Edema in wound management
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
what is edema?
The abnormal accumulation of interstitial
tissue fluid
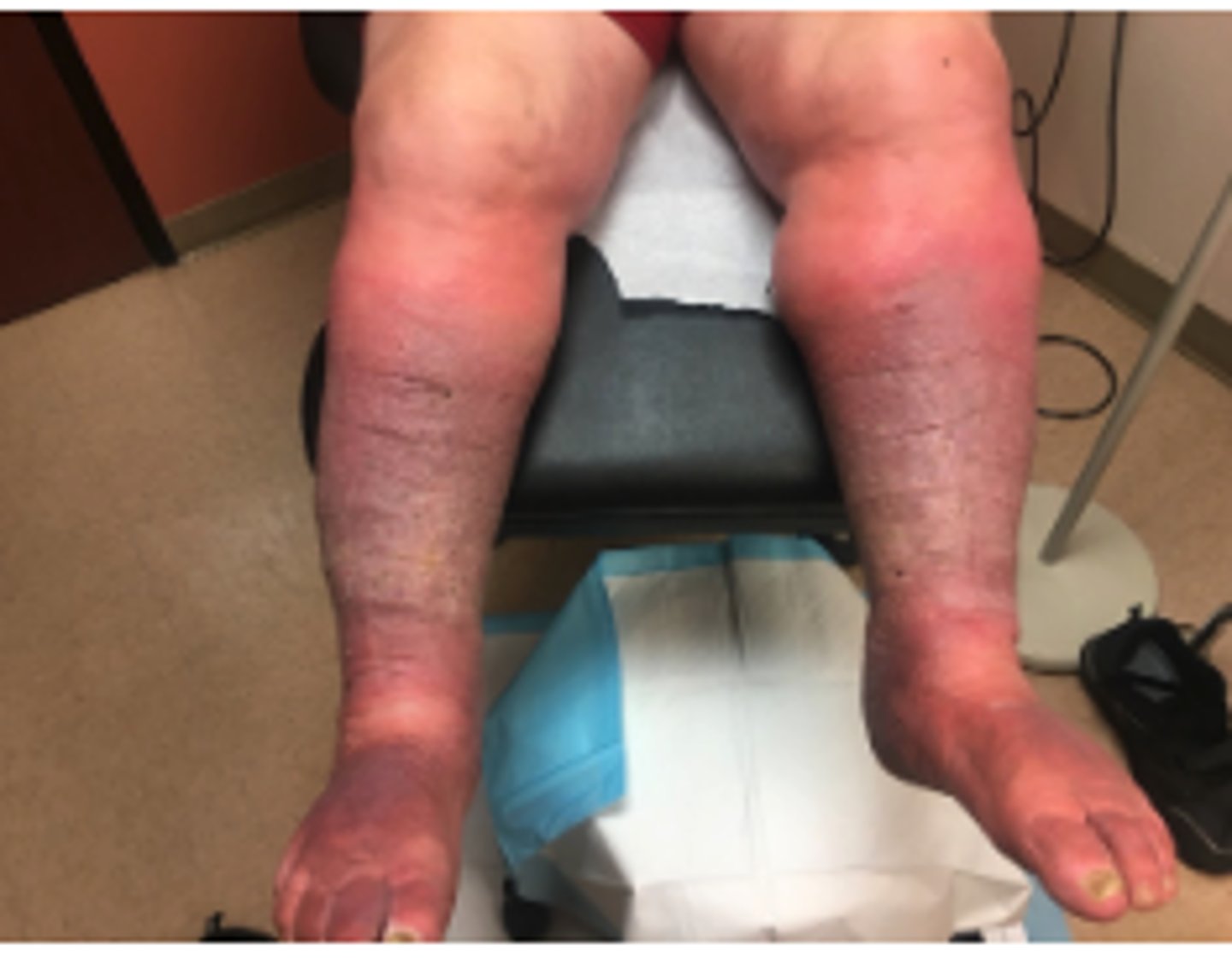
where is peripheral edema common?
legs and feet
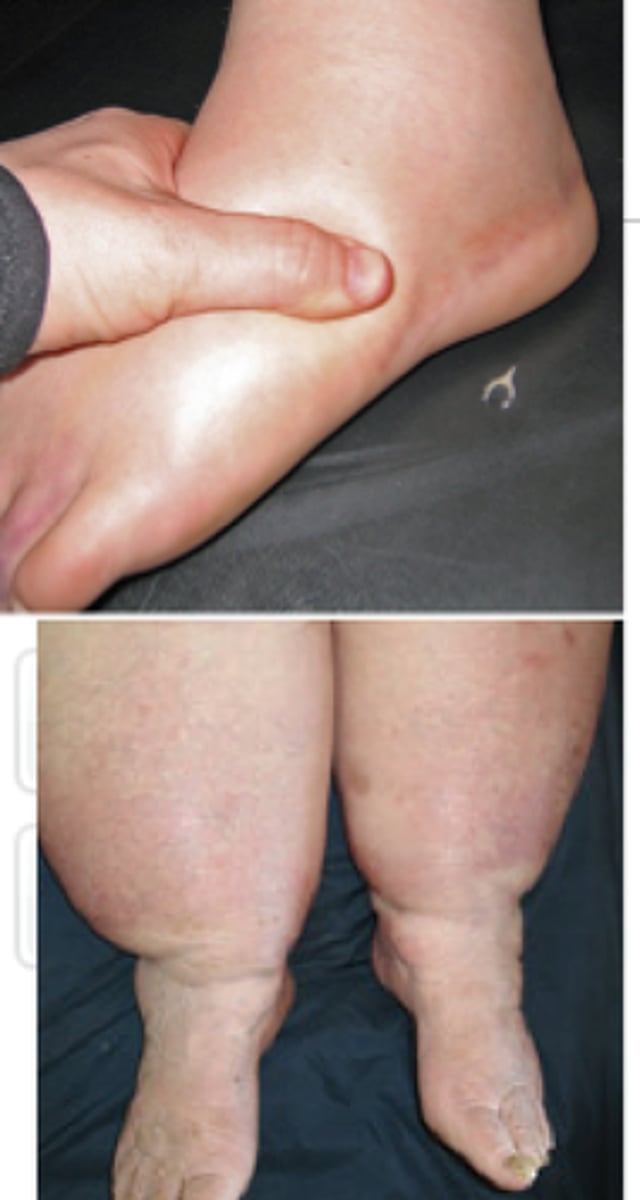
what are the different types of edema? (7)
venous
cardiac
lymphedema
inflammatory
idiopathic
hypoproteinemic
renal
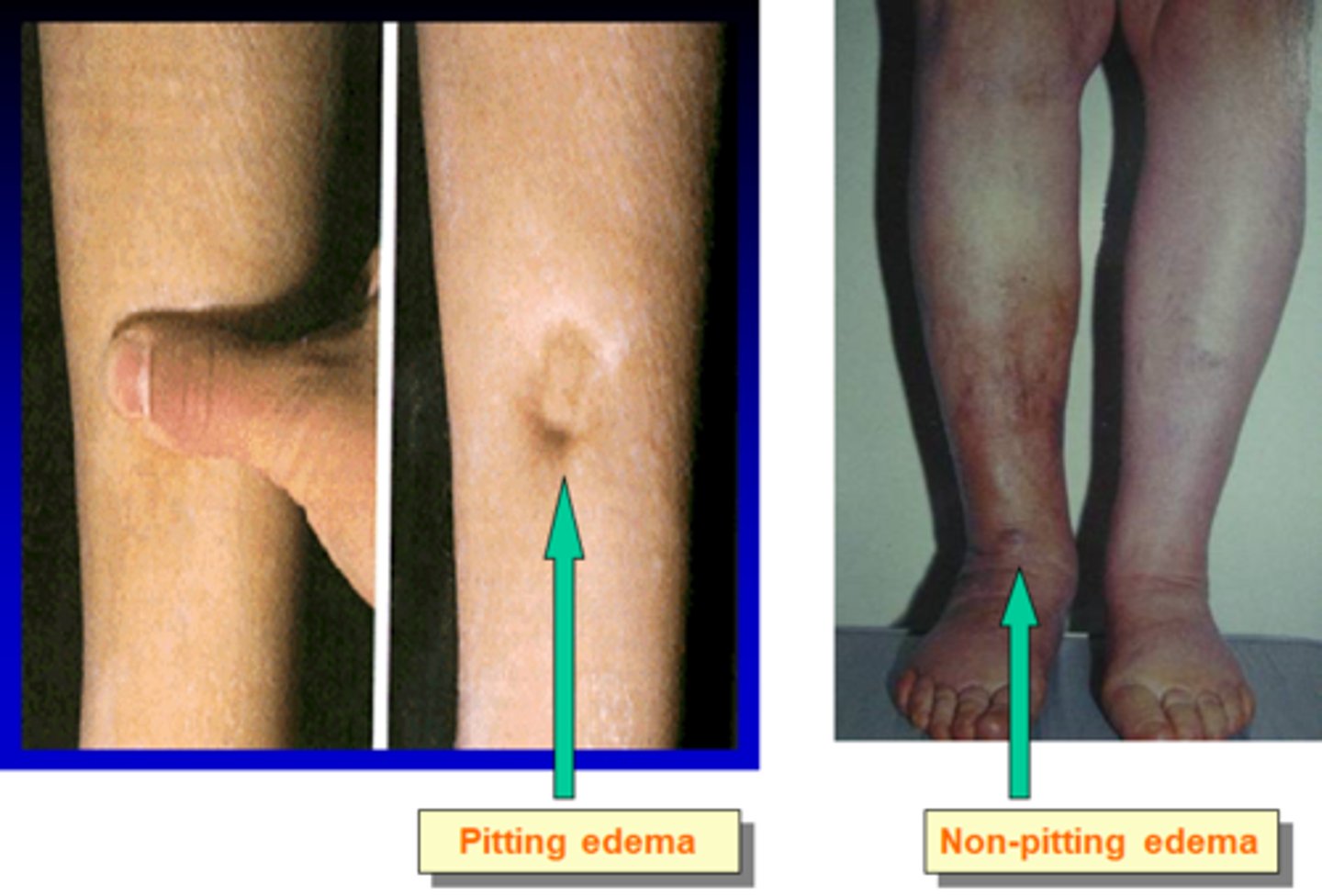
what is pitting vs non pitting edema?
early edema (pitting) vs progressed with fibrosis (non-pitting)
how do we treat edema?
-Medical team managing medical conditions
i.e. heart failure, kidney disease
-Compression
-Exercise
-Elevation and moving often during day
-Skin care
-Manual lymph drainage if indicated
what are the benefits of compression?
-Reduces diameter of veins, causing endothelial cells to become tighter therefore reducing fluid leakage from the veins
-Produces increase in blood flow toward heart and reduces venous reflux
-Facilitates lymphatic fluid movement
what is the degree of compression determined by? (5)
-Elasticity of bandage
-Number of bandage layers
-Shape and size of limb
-Skill and technique of bandager
-Nature of physical activity undertaken by
patient
what is Laplace's Law/
Sub Bandage Pressure (mmhg) = (Tension) x (Number of Layers) x (4630) \ (Limb Circumference) x (Bandage Width)

what does laplace's law show?
sub bandage pressure is directly proportional to bandage tension and number of layers but inversely proportional to the limb circumference to which it is applied and the bandage width.
When compression bandages are applied evenly, there will be a greater pressure at a (larger/smaller) radius leg due to distribution of the same tension over the greater or lesser area
smaller
Increased bandage tension = (increased/decreased) sub bandage pressure
Increased
Increased # of bandage layers = (increased/decreased) sub bandage pressure
increased
Increased leg circumference = (increased/decreased) sub bandage pressure
decreased
Increased bandage width = (increased/decreased) sub bandage pressure
decreased
what are the 2 main bandage types (stretch), and what are they used for?
long stretch: ace wrap used for more aggressive compression
short stretch: unna boot is safer than long stretch due to less extensibility and therefore less tension to limb
what is the difference between resting pressure and working pressure?
Pressure bandage exerts on the tissues at rest
Pressure bandage exerts against working
musculature
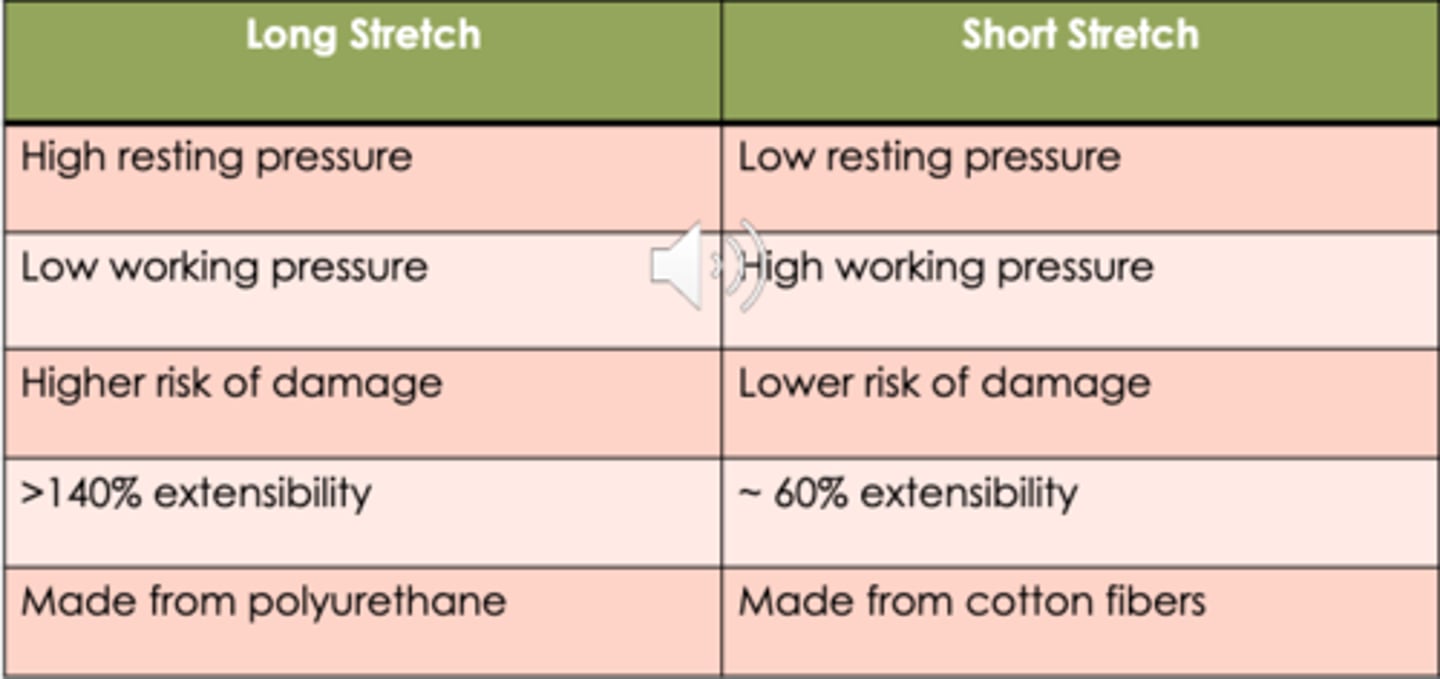
Long Stretch Bandages:
(high/low) resting pressure
(high/low) working pressure
(high/low) risk of damage
(140%/60%) extensibility
(polyurethane/cotton) material
high
low
high
140%
polyurethane
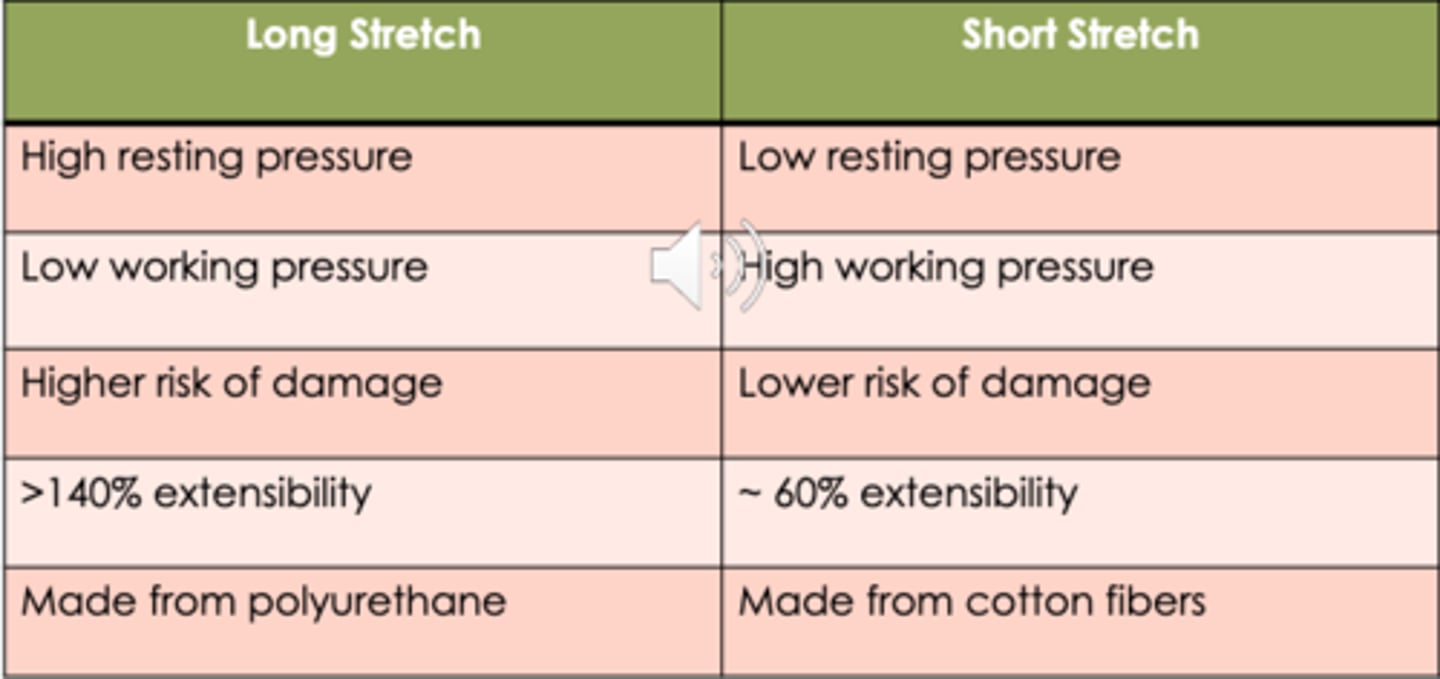
Short Stretch Bandages:
(high/low) resting pressure
(high/low) working pressure
(high/low) risk of damage
(140%/60%) extensibility
(polyurethane/cotton) material
low
high
low
60%
cotton
what are the precautions for compression? (7)
-DM
-Peripheral arterial disease
-Acute cellulitis/infection
-Neuropathy
-Acute heart failure
-Low ejection fraction
-Fragile skin
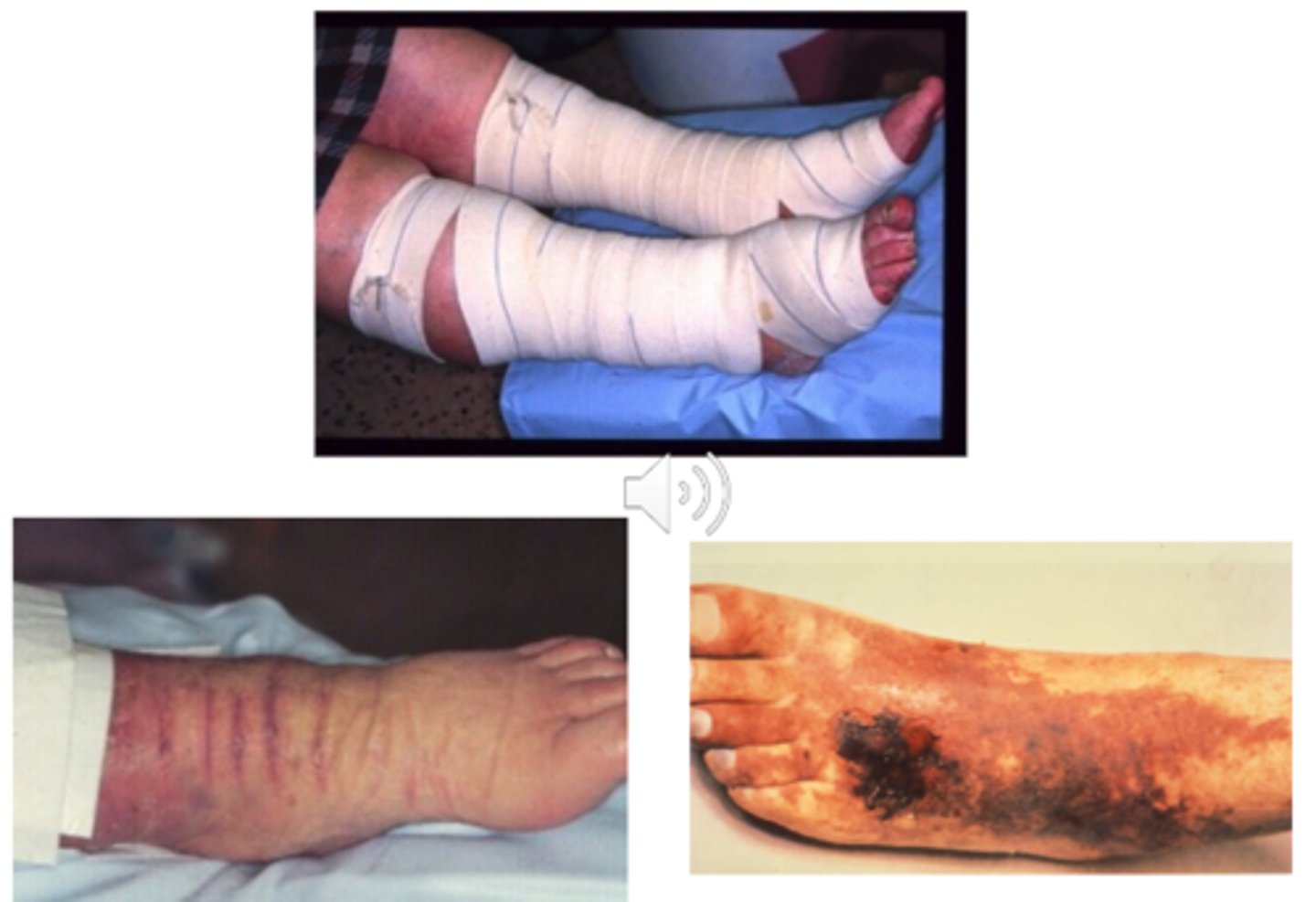
what are the contraindications for compression?
-ABI less than 0.5
-High compression (30-40 mmHg) with ABI
<0.8

what is the progression for compression from open wounds to closed wounds?
1) open wounds: compression wraps (may consider velcro compression garment but not ideal)
2) closed wounds: compression stockings or compression garments
→wraps to stockings!

what are compression stockings indicated for?
indicated for legs with hx of ulcers; edema or risk for edema; varicosities or spider veins; history of DVTs; or history of cellulitis

what are compression stockings usually not indicated for?
open wounds (compression wrapping is best)

Compression Garments:
Class 1: ___-____mmHg is most common
Class 2: ___-____mmHg recommended for DVT
Class 3: ___-____mmHg
Class 1: 20-30 mm Hg most common
Class 2: 30-40 mm Hg recommended for DVT
Class 3: 40-50 mm Hg
what mmHg compression garments are recommended for DVT?
30-40mmHg
what mmHg compression garments are most common?
20-30mmHg
How do we instruct and educate our patients on compression therapy?
-Instruct patient in compression garment use:
-Wear during waking hours, whenever out of bed
-Wash regularly
-Take 45-60 minute breaks 3 times per day to elevate legs above heart
-Limit prolonged standing (>10 minutes) and prolonged sitting (>30 minutes) without getting up
-Move legs every 15-20 minutes while sitting