Intraoral Radiographic Interpretation
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
% mineralized?
Enamel: ?
Dentin?
Cementum
Pulp Chamber?
Enamel: 92%
Dentin: 65%
Cementum: 50% cannot be visualized radiographically, too thin
Pulp Chamber: radiolucent
Radiopaque vs radiolucent
Radiopaque = bright white, things like bone etc
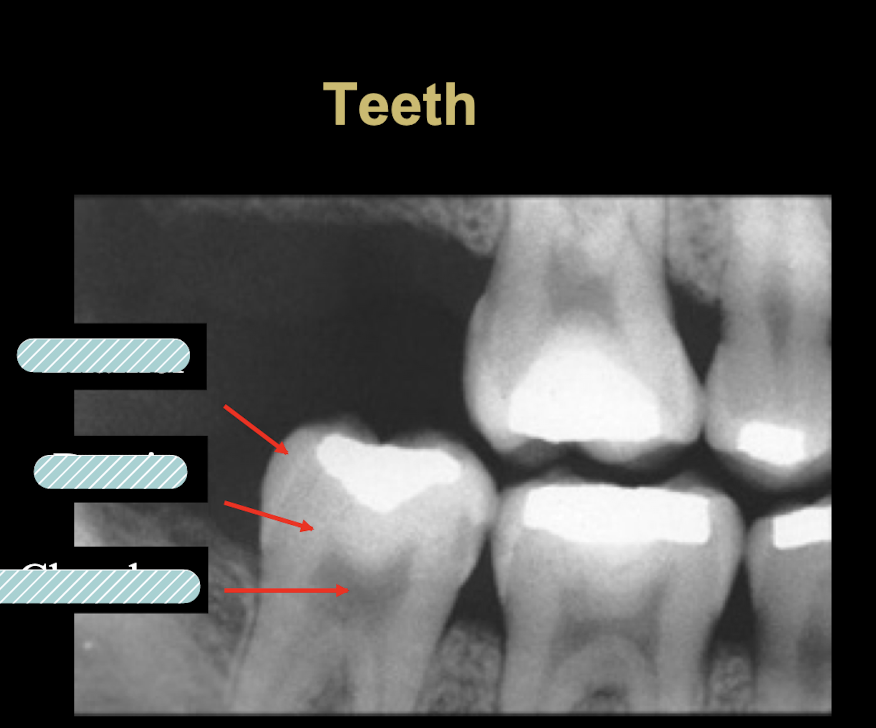
Enamel, dentin, pulp chamber
Supporting Structures? (5)
lamina dura
Alveolar crest
Periodontal Ligament Space
Cancellous Bone
Nutrient Canals
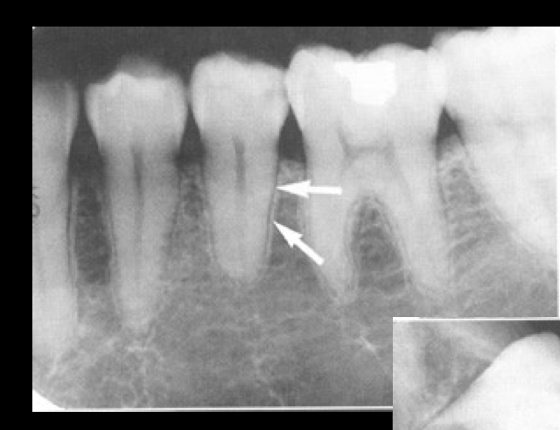
lamina dura
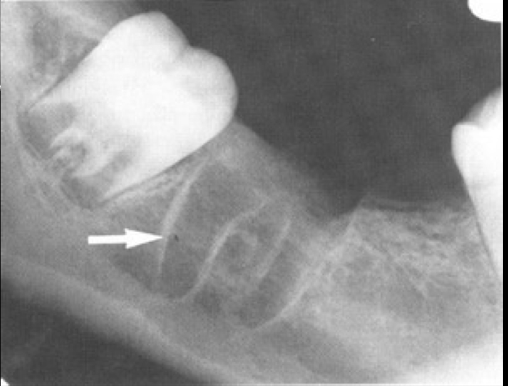
lamina dura
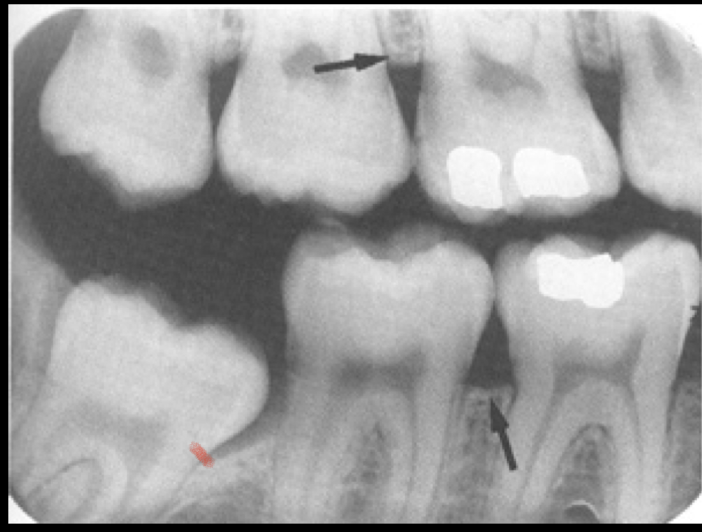
Alveolar crest
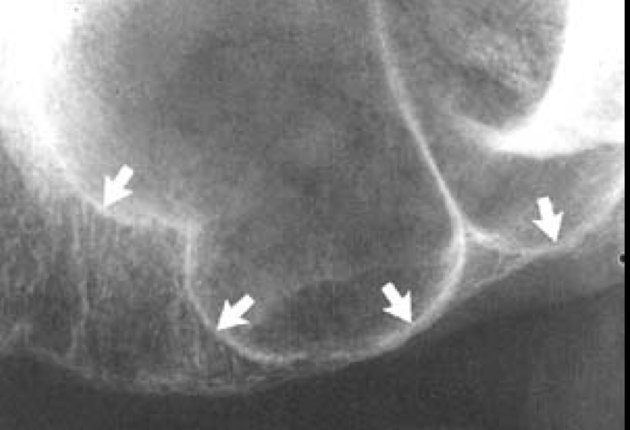
Bone loss is seen on __ and is ?
bitewings, CEJ + bone crest = 2 mm
How can you tell if tooth is erupting?
Roots are open = erupting
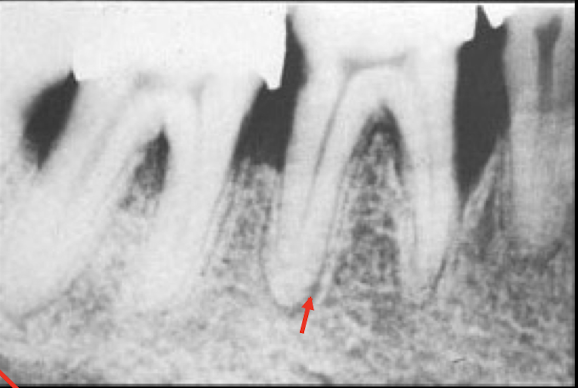
PDL space
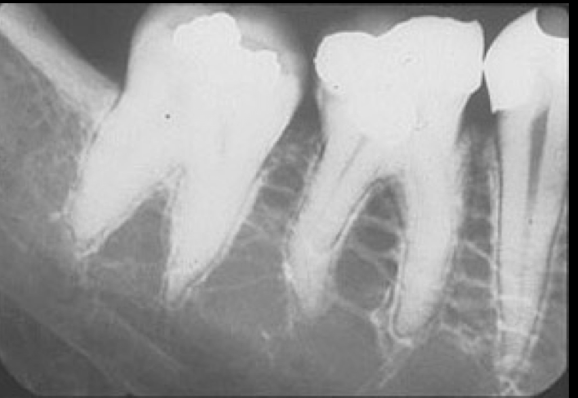
cancellous bone
cancellous bone
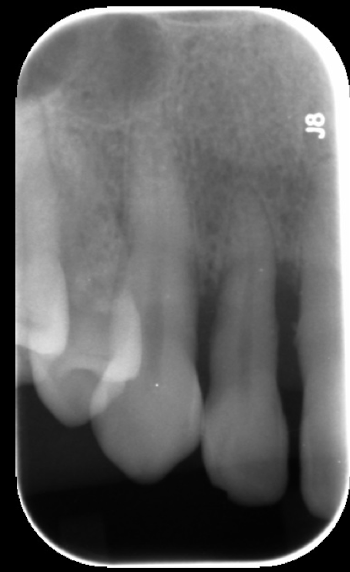
nutrient canal
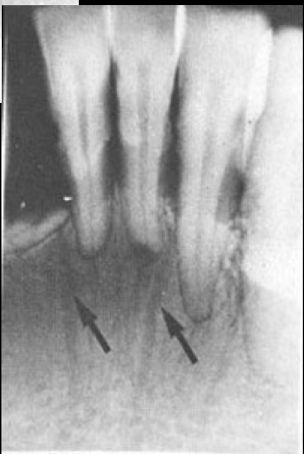
nutrient canal
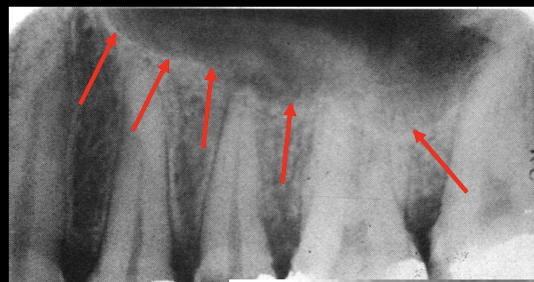
max sinus floor - radiopaque, space is sinus
septum of max sinus
Zygo process: radiopaque over molars U shape
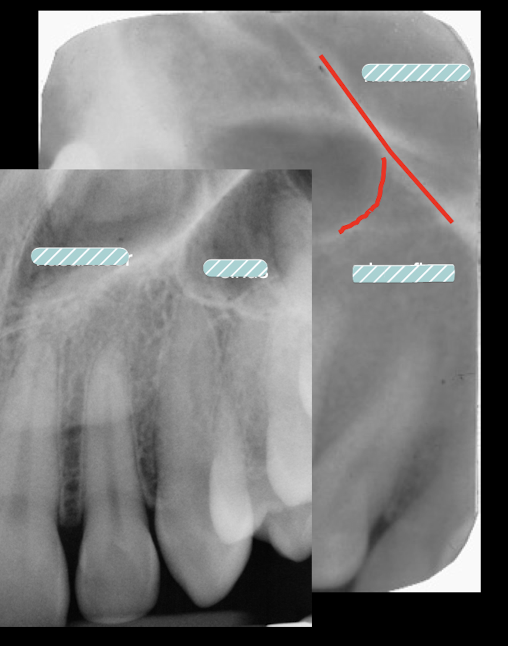
Nasal Floor runs toward Central incisors, sinus runs toward molars
lateral fossa
where do you find lateral fossa?
depression in maxilla of apex of lateral incisor:
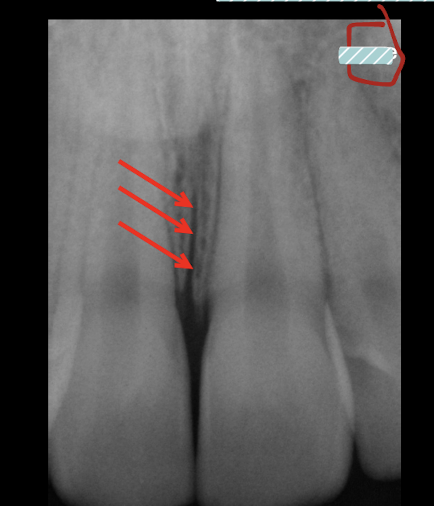
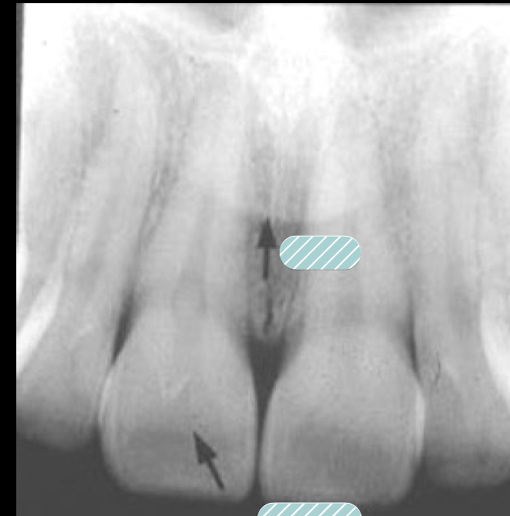
intermaxillary suture
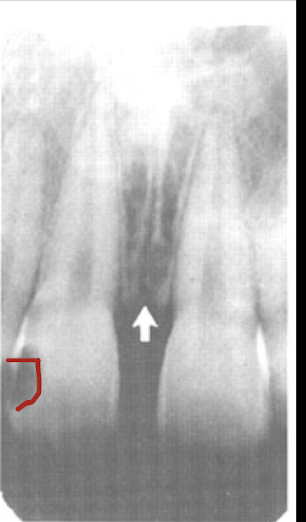
intermaxillary suture
intermaxillary suture/ median suture is?
From anterior nasal spine thru crest between central incisors: radiolucent line
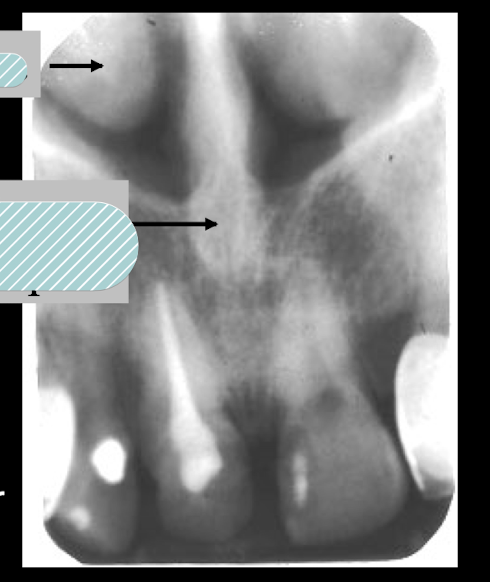
anterior nasal spine and nasal fossa, top is concha
ANS (ant nasal spine) is located __ to the alveolar crest
1.5 to 2 mm superior
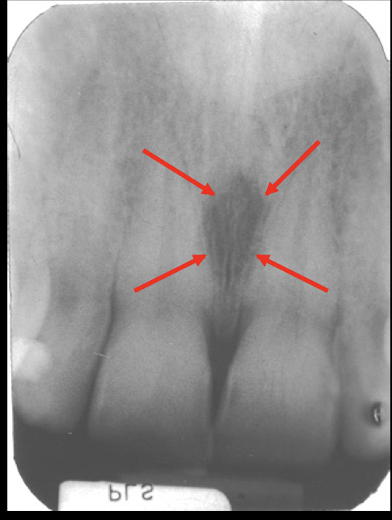
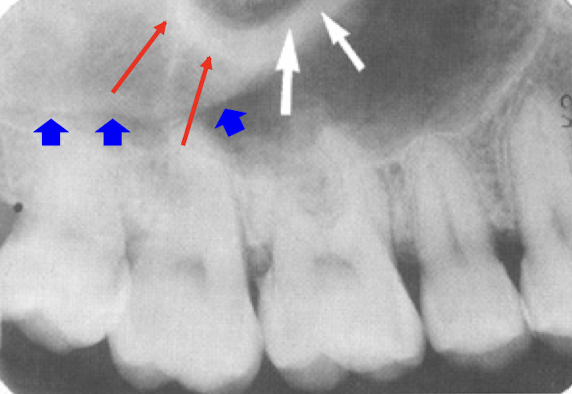
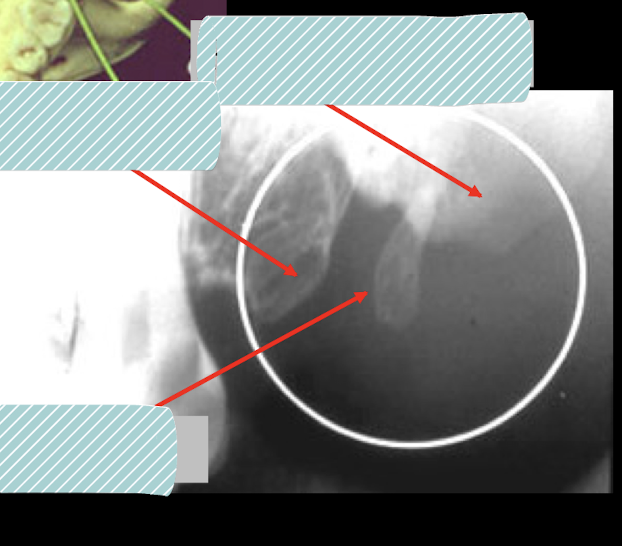
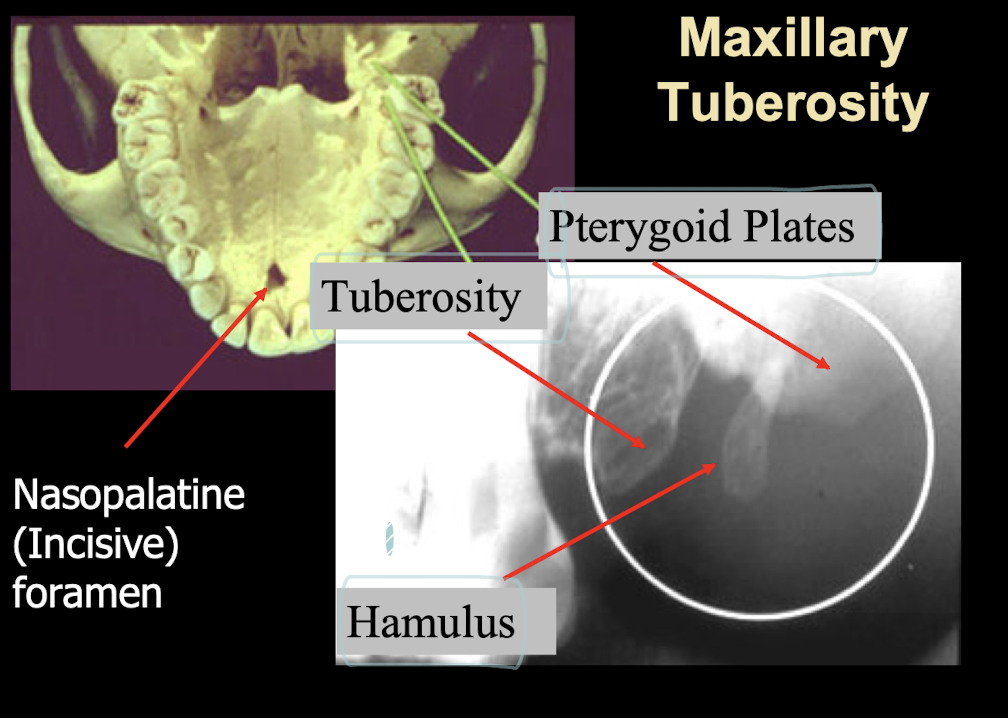
Incisive/Nasopalatine foramen
The incisive/nasopalantine foramen is projected where? When do you think duct cyst?
between roots and middle and apical thirds of central
Size exceeds 1 cm or when enlargement may be demonstrated on sucessive radiographs
nose and lip lines
nasolabial fold
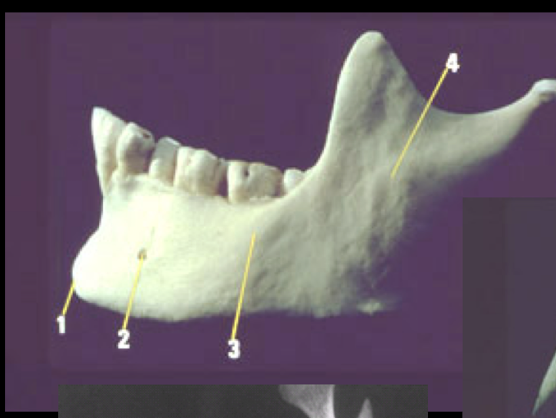
Mentum (chin)
Mental foramen
Body of mandible
Ramus
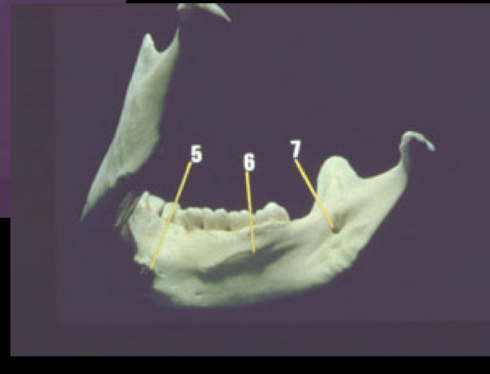
genial tubercles
mylohyoid/internal oblique
Mandibular foramen
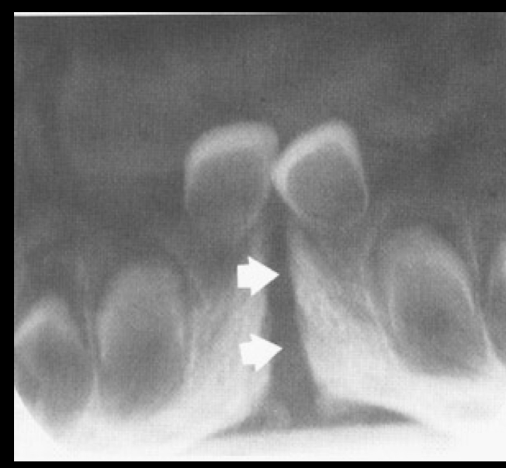
symphisis
where do you see symphisis?
radiolucent line thru midline of mandible of central incisors in Infants: suture usually fuses by end of first year
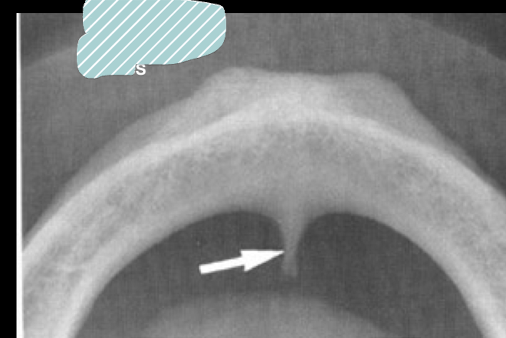
genial tubercles/lingual foramen
opacity = genial tubercle, ladiolucent = lingual foramen
opacity = genial tubercle, ladiolucent = lingual foramen
genial tubercles serve as ?
attachment of genioglossus muscle as superior tubercles, and geniohyoid mucles at inferior tubercles
lingual foramen may contain?
branch of lingual artery
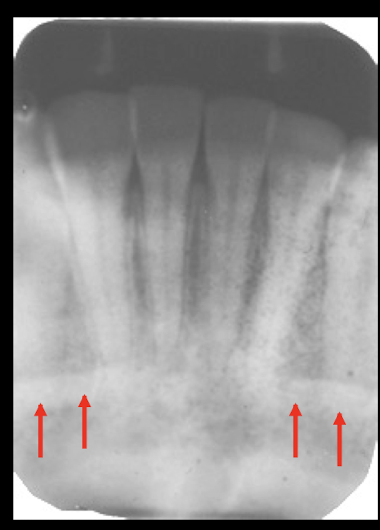
mental ridge
tori
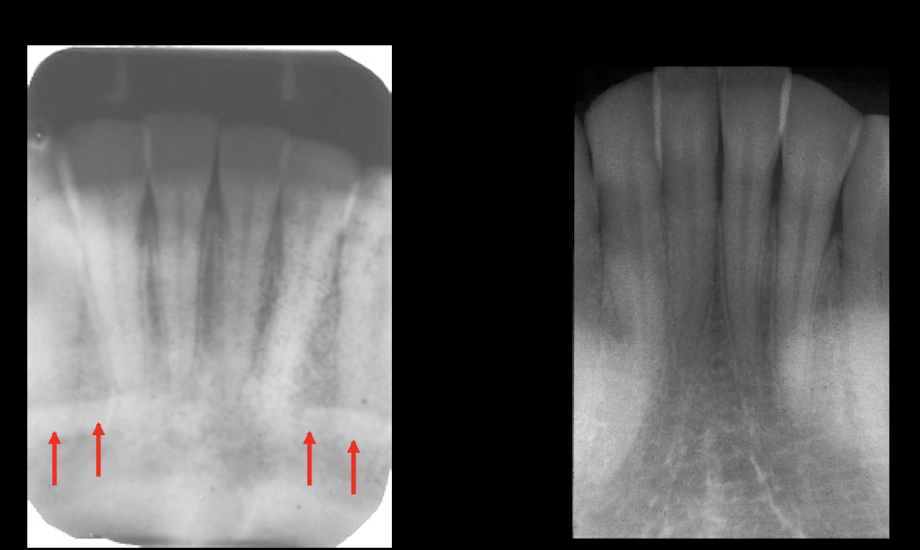
mental ridge is flat, tori is rounder and a little higher
mental fossa
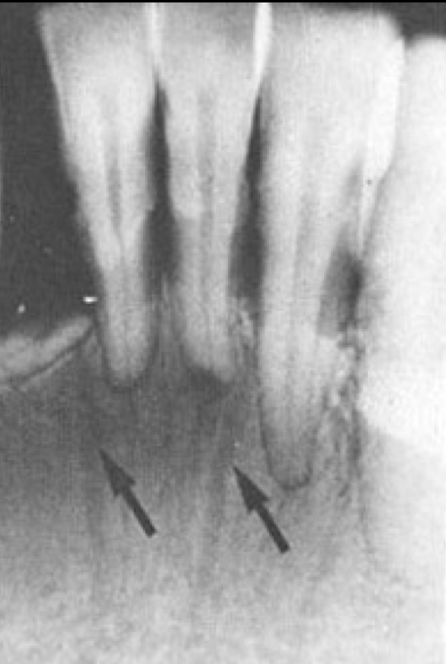
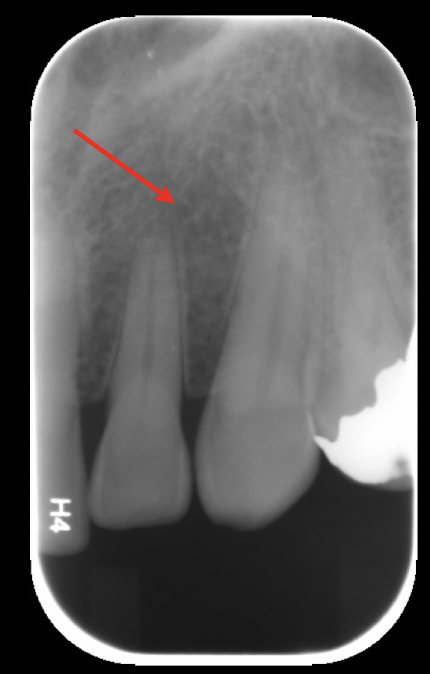
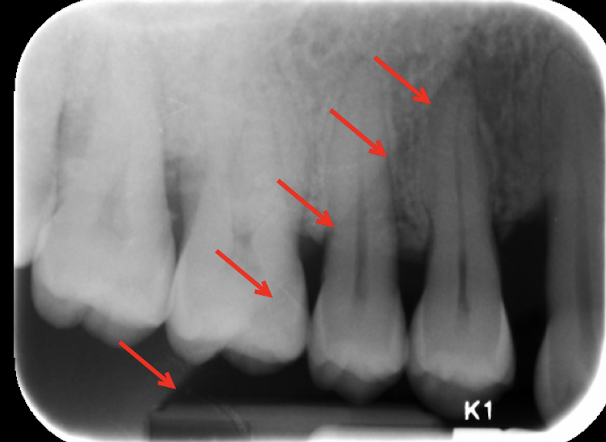
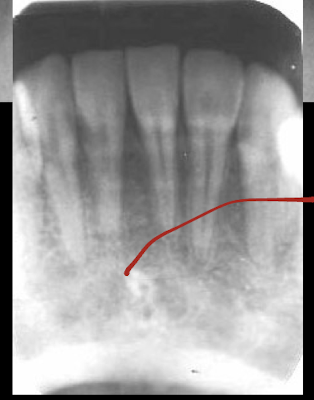
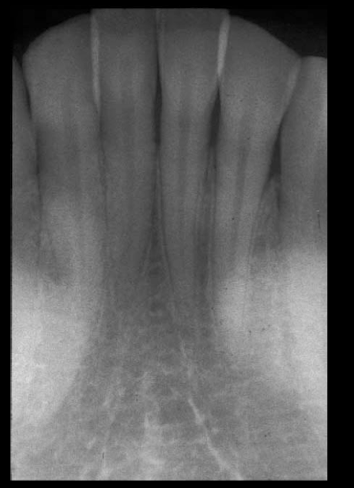
nutrient channels
most often see nutrient channels where? (maxilla/mandible, what radiograph, specifics?)
mandibular anterior PA running vertically from inferior alveolar canal to apex?
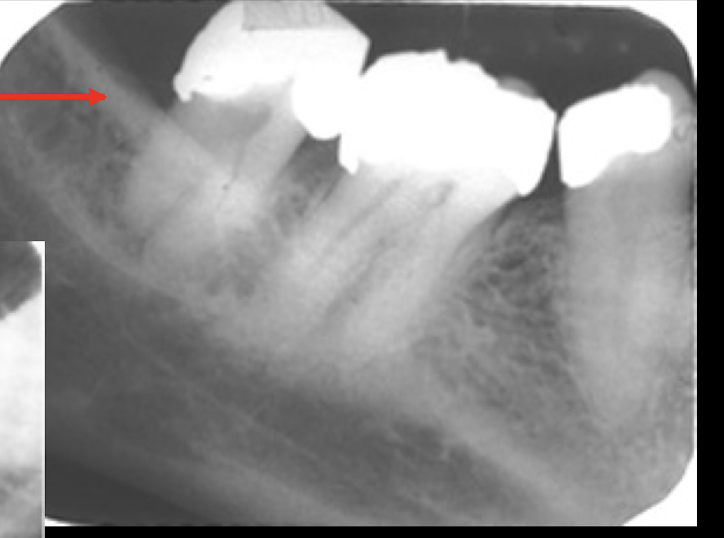
external oblique
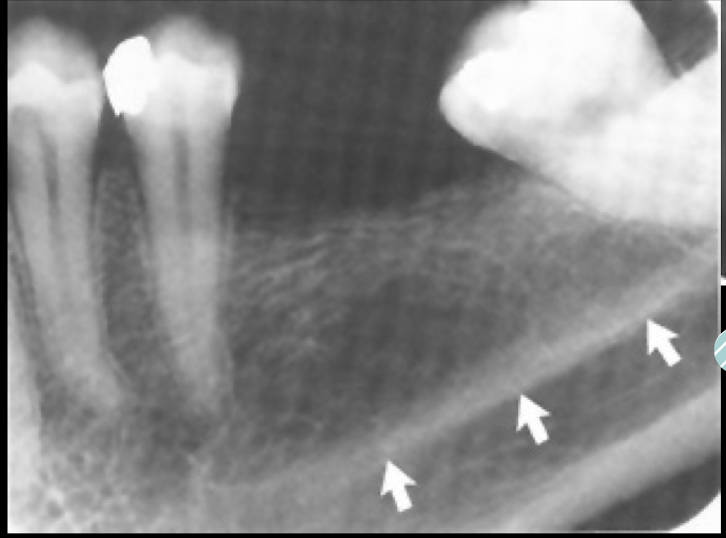
mylohyoid ridge
The external oblique is a continuation of?
The mylohyoid ridge is a crest of bone where? What does it attach?
ex: ant border of mandibular ramus
ridge: crest of bone of lingual surface of mandibular body, attaches mylohyoid muscle
Mylohyoid ridge vs external oblique?
Ext runs thru roots, mylohyoid should be under
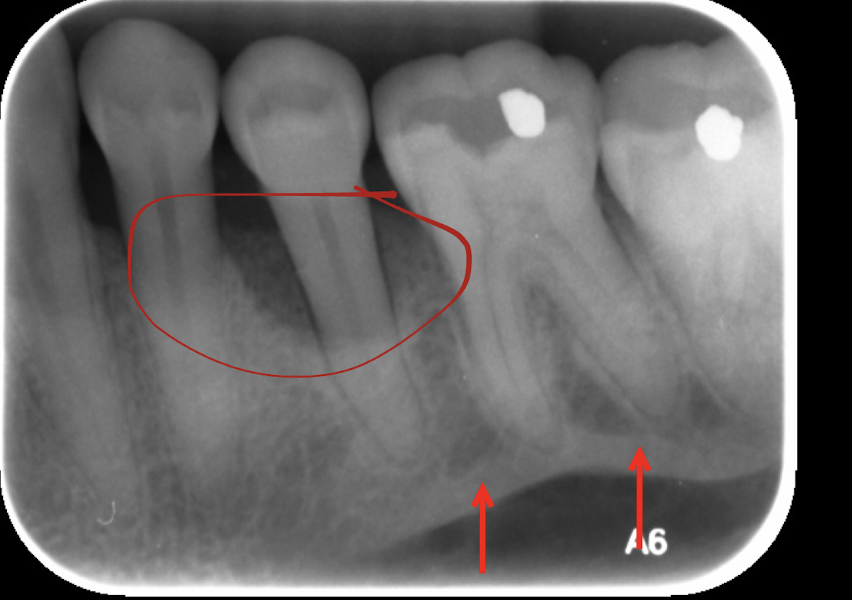
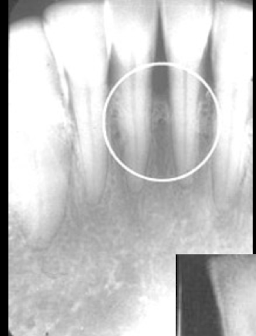
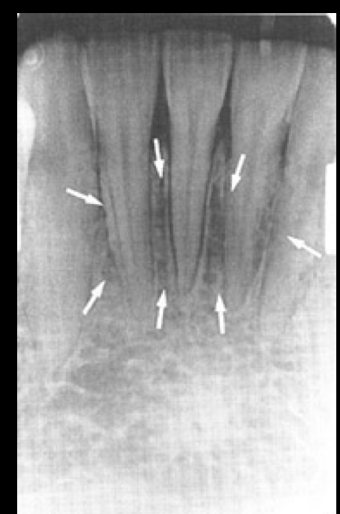
circle? arrows?
bone loss, mylohyoid line
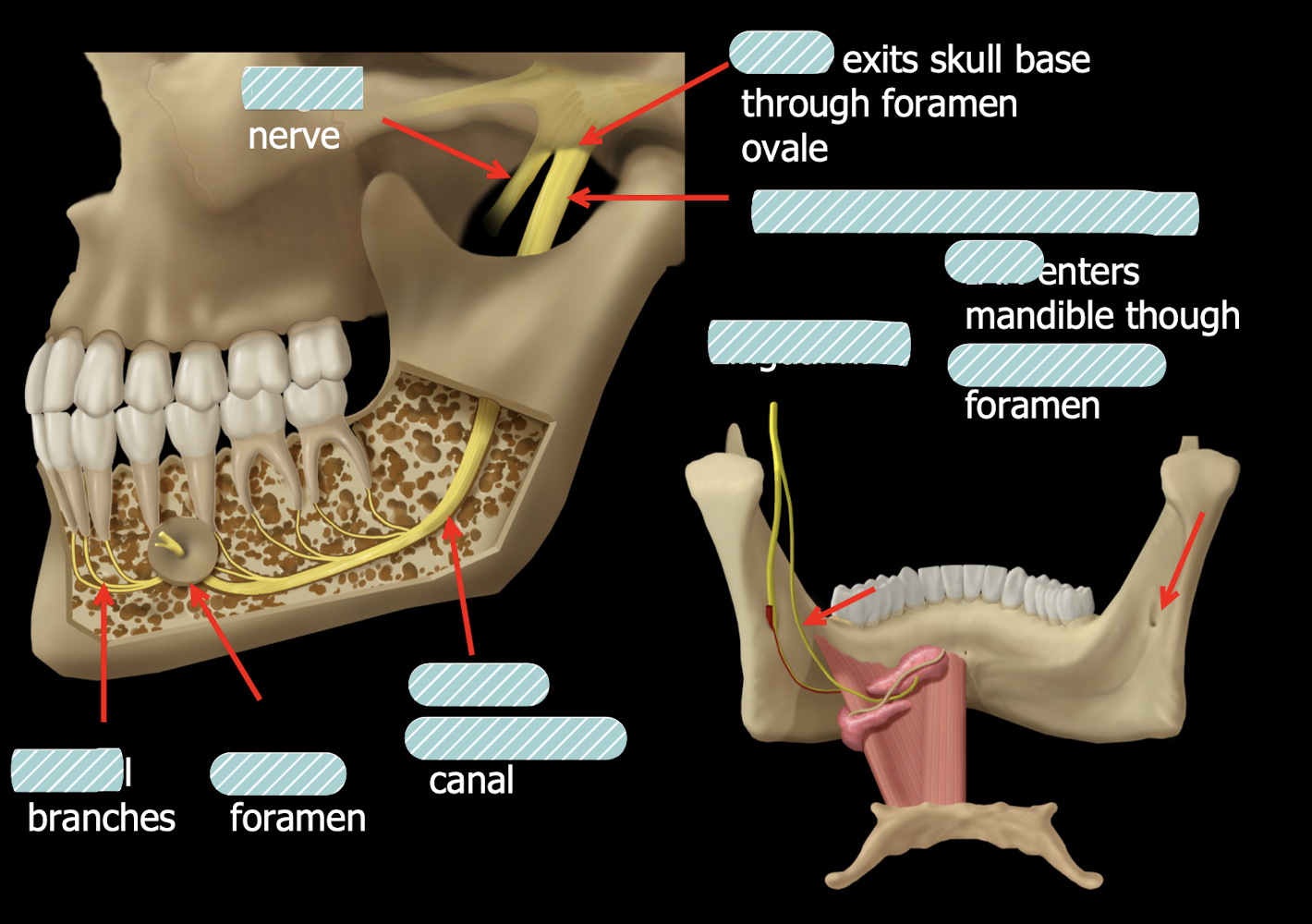
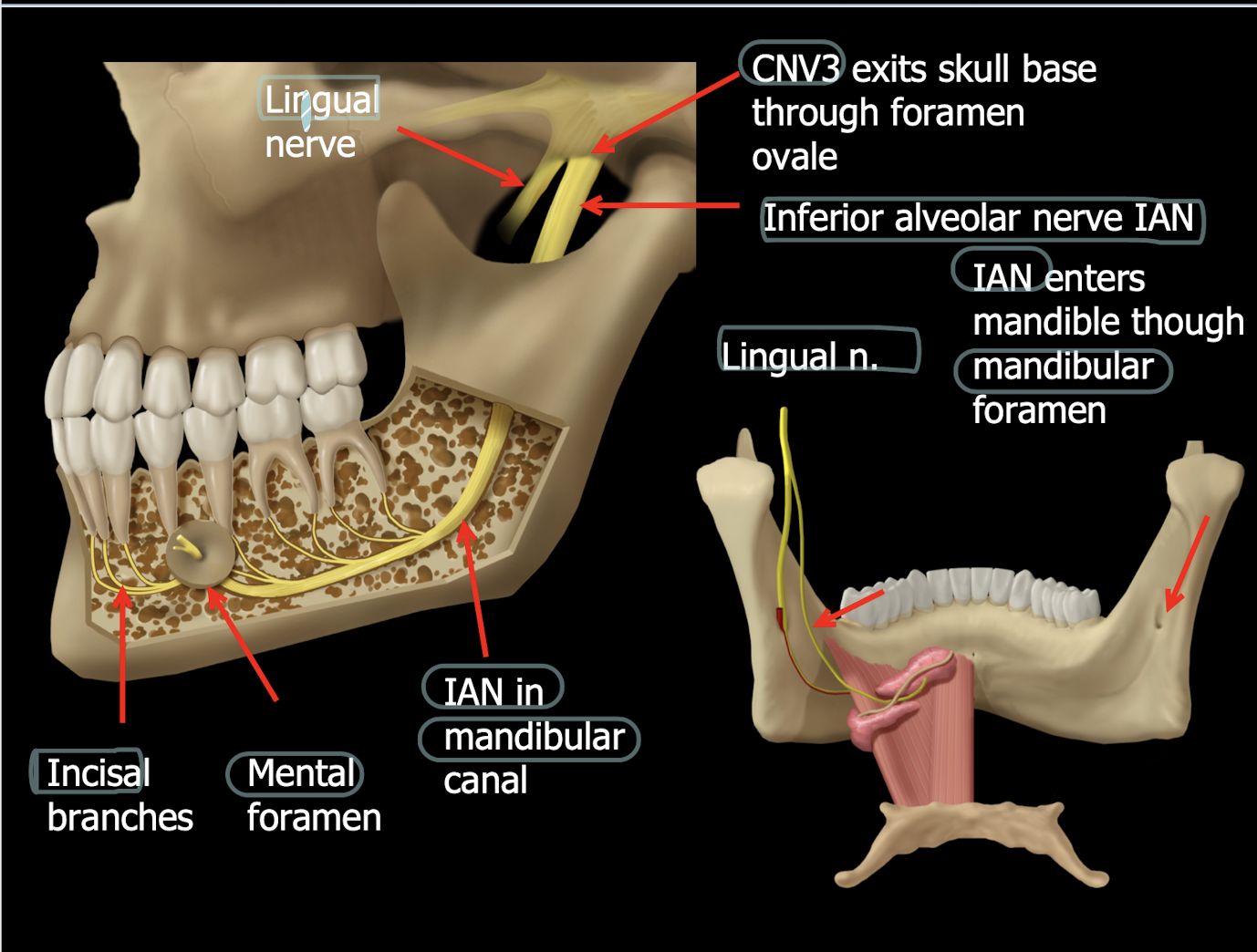
mandibular canal
the mandibular canal is __ and the space around it is?
radiopaque, submandibular gland fossa is surrounding radiolucent area
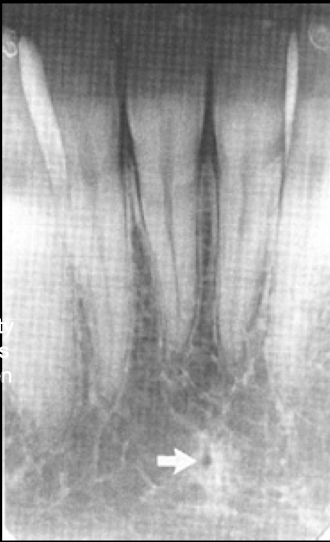
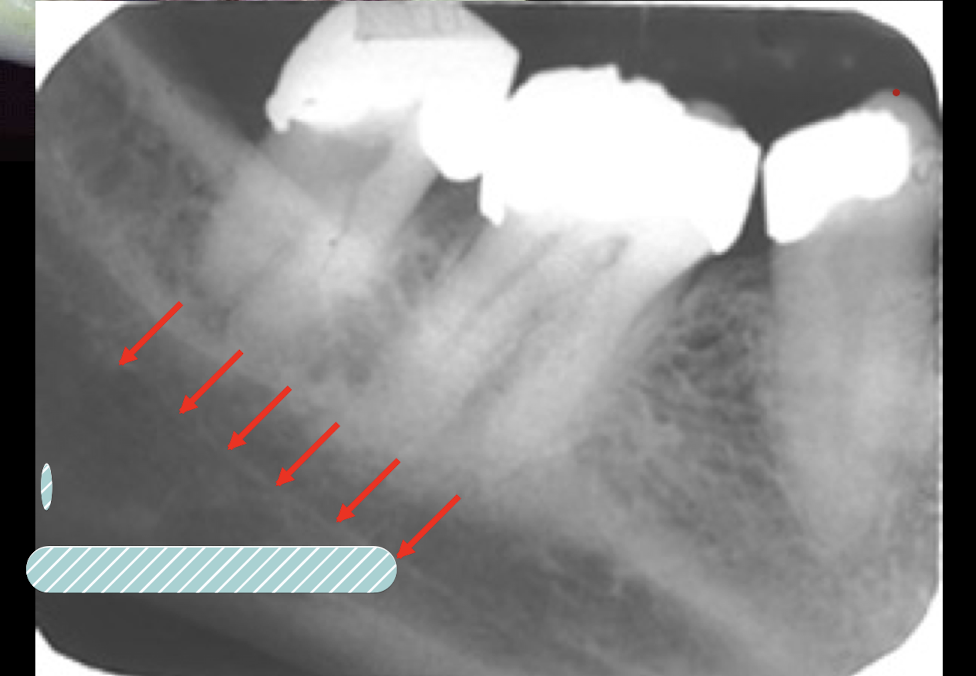
mental foramen
how to tell if mental foramen or decay?
lamina dura should be continuous, foramen is not centered under root
where can you find mental foramen?
mesial of 1st molar to mesial of 1st premolar
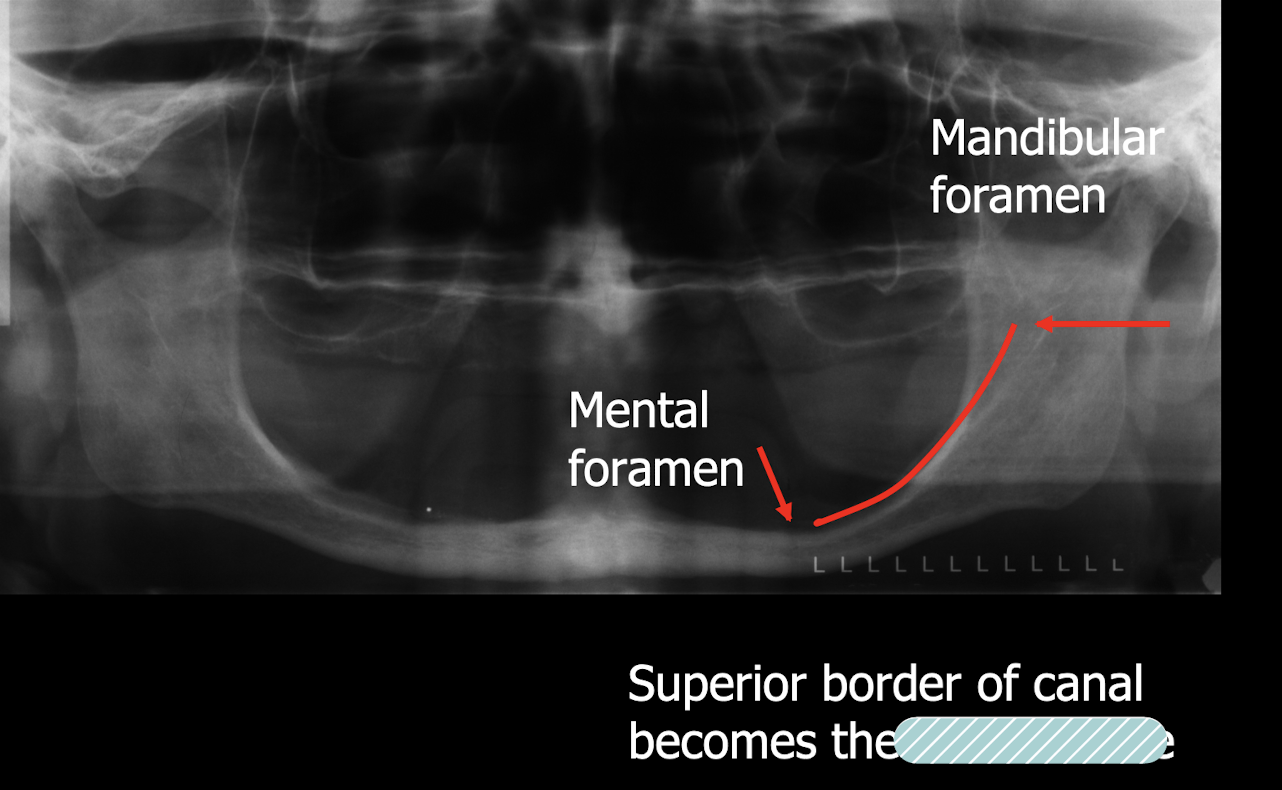
canal becomes crestal bone
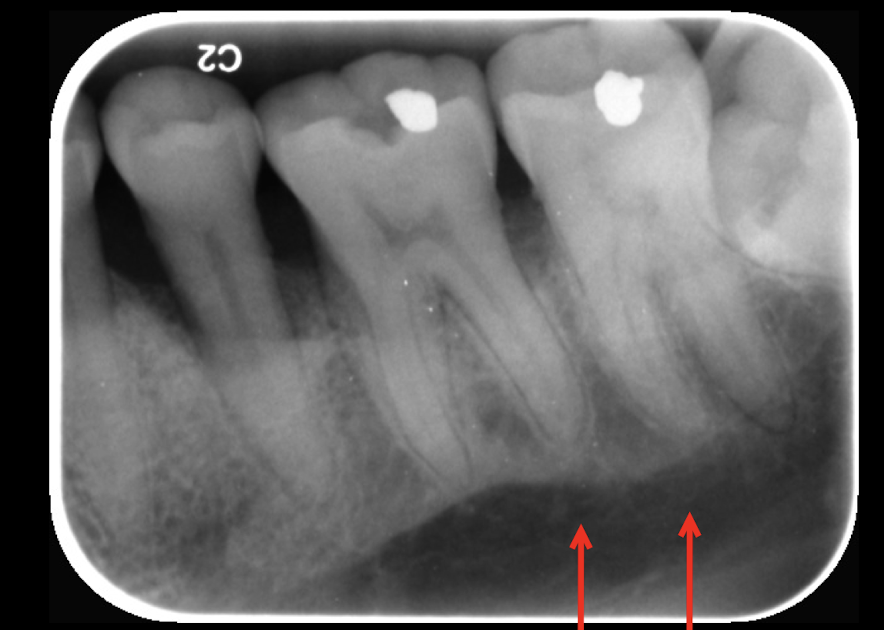
submanidbular gland fossa
Immeditely under mylohyoid line = ?
Submandibular gland fossa
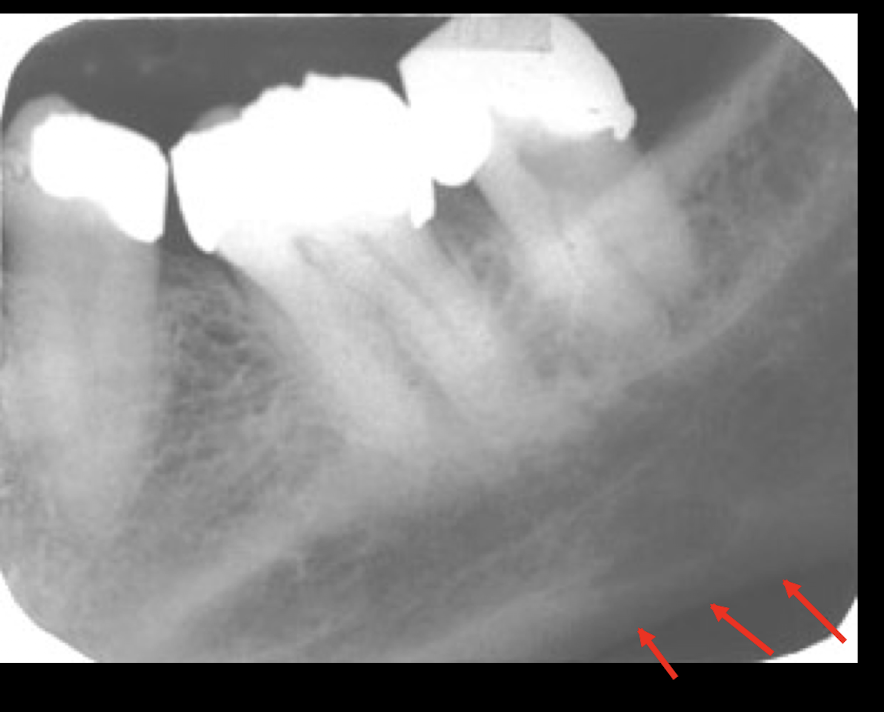
inf border of mandible
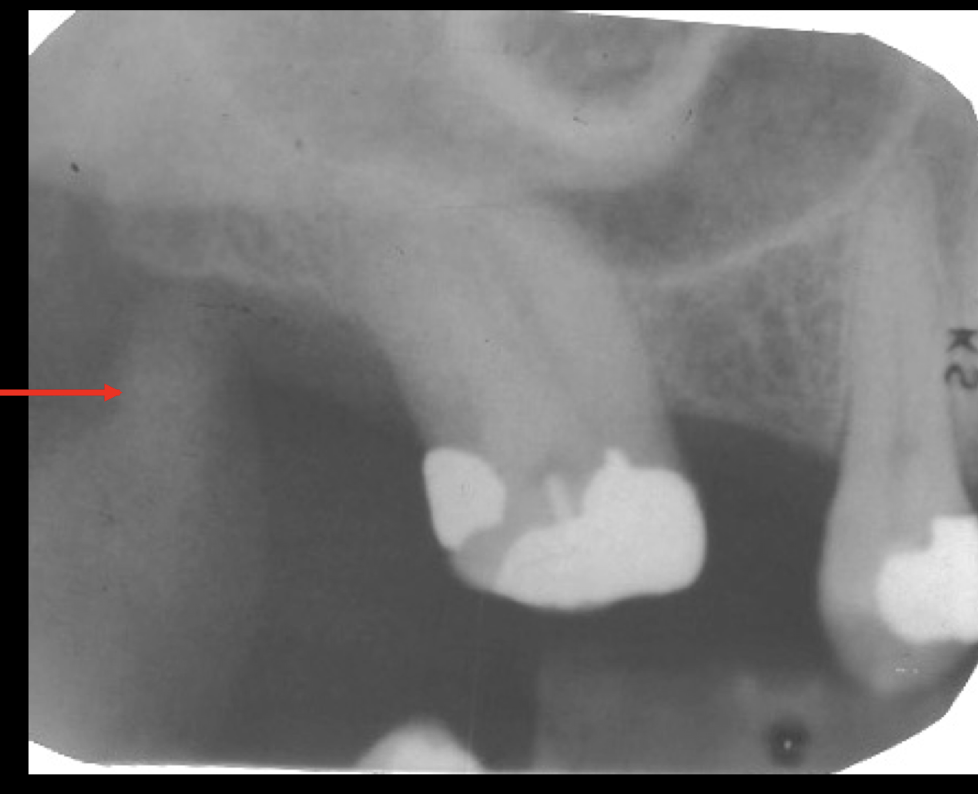
cornoid process
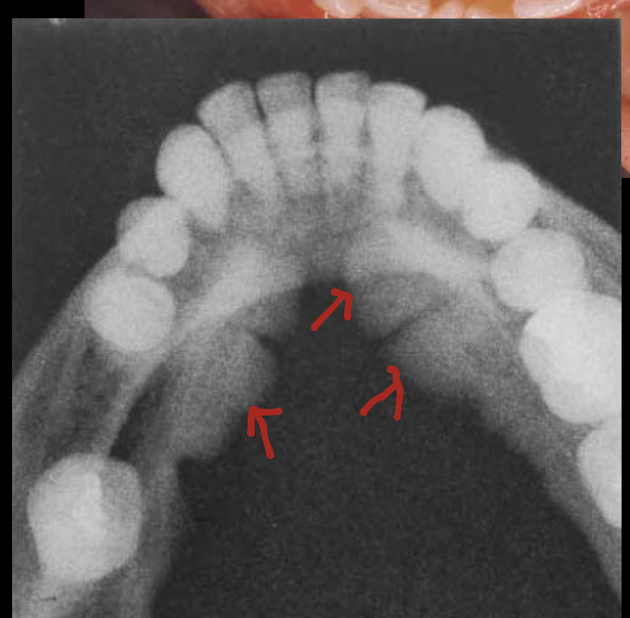
mandibular tori
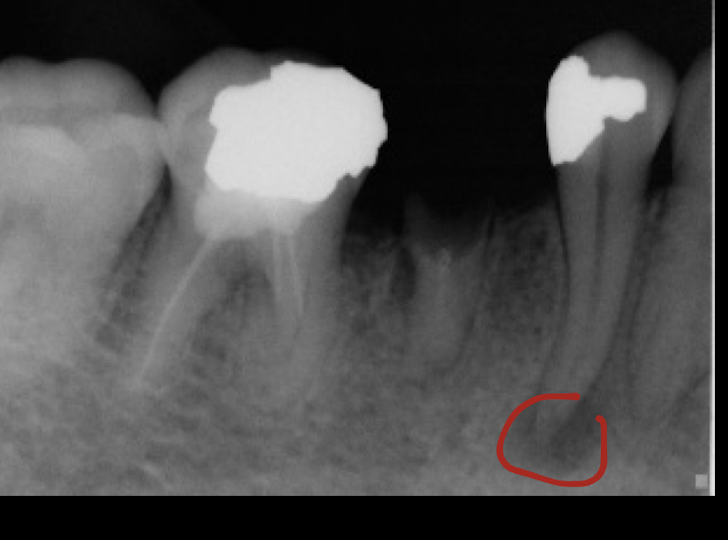
pathology
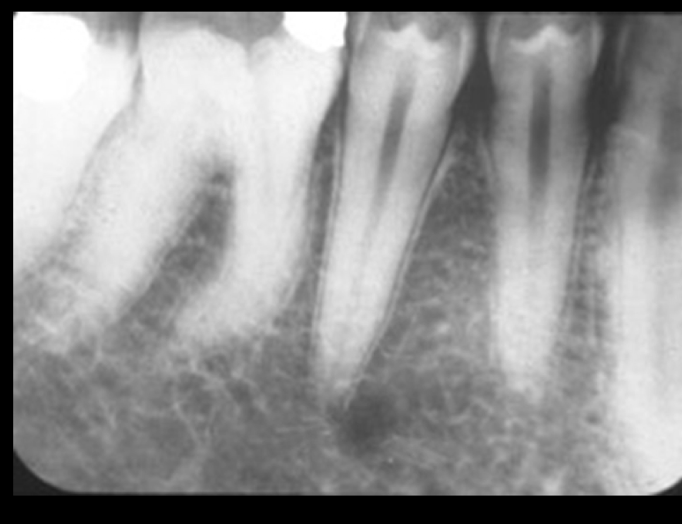
mental foramen
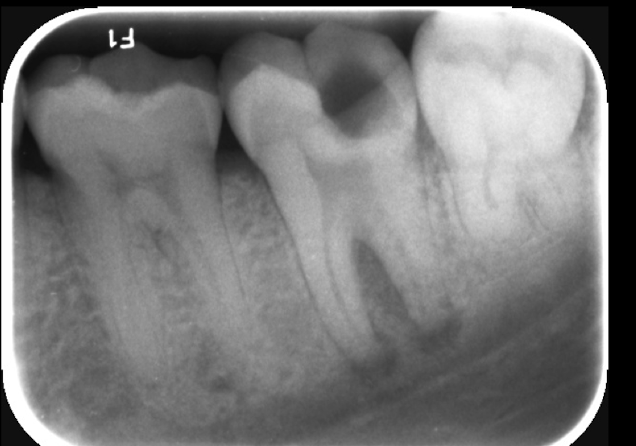
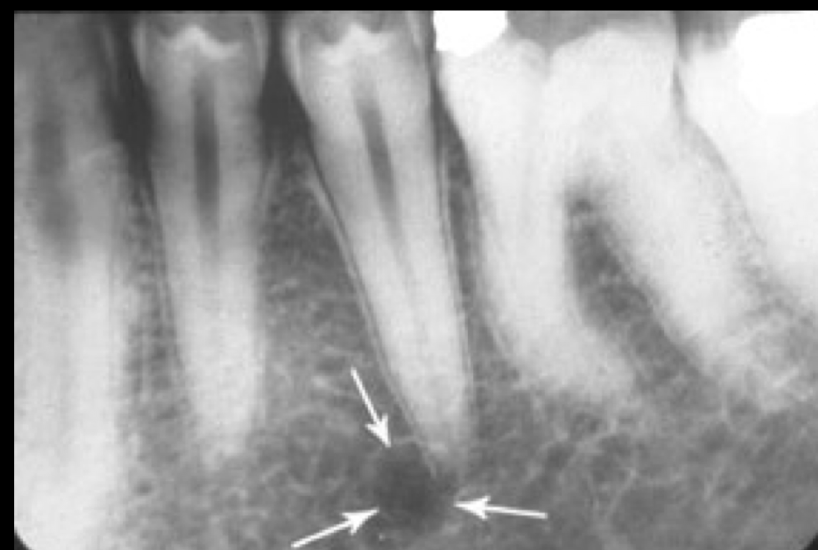
loss of lamina dura
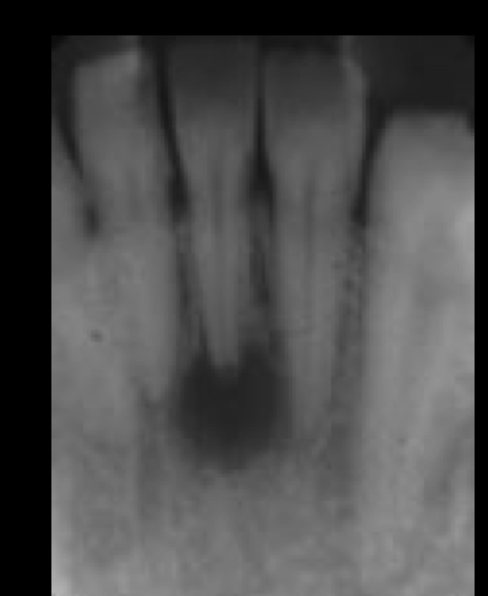
periapical abcess, granuloma, or cyst
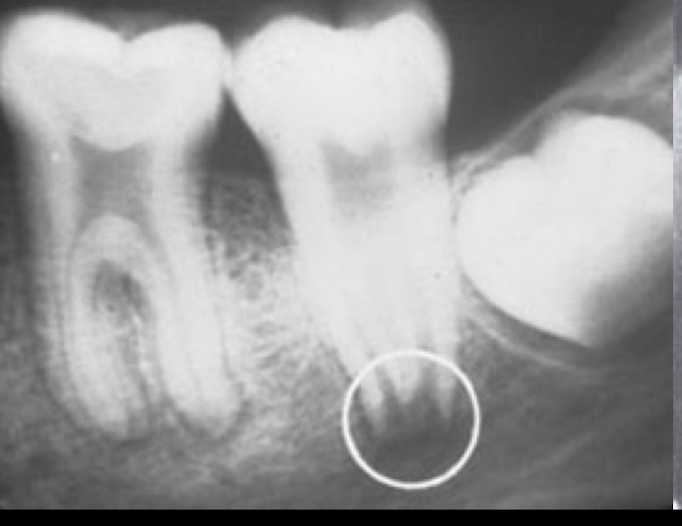
Developing tooth
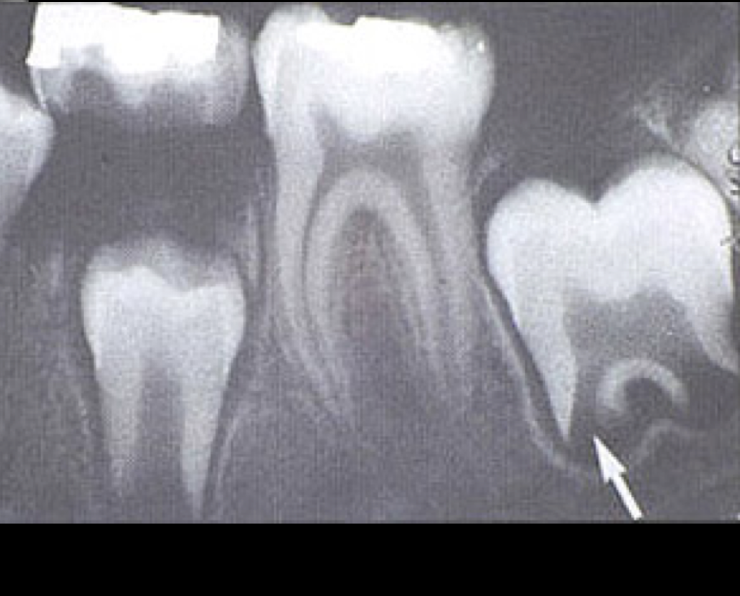
developing tooth