AP Psych Levels of Consciousness Notes
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Consciousness
The awareness of one’s environment and mental processes
Most early psychologists studied levels of consciousness
varies throughout the day
Higher level of consciousness= better to process info
William James’ definition of Consciousness
Always Changing
A personal experience
different for everyone
Continuous
Selective
Freud’s View on Consciousness
Iceberg Theory
Conscious- ideas, memories, feelings, or motives of which we are actively aware
Preconscious- aspects of our experience that are not conscious but can easily be brought to awareness
more info based like old locker number
Unconscious- cognitions, feelings, or motives of which we are not aware
takes time and effort to bring to awareness
need hypnosis
Sleep
an altered state of consciousness
a form of consciousness
a lot of processing goes on when we sleep
Electroencephalogram
One of the devices used to determines a person’s sleep stages
EEG- best measure of brain electrical activity
measures electrical activity of the brain
Electromyogram
Measures Muscle tone, another indicator of sleep stages
also used in sleep studies to help indicate sleep level
if have major sleep issues, you will be prescribed a sleep study
measures what the sleep actually looks like
4 brainwave stages
Beta- awake and REM, 13-30 Hz
dreams in REM sleep are more vivid, not the same as NREM dreams
Alpha- stage 1 sleep, 7-13 Hz
Theta- transitional sleep (when brain is transitioning between stages of sleep), 3.5-7 Hz
Delta- deep sleep, 0.5-3.5 Hz
stages 3 and 4
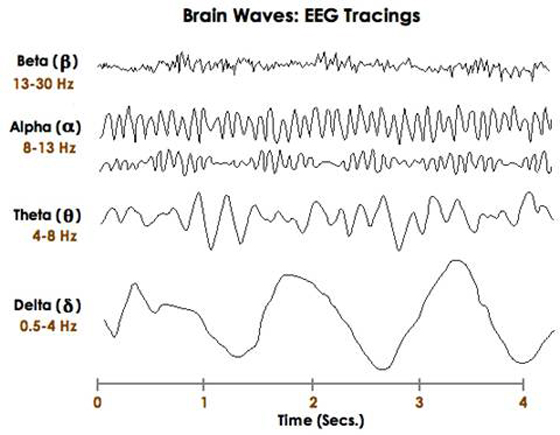
How many stages of NREM sleep are there?
4
NREM
Non Rapid Eye Movement
Dreams can occur, but not the same as REM dreams
Stage 1 of Sleep
Stage 1: Brief transitional stage usually lasts 5-10 minutes
shallow sleep, short nap
Alpha waves give way to Theta waves
Predominatly alpha waves with theta waves towards the end
very light sleep
hypnotic state
change one’s habits through hypnotic suggestions
Hypnic jerk
Hypnotic state
at the beginning of sleep and at the end when waking up- not with alarm
change one’s habits through hypnotic suggestions- right before falling asleep
right before going to sleep feels like about to go into hypnosis
Hypnic Jerk
feeling of falling followed by a jerk into wakefulness
almost like the brain does want to do to sleep yet
Stage 2 of Sleep
Stage 2: Characterized by brief burst (spindles) of higher frequency brain waves, sleep spindles- fairly regular intervals
relatively easy to be awakened
predominantly theta waves
transitional waves that happens between stages of sleep
Sleep spindles- unique to this stage
K-complex- unique to this stage
Sleep Spindles
unique to Stage 2
short bursts of brain activity
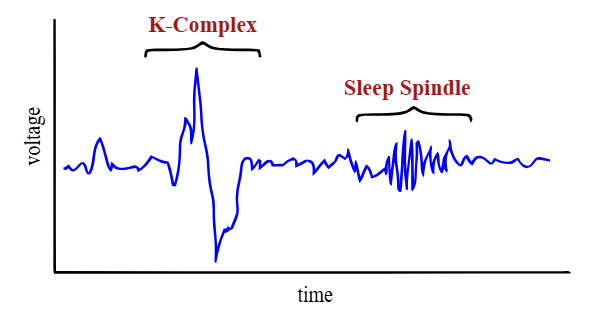
K complex
unique to stage 2
the brain is shutting out external stimuli (ability to hear and sense of surroundings)
shut out what we don’t need so brain can go into deep sleep
Stage 3 of Sleep
20% of EEG activity DELTA WAVES
predominantly delta waves, deep sleep waves
very difficult to awaken
internal functions slow down, brain is most inactive in deep sleep
“deep sleep” or physical restful sleep
get most physical restfulness
more 3 and 4 at the beginning of the night, less as night goes on
stage 3 and 4, tossing and turning occurs
stage 3 sleepwalking occurs, motor cortex is activated in this stage
somnambulism
Sleepwalking
also known as somnambulism
occurs in stage 3
motor cortex in the brain is activated which allows sleepwalking to occur
Stage 4 of Sleep
More than 50% of EEG DELTA WAVES
last stage of NREM sleep
at the end of stage 4 brainwaves start to increase as you travel up stages 3,2,1 and then enter your first period of REM sleep (vivid dream time)
What is the ideal amount of sleep per night?
7-8 hours
B-A-T-D back to B
Beta
Alpha
Theta
Delta
Back to beta
REM Sleep
Rapid Eye Movement
Brain is just as active as when it is awake
Beta Waves- same as awake and alert
REM is caused by the visual cortex (occipital lobe which is 1 of 4 main parts of the brain, located in the back) of the brain being activated during dreaming
adults typically spend 25% of night in REM sleep
teens spend more
REM is most essential for our cognitively ability and mood
REM increases as the night goes on and during stressful times
FMRI
Functional Magnetic Residents Imagining
machine that reads activity in the brain as it is going on
a lot of activity in REM sleep
Time for entire sleep cycle
90 minutes
Time for stages 1-4 of sleep
60 minutes
Freud on Dream
Believed Dreams had meaning and sought to decode their meanings
“Dreams the royal route to the unconscious”
Wrote Interpretation of Dreams in 1899
Latent Content: unconscious drives and wishes that would be threatening if expressed directly
Manifest Content: obvious or known meaning to the dream
Latent content
unconscious drives and wishes that would be threatening if expressed directly
meaning of the dream that is hidden
true, underlying, meaning of the dream that resides in a person’s unconscious mind
Manifest Content
obvious or known meaning to the dream
content of which the dreamer is consciously aware
3 Dream Theories
Information processing
Physiological Function
Activation Synthesis
Information Processing
the brain sifts through the day’s events and keeps what is needed and discards unnecessary info
files away what we need, trashes what we don’t
Recent studies support this theory
has most research supporting it
House Keeping of the Brain
Physiological Function
REM occurs as a result of brain and body growth
may explain why infants and children dream more than adults
Dreams provide the sleeping brain with periodic stimulation to develop and persevere neural pathways
Neural networks of newborns are quickly developing therefore they need more sleep
Activation Synthesis
Random neural firings occur during REM
the brain is simply trying to make sense of these random neural firings
Dreams are activated via physiological mechanism in the brainstems
brainstem generates neural activity
cerebral cortex synthesizes the activity into meaningful “stories”
mor research evidence than Freud’s theory
Suggests that the brain engages in a lot of random neural activity
dreams make sense of this activity
Sleep Disturbances
Nightmare
Night Terror
Sleepwalking
Nightmares
anxiety producing dreams that usually lead to awakening
mare is an old English phrase that means spirit or goblin
younger kids have more
Night Terrors
aka Incubus Attack or devil on your back
Abrupt awakening from dream or nightmare that occurs during NREM sleep (reason they are so disruptive to sleep)… accompanied by intense feelings of panic (wake up screaming, heart racing)
Often associated with PTSD
Disrupts the balance of sleep
Sleepwalking
Somnambulism
occurs when a sleeping person arises and wanders about in deep NREM sleep (stage 3 or 4, mostly 3)
more common when you are younger
motor cortex is responsible for big motor functions like walking
talking in sleep also occurs at this time
Sleep Disorders
DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders) classifies 3 groups of sleeping disorders
Insomnia
Narcolepsy
Sleep Apnea
Insomnia
Inability to fall asleep or stay asleep for the entire night
3 different kinds
Onset- inability to fall asleep, beginning of sleep
Maintenance- inability to stay asleep, wake up in the middle of the night
Termination- waking up early and not able to return to sleep
wake up hours before the alarm
Pseudo insomnia- dreaming of being awake, when in reality you are asleep… can often have the same effects as insomnia
dream about not being able to sleep
Solutions to help you fall asleep faster
Sleeping Pills and Alcohol- not good long term
Reduce Blue Light/ Blue Light Filter
Melatonin
Sleeping Pills and Alcohol
may make you sleepy, but they can be addictive and suppress the amount of REM sleep you get
not good, we want REM
the use of sedatives is not recommended for long term use
can gain tolerance to them
Blue Light Reduction
blue light emitted from electronic devices are also known to reduce REM
exposure to these should be REDUCED OR ELIMINATED at least 1-2 hours before bedtime
Blue light filter on devices can also help
Melatonin
Hormone found in the body which helps to regulate sleep
a reduction of melatonin is seen in people who are taking high doses of aspirin and ibuprofen
Lack of sunlight also causes less melatonin production
Melatonin supplements can be helpful if you have a melatonin deficiency
Melatonin is the all natural night ca, our bodies natural hormone that we produced to sleep
Amount produced by our body lessens as we get older
Narcolepsy
feeling of extreme sleepiness which can occur at any time
can fall asleep very quickly and easily
genetic component
Cataplexy- most common symptom, sudden and extreme muscle weakness
a sudden feeling of extreme sleepiness and a need to sit
around 1 in 2000 may have
truck driver/ bus driver is not a recommended occupation if you have
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
characterized by repeated awakenings throughout the night as a result of not being able to breath
Breathing may be stopped for as long as a minute, results in person waking up gasping for breath
have no memory of event the next morning
airway is shutting off
can occur as often as 300-400 times per night
Loud snoring is a Warning Sign
airways collapse and block air flow to lungs
remedy- CPAP Machine- Continues Positive Airway Pressure
Zepbound: new medication for sleep apnea, GLP-1 medication
Voluntary Alternations of Consciousness
Hypnosis
Meditation
Hypnosis
an altered state of consciousness one enters voluntarily
discovered by Franz Mesmer- Freud used hypnosis a lot with patients
able to access thoughts and memories in the past
increase in suggestibility- open to suggestions that a hypnotherapist may place in your subconscious- most often used in weight reduction, smoking, and phobias
can be used to block pain- painless child birth
hypnotherapist use hypnosis to suggest positive things unconscious when in hypnosis so conscious will take in
some are more open to hypnosis than others- more intelligent and better daydreamers tend to by more easily hypnotized
can give dissociation from pain
Highway Hypnosis: person drives a great distance responding to traffic signals and other cars with no recall of any consciousness effort to do so
Meditation
self induced state of altered consciousness
“mantras” often used to help focus one’s attention to relax
Psychoactive Drugs
Psychoactive Drugs are chemical substances that modify mental, emotional, or behavioral functioning
alteration of neural activity in the brain; speeds up, slows down, or interferes with neurotransmitters as they cross the synphase
not to be confused with psychotropic drugs
Psychotropic drugs
medications used to treat and help those with mental health issues
anxiety, depression, etc.
Dependence
depend on drug to fell normal or happy
many people are dependent on caffeine
Tolerance
need more of a drug to feel same effect
Withdrawl
a negative response to an ending of a drug
Addiction
extreme willingness to do anything for the continued use of drug
Drug Abuse
lack of control, disruption of normal function to satisfy the user
Stimulants
are drugs that tend to increase central nervous system activation and behavioral activity
Are agonists- agents that increase nervous system activity
Types of Stimulants
Caffeine
Nicotine
Cocaine
Amphetamines
Caffenine
found in many foods (chocolates), drinks (coffee, energy drinks, tea), and pain killers (Anacin and Excedrin)
the MOST widely abused drug worldwide
sudden stop will cause side effects, headaches
Adenosine: neurotransmitter, causes humans to b/cm tired
caffeine blocks adenosine by binding to receptors
as a result of block adenosine, adenosine floats around and speeds up adrenaline
More caffeine you take, more receptors for adenosine to bind to are made
causes a tolerance of caffeine to build up
Takes 7-12 days for extra receptors to go away after quitting caffeine
Most abused Stimulant
Caffeine
Nicotine
activate excitatory synapse in both CNS and PNS- usually ingested by smoking
when nicotine gets into the brain, it attaches to acetylcholine receptors and mimics its actions
nicotine also raises levels of dopamine
Dopamine
the reward/pleasure neurotransmitter
Cocaine
elevates blood pressure and heart rate
produces a euphoric or “high” feeling
also effects the neurotransmitter dopamine
Amphetamines
Effects Norepinephrine and Dopamine- both affect a persons mood
common names: bennies, uppers, dexies, or jelly babies
a stimulant that helps mask fatigue
can be addictive because it stimulates the release of dopamine and norepinephrine
Depressants
reduces one’s awareness of external stimuli
all depressants are antagonists
Types of Depressants
Alcohol
Alcohol
most commonly used of all depressants
especially dangerous in pregnant women
affects GABA and glutamate (affect anxiety)
both are excitatory neurotransmitters
Most used Depressant
Alcohol
Opiates (Narcotics)
can reduce or eliminate sensation of pain, tend to ignore real world stimuli
Ex. Heroin and Morphine
strongly addictive and dependency can quickly occur
sudden removal results in pain and depression
Barbiturates
synthetically produced sedatives (all others we have talked about have something natural)
slows nervous system activity by blocking neural receptors
Hallucinogens
are a diverse group of drugs that have a powerful effect on the mental and emotional functioning
distortions in sensory and perceptual experiences
LSD (Lysergic Acid Diethylamide)
lead to hallucinations, usually visual - seeing or hearing visions or voices
Affects serotonin, can affect one’s mood directly, mimics neurotransmitters
Maijuana
A mild, relaxed euphoria, accompanied by enhanced sensory awareness and a distorted sense of time
low doses acta as a depressant, high doses act as hallucinogenic
active ingredient is THC
impair judgement and memory… larger dose can cause hallucinations
can be used for medicinal purposes Ex. Cancer Patients- chemotherapy, help reduce nausea
use can affect offspring, whether mom or dad use it
Serotonin
a neurotransmitter that regulates mood
Active ingredient in Marijuana
THC