Session #8 Notes - HSML 6209
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
Types of Costs
- Traceability
- Relation to activity
- Management Responsibility (or not)
- Relation to time
Traceability types
Direct + indirect
Relation to activity types
Variable + fixed + semi-fixed
Management responsibility types
Controllable + non-controllable
Relation to time types
Avoidable + sunk
Direct (traceability cost type)
Can be traced back to a specific department
Examples: lab salaries, lab office supplies, lab contracts (leases + depreciation expense)
Indirect (traceability cost type)
Cannot be traced back to a specific department
ALWAYS REQUIRES AN ALLOCATION METHODOLOGY
Examples: whole building depriet., shared costs (housekeeping), HR+marketing+legal
Allocation methodology examples
Housekeeping/environment services, utilities, lab space
Housekeeping/environment services are allocated by...
# of beds (or laundry by Ibs of linens)
Utilities & lab space are allocated by...
Square feet
Additional depts (HR, legal, marketing) are allocated by...
# of employees per dept
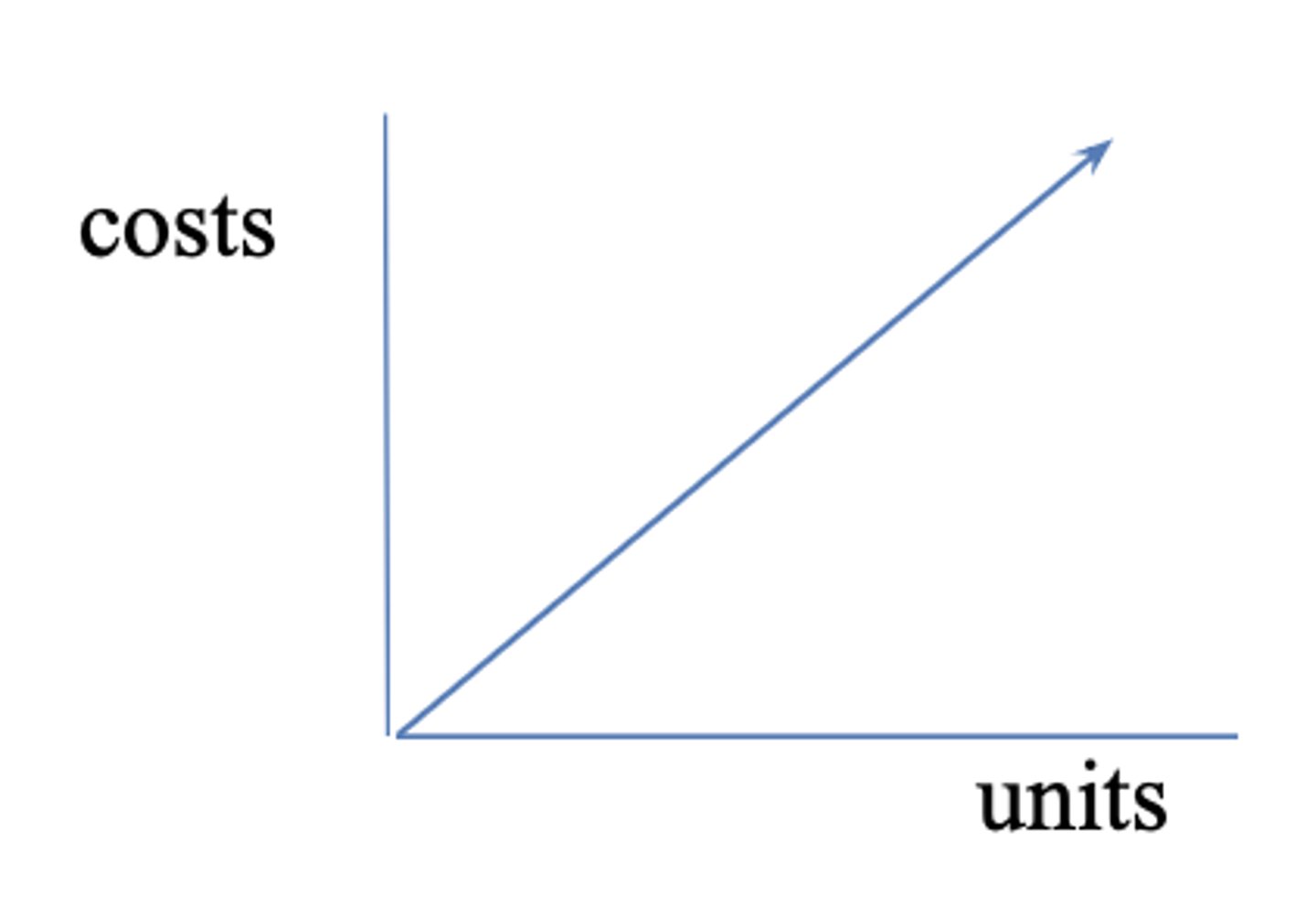
Variable (relation to activity cost type)
Changes PROPORTIONALLY according to change in volume
example: always supplies (every time you draw CBC, cost $2)
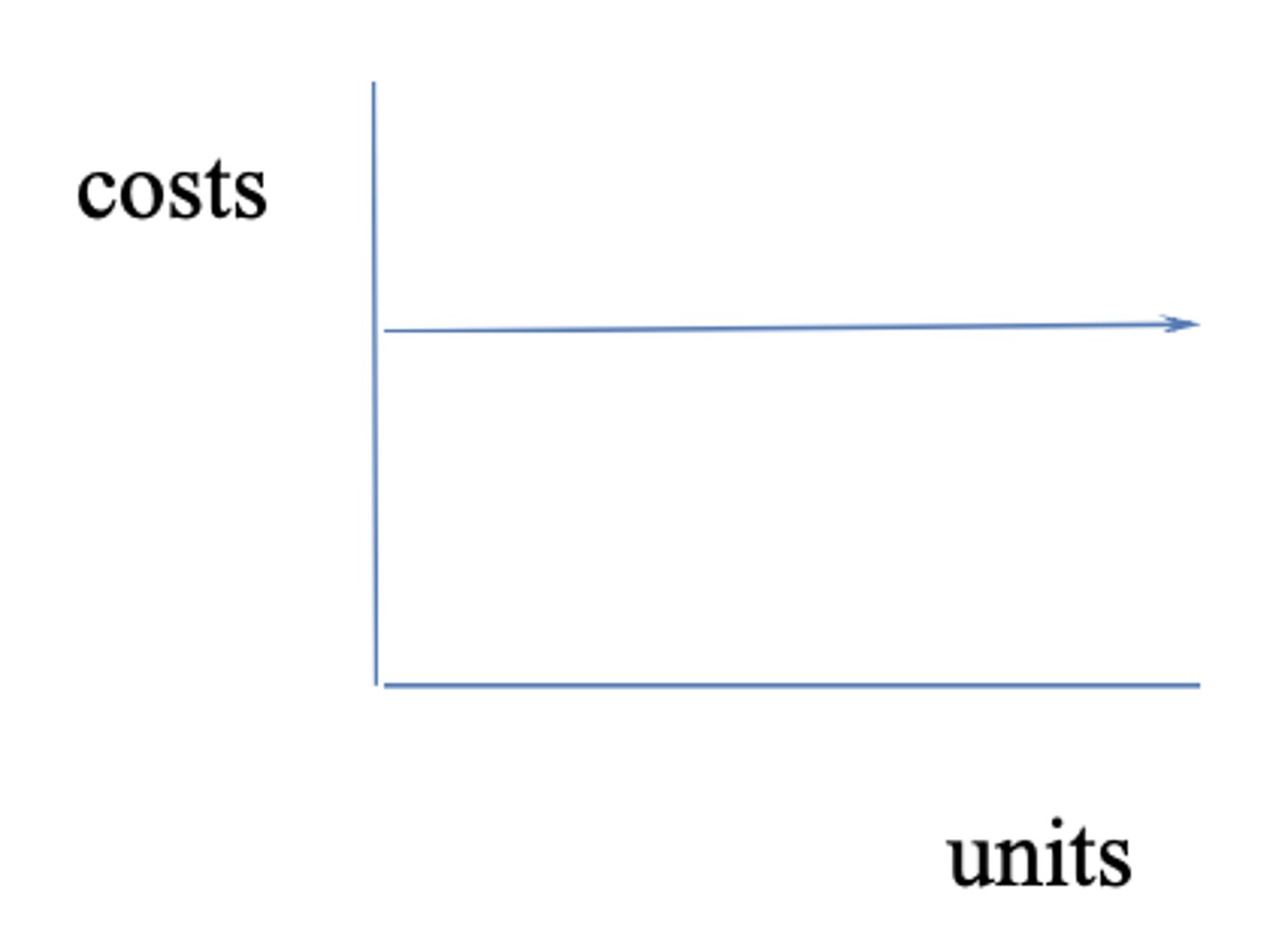
Fixed (relation to activity cost type)
DOES NOT change according to change in volume (no matter volume, cost never changes)
example: lease fee on lab machine is $2000/month regardless of usage
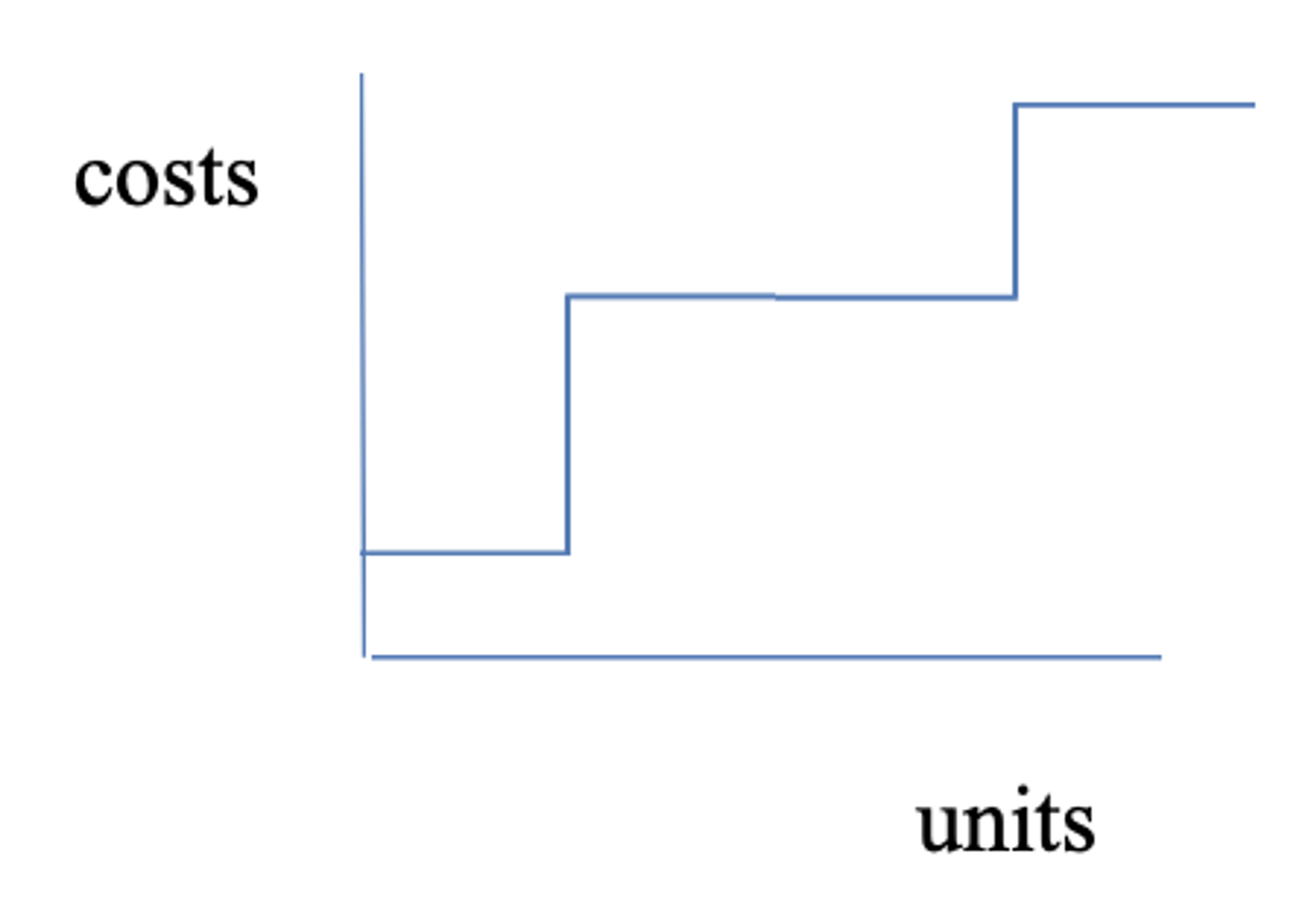
Semi-fixed (relation to activity cost type)
Changes but NOT PROPORTIONALLY according to changes to time in volume ("stair-step")
example: staffing (aka salaries - salary expense of lab staff)
Controllable (management responsibility cost type)
The department manager can control within the defined time period
example: salaries + supplies
Non-controllable (management responsibility cost type)
The department manager cannot control within the defined time period
example: employee benefits (health plans), indirect expenses (rent, utilities)
Avoidable (relation to time cost type)
If you change operations, the cost goes away
example: close lab - no longer pays for salaries
Sunk (relation to time cost type)
If you change operations the cost doesn't go away
example: close lab - still required to pay remaining lease, depreciation expense, + admin costs (HR, legal, marketing)
60%
The amount healthcare orgs allocate toward personnel expenses.
Payroll department
Responsible for orgs employees under controller (can be in-house or outsources)
2 most common outsourcing companies for payroll
ADP + PayChecks
ADP
An outsourcing payroll company for larger + international/multistate companies
Paychecks
An outsourcing payroll company for usually smaller + 1-3 state companies
Payroll for single-state companies
Are more likely to be in-house
Payroll for multi-state companies
Are more likely to be out-sourced
Three guidelines to differentiate between employee or indept. contractor - "Resting B*tch Face"
Relationship of parties
Behavioral control
Financial control
Requirements for ER if hiring an EE
- Must follow payroll laws
- Set EE up in payroll system
- Must pay a share of taxes
- Responsible for holding EE's share of taxes
*END-YEAR - ER must provide EE with a IRS W2 doc.
ER share of taxes for an EE is marked as what in an IS/SOO?
Benefit expenses
EE share of taxes that ER holds is documented as what on BS?
Current liabilities (only until paid to IRS)
IRS W2
Document that ER must provide to EE (is a list of tax information)
Hiring Independent Contractor
- Self-employed individuals who are contracted
- Provide expert services on a specific subject/area
- Contract length can be over weeks/months/years
- Paid through A/P
*END-YEAR - Company sends IRS 1099 Form to I.C.
Examples of Independent Contractors
Accountants, attorneys, architects
Steps of how I.C. gets paid
I.C. provides company with an invoice → Companies A/P pays I.C.
IRS 1099 Form
Document that a company must provide to I.C. (I.C. could have more than one depending on how many companies they worked for)
Hiring Temporary Agencies
- Companies that are contracted to provide individual workers
- Contract length could last day/week/months
- Company is paid with A/P
*THESE ARE VERY EXPENSIVE*
Steps of how temporary agency gets paid
The temporary agency provides company with an invoice → Companies pays agency through A/P
Examples of Temporary Agency
Travel nurses + clinical workers
Problem w/Temp agency
The hourly rate that is being charged is 2x then regular amount - due to admin fees (i.e. background checks/drug tests)
Hiring Outsourced Work
- Companies contracted to provide services as a whole
- Contracts are routine basis (not a one time thing)
Steps of how outsourced work gets paid
They send a monthly invoice → companies pay through A/P
Outsourced work examples
Marketing Firms + security + environmental service companies
1938
FLSA (Fair Labor Standards Act) passed under U.S. department of labor
*FOR NON-EXEMPT WORKERS*
FLSA established these requirements - "Fast Horses Read Yelp"
- Federal minimum wage
- Hours worked more than 40hrs/week = paid time+1/2
- Record keeping
- Youth employment standards (ages 13-17)
Federal Minimum Wage under FLSA
Originally was $7.25/hr
*State rate must be more generous than the federal rate
2009
States created "living wages" for minimum wage
Hours worked under FLSA
If EE work more than 40hrs/week must be paid time + 1/2
*Holidays+sick days don't count toward hours worked
Record keeping under FLSA
EE's must track hours worked - can include work preformed at home/travel time/training - time clocks now created
Exempt Workers (exempt from FLSA)
- Workers are paid a flat rate salary
- Paid the same amount each pay period no matter amount of hours worked
- Are paid CURRENT
Examples of exempt workers
Managers + professionals (people who conduct independent decision-making)
Type of workers paid current
Exempt workers (ex. if work from 9/1-9/30 - gets paid 9/30)
Non-Exempt Workers (not exempt from FLSA/it applies)
- Workers are paid hourly
- Paycheck is different each pay period based on hours worked
- Are paid ARREARS
Type of workers paid arrears
Non-exempt workers (ex. if work 9/1-9/14 - gets paid 9/21)
When workers are paid, depends on state laws
Why it is important to know the difference of exempt vs. non-exempt as a manager?
- Non-exempt workers must be set up in time+attendance
- You have to approve EE requests for leave
Payroll has three options
- Direct deposit
- Hard checks
- Paycards
Paycards
- A reloadable debit card
- Funded with employee wages from each pay period
- Strict laws for federal+state related to fees charged (must be disclosed)
BEST PRACTICES for Paycards
- Cannot be mandatory
- ER must disclose all fees+rules around usage
- Easy availablity
- Need to permit full withdrawal w/limited fees
Unbankable employees
Don't have bank accounts (could be due to legal/bankruptcy) - DD + check is not an option for them (pay cards are best)
2019 (pre-Covid)
Bureau of Labor Statistics - 24% of workers performed some work at home on average day. With Covid accelerating WFH arrangements, issuing bulletin
1961
When DOL last issued interpretive rules for FLSA record-keeping - states:
"If the employer knows or has reason to believe that the work is being performed, he must count the time as hours worked, and pay for it, even if they did not ask for or want the work, Burden is on ER to ensure that work is not performed that they do not wish to be performed. Applied to all EEs, regardless of where work is done (telework)."
Steps in Payroll Process - "Students Try To Stay Positive Exam Semester"
- Set up new EE
- Time and attendance system
- Time passes to payroll sub-ledger
- Salary calculated
- Paychecks prepped + sent as paper/DD/pay card
- Expenses from payroll sub-ledger go to GL
- Submit withheld taxes + benefits deductions to appropriate entity
Step 1 → Set Up New Employee (payroll process)
- EE must be coded to correct dept+account via chart of accounts
- Enter salary or hourly/weekly rate → exempt vs. non-exempt
- Form W4
- HR form for health plan selection/deductions
Chart of accounts
A document that lists the amount (expenses) for each dept (different for every company)
IRS W4 Form
A document for tax withholds filled out by EE prior to working
Step 2 → Time + Attendance System (payroll process)
- Time is tracked
-Time is approved by manager (only signs off on ours, not amount being paid)
Step 4 → Salary Calculated (payroll process)
- Based on hourly rate, OT, differentials
- calculate taxes and benefits to get total expenses
Step 6 → Expenses from SubL pass to GL (payroll process)
- Salary → based on charts of accounts
- Benefits depends on if they are treated as direct/indirect (allocated by %)
What is included in pre-tax benefits?
- Health/dental ins premiums
- Health savings account
- Flex spending account
- Retirement → 401K or profit sharing
Health/Dental Ins Premiums
- BOTH EE+ER contribute
- Required for large ER with more than 50 FTEs
Health Savings Account (HSA)
- BOTH EE+ER contribute
- Only used with HDHP
Retirement - 401K or profit sharing
- BOTH EE+ER contribute
- Completely optional for ERs to offer
- EE max roughly $20K (updated by IRS yearly)
Pre-Tax Benefits
ER must submit to vendor based on contract
What is included in taxes?
- Soc Security 6.2% each - up to IRS limit
- MC Part A fund 1.45% each, no limit
- FUTA 6% of $7000
- Fed Income
- State Income
- Local Income
Taxes
Large ER must submit both EE+ER portions to IRS by Wednesday following pay date
Out of taxes, what are the only two things that EE's do not contribute too?
FUTA 6% of $7000 + SUTA/SUI varies
Soc Security 6.2% each - up to IRS limit
- BOTH EE+ER contribute
- Limit changes each year, 2019 = $132,900
MC Part A fund 1.45% each, no limit
- BOTH EE+ER contribute
FUTA 6% of $7000
- ONLY ER contributes
- Can be reduced if paying SUTA
SUTA/SUI varies by state
- ONLY ER contributes
- % rate calculated annually based on company's unemployment data
Fed Income
- ONLY EE contributes
- Based on salary level and Fed W4 form compared to IRS withholding tables
State Income
- ONLY EE contributes
- In 41 states and DC - based on salary level and Fed W4 form and state withholding tables
Local Income
- ONLY EE contributes
- Can be flat % or based on state info
If it were a for-profit hospital, which three tax categories would ER end up contributing to?
Fed, State, Local Income tax
What is included in other benefits?
- Short-term disability
- Long term disability
- Garnishments
- Charitable contribution
Short-term disability (STD) - benefits
- BOTH EE+ER contribute
- Optional for ER's to offer, generally covers from 6 weeks to 6 months after disabling event
Long-term disability (LTD) - benefits
- BOTH EE+ER contribute
- Optional for ERs to offer, generally covers % of salary from 6 months to age 65
Garnishments - benefits
- ONLY EE contributes
- Court ordered withholding for debts not paid (ex.taxes+childsupport)
Charitable Contribution - benefits
- BOTH EE+ER contribute
- Optional for ER's - is a volunteered amount EE will have taken out of paycheck (sometimes ER matches amount)
How is money contributed by EE recorded under payroll taxes and benefits?
Recorded as deductions from EE paycheck
How is money contributed by ER recorded under payroll taxes and benefits?
Recorded as "fringe benefit expense" on SOO
Type of taxes under FICA
Social Sec. 6.2% each & MC Part A fund 1.45%
FICA
Federal Insurance Contributions Act - *#1 thing ER contributes too
1961
Department of Labor issued the last interpretation and just added clarifying info on telework