2nd part opd
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
max 1st pm
symmetrical groove
max 2nd pm
crumpled look
developmental grooves
mand 1st pm
snake eyes
mesial & distal pits
mand 2nd pm
Y-groove
supplemental grooves
max 1st molar
biggest, trapezoid
buccal & lingual dg
lingual pit
cusp of carabelli
max 2nd molar
smaller
no cusp of carabelli
max 3rd molar
heart shaped
mand 1st molar
biggest, rectangular
5 cusps (distal)
mand 2nd molar
smaller
cross-like dg
mand 3rd molar
smaller than 1st & 2nd
dental caries
- multifactorial
- transmissible
- oral disease
acidogenic chemicoparasitic theory
proteolysis chelation theory
caries balance concept
3 etiological theories explain
pits and fissure caries
smooth surface caries
root caries
according to anatomical site
primary caries
recurrent caries
residual caries
according to new or recurrent lesion

according to speed or progression
EARLY CHILDHOOD CARIES – primary dentition
BOTTLE/NURSING CARIES – 4 maxillary incisors
XEROSTOMIA-INDUCED – from radiotherapy treatment
rampant caries explain
incipient caries
demineralized enamel only
cavitated caries
beyond enamel into dentin
1. simple caries
2. compound caries
3. complex caries
according to number of tooth surface involved

non carious defects
non hereditary enamel hypoplasia
disruption/trauma during tooth development
pits, linear defects, no enamel
localized non hereditary hypocalcification
enamel mineralization is defective, lesion color varies from chalky, yellow, brown to gray
dentinogenesis imperfecta
- genetic defect in collagen formation
- enamel is uniformly brown - purplish & translucent
visual method
tactile method
radiographic method
caries detection
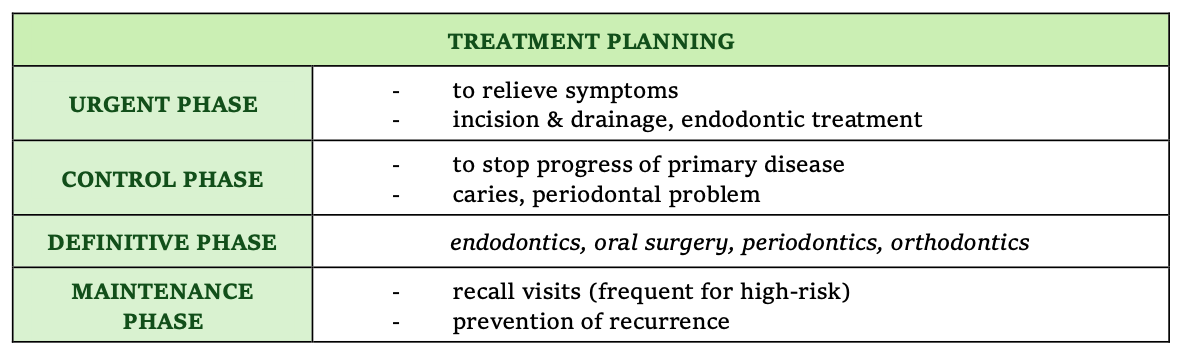
treatment planning