Organic Chemistry 3 Test Review
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
alkyne formula
CnH2n-2
Acetylene
H-C≡C-H
same as ethyne
all carbons are sp hybridization
linear
enynes
compounds with both double and triple bonds
how to name enynes
start on side closest to either double or triple bond, in a tie, go to double bond first
When triple bond is a branch
add -yl (ex. ethynyl)
vicinal dihalide
Halides (X) not on same carbon
geminal dihalide
Halides(X) on the same carbon
For addition reactions, equally substituted means there are..?
2 products
RC≡CR + HX or X2 →
alkene
RC≡CR + 2HX or 2X2 →
alkane
mercury catalyzed hydration
-OH goes to more substituted carbon
h2SO4,H2O—>HgSO4(bottom)
Hydroboration
-OH goes to less substituted carbon
—BH3/H2O2(bottom) —>
Terminal
at end
Acidity order of what will be removed first with a base
-COOH > -OH > yne > ene/ane
only terminal alkenes can act as…?
weak acids
alkyne is the most stable because of more …?
S character (50%)
CH3CH3OH
weak acid
CH3CH3ONa
strong base
NaH
strong base
NH3 is a ____ ___, -NH2 is a ____ ____ ____
weak acid; strong conjugate base
carbon is an _____ with a halogen
electrophile
oxidation level formula
(Total # of C-O/C-H/C-X) - (Total # of C-H)
ex. C=O would count as 2
decrease number of C-H bonds
Oxidation
increase number of C-H bonds
Reduction
trans is more stable than cis because…?
less energy is released and less steric strain
Product of oxidative cleavage when terminal
CO2
product of oxidative cleavage when not terminal
-COOH (carboxyl acid)
How to tell smth is terminal in oxidative cleavage cut
H at end
How do you plan a synthesis?
Trial and error & retrosynthetically
Tautomerism
an enol interconverts into its isomeric ketone or aldehyde through hydrogen transfer
R≡R —-H2/Pd-C(bottom)—>
alkane
R≡R —-H2/Lindlar’s catalyst(bottom)—>
cis alkene
R≡R —.Na/NH3(bottom)—>
trans alkene
Pd-C
adam;s catalyst
lindlar’s catalyst
contains heavy metal
substitution reaction product
inversion
elimination reaction product
pair of enantiomers
solvents are either…?
protic or aprotic
protic
forms H+ bonds (ex. H2O, ethanol)
Aprotic
will not form H-bond or have H+
leaving groups
weak bases
right side of periodic table
lower on periodic table (bigger)
same for all reactions
strong nucleophiles
negative charges are better than neutral
strong bases
nucleophilicity improves going right to left and down in the periodic table (polarizability) (ex. -OH < -SH)
less substrated means …?
less steric hinderance
strong base, weak nucleophile, and bulky is better for..?
E2 reactions
polar protic solvents for SN1
H2O > CH3OH > CH3CH3OH > (CH3)3COH > CH3CO2H
what does SN2 stand for
Substitution, nucleophilic, and 2 reactants in the rate limiting step
SN2 substrate
less crowded (less substituted)
SN2 nucleophile
strong
SN2 solvent
aprotic (so it doesn’t attach to nucleophile)
what happens to the rate when the nucleophile or alkyl halide doubles in a SN2 reaction
reaction rate doubles
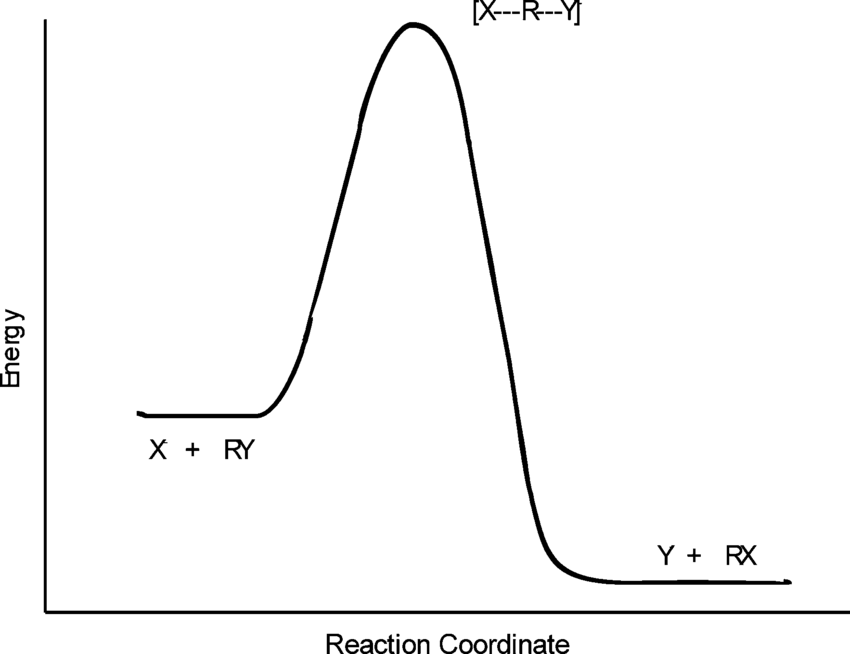
how many steps in SN2 reaction?
one
SN2 graph
SN1 graph
SN1 Substrate
more crowded (more substituted)
SN1 Nucleophile
weak
SN1 Solvent
protic (to stabilize intermediate/carbocation)
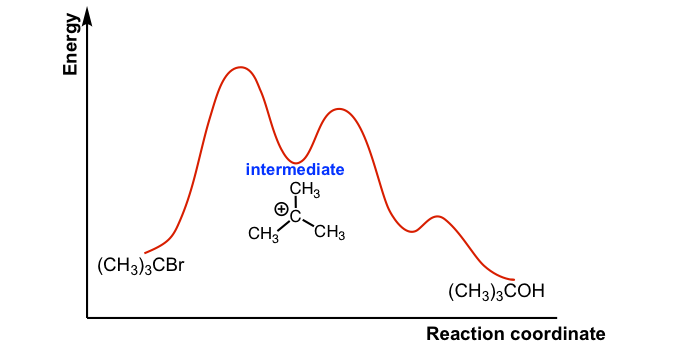
how many steps in a SN1 reaction
two (leaving group leaves in 1st, carbocation forms trigonal planar geometry in 2nd)
what happens to reaction rate in a SN1 reaction if you double the nucleophile
no change because nucleophile not in rate limiting step
what happens to reaction rate in a SN1 reaction if you double alkyl halides
doubles
1st in a reaction
rate limiting step (slowest)
which substrates are the best for SN2 reactions
methyl halides (CH3-X)
more hydrogen means…?
more reactive and less crowded
less reactive means…?
slower reaction
Zaitsev’s rule
The stability of alkenes increases with substitution, thus the major product in beta elimination has the more substituted double bond
what product does MCPBA give?
epoxide
vinyl halide
X directly attached to doubly bonded carbon
aryl halide
benzene ring
allylic halide
not directly (carbon in between) X and double bond
benzylic halide
benzene ring with CH3
alpha carbon
carbon directly connected to halogen
beta carbon
carbon connected to alpha carbon
elimination reaction product
alkenes
identical groups on the same doubly bonded carbon means..?
no cis or trans (no stereoisomers)
what happens in E1 reactions
leaving group leaves and forms cation
what does an E2 reaction need
strong base and antiperiplanar geometry
what happens in E2 reactions
Base takes proton, leaving group leaves
E2 solvent
aprotic solvent
E2 substrate
tertiary substrate (because more substrated alkene produced)
more reactive in E2 reaction
tertiary
base in E1
weak (because carbocation present)
Solvent in E1
polar protic
substrate in E1
tertiary substitution (because more substrate alkene produced)
radical reaction steps
initiation, propogation, termination
initiation step in radical reaction needs..?
UV or heat
allylic radical
more stable than tertiary (resonance)
tertiary radical
more reactive than secondary and primary
allylic position
radical not on doubly bonded carbon
Grignard reagents
organometallic compounds that contain a carbon-magnesium bond. Formally the Mg salt of a carbonic acid, and thus a carbon anion, a strong base.
Reaction of R-X with Mg in ether or THF
product of R-MG-X is an organometallic compound (alkyl-metal bond
X= Cl,Br,I
R= alkyl
electrophilic to basic and nucleophilic
carbon is partial positive with X but partial negative with Magnesium
leaving group examples
OH-/NH2 -/OR- < F- < Cl- < Br- < I- < TosO-
protic and aprotic examples
CH3OH (protic) < H2O (protic) < DMSO (aprotic) < DMF (aprotic) < CH3CN (aprotic) < HMPA (aprotic)
nucleophile strength from least to most
H2O < CH3CO2- < NH3 < CL- < OH- < CH3O < I- < CN- < HS-
R-X have a higher boiling point than …?
alkanes (increases with an increased size of X or the chain)