NU 310: Care of a Client with Cardiovascular Alterations
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
any abnormality in the normal electrical conduction of the heart.
What are dysrhythmias?
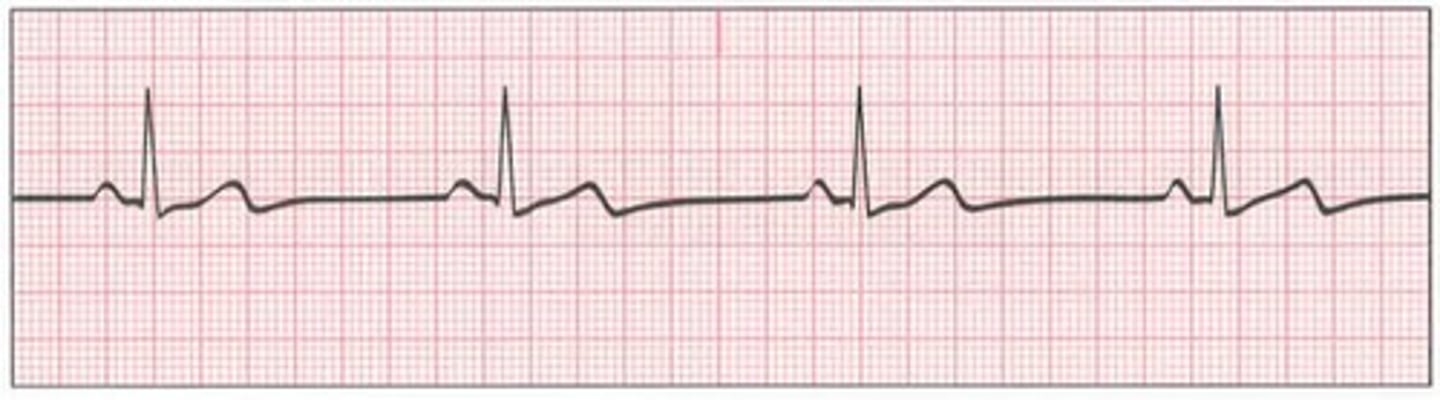
impulse originates from the SA node and follows all proper conduction channels
what is normal sinus rhythm?
normal sinus rhythm
decreased ventricular and atrial rate of
What is sinus bradycardia?
lower metabolic needs (sleep, athletes, hypothyroid), vagal stimulation (vomiting, suctioning, pain), medications (calcium channel blockers, amiodarone, beta blockers)
what is sinus bradycardia caused by?
decreased CO (hypotension, decreased brain perfusion - LOC, decreased UOP), fatigue, memory loss, SOB (d/t hypoxemia)
what are s/s of sinus bradycardia?
IV atropine, epinephrine, dopamine
How is sinus bradycardia treated?
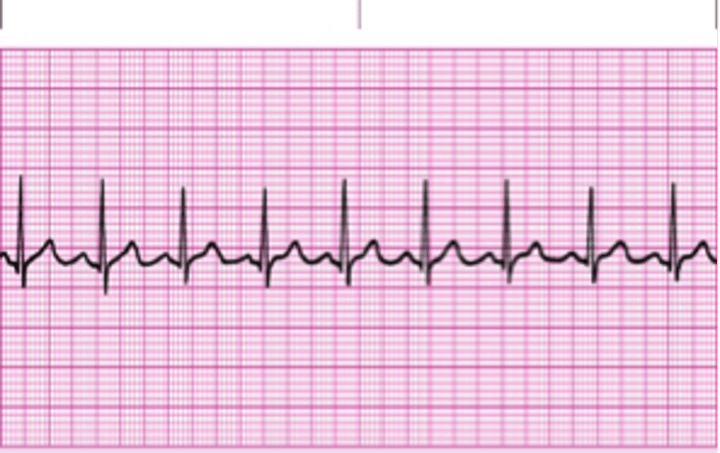
Sinus bradycardia
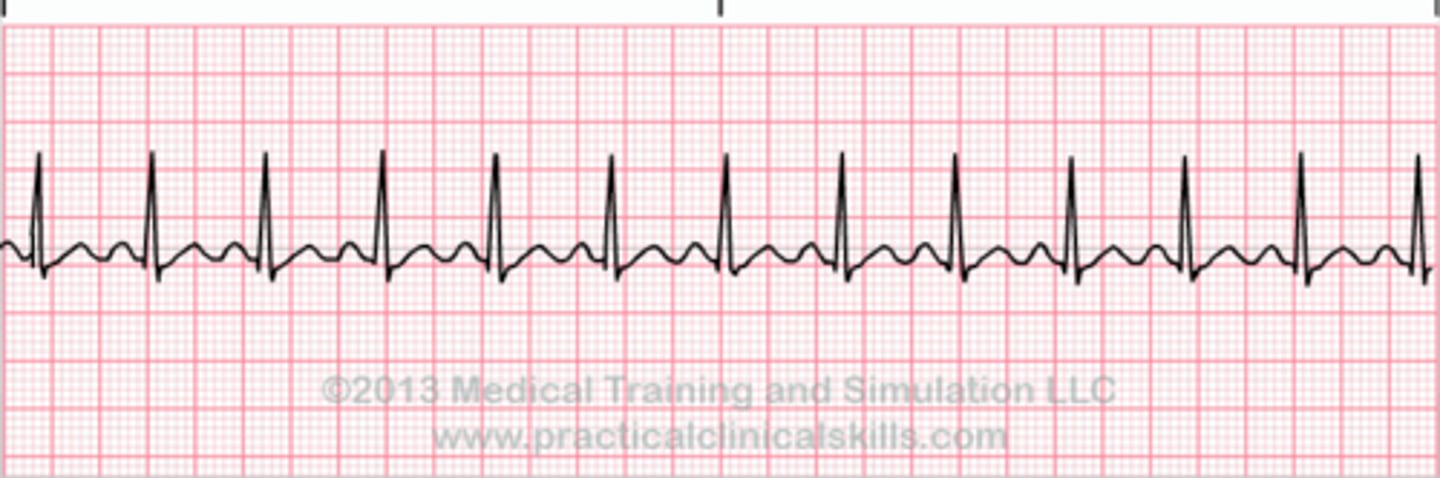
increased ventricular rate between 100 and 120 bpm
what is sinus tachycardia?
physiologic or psychologic stress (exercise, infection, hypovolemia, hypoxia, MI), medications, stimulants (caffeine, nicotine), drugs
what are the causes of sinus tachycardia?
decreased CO causing hypotension, LOC, poor perfusion
what are s/s of sinus tachycardia?
eliminating cause, adenosine (slows HR), catheter ablation
How is sinus tachycardia treated?
Sinus tachycardia
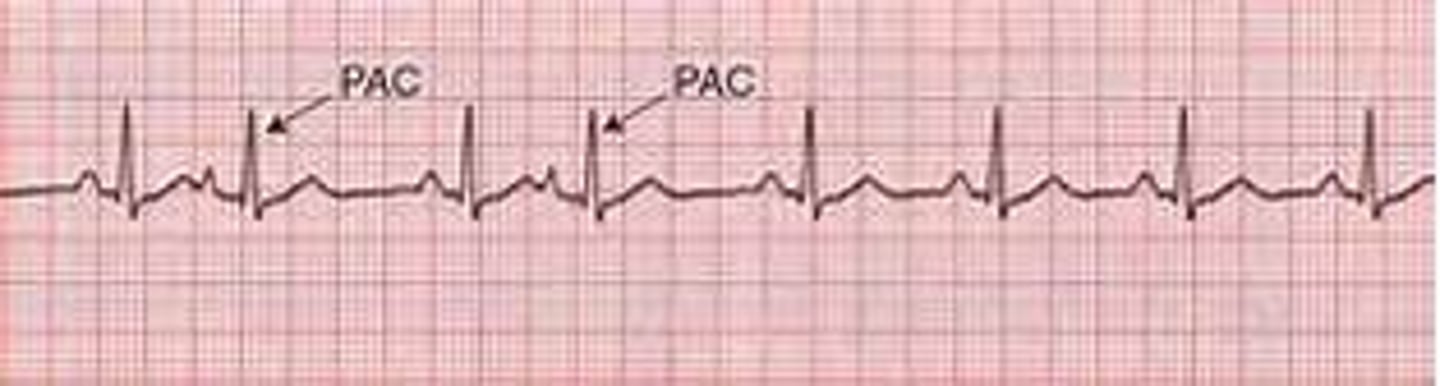
atrial contraction appeared to early before SA node fired normal conduction - P wave appears earlier than it should have
what is premature atrial complexes (PACs)?
caffeine, alcohol, smoking, hypokalemia, anxiety, hypervolemia, damage to atria
what are causes of premature atrial complexes (PACs)?
drink less coffee, alcohol, smoking cessation, decrease fluid overload, treat anxiety, correct K levels, treat ischemia
what are treatments of premature atrial complexes (PACs)?
premature atrial complexes (PACs)
atrial rate is much faster than ventricular rate causing incomplete emptying of blood from the atria (sawtooth shape on ECG)
What is atrial flutter?
diseases in heart and lungs - CHF, previous MI, COPD, pulmonary HTN, issues with mitral and tricuspid valves
what are causes of atrial flutter?
chest pains, SOB, low BP
what are s/s of atrial flutter?
control atrial rhythm, vagal maneuvers, IV adenosine
How is atrial flutter treated?
Atrial flutter
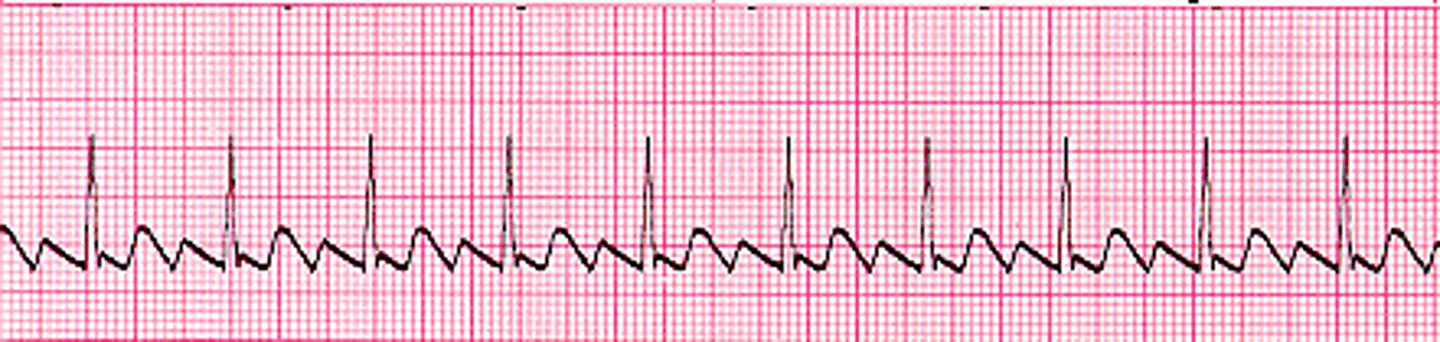
highly irregular atrial rhythm causing rapid and uncoordinated twitching of the atria (can cause blood stasis and clotting - stroke, PE, DVT)
What is atrial fibrillation?
after major surgeries, valve diseases, pulmonary HTN, HTN, hyperthyroidism, excessive alcohol intake
what are causes of atrial fibrilation?
increased age, male, high BMI, SBP >160 mmHg, heart failure
what are risk factors of atrial fibrillation?
irregular palpitations, SOB, fatigue, exercise intolerance, hypotension, chest pains, pulmonary edema, altered LOC
what are symptoms of atrial fibrilation?
calcium channel blockers, beta blockers, digoxin, cardioversion (shocking heart), cardiac ablation (surgically shaving heart to decrease activity), ACE inhibitors and ARBs (decreases incidence of Afib), antithrombotic therapy (to dissolve clots and prevent stroke, DVT, PE)
How is atrial fibrillation treated?
atrial fibrillation
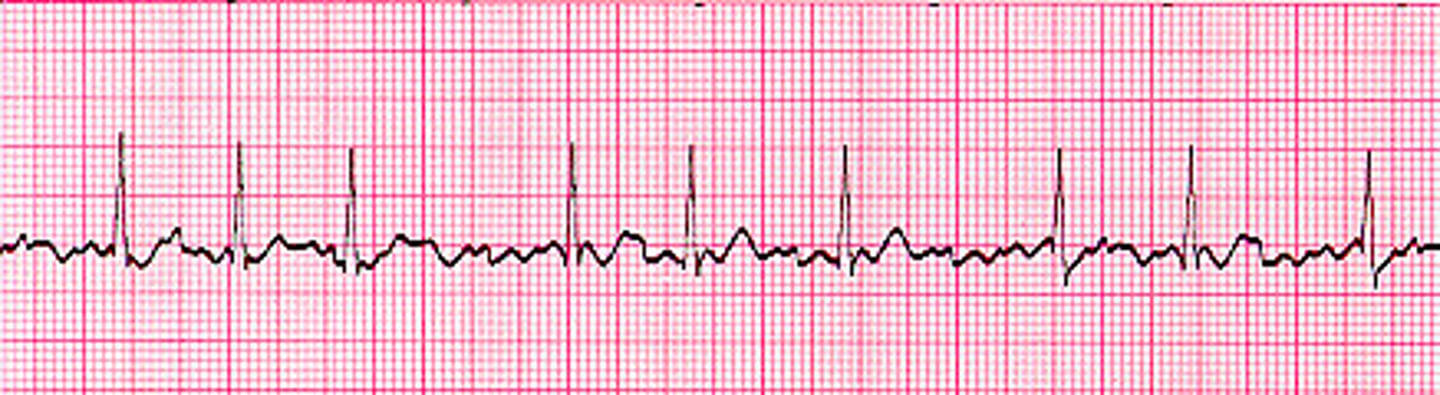
premature and wider than normal QRS caused by ventricular impulse before normal SA node is generated
what are premature ventricular complexes (PVCs)?
caffeine, alcohol, smoking, MI, hypoxia
what are causes of premature ventricular complexes (PVCs)?
fix electrolytes, give oxygen, correct acidosis, treat MI
how are premature ventricular complexes (PVCs) treated?
ventricular tachycardia
what do 3 or more consecutive premature ventricular complexes (PVCs) indicate?
premature ventricular complexes (PVCs)
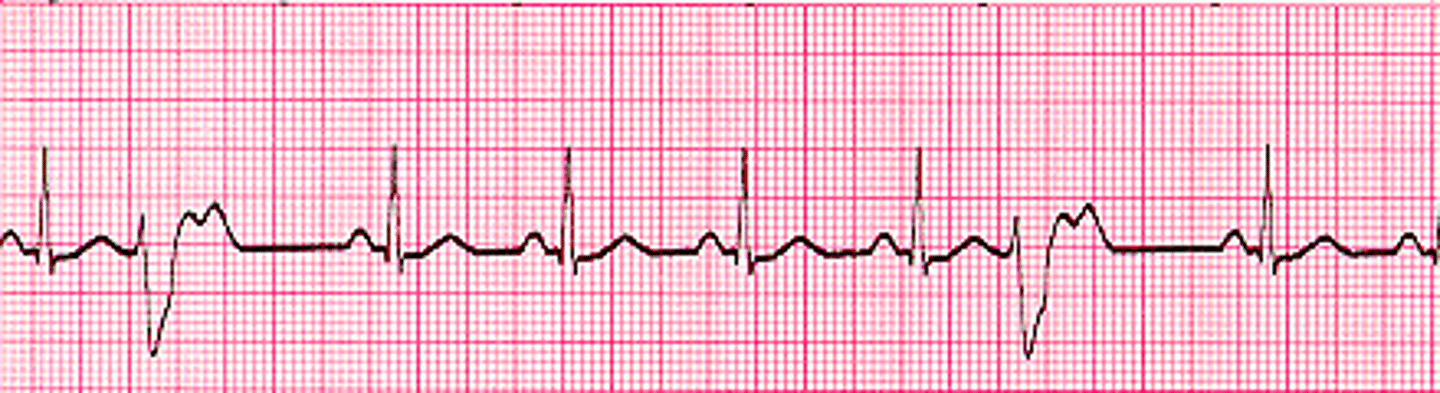
three or more consecutive PVCs caused by decreased and inadequate filling of the ventricles
What is ventricular tachycardia?
cardioversion, propenamide IV, amiodarone, lidocaine IV push
what are treatments of ventricular tachycardia?
ventricular tachycardia
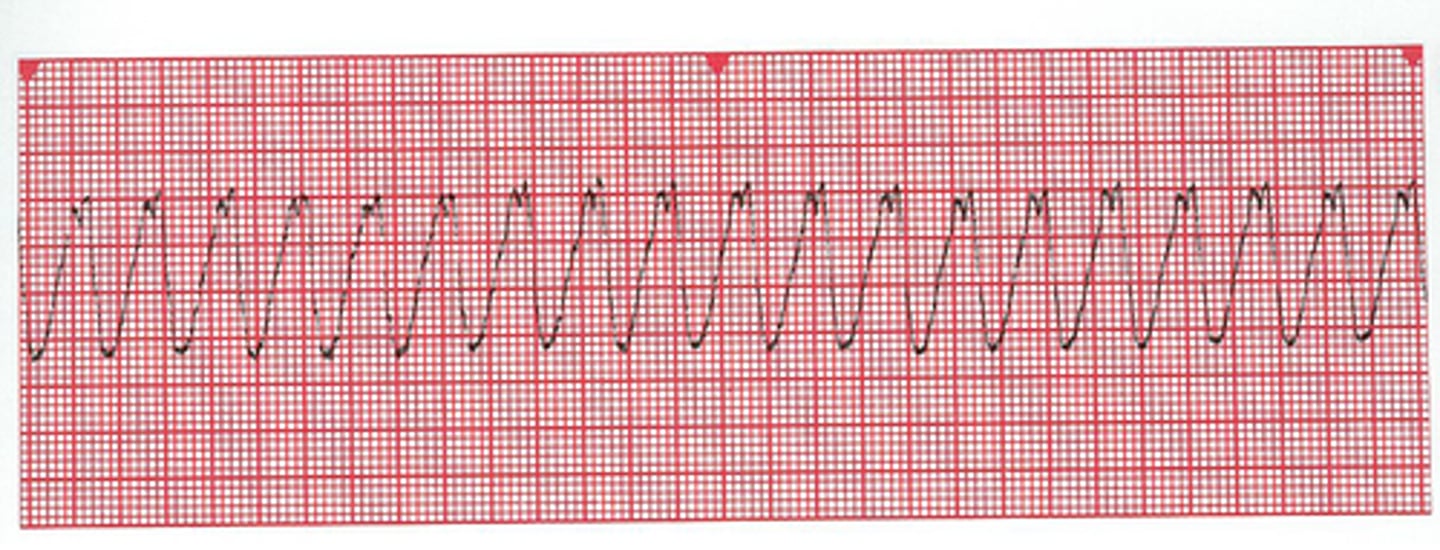
rapid and disorganized ventricular rhythm causing shaking of the ventricles
What is ventricular fibrillation?
untreated PVCs and Vtach
what are causes of ventricular fibrillation?
LOC, absent pulse, cyanosis
what are symptoms of ventricular fibrillation?
CPR, epinephrine Q3-5 mins, vasopressin, amiodarone, lidocaine
How is ventricular fibrillation treated?
ventricular fibrillation
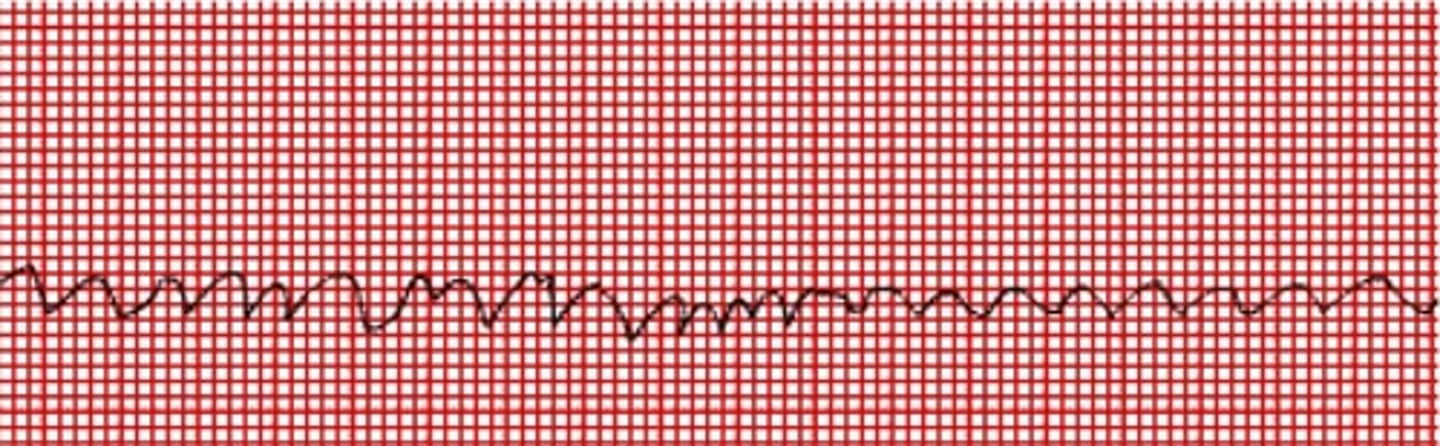
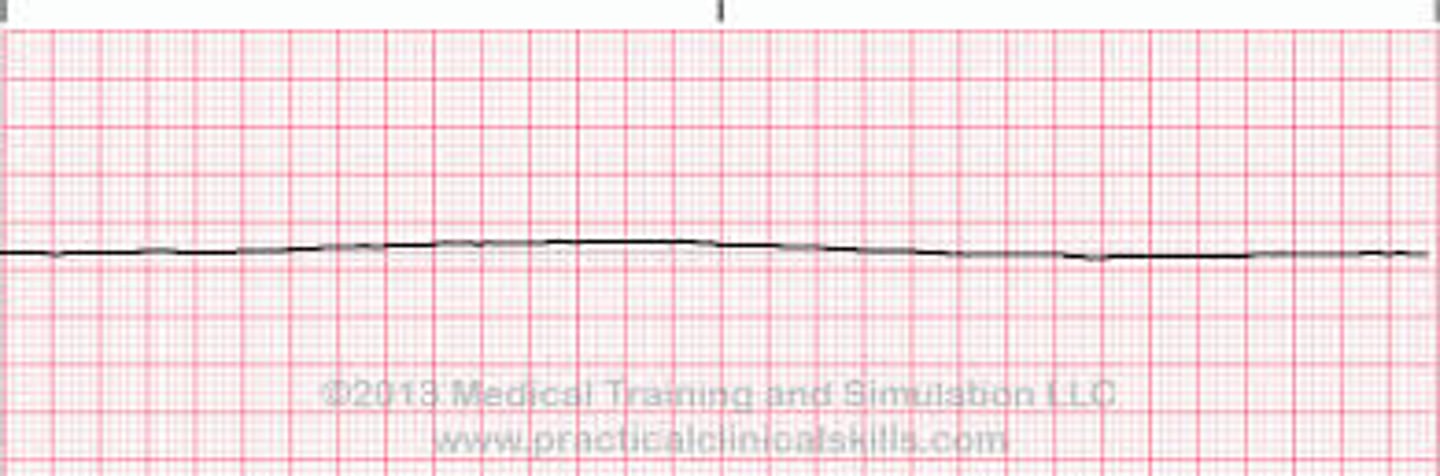
flatline - no heart beat, pulse, or resps
what is ventricular asystole?
CPR, intubation, place IV line - give epi
how is ventricular asystole treated?
ventricular asystole
narrowing of the small vessels that supply blood and oxygen to the heart (most commonly caused by atherosclerosis)
What is coronary artery disease?
chest pain radiating to LA or jaw, epigastric distress, common among women: indigestion, nausea, palpitations, numbness
what are s/s of coronary artery diseases?
increase in LDL, decrease in HDL, smoking, tobacco, alcohol, obesity, stress, inactivity, DM, metabolic syndrome
what are modifiable risk factors of coronary artery disease?
what is normal LDL cholesterol level?
what is normal total cholesterol level?
>40 mg/dL in males, >50 mg/dL in females
what is normal HDL cholesterol level?
what is normal triglyceride level?
3 of the following: insulin resistance, central obesity, dyslipidemia, HTN, high CRP, high fibrinogen
What is metabolic syndrome?
age (men >45, females >55), gender (men higher risk), race (african american men higher risk), family Hx
what are nonmodifiable risks of coronary artery disease?
controlling cholesterol (to prevent atherosclerotic growth), healthy diet, exercise, smoking cessation, manage HTN and diabetes, baby aspirin to prevent clots
how can coronary artery disease be prevented?
chest pain caused by decreased oxygenation and blood flow to the myocardium and heart muscles
What is angina pectoris?
physical exertion, exposure to cold, eating a heavy meal, stress/emotional situations
what are triggers of angina pectoris?
exercise induced chest pain relieved by rest or nitroglycerin
What is stable angina?
Angina that is not relieved by taking away the stressor or nitroglycerin
What is unstable angina?
evidence of ischemia but pt reports no pain
What is silent ischemia?
indigestion, chest tightness, SOB, overwhelmingly fatigued
what are s/s of anginas in women?
sudden retrosternal pressure w/ chest pain radiating to shoulders and arms, SOB
what are s/s of anginas in men?
Hx of ischemia/ischemic symptoms, FHx of cardiac events, place on ECG to look at T wave elevation, give O2 is O2 stat is low, blood to look for elevated troponin and CKMB, echo to look at heart muscle function, cardiac cath (bed rest for 8hrs, keep extremity straight, check pulse Q15 mins), stress test (see how heart functions during exercise)
How is angina diagnosed?
decrease oxygen demand, eliminate triggers, give oxygen, meds: nitroglycerin, beta and calcium channel blockers, antiplatelets, anticoagulants, procedures that inc perfusion: PTCA, CABG
How is angina treated?
acute onset of myocardial ischemia causing death of the myocardium caused by atherosclerosis, thrombi, embolus, blood loss
What is acute coronary syndrome?
unstable angina, STEMI (complete blockage of coronary artery), non-STEMI (incomplete blockage of coronary artery)
what are examples of acute coronary syndromes?
ischemia in heart causing other areas to work harder to pump blood causing heart muscles to overwork and die
What is a myocardial infarction?
60%
what is normal ejection fraction of the heart?
What ejection fraction indicates heart failure?
ECG changes (T wave inversions, ST elevation, abnormal Q wave), blood tests: troponin, CKMB
How is an MI diagnosed?
dilates blood vessels (can cause hypotension)
What does nitroglycerin do?
ischemia
what does T wave inversion indicate?
muscle injury
what does ST segment elevation represent?
MI
what do tall and narrow T waves represent?
necrotic tissue preventing depolarization
what do prominent Q waves indicate?
minimize and control myocardial damage, preserve myocardial function, prevent further myocardial damage
what are the goals of MI treatment?
MONA: morphine, O2, nitroglycerin, aspirin, give beta blockers and angiotensin converting enzymes within 24 hours, anticoagulants
what are routine interventions of treating acute MI?
nonsurgical procedures to open up the coronary arteries, atherectomy (break up and remove plaques), stents (mesh wire devices to hold coronaries open), PTCA (balloon to dilate arterial lumen)
what are examples of percutaneous coronary interventions?
give aspirin upon arrival, thrombolytic therapy within 30 mins, percutaneous coronary intervention within 90 mins
what are core measure of treating acute MI?
ventricular dysrhythmias, CHF with pulmonary edema, cardiogenic shock (decreased CO causing >40% loss of L ventricular function)
what are major complications of MI?
ventricles are unable to fill and eject blood
What is congestive heart failure?
impaired contraction caused by weakened heart muscles
what is systolic dysfunction?
impaired filling of the heart caused by stiff heart muscle
what is diastolic dysfunction?
no major damage and no limitations on physical activity
what is stage I heart failure?
slight limitations, frequent resting
what is stage 2 heart failure?
frequent breaks, tired, SOB, palpitations
what is stage 3 heart failure?
many limitations and severe exhaustion even at rest
what is stage 4 heart failure?
CAD, atherosclerosis, ischemia, MI, HTN, cardiomyopathy, dysrhythmias, valve diseases, renal dysfunction (causing fluid overload), diabetes, hypoxia, acidosis, electrolyte imbalances (especially K)
what are causes of CHF?
pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs
What does the right side of the heart do?
Pumps oxygenated blood around the body
What does the left side of the heart do?
backflow of blood into the vascular system
What is right sided heart failure?
JVD, pitting edema in LE, hepatomegaly (backflow of blood into the liver), ascites, weight gain (fluid retention), anorexia, N/V, abdominal pain
What are the s/s of right sided heart failure?
backflow of blood into the pulmonary system
What is left sided heart failure?
dyspnea, SOB, orthopnea, difficulty breathing, cough, crackles, low O2 stat, extra heart sound - ventricular gallop, unable to lay down, decreased UOP (decreased blood flow to kidneys), indigestion (decreased perfusion)
what are s/s of left sided heart failure?
Hx and physical assessment - pulmonary or peripheral edema, renal failure or COPD, echo (measures ejection fraction), cardiac cath, stress test, angiogram, CXR, ECG, lab studies (elevated BNP is major indicator)
How is heart failure diagnosed?
improving cardiac function by decreasing preload and afterload, reduce symptoms to lower risk of hospitalization, delay progression to extend life expectancy
what are goals of treating CHF?
decreases preload and afterload by causing vasodilation and diuresis
What do ACE inhibitors do?
blocks vasoconstriction effects
What do angiotensin receptor blockers do?
blocks SNS to relax blood vessels (decreases BP, afterload, and workload)
What do beta blockers do?
increases contractility force of the heart
What does digoxin do?
anorexia, nausea, visual disturbances, confusion, bradycardia
What are the s/s of digoxin toxicity?