Lecture 19: Francisella, Morexella, and Taylorella spp.
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What are the characteristics of Francisella tularensis?
Gram _
Motility?
Shape?
Respiratory Pattern?
Unique requirement?
Gram -
Non-motile
Capsulated coccobacilli
Obligate Aerobe
Therefore oxidase +
Requires cysteine for growth
Is Francisella tularensis a notifiable disease?
Yes!!
It is a nationally notifiable disease in the US and Canada
Also a CDC category-A biological/bioterrorism agent
How well does Francisella tularensis survive in the environment? Can it be killed via cleaning?
3-4 months in mud, water or dead animals
3 years in frozen meat
Easily killed via disinfectants or heat
Francisella tularensis causes _______ a zoonotic, plague like disease
Tularemia
What are the reservoirs of Francisella tularensis?
1° reservoirs are rodents and Lagomorphs
What are the vectors of Francisella tularensis?
Ixodid ticks
Mosquitos
Deer fly

What are the main animals that Francisella tularensis affects?
Dogs
Cats
HJumans
Francisella tularensis is _______ in the US, where is it most common?
Endemic
South-Central U.S and Martha’s Vineyard
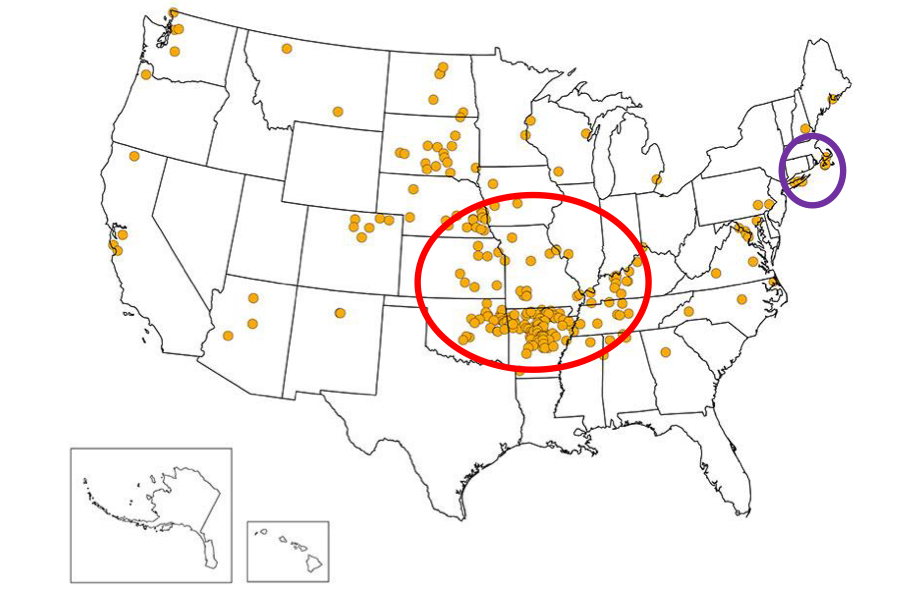
How does weather play a role in the spread of Francisella tularensis subspecies tularensis?
There are significantly higher cases during years with increased rainfall
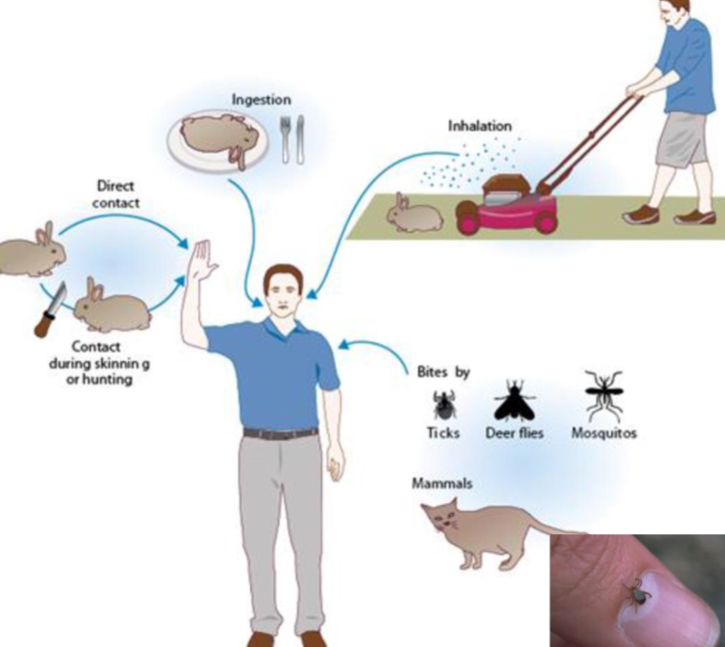
What are the routes of infection of Francisella tularensis subspecies tularensis?
Arthropod bites
Respiratory tract
Franscisella tularensis requires what for growth?
Cysteine
Francisella tularensis subspecies tularensis is a _____ pathogen
Primary Pathogen
What is the difference between Francisella tularensis subspecies tularensis and Francisella tularensis?
Francisella tularensis subspecies tularensis is the most virulent strain
How does Francisella tularensis present grossly?
Acute Septicemia
Microabscesses and pyogranulomas

How does humans get infected with Francisella tularensis (Tularemia)?
Skin contact/insect bite
Ingestion
Inhalation
T/F: Tularemia can be spread human to human
False
How do you treat Tularemia?
Antibiotics (Streptomycin)
T/F: Recovery from a Tularemia infection does not provide life-long immunity
True
How can Tularemia be prevented in dogs/cats?
Tick control
No unsupervised outdoor roaming
Moraxella bovis causes ____ ___ in cattle
Pink Eye (Infectious Bovine Keratoconjunctivitis (IBK))
What are the characteristics of Moraxella bovis?
Gram _
Respiratory pattern?
Morphology
Unique feature?
Gram -
Strict Aerobe
Short paired rods (diplobacillus)
Narrow zone of complete hemolysis and don’t grow on Maconkey

What animal acts as a mechanical vector for Moraxella bovis? (Use hint if needed)
Flies
T/F: Moraxella bovis can infect other ruminants
False, it is an obligatory pathogen of cattle
IBK presents _____ (answer with a timeframe) and is very contagious
Acutely
T/F: Moraxella bovis can cause permanent blindness
True
Which age range of cattle are most susceptible to Moraxella bovis?
Calves, they don’t have pre-existing immunity
What factors would pre-dispose cattle to Moraxella bovis?
Viral infections
Physical trauma
UV light damage/Chemical Trauma
Stress
Moraxella bovis can survive for up to 72 hours in the _______ organs of cattle
Salivary organs
What are the virulence factors of Moraxella bovis
Q-Fimbrae
Aids in colonization
I-Fimbrae
Local persistence
MBxa Haemolysin (RTX Toxin)
Haemolytic and cytotoxic causes breakdown of collagen matrix of cornea
Strains of M. bovis that lack cytotoxin of fimbriae are _______
avirulent
If a cow is deficient of the lysozyme in lacrimal secretions, how does that affect its susceptibility/resistance to Moraxella bovis?
It makes it more susceptible
What are the C.S of Moraxella bovis?
Stage 1
Excessive lacrimation, conjunctivitis, sensitivity to light
Small ulcer
Stage 2
Ulcer spreads across the cornea
Cornea becomes more cloudy
Blood vessels make the cornea appear “pink“
Stage 3
Ulcer covers most of the cornea
Inflammation spreads to the inner eye
Inside of eye fills with fibrin
Stage 4
Ulcer completely extends through the cornea
Eye is now blind

What is the difference between summer and winter pinkeye?
Summer pinkeye
Caused by M. bovis and or M. bovoculi
Winter pinkeye
Mainly M. bovoculi
Winter pipnkeye can be confused with IBR, what is a distinguishing factor between the 2?
IBR doesn’t cause corneal ulcers like Moraxella bovis does
T/F: Moraxella bovis has little to no economic impact on the cattle industry
False, it costs over 150 million per year
How is Moraxella bovis diagnosed?
Collect a lacrimal secretion
Test via…
Fluorescent antibody test (FAT)
Culture/identification
PCR
How can Moraxella bovis be controlled?
Insect/fly control
Manure control
Pasture management
What disease causes pinkeye (IBK) in sheep/goats?
Moraxella ovis
Taylorella equigenitalis is found where?
The genital tract of stallion, mares, foals
Taylorella equigenitalis causes what disease?
Contagious Equine Metritis (CEM)
Contagious Equine Uterus Inflammation
Taylorella equigenitalis usually causes a ____-_____ infection in mares
Self-Limiting
Mucopurulent vaginal discharge in mares 2-14 days after breeding
T/F: Taylorella equigenitalis can cause permanent infertility in severe cases
False
T/F: CEM is zoonotic
False
What is the difference in infection of Taylorella equigenitalis between Thoroughbred and Non-thoroughbred breeds?
Thoroughbred
Causes acute clinical disease
Non-thoroughbred
Endemic and subclinical disease
What diseases does Taylorella equigenitalis cause in mares?
Endometritis
Cervicitis
Vaginitis
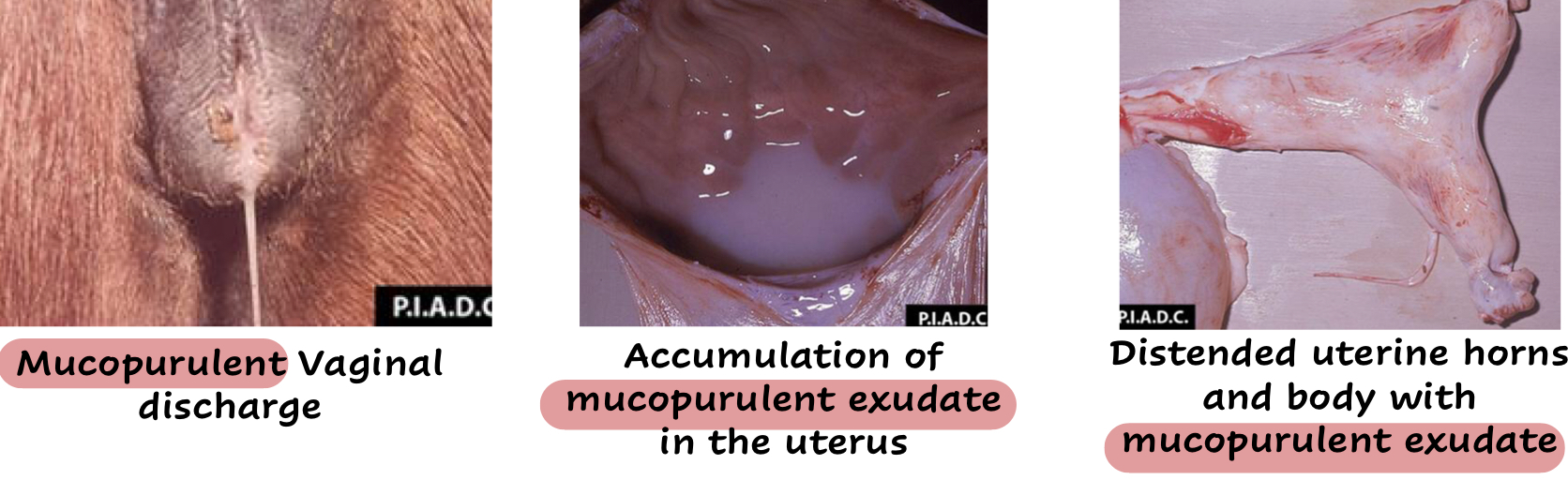
T/F: Mares infected with Taylorella equigenitalis can transmit the infection to foals during birthing
True
T/F: Taylorella equigenitalis can cause abortions
True, but is uncommon
How is Taylorella equigenitalis tested for?
Testing is OIE-mandated
Culture via federally approved labs
qPCR
Serology test in mares
Test breeding of imported stallions
How can CEM/Taylorella equigenitalis be controlled?
Test imported horses
Topical disinfectant and antibiotic treatments to determine carrier state
Removal from breeding
T/F: There is a vaccine for Taylorella equigenitalis (CEM)
False
Francisella tularensis is endemic worldwide, with wild rodent and lagomorphs as the reservoir hosts. T / F
True
Cats and dogs are not at risk of infection with F. tularensis. T / F
False
Transmission by face flies is the main cause of summer outbreaks of infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis (pinkeye). T/ F?
True
Winter pinkeye outbreaks in cattle could be misdiagnosed as IBR infection. T /F?
True
Taylorella equigenitalis causes an acute suppurative endometritis in mares of all horse breeds. T / F
False, only in thoroughbred mares
Detection of CEM is difficult because it is endemic and non-clinical in nonThoroughbred breeds in many countries. T / F?
True