Respiratory substrates
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Do cells only respire glucose?
No
Also respire other carbohydrates, lipids, & proteins
Respiratory substrates
Organic molecules broken down in respiration to release energy
Which respiratory substance enter at the Krebs Cycle
Proteins and lipids
How are triglycerides broken down to release energy for ATP synthesis?
Hydrolysed to fatty acids (2C) → Acetyl CoA
Glycerol → pyruvate → acetyl group → Acetyl CoA
Pyruvate undergoes oxidative decarboxylation
Acetyl group picked up by coenzyme A = Acetyl CoA
How are proteins broken down to release energy for ATP synthesis?
Hydrolysed to Amino acids
Deaminated
Pyruvate → Acetyl Group → Acetyl CoA
What respiratory substrate has the highest energy value?
Lipids - 39.4
Proteins - 17.0
Carbohydrates - 15.8
Why does _ have the highest energy value?
Fatty acid lipids made of long hydrocarbon chains w. many H atoms, which are released when lipid is broken down
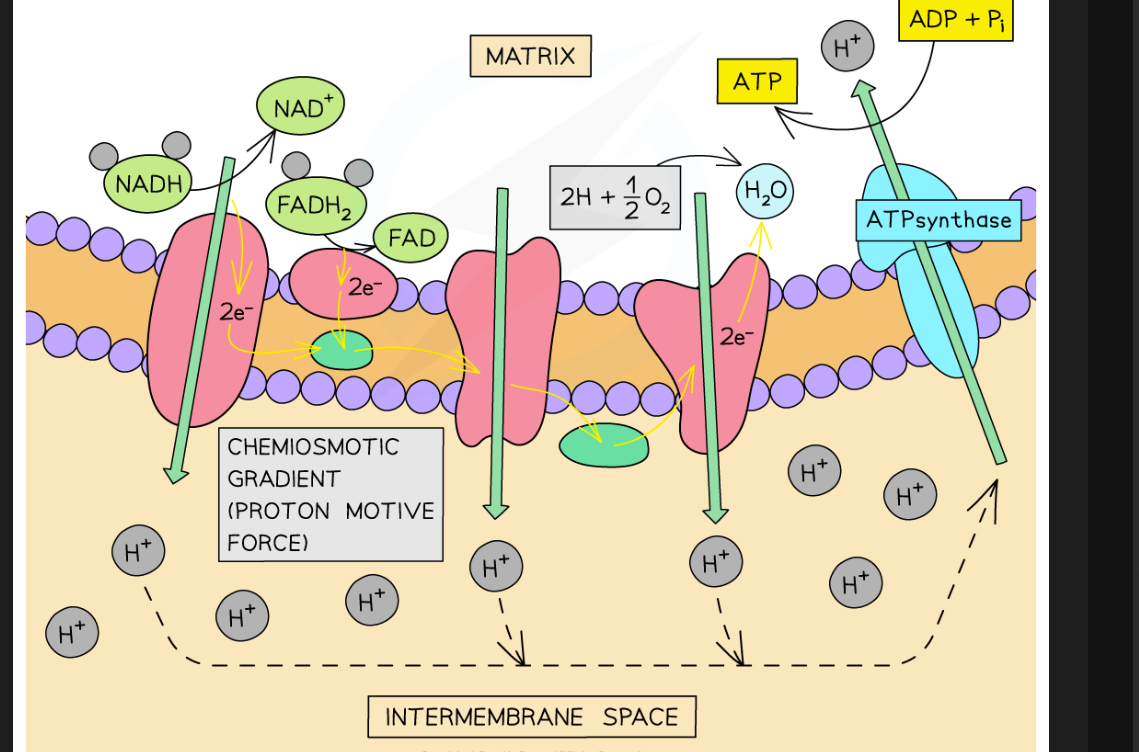
More H transported by NAD + FAD to mitochondrial inner membrane
Greater chemiosmotic / proton gradient
More ATP produced via chemiosmosis
How does having many H atoms benefit a resp. substrate?
Most ATP is made in oxidative phosphorylation, requiring H atoms from NADH & FADH
Will result in a greater proton gradient across the mitochondrial inner membrane and matrix, allowing for the formation of more ATP via chemiosmosis
Respiratory substrates that have more H atoms per unit of mass cause more ATP to be produced when respired
Mitochondrial inner membrane, matrix thingy