Chapter 1
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The Study of Change
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Chemistry
the central science studying the composition, structure, properties, and changes of matter
Health and Medicine
• Sanitation systems
• Surgery with anesthesia
• Vaccines and antibiotics
• Gene therapy
Energy and the Environment
• Fossil fuels
• Solar energy
• Nuclear energy
Materials and Technology
• Polymers, ceramics, liquid crystals
• Room-temperature superconductors
Food and Agriculture
• Genetically modified crops
• “Natural” pesticides
• Specialized fertilizers
Macroscopic
Observation of large scale phenomenon
Microscopic
Explanations lie in the microscopic world of atom and molecules
Chemical Reaction
bonds between atoms break and form, resulting in different substances with different properties.
scientific method
a systematic approach to research.
Observation - Representation - Interpretation
hypothesis
a tentative explanation for a set of observations.
Tested -
law
a concise statement of a relationship between phenomena that is always the same under the same conditions
Force = mass x acceleration
theory
a unifying principle that explains a body of facts and/or those laws that are based on them.
Chemistry
the study of matter and the changes it undergoes.
Matter
anything that occupies space and has mass.
substance
a form of matter that has a definite composition and distinct properties.
mixture
a combination of two or more substances in which the substances retain their distinct identities.
Homogenous mixture
composition of the mixture is the same throughout
Heterogeneous mixture
composition is not uniform throughout
Physical means
can be used to separate a mixture into its pure components.
element
a substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances by chemical means.
compound
a substance composed of atoms of two or more elements chemically united in fixed proportions.
only be separated into their pure components (elements) by chemical means.
physical change
does not alter the composition or identity of a substance.
chemical change
alters the composition or identity of the substance(s) involved.
extensive property of a material
depends upon how much matter is being considered.
• mass
• length
• volume
intensive property of a material
does not depend upon how much matter is being considered.
• density
• temperature
• color
Matter
anything that occupies space and has mass
mass
measure of the quantity of matter
kilogram (kg)
weight
force that gravity exerts on an object weight
= a x mass
Volume
cubic meter (m3)
Density
kg/m3
K to C
K = 0C + 273.15
F to C
0F = 9/5 x 0C + 32
Any digit that is not zero
significant
Zeros between nonzero digits
significant
Zeros to the left of the first nonzero digit
not significant
If a number is greater than 1, then all zeros to the right of the decimal point
significant
If a number is less than 1, then only the zeros that are at the end and in the middle of the number
significant
1.234 - how many figure?
4
606 - how many figure?
3
0.08 - how many figure?
1
2.0 - how many figure?
2
0.00420 - how many figure?
3
478
3
6.01
3
0.825
3
0.043
2
1.310 × 1022
4
7000
may be four (7.000 × 103), three
(7.00 × 103), two (7.0 × 103), or one (7 × 103).
Accuracy
how close a measurement is to the true value
Precision
how close a set of measurements are to each other
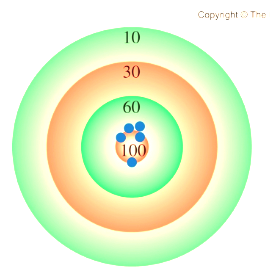
accurate & precise
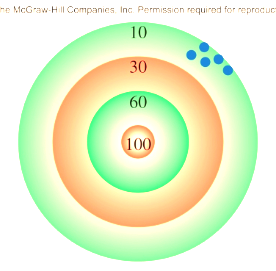
precise but not accurate
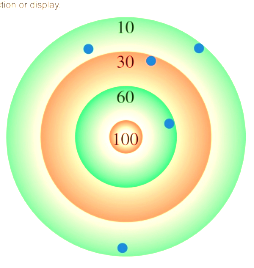
not accurate & not precise