05.F BIO, HN The Calvin Cycle (PART F)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Light Independent Reaction
Reactions that do not require light that occur in the stroma of the chloroplast; also referred to as the Calvin cycle after the scientists who identified the reactions
Calvin Cycle
Also known as the light independent reactions; occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast; the cycle builds sugar from CO2 and a five carbon sugar called RuBP by using ATP and the reducing power of electrons carried by NADPH; this is a cycle because the starting material (RuBP) is regenerated
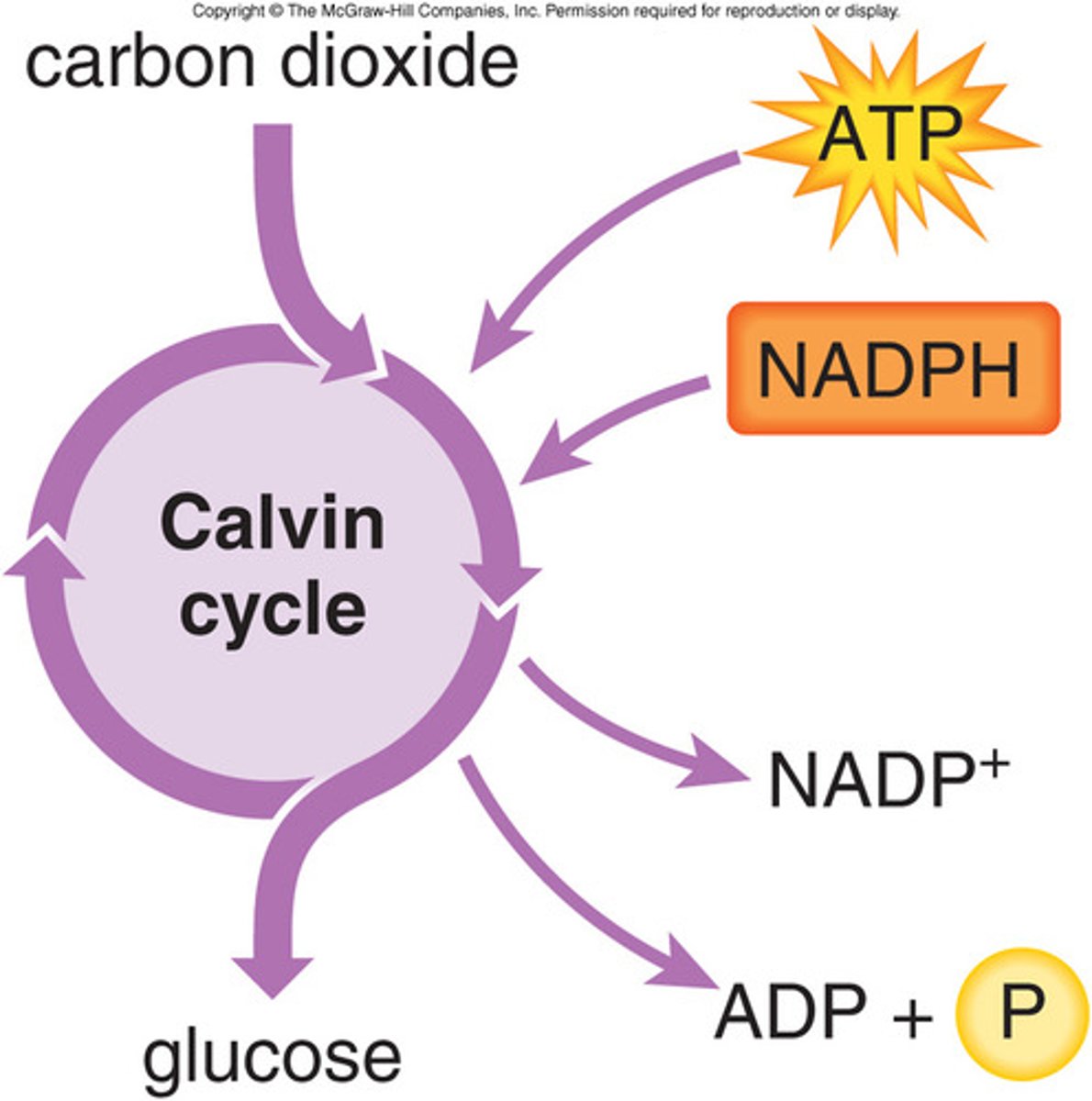
The Calvin Cycle (Reactants)
Carbon dioxide (CO2), RuBP, ATP and NADPH
The Calvin Cycle (Products)
PGAL, ADP, phosphate and NADP+ are produced and can be reused in light reactions
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Atmospheric gas that is taken up by plants through the stomata and used to make sugars during photosynthesis
RuBP (Ribulose bisphosphate) (Description)
A 5-carbon sugar that is the starting material in the Calvin Cycle; combines with carbon dioxide to produce an unstable 6-carbon molecule
RUBISCO
The enzyme that catalyzes the first step of the Calvin cycle (the addition of CO2 to RuBP, or ribulose bisphosphate).
G3P
A 3-carbon sugar named glyceraldehyde-3- phoshpate (G3P); also known as PGAL
PGAL
A three-carbon molecule formed in the second step of the Calvin cycle that can leave the cycle and be used to make other organic compounds
Calvin Cycle (Four Phases)
Carbon fixation
Reduction
Release of PGAL
Regeneration of the CO2 acceptor (RuBP)
Carbon Fixation
The initial incorporation of carbon into organic compounds; during photosynthesis carbon fixation occurs during the Calvin Cycle when CO2 is combined with a 5 carbon compound called RuBP (starting material); results in a 6-carbon molecule is unstable and immediately splits into two 3 carbon molecules called PGA
Reduction of PGA
During this phase of the Calvin cycle 12 ATP and 12 NADPH are used to reduce PGA and make 2 PGAL; ATP provides a phosphate group and NADPH provides a H+
Release of PGAL
For every 6 CO2 that enter the cycle two PGAL are released; PGAL are 3C molecules that can be used to make sugars and other compounds; Some PGAL are used to make organic molecules; most are used to regenerate the 5C starting material
Regeneration of RuBP
For every 6 CO2 that enter the cycle ten PGAL are used to regenerate the 5C starting material called RuBP; the regeneration of 10 RuBP requires 6 ATP; RuBP then continues the cycle and is available to fix the CO2
Synthesis of Glucose from PGAL
2 PGAL are used to produce glucose; for net synthesis of 2 PGAL, the cycle must take place six times, fixing six molecules of CO2