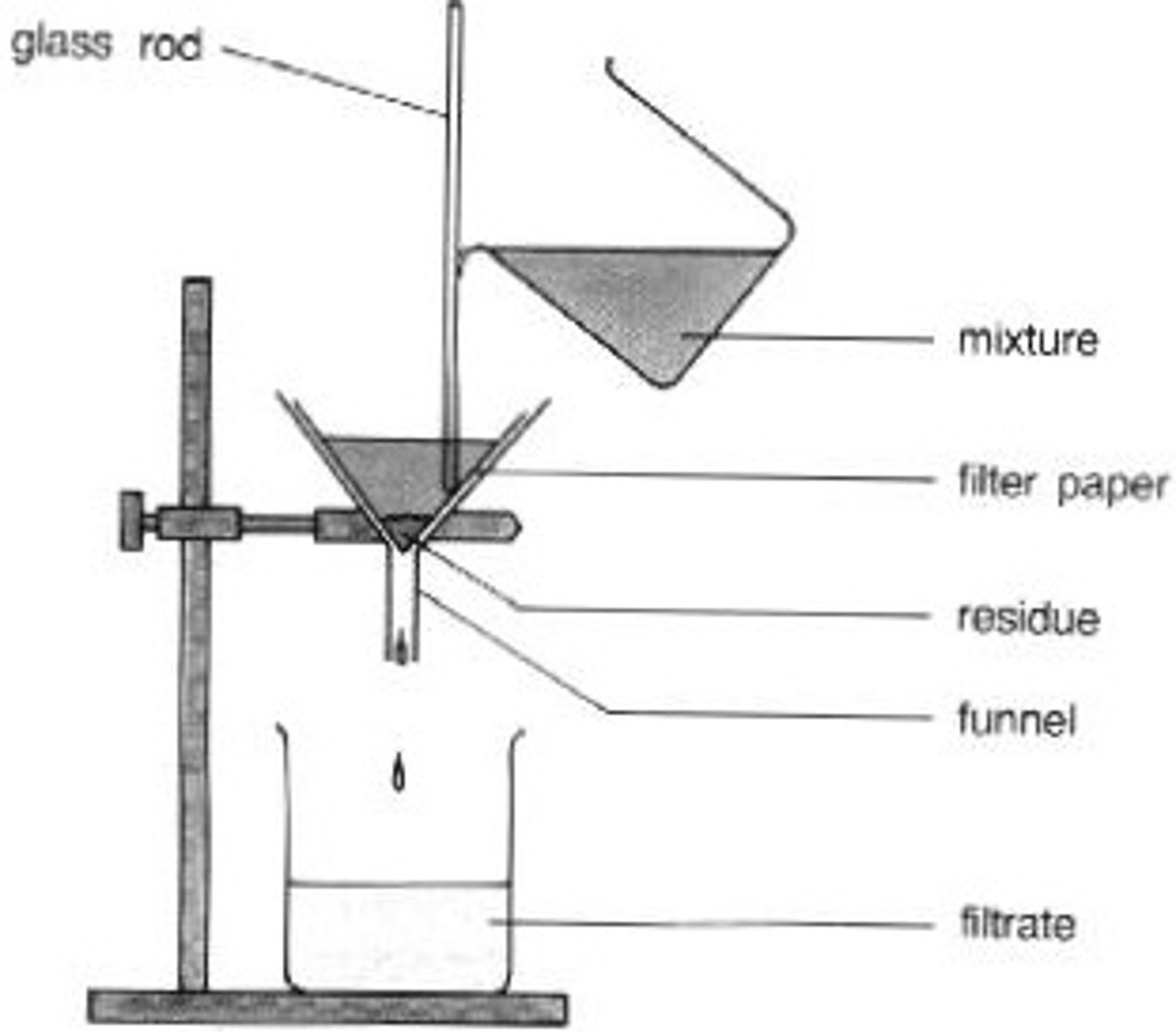
Filtration
A process which can separate solids like grit and leaves from water.
Sterilization
A process which kills bacteria and viruses
Potable
Safe for drinking

Pollutants
Chemicals which may be harmful to living organisms. Not naturally found in the water supply.
conservation
the preservation or protection of natural resources; the use of less of a resource to make the supply last longer.
Non-renewable resource
a resource that, once used, cannot be replaced within a human lifetime.
pollution
any change to the natural environment that can harm living things.
reduce
to reduce or lessen the amount of waste you create.
reuse
to use something again that would usually be thrown away such as plastic bags from the grocery store.
recycle
turning waste into reusable materials such as plastic or metal
What is meant by a natural resource?
something we use for a purpose that comes from nature
What is potable water?
water that is safe to drink
What is pure water?
contains only water molecules (boils at exactly 100'C)
Describe stages in making water potable?
1. fresh water obtained from reservoirs/lakes
2. pass water through filtration beds - insoluble solids removed
3. sterilisation (bacteria killed by using UV, chlorine or ozone)
Describe how drinking water can obtained from salt water (brine)
by distillation
heat to 100'C so water turns to a vapour
Condense the water vapour back to a liquid using cold water in a condenser
State the stages in treating sewage water (4)
Sewage treatment includes:
• screening and grit removal
• sedimentation to produce sewage sludge and effluent
• anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge
• aerobic biological treatment of effluent.
How does phytoming extract copper?
plants (plants take up copper in the soil, plants are burnt, ash contains the copper) electrolysis used to obtain copper from ash
How does bioleaching extract copper
bacteria ingests copper compounds and makes leachates that contain copper. Electrolysis is used to obtain copper from leachate
What 4 stages need to be considered in Life Cycle Assessments
extraction, manufacture, use, disposal
What are the Advantages of recycling materials
conserves raw materials
conserves fossil fuels
saves energy
What are the advantages of mining/quarrying materials
Creates jobs
Brings money into the community
What are the Disadvantages of mining/quarrying materials?
mining or quarrying scars the landscape
destroys mining habitats
Use fossil fuels
Noise pollution
Air pollution
Why is potable water not the same as pure water?
It contains other dissolved substances
resources
materials found in the earth that people need and value
sustainable
able to meet the current demand for a resource without depleting the future supply

agricultural product
fertilisers that are manufactured formulations that supply nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium to increase crop growth and yield.
synthetic product
any man‑made substance created through chemical processes rather than occurring naturally.
dissolved salts
ionic compounds that separate into their ions when mixed with water, making the solution able to conduct electricity.
groundwater
water that fills the cracks and spaces in underground soil and rock layers
sterilising agents
a chemical used to kill microorganisms (like bacteria and fungi) to prevent contamination or infection.
eg : chlorine
desalination
the removal of salt from seawater to make it usable for drinking and farming
reverse osmosis
A technique for purifying water by forcing it through a semipermeable membrane.
purification
the act of cleaning by getting rid of impurities
organic waste
waste material from living organisms eg sewage or manure
chemical waste
hazardous waste that is usually a byproduct of industrial processes
metal ore
Rocks containing metal compounds which can be used as a source of the metal.

phytomining
The process of extraction of metals from ores using plants
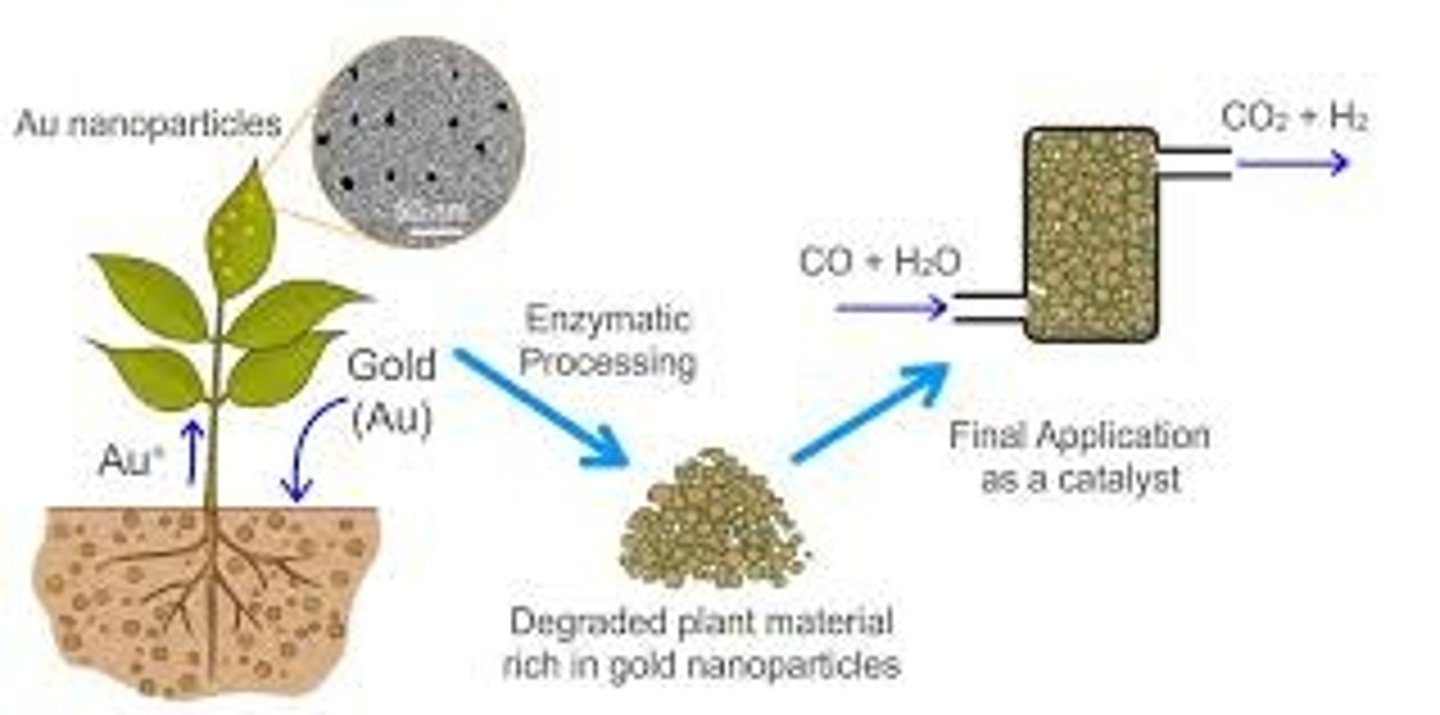
bioleaching
Using bacteria to extract metals from their ores.
life cycle assessment
analysis of environmental impacts of products from the design stage through end-of-life
recasting & reforming
physical processes where a material is melted or reshaped into a new form without any chemical change.