Su: Anti-HIV Protease Inhibitors
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
name the HIV protease inhibitors
Saquinavir, Ritonavir, Indinavir, Fosamprenavir, Lopinavir, Nelfinavir, Tipranavir
what is the suffix for HIV protease inhibitors?
-navir
HIV protease is responsible for ____of core proteins into structural proteins
post-translational modification
HIV protease cleaves the viral ____ and ____ polyproteins into smaller functional proteins
Gag and Gag-Pol
what does the HIV gag gene code for
virus and the coat proteins
what does the HIV gag-pol genome code for
Codes for reverse transcriptase and other enzymes
If you inhibit the protein HIV protease it cannot _____ responsible for making the viral particle that spreads.
cleave the proteins
HIV protease is produced by the ____ gene
pol
what are the two options for blocking HIV protease or the Pol gene that makes it?
Terminator 1 - Target the gene before HIV protease protein is made.
Terminator -2 Terminate the HIV protease which helps to make the virus particle.
HIV protease is a _____ enzyme
symmetric dimer
what class does HIV protease belong to
aspartic protease
the drugs that inhibit HIV protease should not inhibit…
mammalian aspartic proteases
which CYP is the most important for metabolism of xenobiotics in the body
CYP3A4
where can you find the most CYP3A4 in the body
livah (liver)
most protease inhibitors act as substrates for _____
CYP3A4
the use of other drugs that are metabolized by CYP3A4 may be ____ if used with HIV protease inhibitors
contraindicated
the active site of HIV protease contains which amino acid sequence?
Asp-Thr-Gly
HIV protease cuts the ___ bond of proteins
amide
what specific amino acid sequence does the HIV protease cut at?
Ser(Thr)-X-X-Tyr(Phe)-Pro
Binding at the enzyme active site is specific, depends on ____
amino acids in the active site.
HIV protease undergoes mutation which leads to
alteration in active site residues and resistance is developed
mutation of ____ in the active site of HIV protease leads to decreased activity of the inhibitors
one or two amino acids
Mutation of one or two amino acids in the active site leads to ____
decreased activity of the inhibitors
mutation of ____ amino acids in the HIV protease leads to resistance to the inhibitors
5 or more
mutation of 5+ amino acids in the HIV protease leads to….
resistance to the inhibitors
where can mutations occur in HIV1 protease (generic answer)
Leu, Val, Ile, Ala, Met, Phe, Thr
brand names of saquinavir
fortovase and invirase
saquinavir is used for…
advanced HIV infection
saquinavir can be used in pts who did not receive ___ or who had prolonged treatment with ___.
ZDV (for both)
combo therapy of saquinavir with ___ seems to have better effects than ____ alone
ZDV or ddC (for both blanks)
bioavailability of saquinavir
4%
hella water insoluble
metabolization of saquinavir
glucuronidation in the liver (small amount tho)
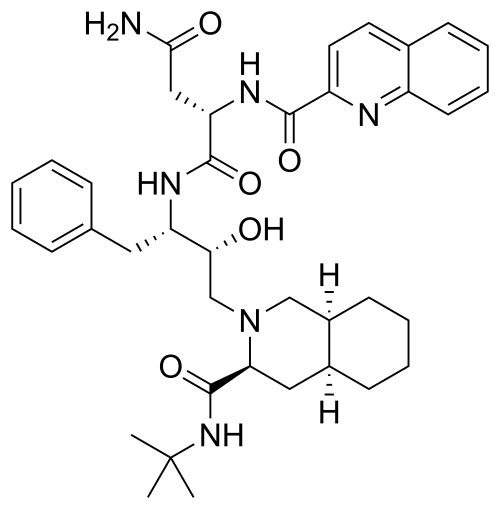
what drug is this
saquinavir
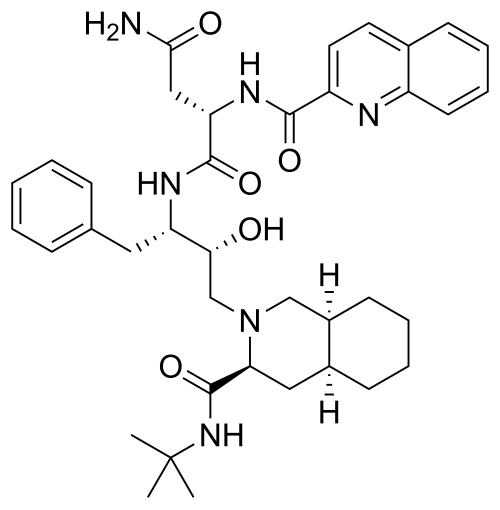
where are the amide bonds on saquinavir
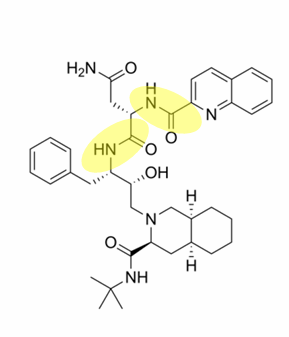
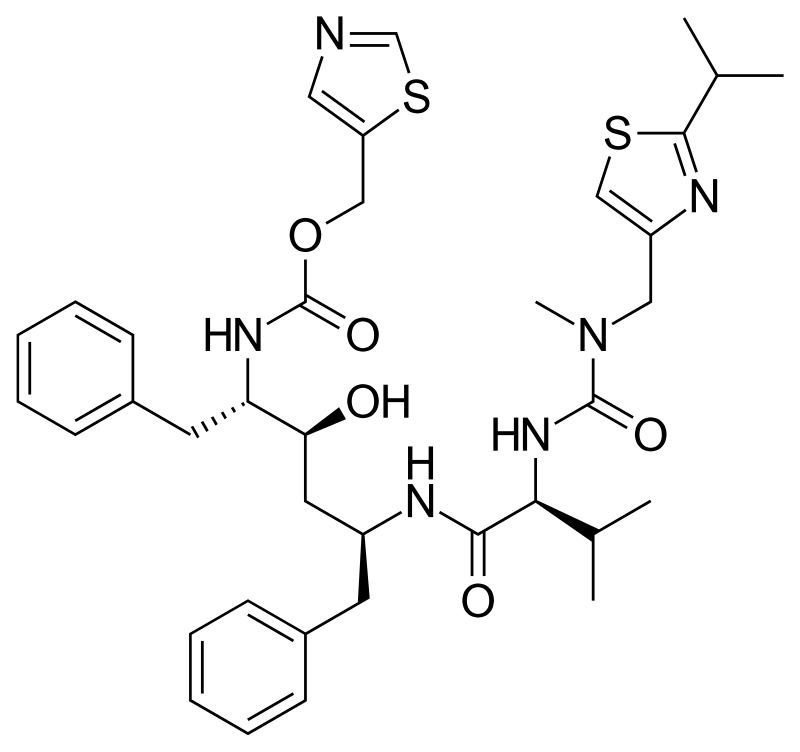
what drug is this
ritonavir
brand name of ritonavir
norvir
what does ritonavir inhibit
both HIV1 and HIV2 proteases
ritonavir can be used alone or in combo with ____ to increase CD4 counts
3TC, ZDV, Saquinavir or ddC
ritonavir can be used alone or in combo with 3TC, ZDV, Saquinavir or ddC to…
increase CD4 counts
how many metabolites of ritonavir are there?
5
where are most of ritonavirs metabolites found?
urine and feces
which CYP metabolizes ritonavir
CYP3A4
ritonavir cannot be used with which drugs due to contraindication
clarithromycin, desipramine, ethinyl estradiol, rifabutin, and sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim (aka bactrim)
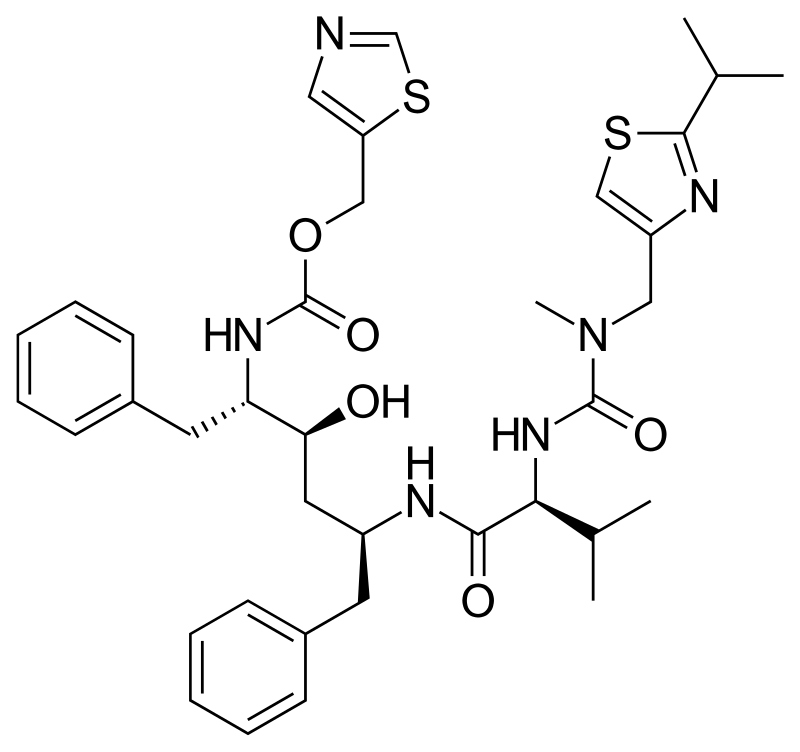
where are the amide bonds on ritonavir?
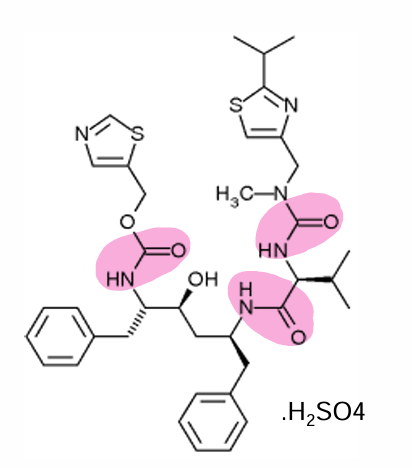
how many amide bonds does ritonavir have
3
how many thiazole rings does ritonavir have?
2
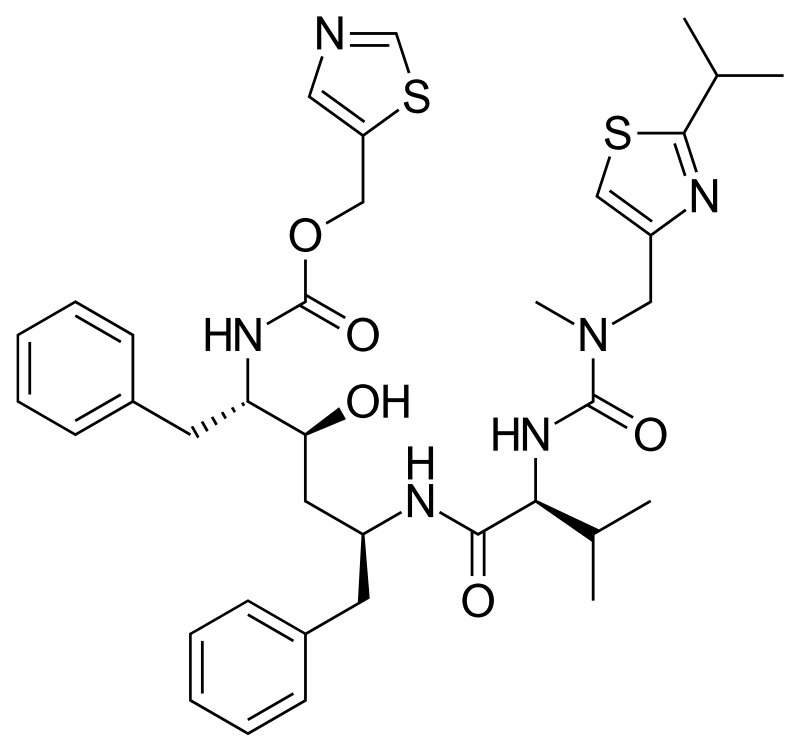
where are the thiazole rings on ritonavir
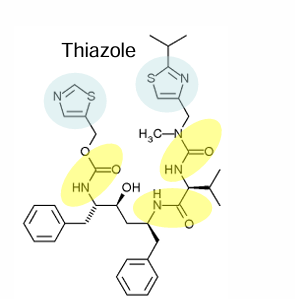
all metabolites of ritonavir are more _____
water soluble
brand name of indinavir
crixivan
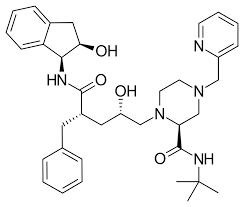
what drug is this
indinavir
indinavir can be given in combo with ____
ZDV and ddl
resistant to ____ is possible in some strains of HIV
indinavir
indinavir is not an inhibitor of ____
reverse transcriptase (duh its a protease inhibitor)
why can indinavir be taken with other nucleoside drugs
bc its not a reverse transcriptase inhibitor
what is the dosing interval used for indinavir
q8h
indinavir is metabolized via which reactions
oxidation and glucuronide conjugation
how many metabolites of indinavir are there
7
why does indinavir have hella drug interactions
bc it inhibits CYP3A4, CYP3A5, CYP3A7
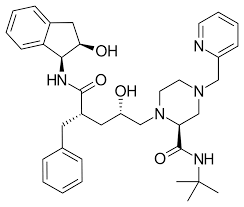
where is the amide bond on indinavir
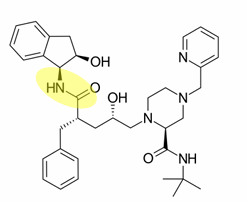
explain the metabolism of indinavir to M1
oxidative N -dealkylation (removal of the indene group)
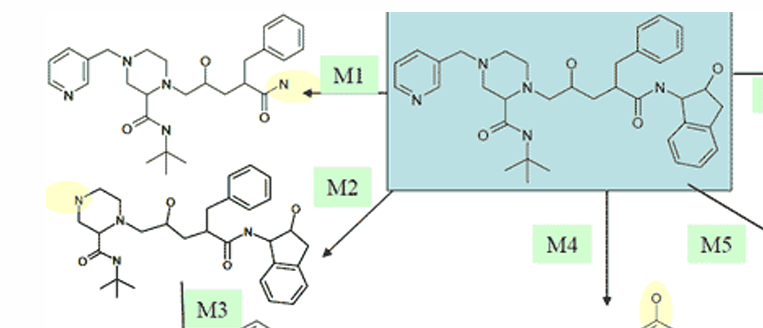
explain the metabolism of indinavir to M2
oxidative N-dealkylation (removal of the purine)
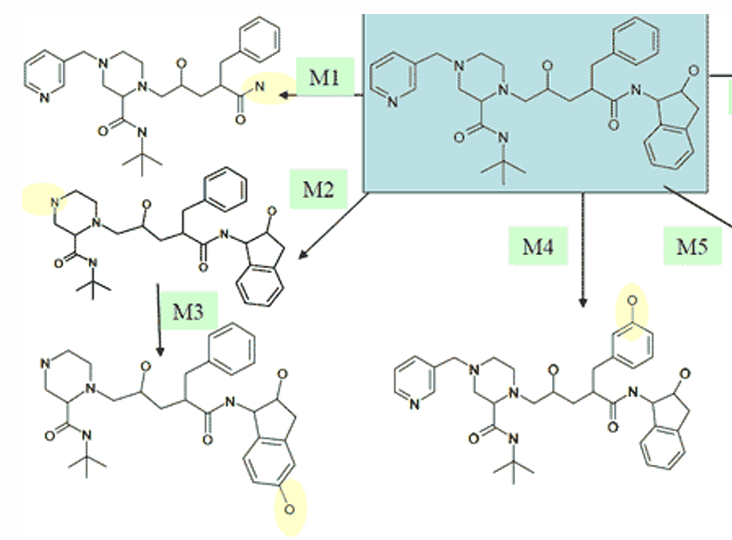
explain the metabolism of indinavir to M3
hydroxylation of the fused benzenes after M2 ahs been formed
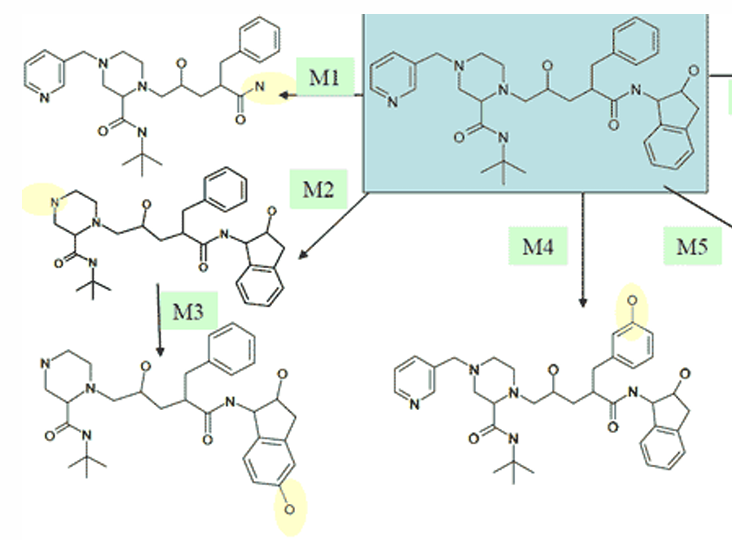
explain the metabolism of indinavir to M4
para hydroxylation of mono-substituted benzene compounds
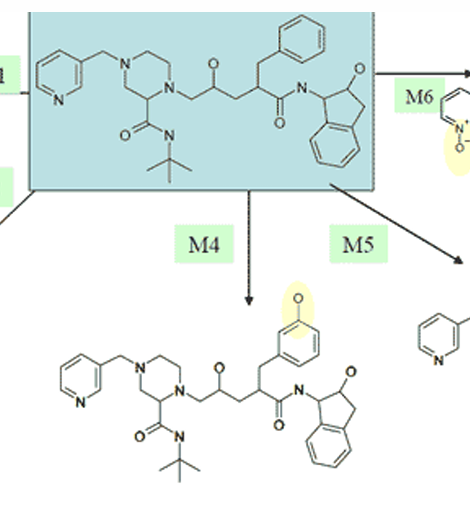
explain the metabolism of indinavir to M5
hydroxylation of fused benzenes
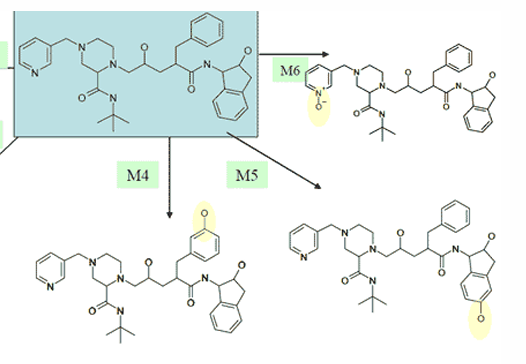
explain the metabolism of indinavir to M6
N-oxidation of aromatic nitrogen
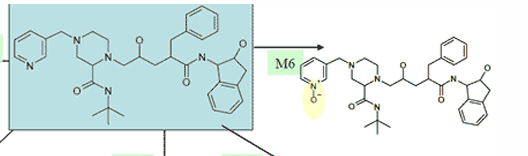
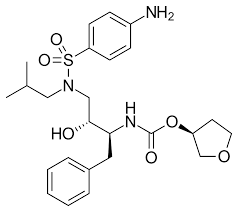
what drug is this?
amprenavir
what is the brand name of amprenavir
agenerase
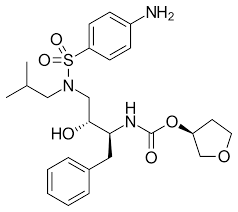
where is the amide bond on amprenavir
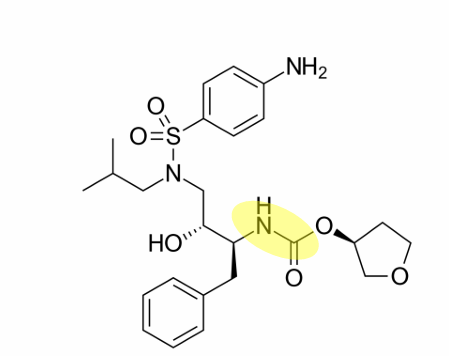
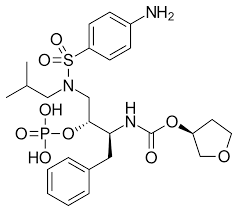
what drug is this
fosamprenavir
what is the brand name of fosamprenavir calcium?
lexiva
fosamprenavir is a ___ of the protease inhibitor and antiretroviral drug amprenavir
pro-drug
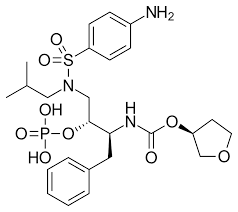
where are the amide bonds on fosamprevnavir
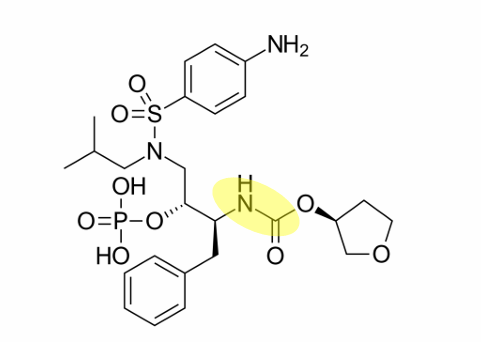
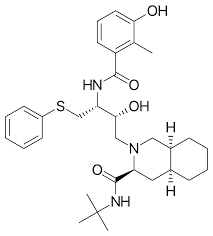
what drug is this
nelfinavir
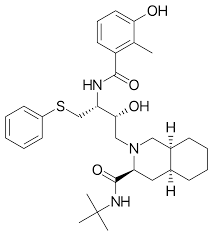
where are the amide bonds on nelfinavir
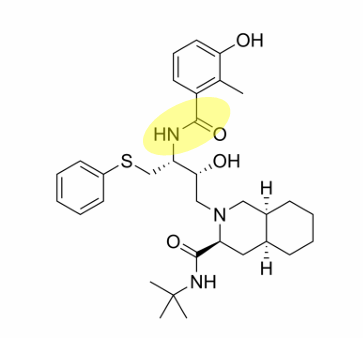
what is the brand name of nelfinavir
viracept
what drug is this
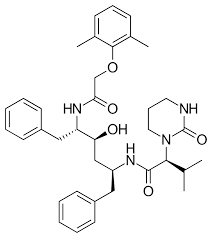
lopinavir
brand name of lopinavir
kaletra
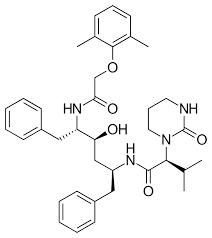
where are the amide bonds on lopinavir
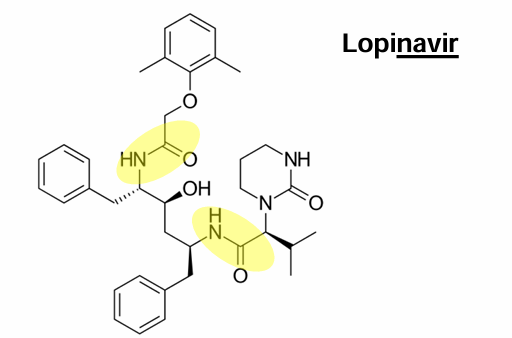
kaletra (lopinavir) is a co-formulation that contains ____
ritonavir
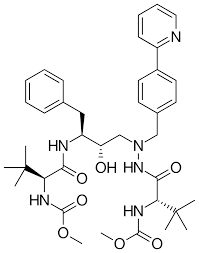
what drug is this
atazanavir
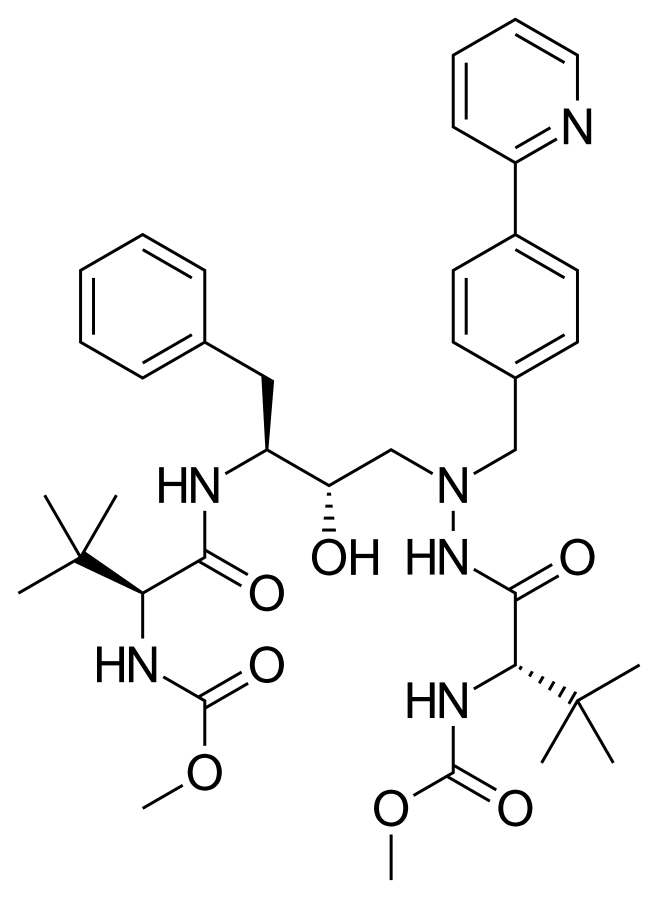
where are the amide bonds on atazanavir
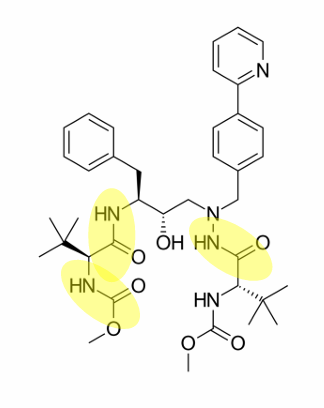
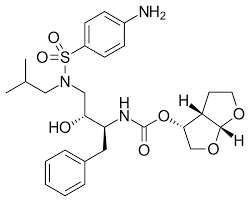
what drug is this
darunavir
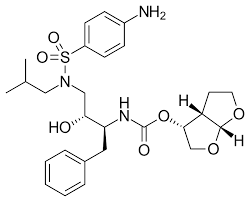
where are the amide bonds on darunavir
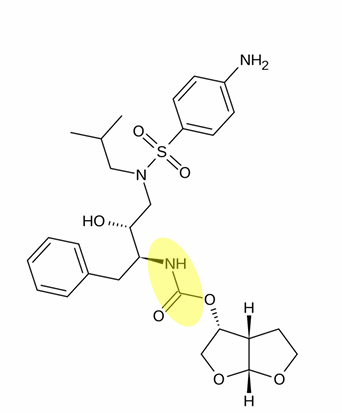
tipranavir is also called
tipranavir disodium
tipranavir is a ______ protease inhibitor
non-peptidic
tipranavir inhibits the replication of viruses that are _____
resistant to other protease inhibitors
who is recommended to get tipranavir
pts who are resistant to other strands
resistance to tipranavir requires ____ mutations
hella