AP Biology Unit 6 - Gene Expression and Regulation
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
The process of DNA to RNA to Protein
Transcription
The synthesis of RNA from DNA
Translation
The synthesis of a polypeptide (protein) from RNA
Codon
A triplet of nucleotides (or letters of nitrogenous bases) on mRNA which codes for an amino acid
64, 20
There are __ codons but __ amino acids
Start
The AUG codon codes for...
Stop
The UAA, UAG, UGA codons code for...
RNA Polymerase
The enzyme which connects to a promoter and unzips DNA during transcription
5' to 3'
Translation can only go in this orientation
Promoter
The area where RNA Polymerase attaches to DNA
Transcription Unit
The portion of DNA being transcribed
TATA Box
The region of the promoter which RNA Polymerase binds to
Ribonucleic Acid
RNA's full name is...
Uracil
In RNA, Thyamine (T) is replaced with...
Messenger RNA
This RNA is made from transcription. It serves as a message for the section of transcribed DNA which codes for the protein needed to be made. Its prefix is "m"
Transfer RNA
This RNA floats around in the cytoplasm. At one end it contains anitcodons which align with the corresponding codons in mRNA. At the other end it contains a corresponding amino acid. Its prefix is "t"
Cap, Tail
mRNA cannot survive outside of the nucleus by itself. Because of this, before it exits the nucleus, a ___ must be put on the 5' end and a ___ must be put on the 3' end
Guanine
On the 5' end, a cap of a special ___ molecule is put on before exiting the nucleus.
Adenine
On the 3' end, a tail of around 50-250 ___ molecules are put on before exiting the nucleus. This chain is called a Poly-A-Tail
RNA Splicing
The process in which the uneeded parts of the mRNA are cut out before it exits the nucleus.
Introns
The non-coding regions of mRNA which are cut out during RNA Splicing
Exons
The coding regions of mRNA which are needed and not cut out during RNA Splicing
Small Nuclear Ribonucleoproteins
snRNA (Small Nuclear Riboneucleic Acid) and proteins combine to create this. This molecule later combines with a spliceosome during RNA Splicing. It is abbreviated as "snRNP."
Spliceosome
A molecule which combines with snRNPs to slice RNA during RNA Splicing.
mRNA
Amino Acids are coded for by the ___'s codon sequences
Polypeptide
A chain of amino acids. Is also another name for a protein
Anticodon
A sequence of 3 nucleotides on tRNA which matches up with another 3-nucleotide sequence on mRNA
Ribosome
An organelle that is made up of 2 subunits called "large" and "small." It is composed of proteins and a special type of RNA. It is where mRNA binds during translation translation and where protein synthesis occurs.
Ribosomal RNA
A special type of RNA which, combined with proteins, is what ribosomes are made up of. Its prefix is "r"
3
Each ribosome has ___ binding sites for tRNA
A Site
The ribosomal binding site that holds the next tRNA in line. Also known as the "entrance" or "accepting" site.
P Site
The ribosomal binding site that holds the tRNA with the polypeptide attached (tRNA with the most recently attached amino acid).
E Site
The ribosomal binding site where tRNA detaches after dropping off its amino acid. Also known as the "exit" site.
Mutation
A change in DNA
Point Mutation
A mutation which causes a change in a single nucleotide base
Frame-Shift Mutation
A mutation which inserts or deletes a base, changing the entire codon sequence after it
Nonsense Mutation
A type of point mutation which causes a stop in the amino acid sequence
Silent Mutation
A type of point mutation which causes no change in the amino acid sequence
Missense Mutation
A type of point mutation which codes for a different amino acid in the sequence
Operons
Genes that can be turned off or on as needed. They are made up of an operator, a promoter, some enzymes, and a gene. Are only present in prokaryotes and very few eukaryotes.
Operator
A segment of DNA which acts as an on and off "switch" for the Operon. Are only present in prokaryotes and very few eukaryotes.
Promoter
A segment of DNA where RNA Polymerase attaches to the operon. It is a nearby control sequence on DNA which allows the binding of RNA Polymerase and Transcription Factors. Are present in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Repressors
Molecules that turn off an operon.
Inducers
Molecules that turn on an operon.
Repressible Operon
An operon that can be turned off (e.g. Trp Operon)
Inducible Operon
An operon that can be induced/stimulated (e.g. Lac Operon)
DNA Packing
A type of gene regulation which coils and folds DNA to allow it to fit into the nucleus. Forms/Levels of DNA packing are nucleosomes, chromatin fiber, looped domains, and chromosomes
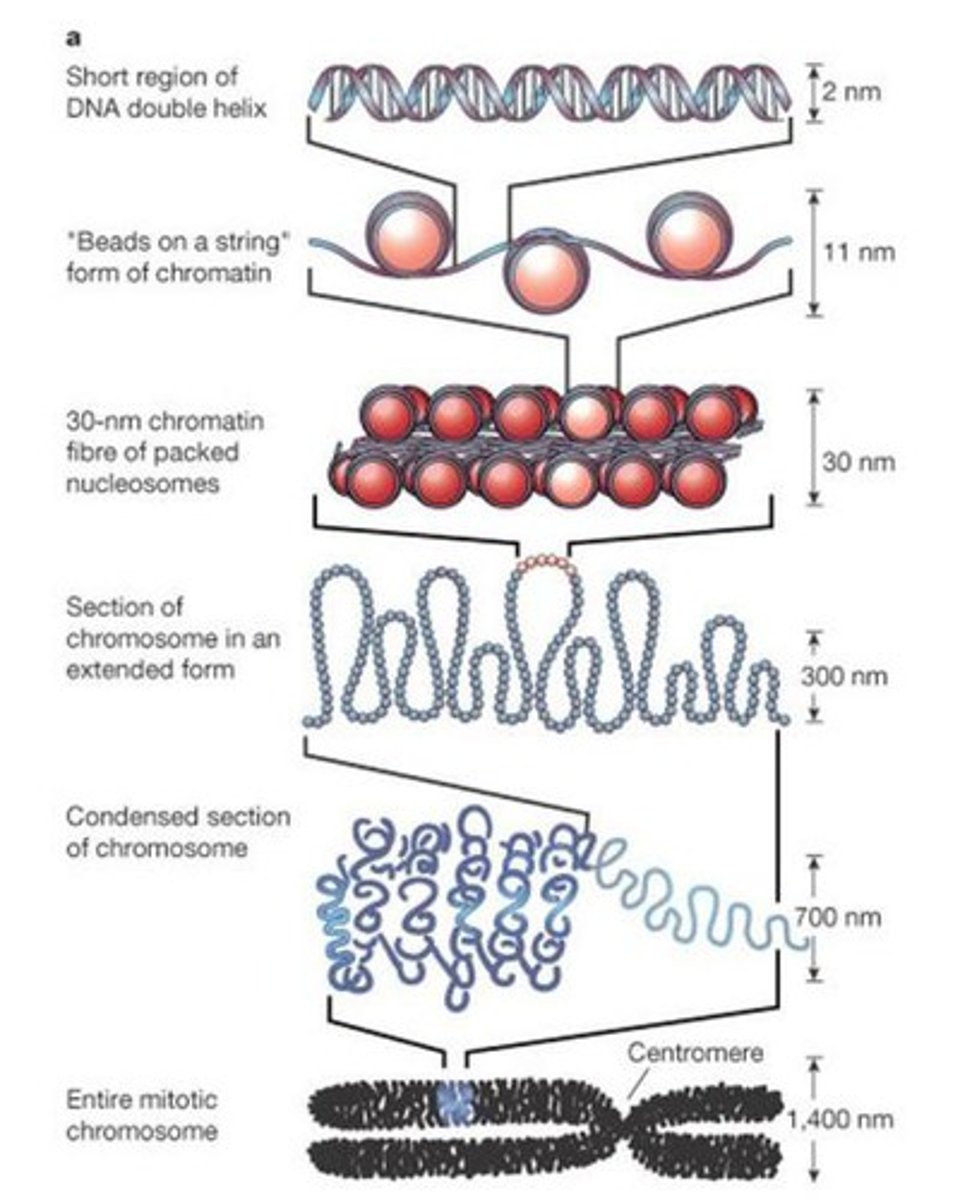
Nucleosomes
The first level of DNA packing where negatively charged DNA wraps around positively charged histone proteins. Looks like beads on a string
Histone Proteins
Positively charged amino acids which, with 8 of them, bind to DNA during the first level of DNA packing.
Off
DNA that is tightly packed around a histone causes a gene to be turned...
On
DNA that is loosely packed around a histone causes a gene to be turned...
Heterochromatin
Tightly packed DNA which appears darker
Euchromatin
Loosely packed DNA which appears lighter
Methylation
A process which blocks DNA transciption factors by attaching methyl groups (-CH3) to cytosine. It blocks transcription and causes genes to be turned off. Causes a near permanant inactivation of genes (e.g. Barr Bodies)
Acetylation
A process which unwinds DNA from aroudn the histones by attaching acetyl groups (-COCH3) to histones. It enables transcription and causes genes to be turned on. Causes a conformational change in histone proteins and allows transciption factors to have en easier access to genes
Transcription
A type of gene regulation which controls regions on DNA being transcribed via nearby (promoter) or distant (enhancer) control, DNA packing, or transcription factors. This controls the initiation of...
Enhancer Sequence
A distant control sequence on DNA which makes enhancer proteins to turn a gene on. These sequences can be turned on or off by silencers or activators. Are present only in eukaryotes.
Activator Proteins
Proteins which are made by the enhancer sequence to stimulate transcription/turn on a gene. Are also called enhancer proteins
Silencer Sequence
A distant control sequence on DNA which makes silencer proteins to turn an enhancer sequence off. Are only present in eukaryotes
Silencer Proteins
Proteins which bind to the enhancer sequence to turn it off and block gene transcription
mRNA Degradation
A type of gene regulation which regulates mRNA's life span which in turn determines amount of protein synthesis. Is a type of post-transcriptional control.
Small Interfering RNA
Short segments of RNA (21-28 bases) which bind to RNA to create segments of double-stranded mRNA. This acts as a "death tag" for mRNa and causes degradation. Its prefix is "si." Is a type of RNA inteference.
Gene Silencing
A type of RNA inteference which turns off the gene after transcription has already occured. Is a type of post-transcriptional control.
Protein Processing
A type of gene regulation which includes the process of folding, cleaving, the adding sugar groups, and the targeting for transport of proteins. Is a type of post-translational control.
Protein Degradation
A type of gene regulation which recycles or degrades protein after translation has already occured. Is a type of post-translational control.
Ubiquitin
A molecule that serves as a "death tag" for the degradation of proteins after translation (post-translational control)
Proteasome
A molecule that degrades and recycles proteins after translation (post-translational control)
Post-Transcriptional Control
mRNA processing, RNA splicing, the placement of caps and tails on RNA, and degradation via siRNA are types of gene regulation called...
Translation
Regulatory proteins can block attachment of ribosomal subunits and initiator tRNA or can attach to the 5' end of mRNA to prevent attachment of ribosomal subunits and initiator tRNA. These are a type of gene regulation that control the initiation of...
Post-Translational Control
Protein processing and protein degradation are types of gene regulation called...
Virus
An infectious agent made of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) in a protein coat. They can only reproduce inside another living organism's cells. By this standard, they are not considered to be alive. Are smaller than ribosomes
Bacteriophages
Viruses that infect bacteria. Are also called "phages" for short.
Lytic Cycle
A reproductive cycle of viruses which kills the host organism
Lysogenic Cycle
A reproductive cycle of viruses which allows replication of the nucleic acid without killing the host organism. Most virsus do this type of cycle.
Retrovirus
A type of virus composed of RNA instead of DNA. They also have a unique enzyme which allows them create DNA out of their RNA after entering a cell
Reverse Transcriptase
A retrovirus enzyme which reverts RNA back into DNA
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
A retrovirus which causes AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome). As of now, it is unknown what triggers the AIDS to show up after obtaining this retrovirus. An infection caused by this virus cannot be stopped or removed from the host after its RNA is released. Its abbreviation is "HIV"
Vaccines
Harmless variants or derivatives of pathogenic microbes which cause the immune system to create defences against the actual pathegen
Bacteria
A microorganism that can reproduce and mutate rapidly. Can be good, bad, or neutral
Nucleoid
The genetic material of bacteria. It is a tight coiled, long strand of DNA.
True
T/F: Using antibacterial soap and antibiotics too often can be bad because it will only kill off the weaker bacteria and leave the stronger bacteria alive, causing super bugs to be created and people to develop antibiotic resistance.
Herd Immunity
When a high percentage of the population is vaccinated, lowering the chance of disease to spread
Innate Immunity
Immune system defences which are present at birth (skin, mucous membranes, antimicrobial proteins, etc.)
Acquired Immunity
Immune system defences which are acquired later in life through exposure
Lysozyme
An enzyme that digests the cell walls of bacteria. Is a type of innate immunity
Phagocytic Cells
Cells that attach to invaders and eat them. Some examples are white blood cells like Neutrophils (the most abundant white blood cell in the body) and Macrophages ("big eaters"). Is a type of innate immunity
Interferons
Proteins that protect against viruses. Is a type of innate immunity
Inflammatory Response
An immune responce that is triggered when tissue is damaged and causes inflammation. Is a type of innate immunity
Mast Cells
Cells which release chemicals to increase blood flow to a damaged site during an inflammatory response.
Histamines
Chemicals that are released by Mast Cells to increase blood flow to a damaged site during an inflammatory response
Natural Killer Cells
Cells which patrol the body and attack virus-infected cells. Is a type of innate immunity
Antigen
A foreign molecule that triggers an immune response
Antibodies
An immune response that will attach to antigens (foreign molecules) and attack them. They are speciliazed for a specific type of antigen. Is a type of acquired immunity.
B Cells
A type of lymphocyte (white blood cell) that will mature into plasma cells that produce antibodies
Memory B Cells
B Cells that store information about/remember a pathogen that has already triggered an immune response in the past to allow for faster antibody production if the pathogen is encountered again
Humoral Immune Response
A type of acquired immunity which produces antibodies to fight off antigens via B Cells
Primary Immune Response
A humoral immune response that occurs after the the first exposure to an anitgen
Secondary Immune Response
A humoral immune response that occurs after the the second exposure to an anitgen
Helper T Cells
T cells that help B Cells mature into plasma cells to release antibodies
Killer T Cells
T cells that target and kill cells infected with a virus by attaching to a targeted cell and releasing a toxic molecule which will poke holes in the targeted cell, causing it to self-destruct