ENTM Exam I
1/193
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
194 Terms
Who developed the system of binomial naming and classification in the mid-1700s?
Carl Linnaeus
What is the primary purpose of standardized binomial classification for entomologists?
It provides a consistent framework to describe and compare species.
List the seven primary levels of biological classification in descending order starting from Kingdom.
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species.
What are the three biological domains?
Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukaryota.
The kingdoms Plantae, Animalia, Fungi, and Protista belong to which domain?
Eukaryota
To which phylum do humans belong?
Chordata
What is the taxonomic Class for humans?
Mammalia
What is the taxonomic Order for humans?
Primates
What is the taxonomic Family for humans?
Hominidae
What is the scientific name of the House Fly?
Musca domestica
What is the taxonomic Order of the House Fly?
Diptera
In the name Homo sapiens, what does 'sapiens' represent?
The species epithet.
What is the meaning of the Greek root 'Arthro' in the word Arthropoda?
Jointed
What is the meaning of the Greek root 'poda' in the word Arthropoda?
Foot
Which major group of arthropods is classified as a subphylum rather than a class?
Crustacea
How many pairs of antennae do members of the subphylum Crustacea typically have?
Two pairs
What are the two primary body regions of a crustacean?
Cephalothorax and abdomen.
How many pairs of legs do most crustaceans possess?
Five to seven pairs.
What type of eyes are characteristic of the subphylum Crustacea?
One pair of compound eyes.
To which class do millipedes belong?
Diplopoda
How many pairs of legs are typically found per body segment in the class Diplopoda?
Two pairs per segment.
What is the characteristic body shape of millipedes compared to centipedes?
They are cylindrical and rounded.
What is the primary food source for most members of the class Diplopoda?
Decaying plant material.
To which class do centipedes belong?
Chilopoda
How many pairs of legs are found per body segment in the class Chilopoda?
One pair per segment.
What is the structural orientation of a centipede's body?
Dorsoventrally flattened.
What specialized structures do centipedes use to inject toxins into their prey?
Forcipules (venomous claws).
How many pairs of legs do members of the class Arachnida have?
Four pairs
How many pairs of antennae are present in arachnids?
Zero
What are the two body regions of an arachnid?
Cephalothorax and abdomen.
What type of eyes do arachnids typically possess?
Six to eight simple eyes.
What is the common name for members of the order Opiliones?
Harvestmen or daddy longlegs.
Which arachnid order includes mites and ticks?
Acari
What is the scientific order name for spiders?
Araneae
What is the scientific order name for scorpions?
Scorpiones
How many primary body segments do insects have?
Three (head, thorax, abdomen).
How many pairs of legs do members of the class Insecta have?
Three pairs
To which subphylum do insects belong?
Hexapoda
Insect muscles are composed of repeating bundles of actin and myosin called _____.
Tonofibrillae
What are the tendon-like structures that attach insect muscles to the exoskeleton?
Apodemes
In what functional arrangement do insect locomotion muscles typically work?
Antagonistic pairs.
Which type of flight muscles attach directly to the wing base to move the wings?
Direct flight muscles.
How do indirect flight muscles move an insect's wings?
They deform the thorax.
In which group of insects are direct flight muscles the primary mechanism?
Palaeoptera (e.g., dragonflies and mayflies).
Which flight muscle type is dominant in advanced orders like Diptera and Hymenoptera?
Indirect flight muscles.
Name the three primary regions of the insect alimentary canal.
Foregut, midgut, and hindgut.
What are the three primary functions of the insect foregut?
Ingestion, storage, and grinding.
What is the primary function of the midgut?
Digestion and nutrient absorption.
What are the primary functions of the hindgut?
Osmoregulation, absorption, and excretion.
What is the function of the insect crop?
Temporary storage of food.
Which part of the foregut is responsible for the mechanical grinding of food?
Proventriculus
What structures in the midgut increase surface area and secrete digestive enzymes?
Gastric caeca
What is the primary site of enzymatic digestion in the insect gut?
Ventriculi
What membrane surrounds the food bolus to protect the midgut epithelium?
Peritrophic membrane
Which structures remove nitrogenous waste from the hemolymph and deliver it to the hindgut?
Malpighian tubules
Which part of the hindgut is the active site for water and ion reabsorption?
Rectum
What form of nitrogenous waste do aquatic animals typically excrete?
Ammonia
What solid nitrogenous waste product allows insects to conserve water?
Uric acid
Which structures in the rectum assist in the near-complete resorption of water?
Rectal pads
What is the name of the main circulatory tube running along the back of an insect?
Dorsal vessel
In the insect circulatory system, what is the anterior portion of the dorsal vessel called?
Aorta
What are the one-way valves through which hemolymph enters the insect heart?
Ostia
Where does hemolymph exit the aorta to bathe the tissues?
At the head.
What is the primary body cavity in arthropods where hemolymph bathes organs directly?
Hemocoel
What are the immune cells found circulating in insect hemolymph called?
Hemocytes
Which immune process involves hemocytes ingesting foreign particles?
Phagocytosis
Which immune process involves hemocytes forming a protective layer around large foreign particles?
Encapsulation
What is the function of the fat body in insects?
Storage of fats, glycogen, and proteins, and regulation of blood sugar.
What are the spiral chitin rings that reinforce insect trachea called?
Taenidia
What are the submicron-diameter tubes where gas exchange occurs at the tissue level?
Tracheoles
How do large or active insects move air through their tracheal system?
Active ventilation using abdominal pumping.
What structures in the respiratory system increase air volume displacement and lack taenidia?
Air sacs
What happens to the tracheal lining when an insect molts?
It is shed.
In which type of respiratory system are only the terminal spiracles functional?
Closed systems
What type of neurons carry messages from sensory receptors to the central nervous system?
Sensory neurons
What type of neurons regulate the contraction of muscles?
Motor neurons
What type of neurons mediate the connections between sensory and motor neurons?
Interneurons
What do neurosecretory neurons produce to control functions like development and metabolism?
Neurohormones
What are the clusters of nerve cells that make up the insect central nervous system called?
Ganglia
The insect central nervous system consists of a brain and a _____.
Ventral nerve cord
What are spermatophores?
Sperm packets encased in a water-tight lipoprotein shell.
In which insect orders are spermatophores most prominently used?
Orthoptera, Lepidoptera, and some Coleoptera.
Where are sperm produced within the insect testes?
Follicles
What are the germ cells that divide by mitosis to form spermatocytes?
Spermatogonia
Which process yields four haploid spermatids from a single spermatocyte?
Meiosis
What are the two major functions of the male accessory glands?
Manufacturing seminal fluid and producing spermatophores.
What are the functional subunits of insect ovaries called?
Ovarioles
What is the name of the female genital chamber where sperm is often received during copulation?
Bursa copulatrix
Which structure in the female reproductive system stores sperm for future fertilization?
Spermatheca
How does the female insect release sperm onto the egg surface?
Muscular contraction across the spermatheca.
What is the primary role of the insect circulatory system regarding oxygen?
It is generally not involved in O2 or CO2 transport.
In hemimetabolous insects, how does the tracheal system change during molting?
It expands incrementally without complete rearrangement.
Which metabolic process in animals is the primary source of nitrogenous waste?
Protein metabolism
What is the structural characteristic of forcipules in centipedes?
They are the first pair of legs modified into venomous claws.
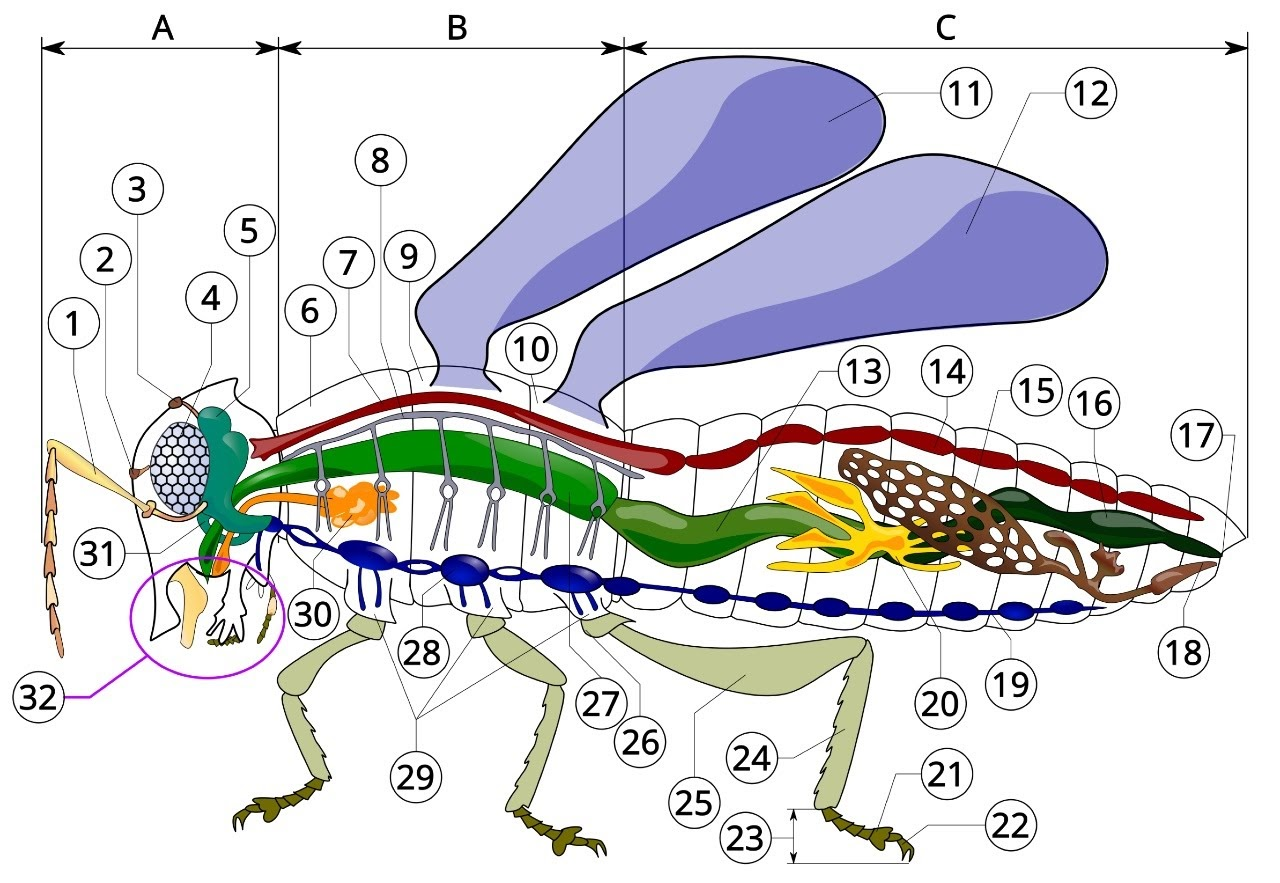
A
head
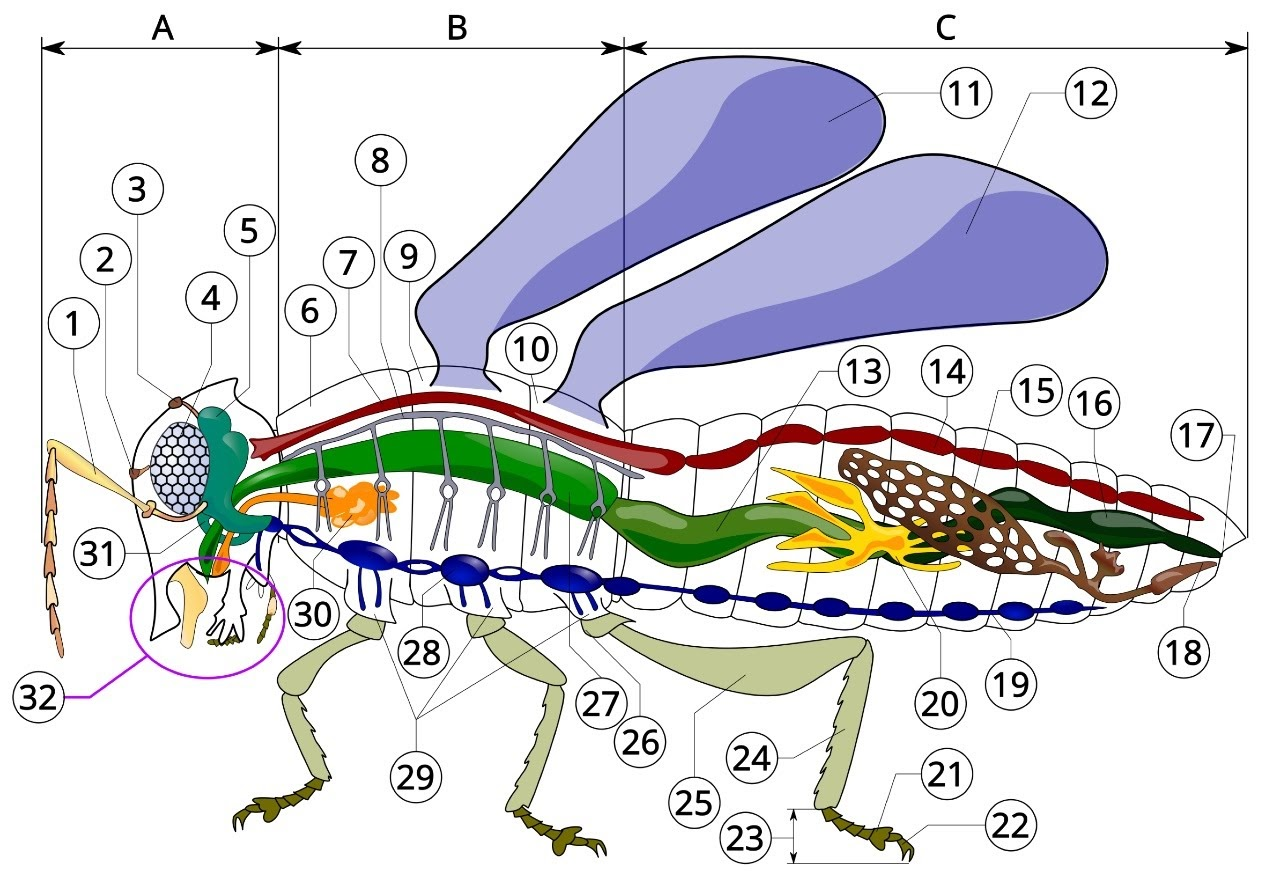
B
thorax
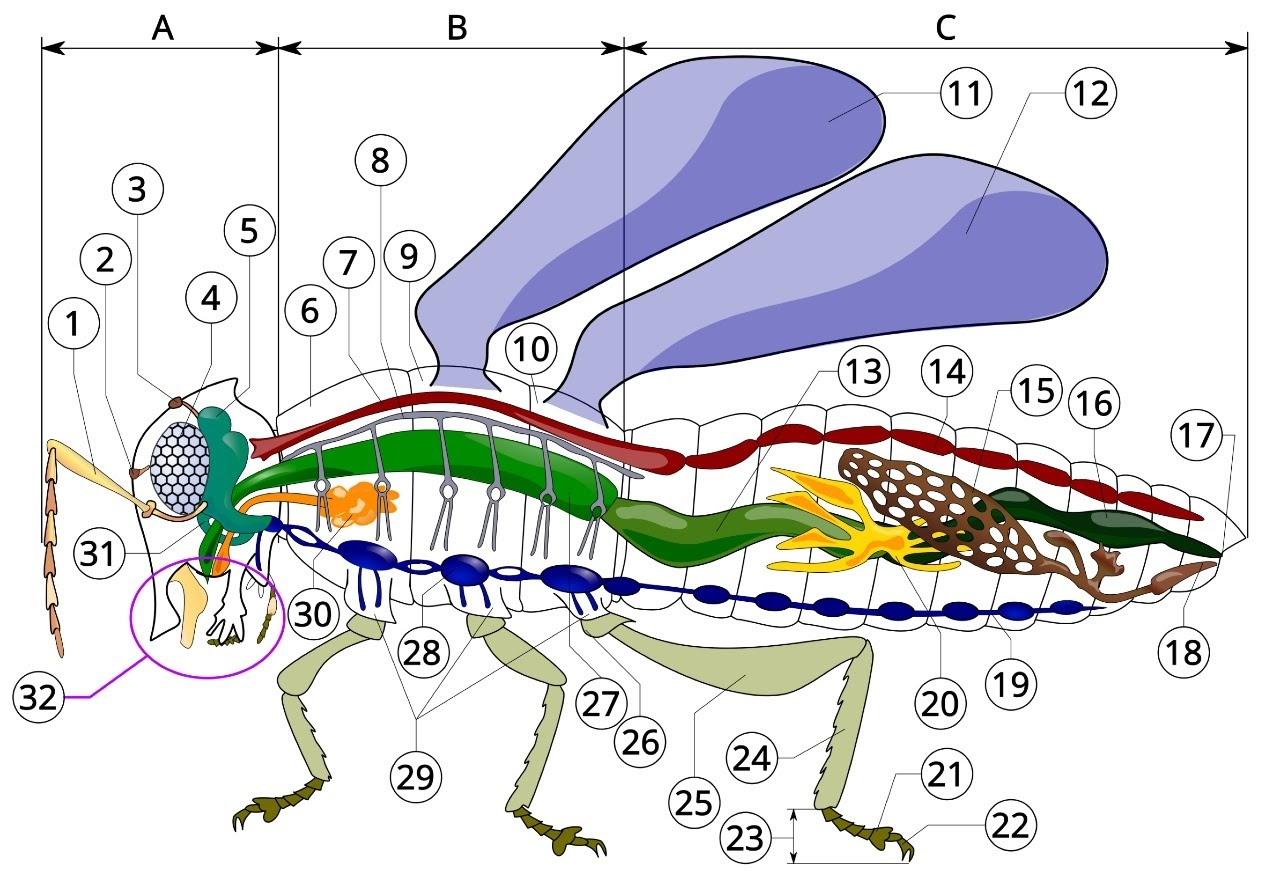
C
Abdomen
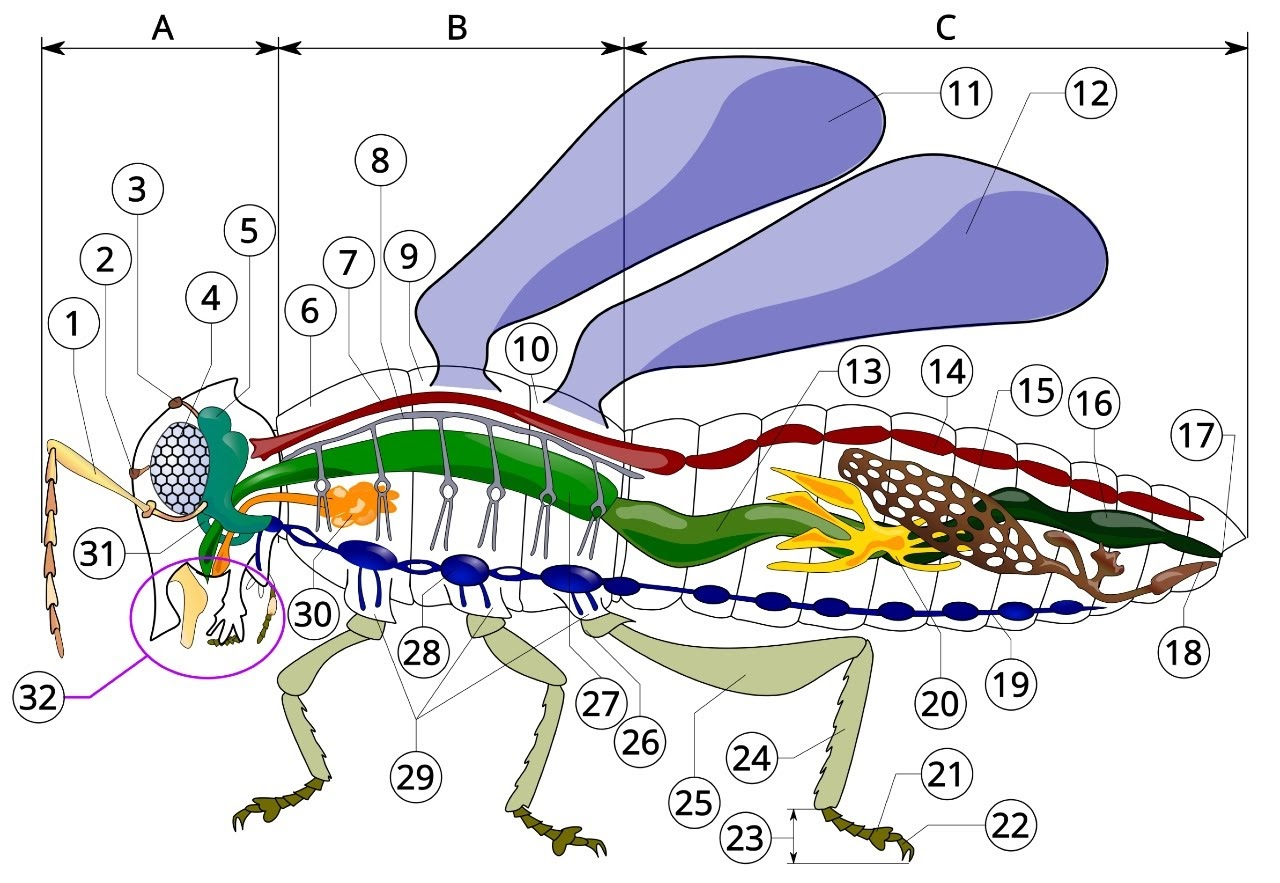
1
antenna
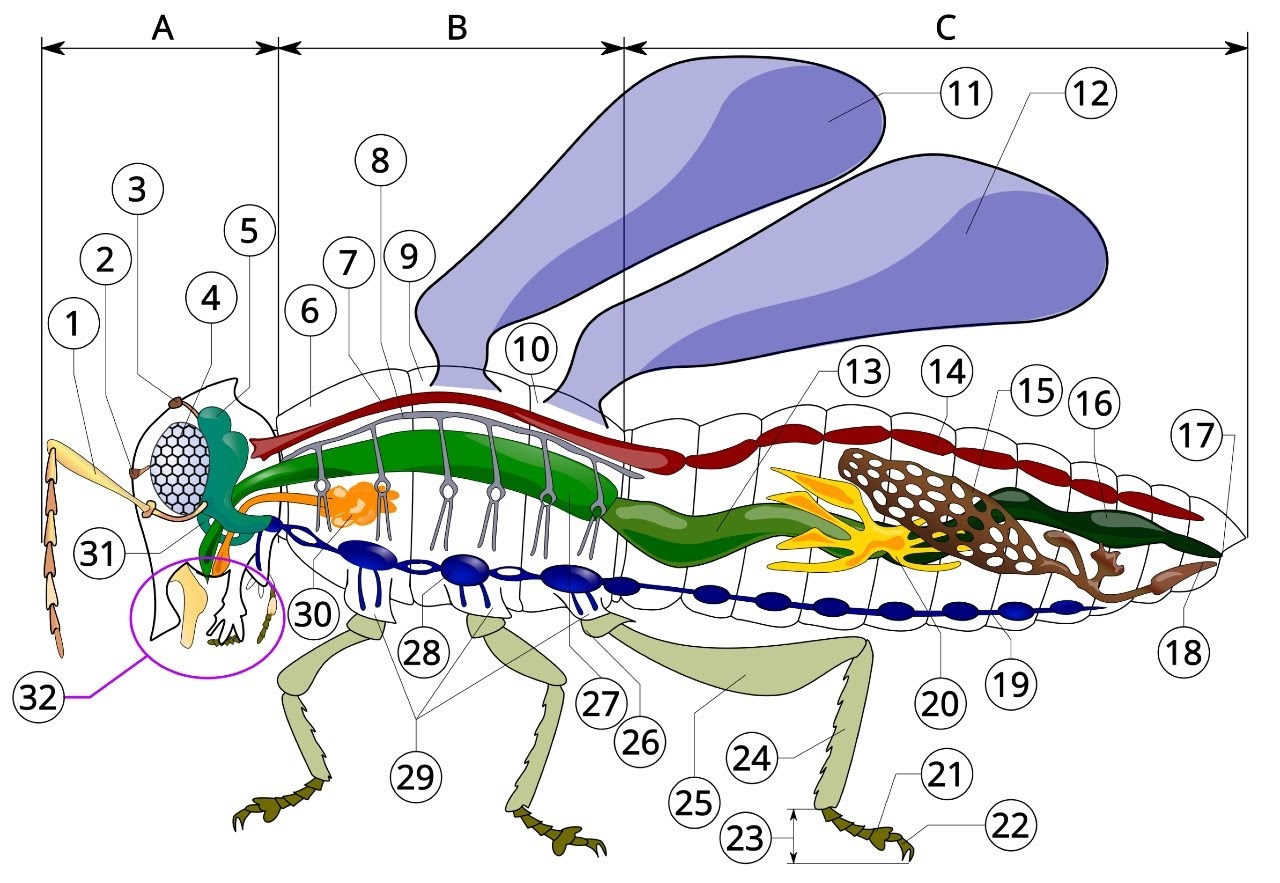
2
ocelli (lower)
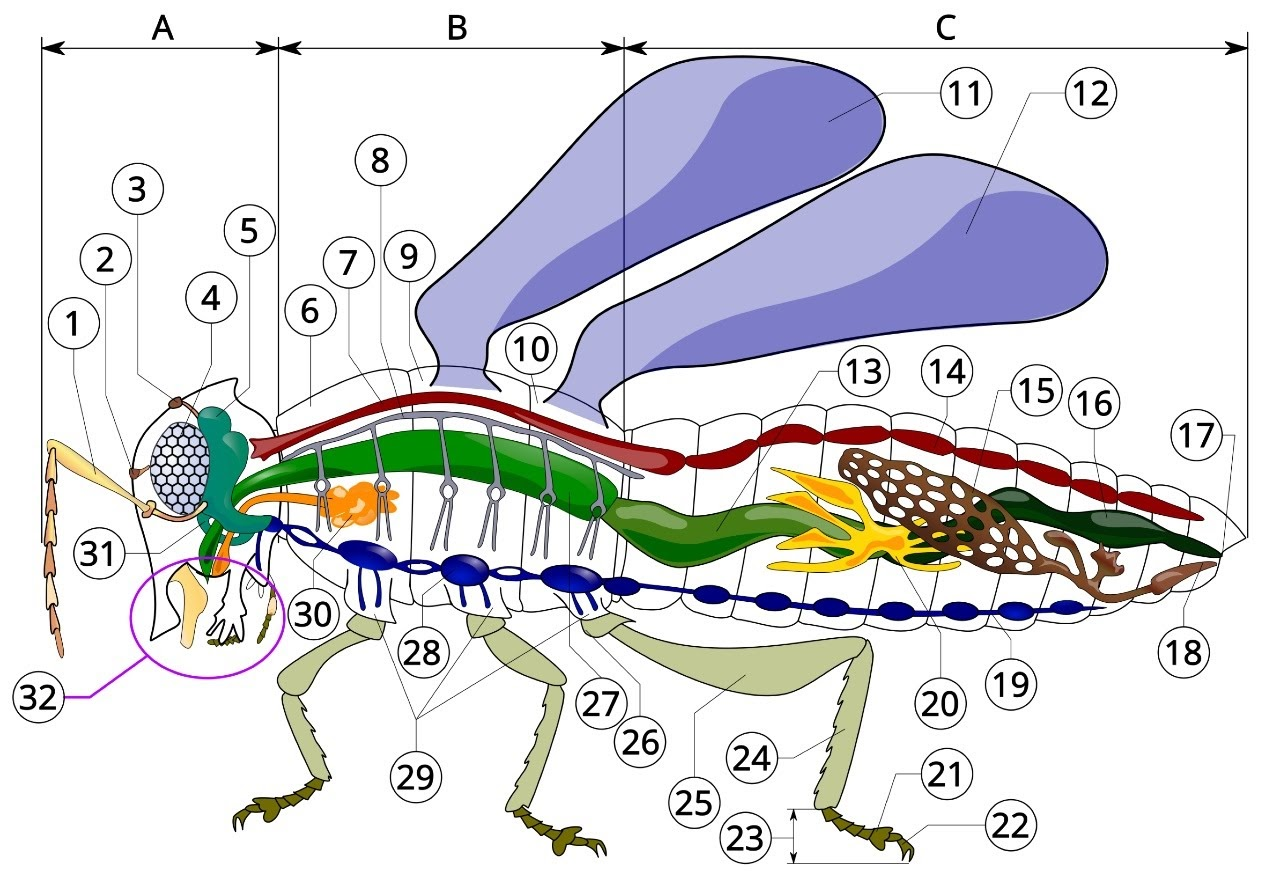
3
ocelli(upper)