Radiology Heart and vessels
1/125
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
Define cardiac silhouette
Delineates external margins of heart/pericardium
3 pitfalls of rads with cardiac stuff
- unable to define internal features of cardiac chambers
- unable to determine wall thickness or chamber size
- unable to delineate valvular morphology
What makes up the dorsal 1/3 and ventral 2/3 cranial border on lat view
Dorsal 1/3
- MPA
- right auricle
- ascending aorta
Ventral 2/3
- wall of right ventricle and outflow tract
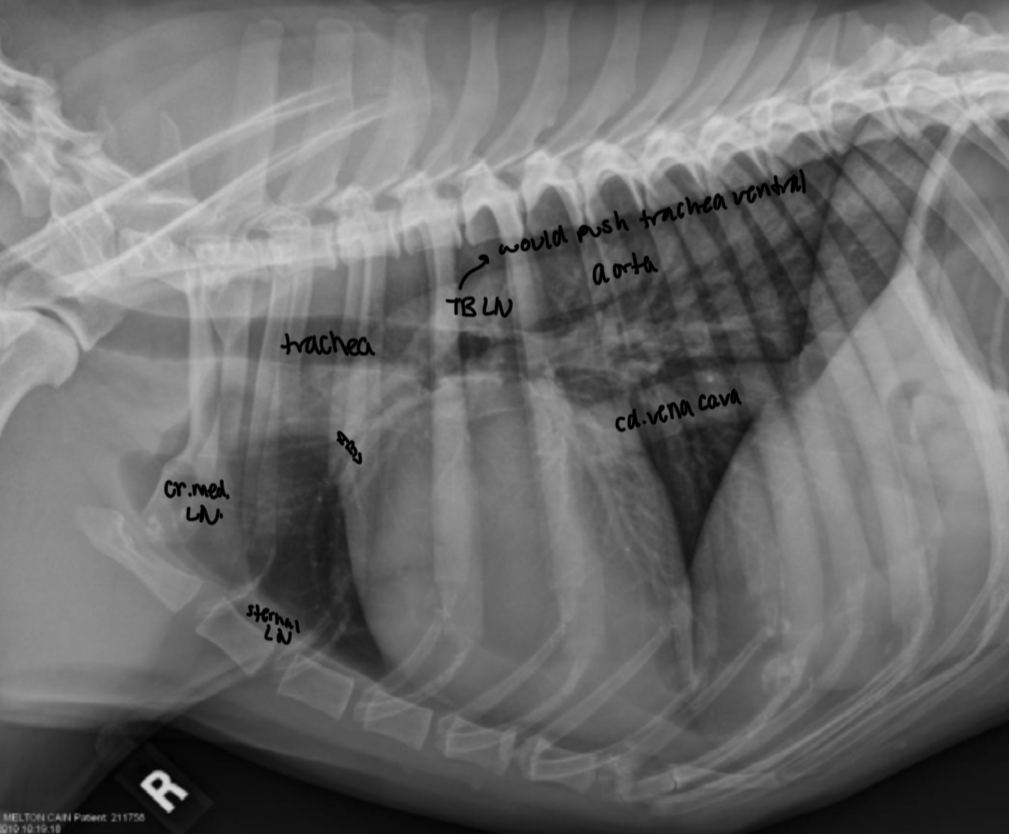
What makes up the dorsal 1/3 and ventral 2/3 of the caudal border on a lateral view
Dorsal 1/3
- left atrium (obscured by overlying pulmonary vessels)
- sulcus at junction of left atrium and left ventricle
Ventral 2/3
- left ventricular free wall
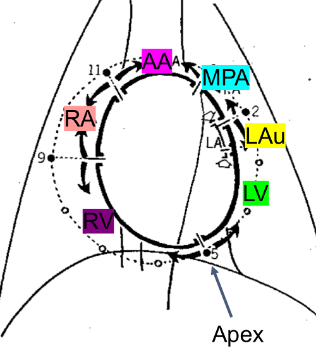
Clock face of the heart
•11:00 – 1:00 Aortic arch (AA)
•1:00 – 2:00 Main pulmonary artery segment (MPA)
•2:30 – 3:00 Left auricle (LAu)
•3:00 – 5:00 Left ventricle (LV)
•5:00 – 9:00 Right ventricle (RV) - large
•9:00 – 11:00 Right atrium (RA)
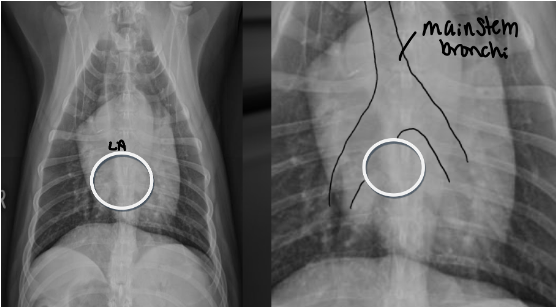
Where does the left atrium sit on the clock face
Located between main stem bronchi which straddle it like a cowboy
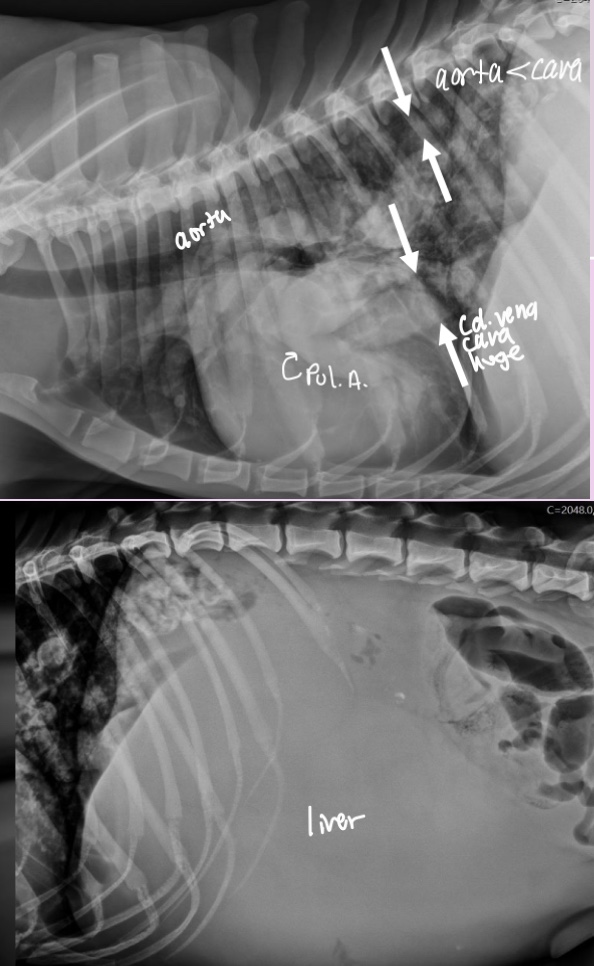
where is the aorta and cd. Vena cava located on VD
Aorta - superimposed with spine and heart on VD
Cd. Vena cava - superimposed with accessory lung lobe in right cd. Thorax on VD
What two diseases can cause segmental enlargement of aorta
- Aortic arch (AA) —> Subarotic stenosis (SAS/AS)
- proximal descending aorta —> PDA (patent ductus arteriosus)
Both of theses are congenital
What 2 pathologies can make the cd. Vena cava small/large
- small = hypovolemia or shock
- big = R. CHF —> secondary hepatomegaly and abdominal effiusion
**remember Cd. Vena cava can vary with cardiac cycle and phases of respiration but that is normal **
Enlargement of MPA is associated with what 2 pathologies
-pulmonary hypertension
-dz of pulmonary outflow tract (pulmonic stenosis, heartworm)
**mild MPA enlargement can be normal in some dogs - eval in light of other findings**
Where is left caudal pulmonary artery and right caudal pulmonary artery located in respect to trachea
Left - dorsal to tracheal bifurcation
Right - ventral to tracheal bifurcation
What is the ordering of pulmonary arteries and veins in relation to bronchi
ABV
-veins are ventral and central
-arteries are dorsal and peripheral
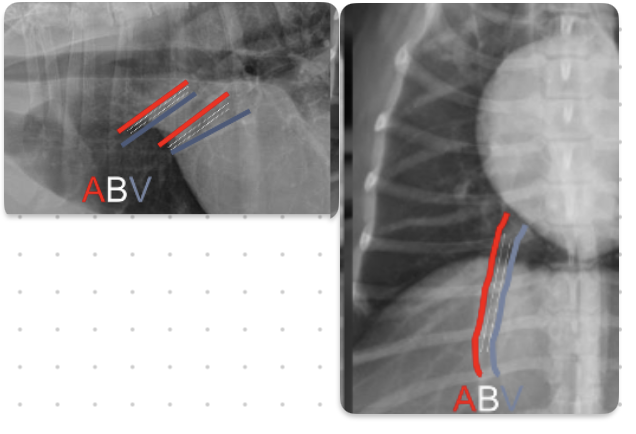
What is the general rule on size of pulmonary vessels
-equal to diameter of 9th rib as they cross it
-make sure arteries and veins are about the same size
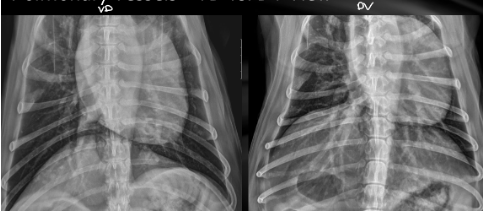
VD/DV how to tell the difference
VD - Mickey Mouse ears diaphragm
-cd. Dorsal lung lobes collapsed (hard to see pathology here)
DV - one diaphragm bump
-cd lobar vessels are more visible
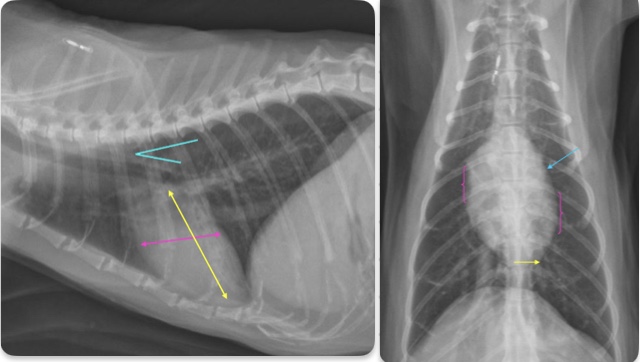
Feline cardiac silhouette and sizing on VD and lateral views
-almond shape
Lat view
-2/3 thoracic height
-2-2.5 IC spaces wide
-trachea deviates from spine
VD
-apex slightly left of midline
-broad convexity in area of right atrium and left ventricle
-flat left auricle area
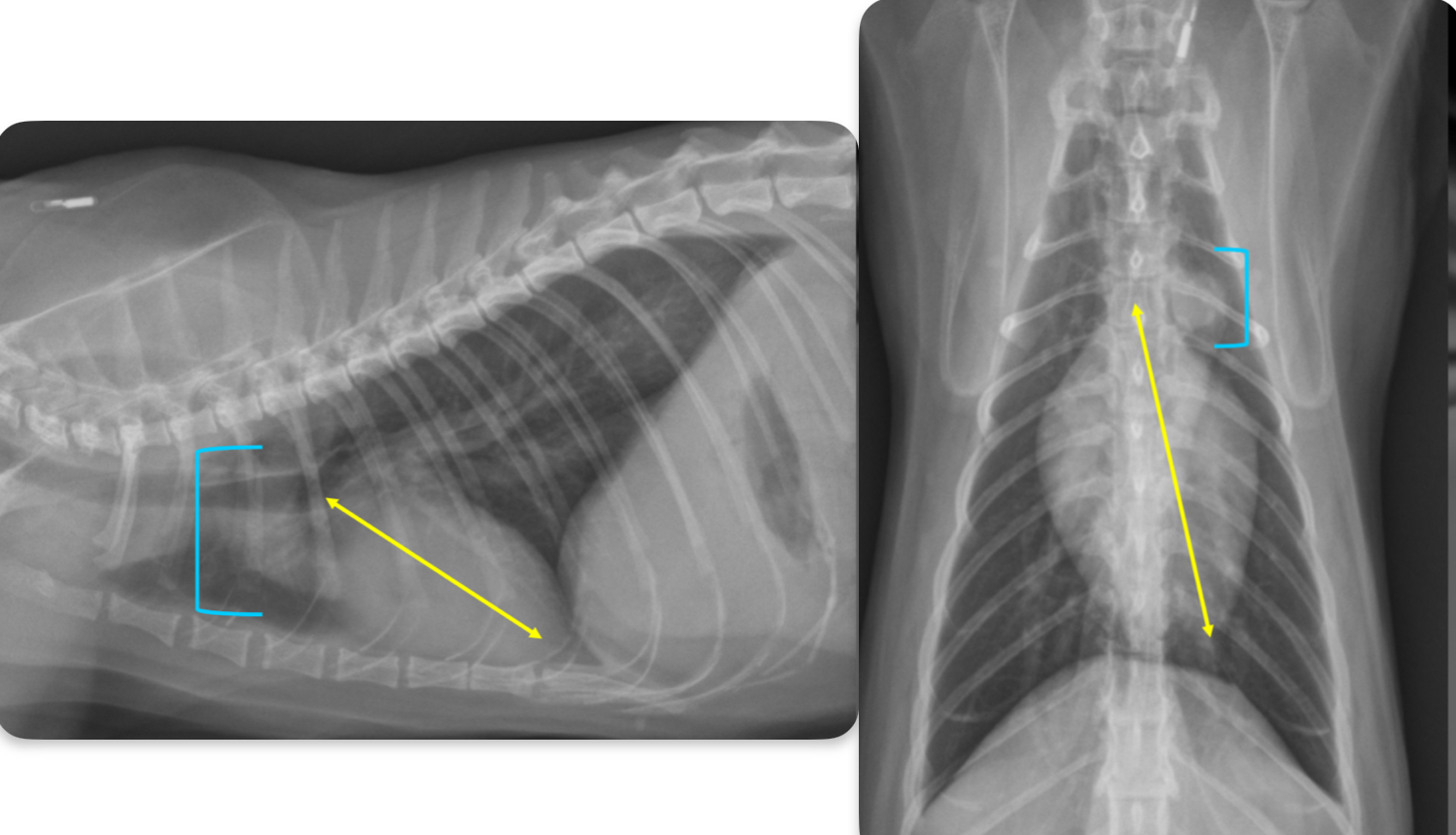
What are two features that you would see on rads with a geriatric cat
Lateral
-cardiac silhouette inclines cranially
-vertical orientation of aortic arch (bump)
VD
-“elonagated heart”
-vertical orientation of AA appears end on like a false nodule
3 features of Deep chested dog hearts on lateral rad
-heart perpendicular to spine, 2/3 DV diameter
-2.5 IC spaces
-trachea deviates from spine
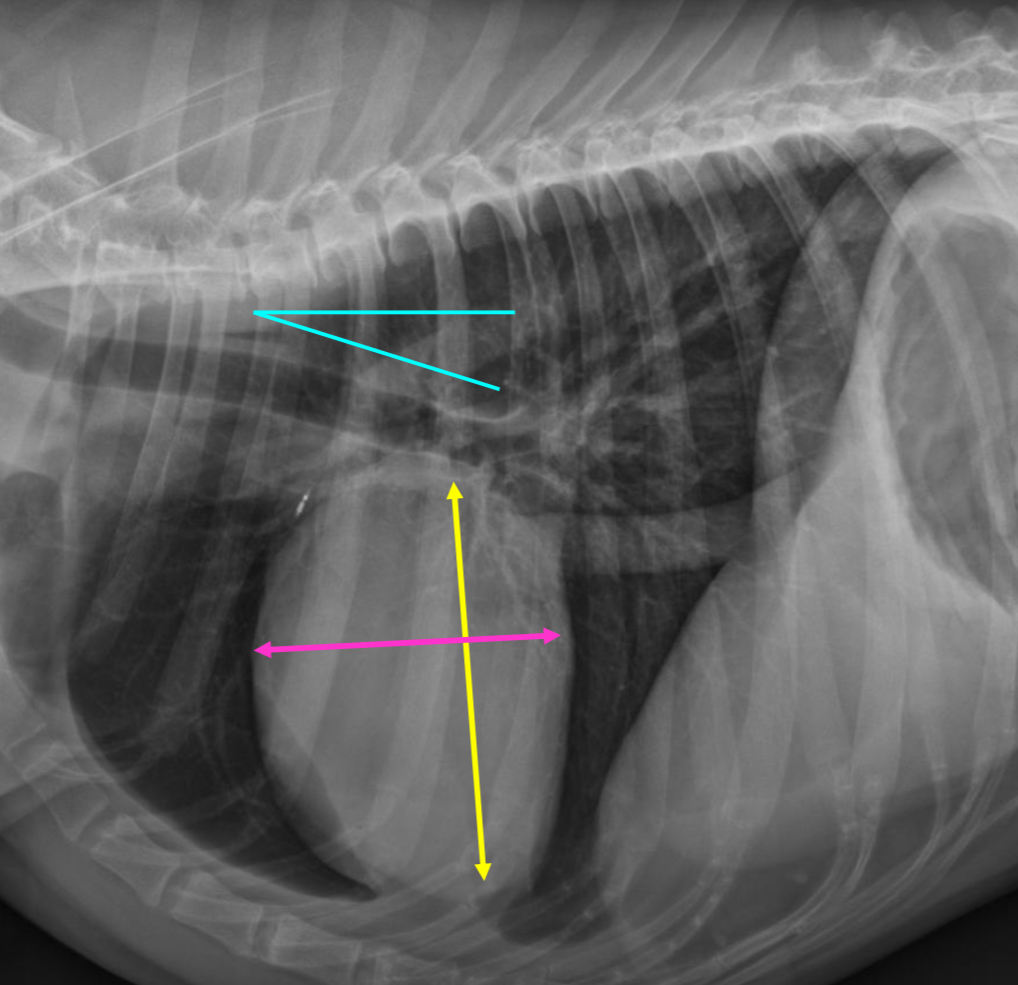
3 features of deep chested dogs hearts VD
-apex slightly left of midline
-circular to ovoid heart
-cupula and heart separation
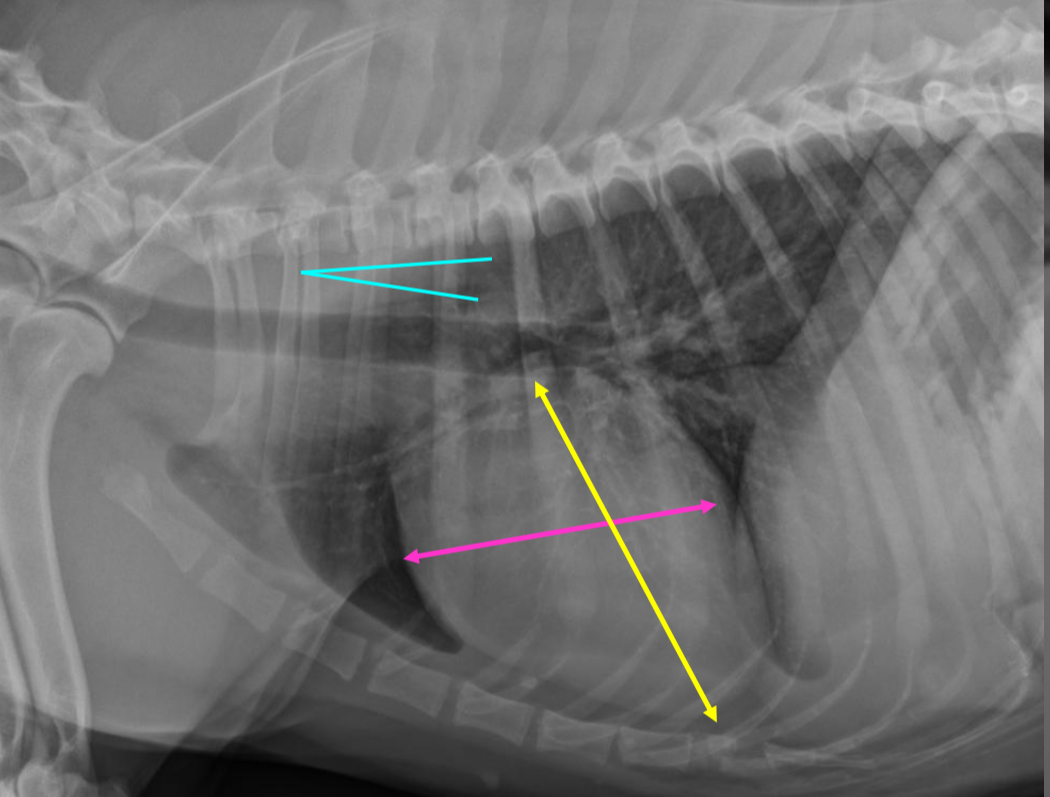
3 features of intermediate dog hearts lateral rad
-3 IC spaces wide
-heart angled cr.dorsal, 2/3 DV diameter
-trachea deviates from spine
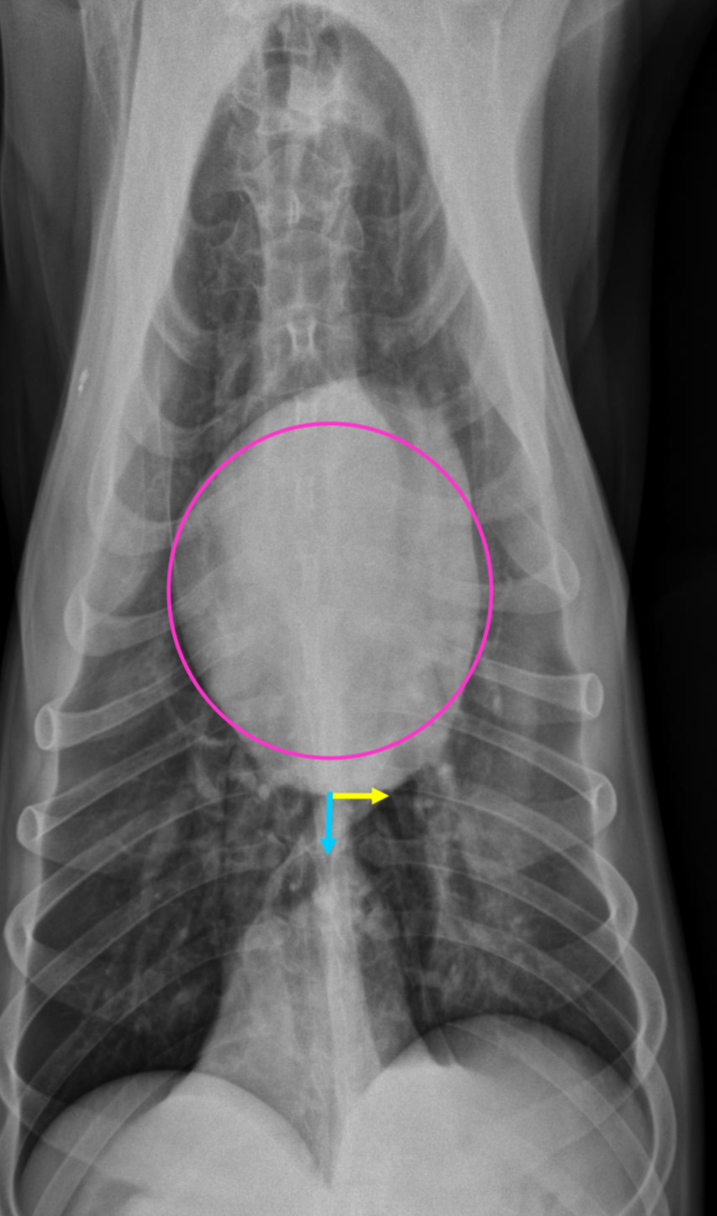
3 features of intermediate dog hearts on VD rad
-more elongated
-apex MORE to left of midline
-less separation between heart and cupula
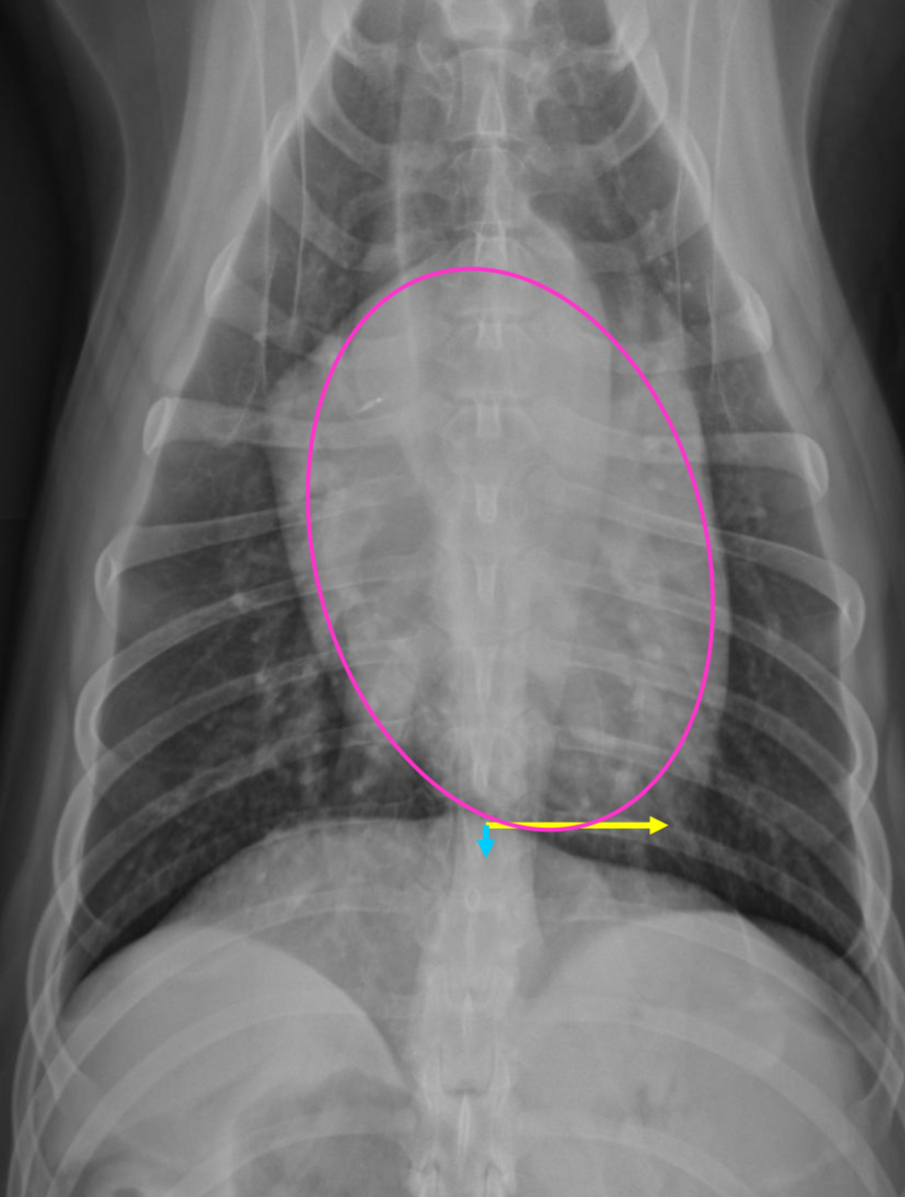
4 features of shallow chested dogs hearts on lateral rad
-round heart
-2/3 or greater DV diameter
-3-3.5 IC spaces
-less tracheal deviation
-greater sternal contact
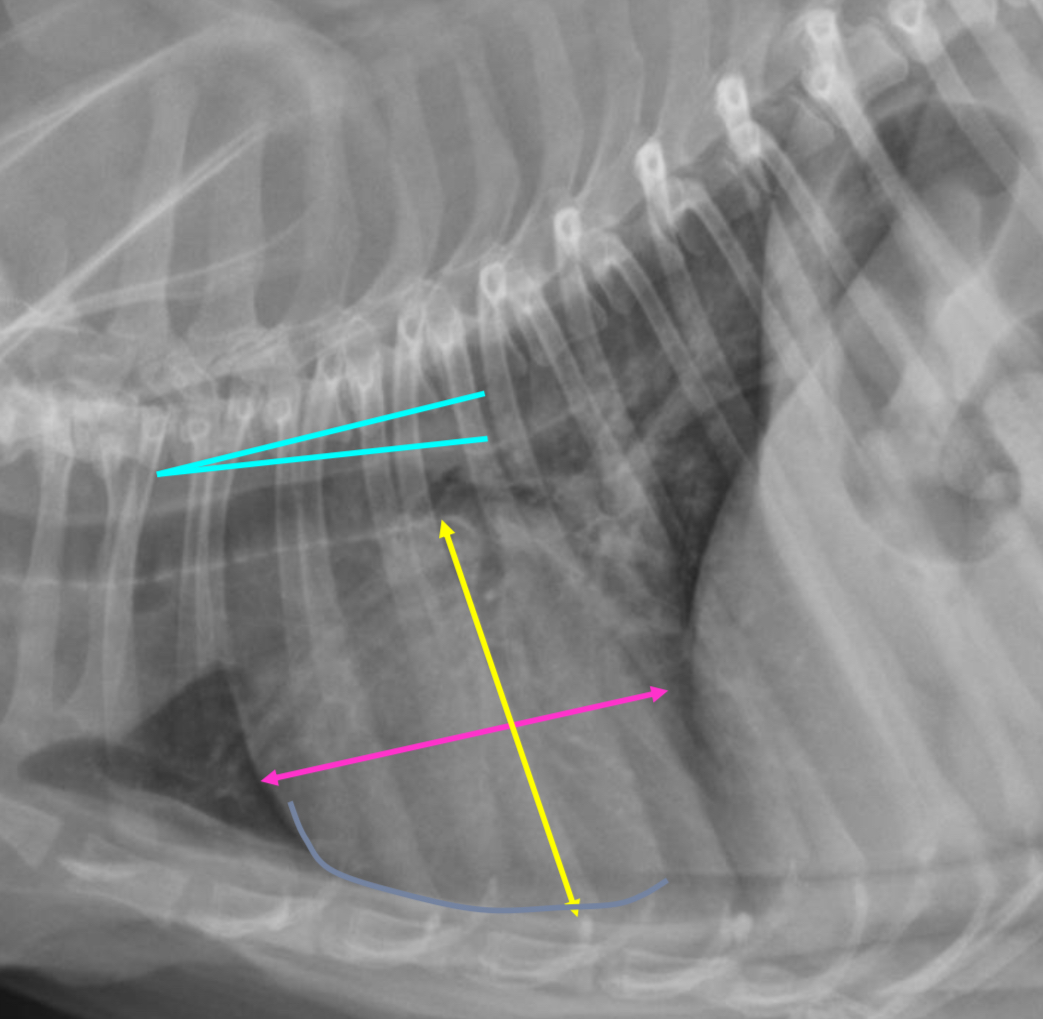
3 features on shallow chested dog hearts VD
-heart round to elongated
-apex VERY left of midline
-heart and cupula practically touching
What are the 2 types of angiocardiography available
Non-selective and selective
Selective angio vs non-selective
Contrast injected in peripheral vein vs Cather in area of interest
Diagnostic angiocardiography largely replaced by
Echocardiography
Why else would we use angiocardiography in vet med
Interventional cardiac procedures
Echo is defined as
Ultrasound of heart
-gold standard in dx most cardiac disorders
What is the most consistent rad indicator of heart disease
Cardiomegaly
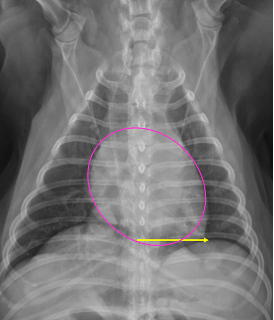
How do we measure heart size on rads
Vertebral heart score
-put the heart width and length along the vertebrae starting at T4 = cumulative sum of vertebra between length and with = vertebral heart score
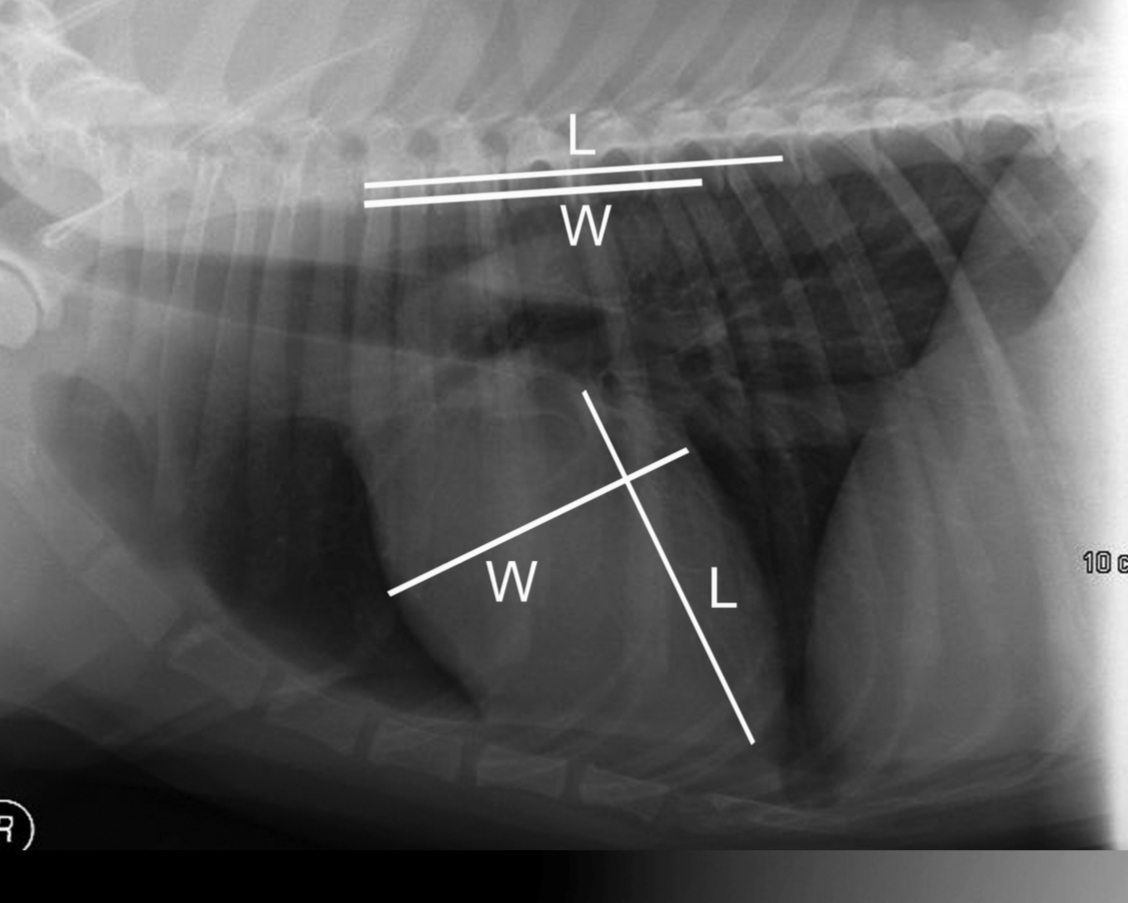
Normal vertebral heart score in dogs and cats
Dog 8.5-10.6 (9.7)
Cat 7.5 ± 0.3
what two parts of the heart will enlarge together
Atrial and ventricular enlargement of affected side go together
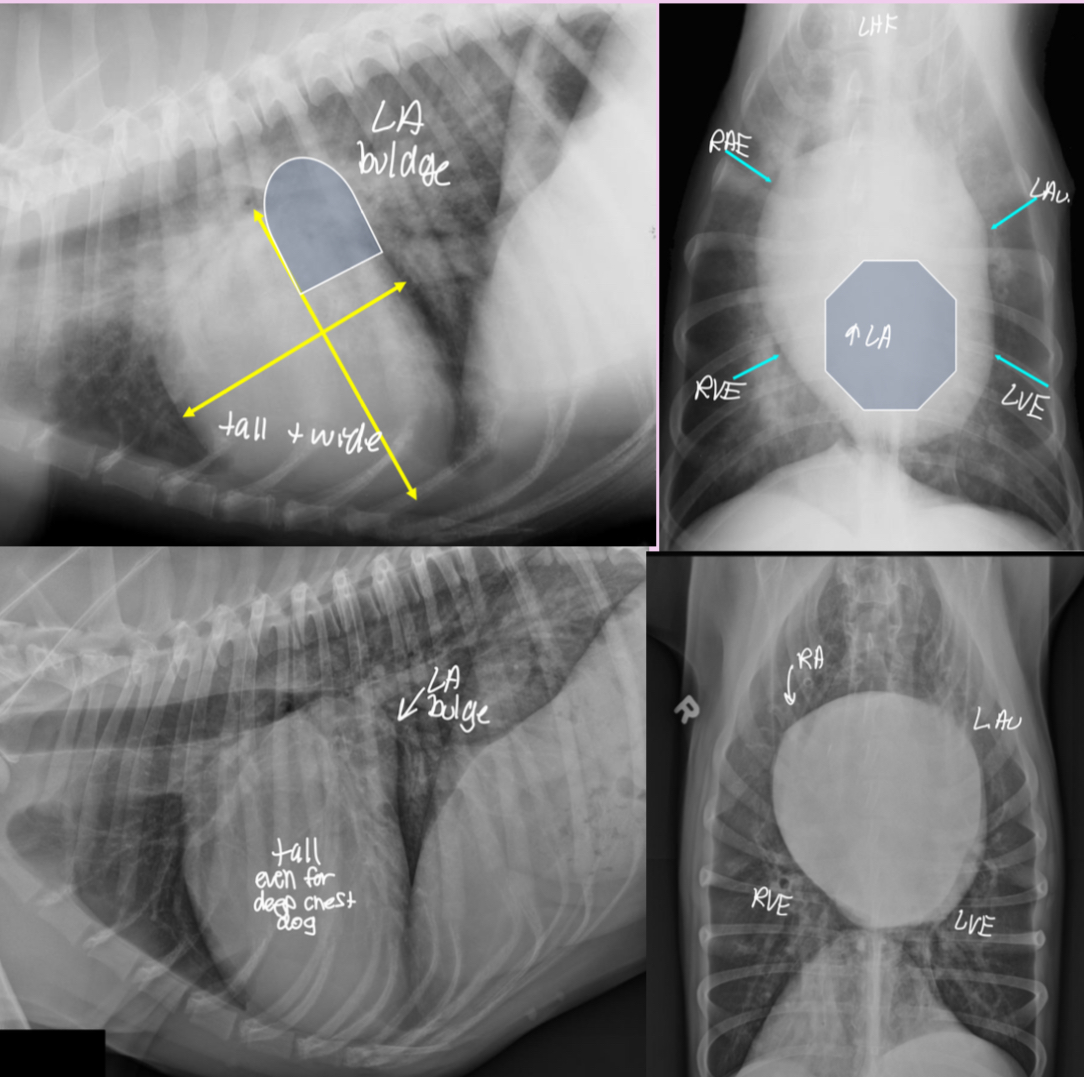
3 features of LAE on lateral
-dorsal displacement of main stem bronchi by a hunchback bump
-increased cd.dorsal cardiac border
-loss of cd.cardiac waist - straightening of cd.cardiac margin
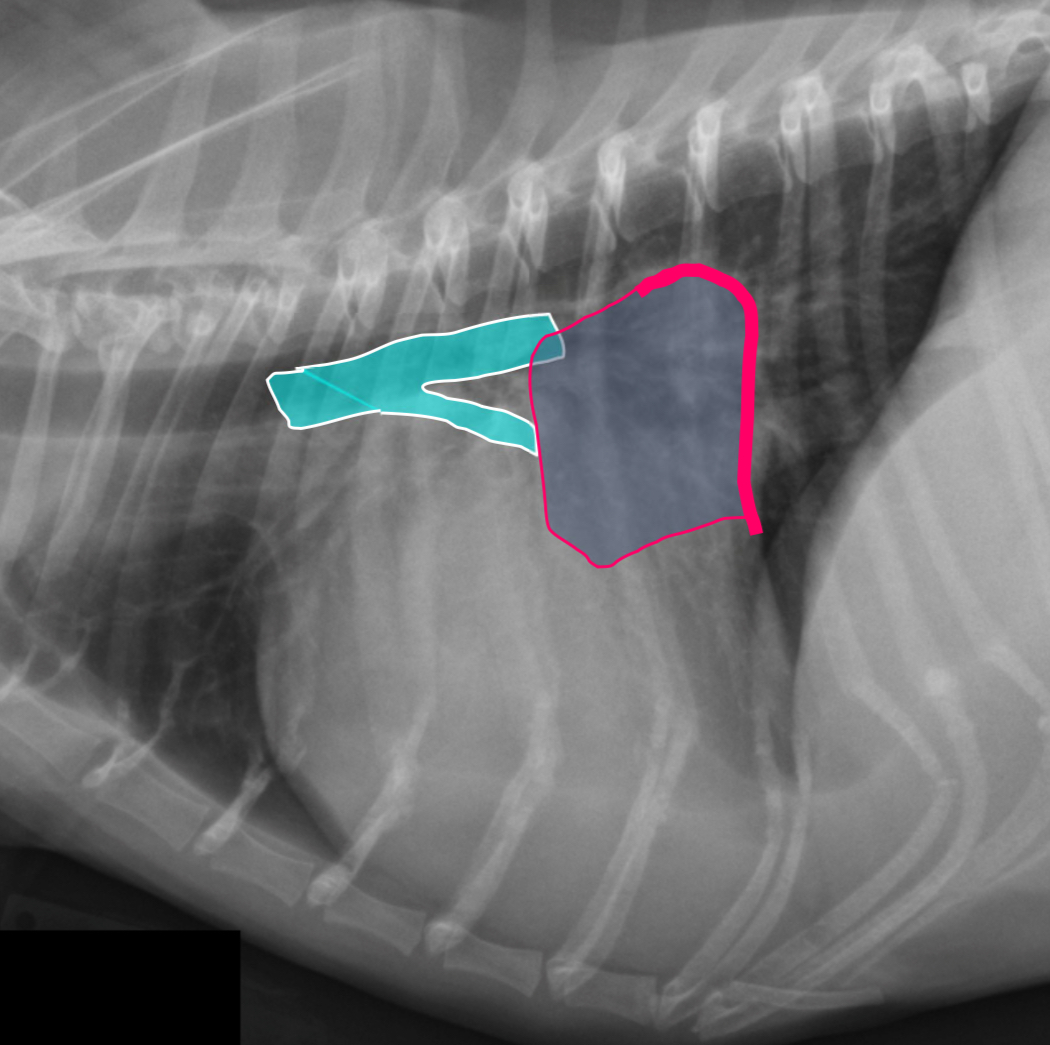
What part of the heart is enlarged
LAE
3 features of LAE on DV
-double opacity sign
-separation of main stem bronchi
-LA bulge at 2:30-3 o’clock
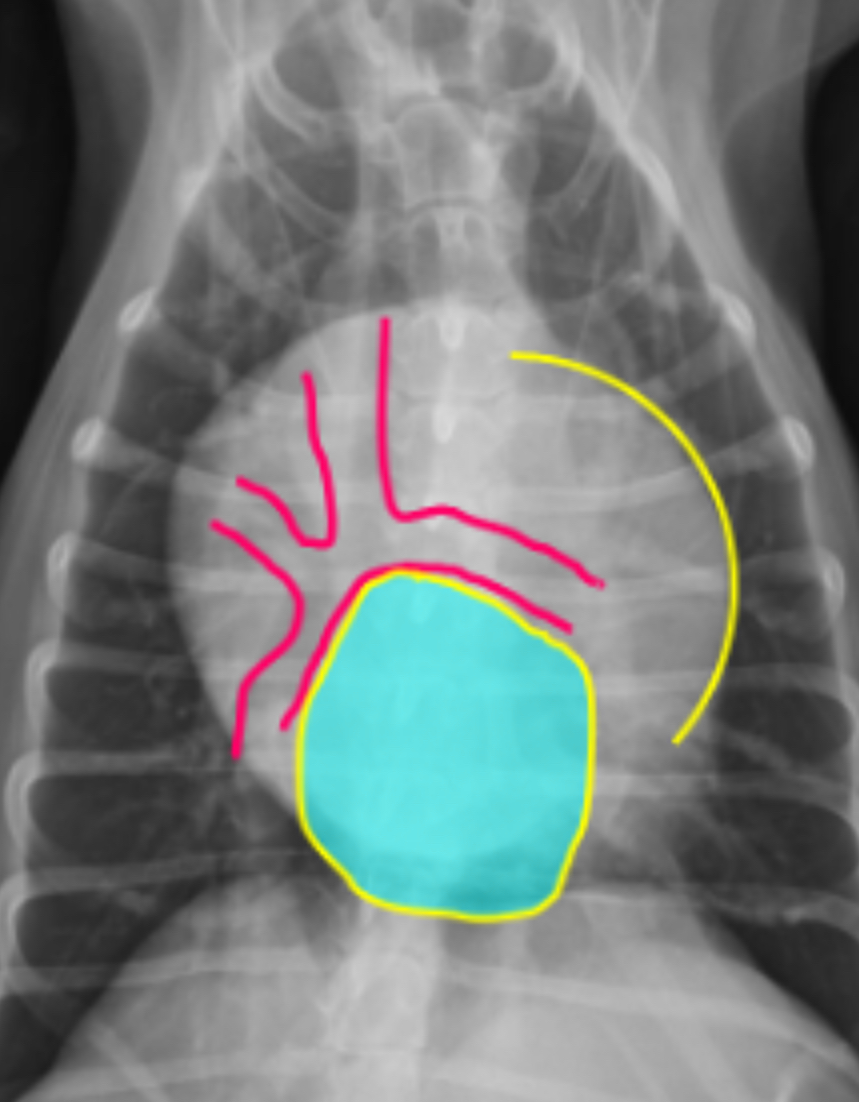
What part of the heart is enlarged
LAE
3 features LVE on lateral
-tall heart (>2/3 DV diameter)
-dorsal displacement of trachea (almost parallel to spine)
-straightening of cd. border of heart
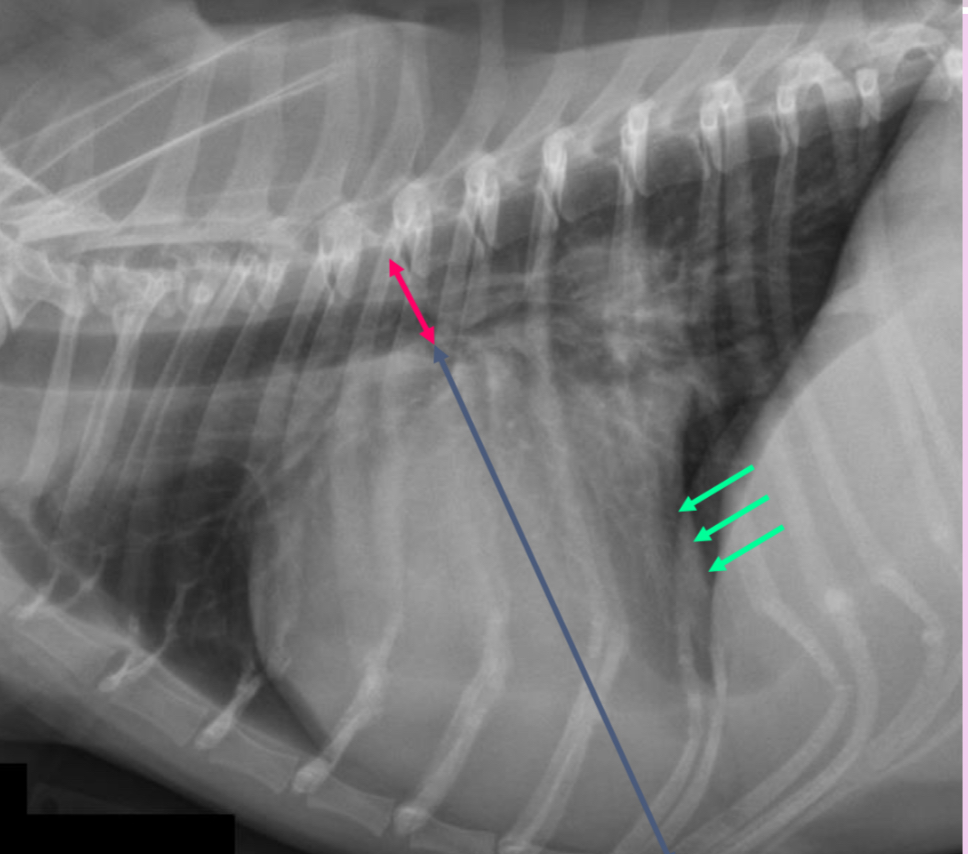
What part of the heart is enlarged?
LVE (technically LAE too) - prof used the same photo for both but outlined different features
3 features of LVE VD
-elongation of cardiac silhouette
-deviation of apex to the left
-bulge at 3-5 o’clock
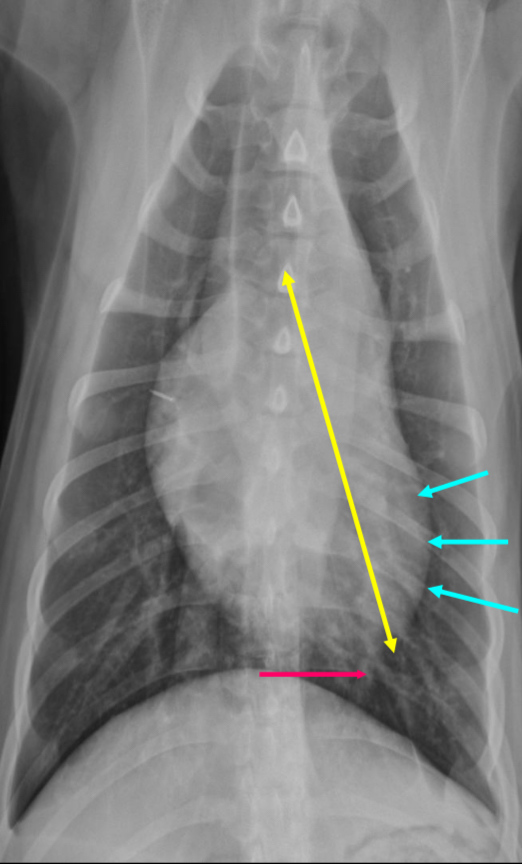
What part of the heart is enlarged?
LVE
2 features of RAE on lateral
-dorsal bowing of trachea over cranial heart base @ bifurcation
-loss of cr.cardiac waist (R.atrium and MPA are here)
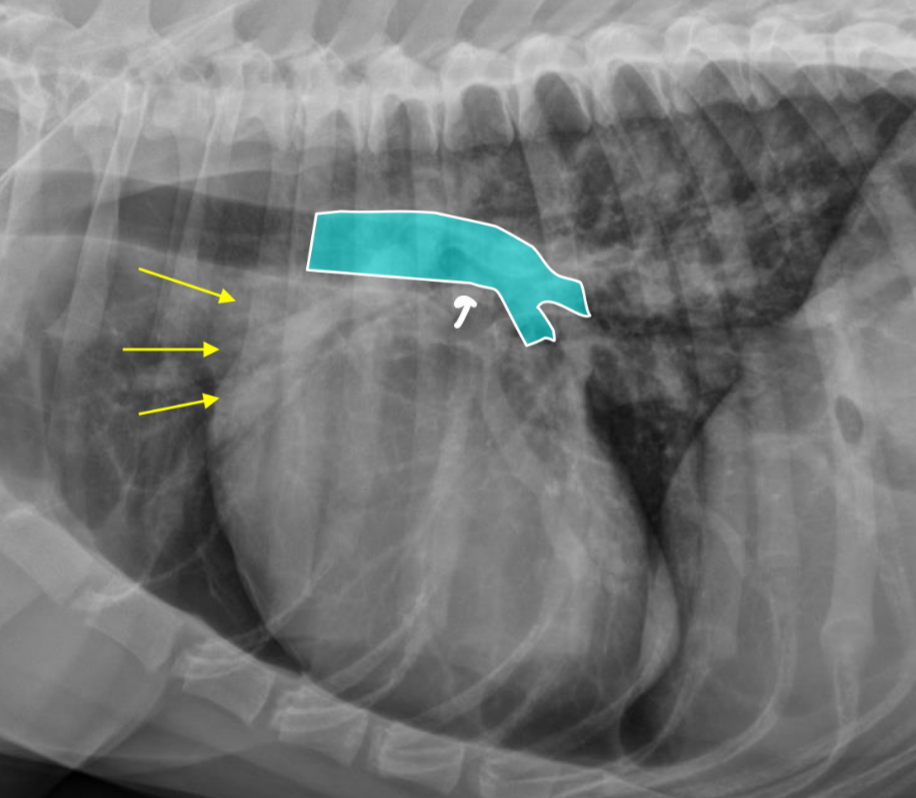
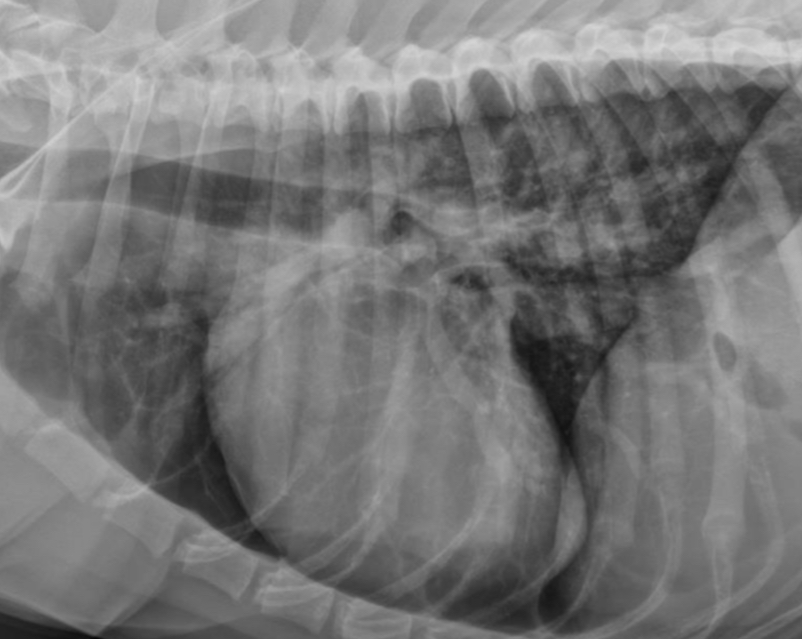
What part of the heart is enlarged?
RAE
RAE feature on VD
Bulge at 9-11 o’clock region ± RVE bulge
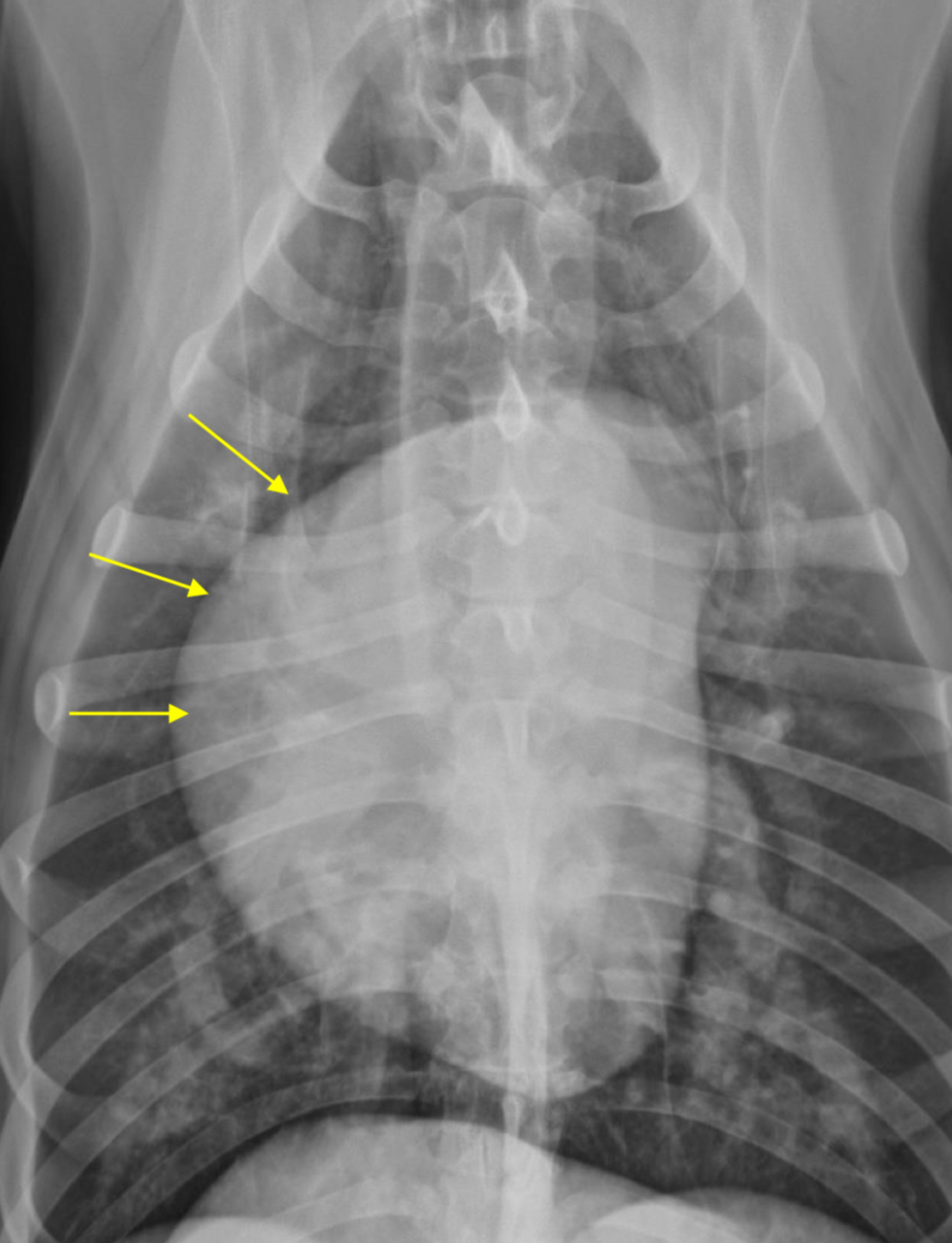
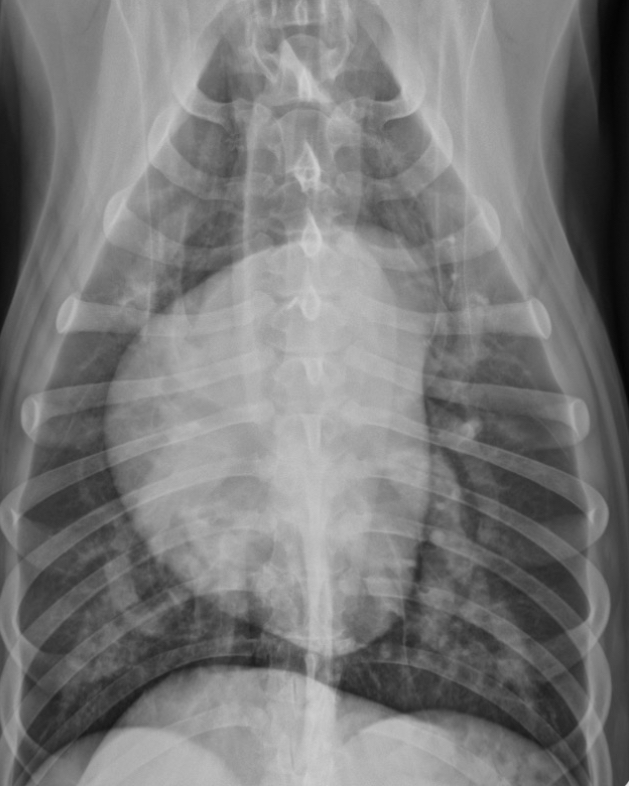
What part of the heart is enlarged?
RAE
2 features of RVE on lateral
-wide cardiac silhouette
-cr.margin super bowed out —> increased sternal contact
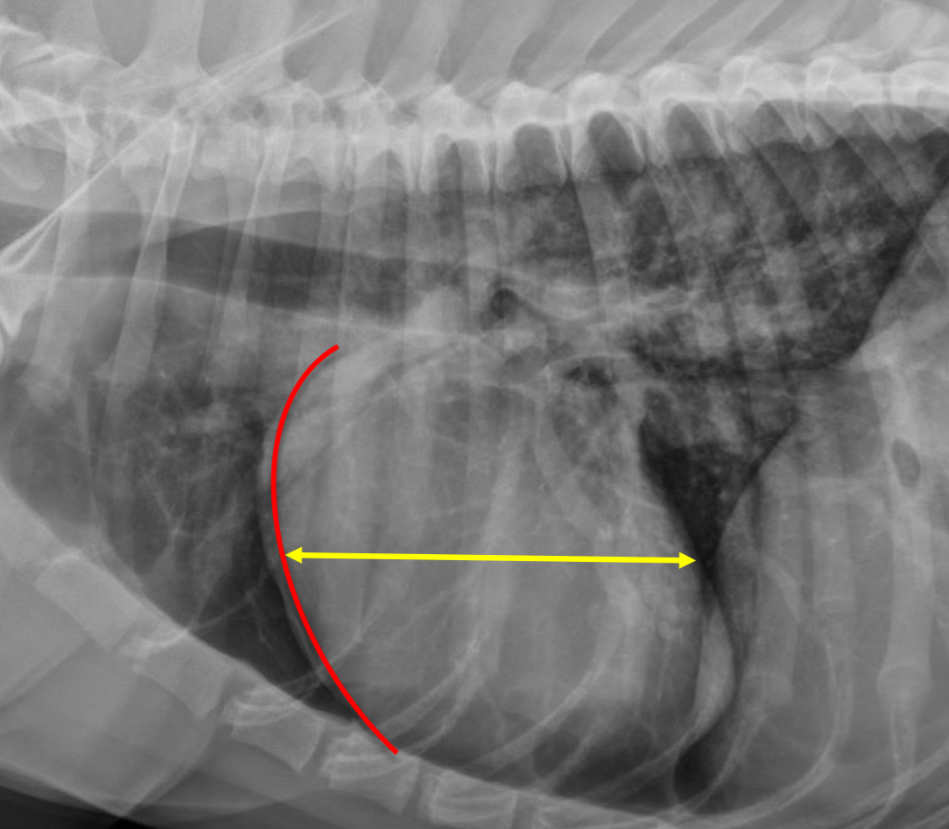
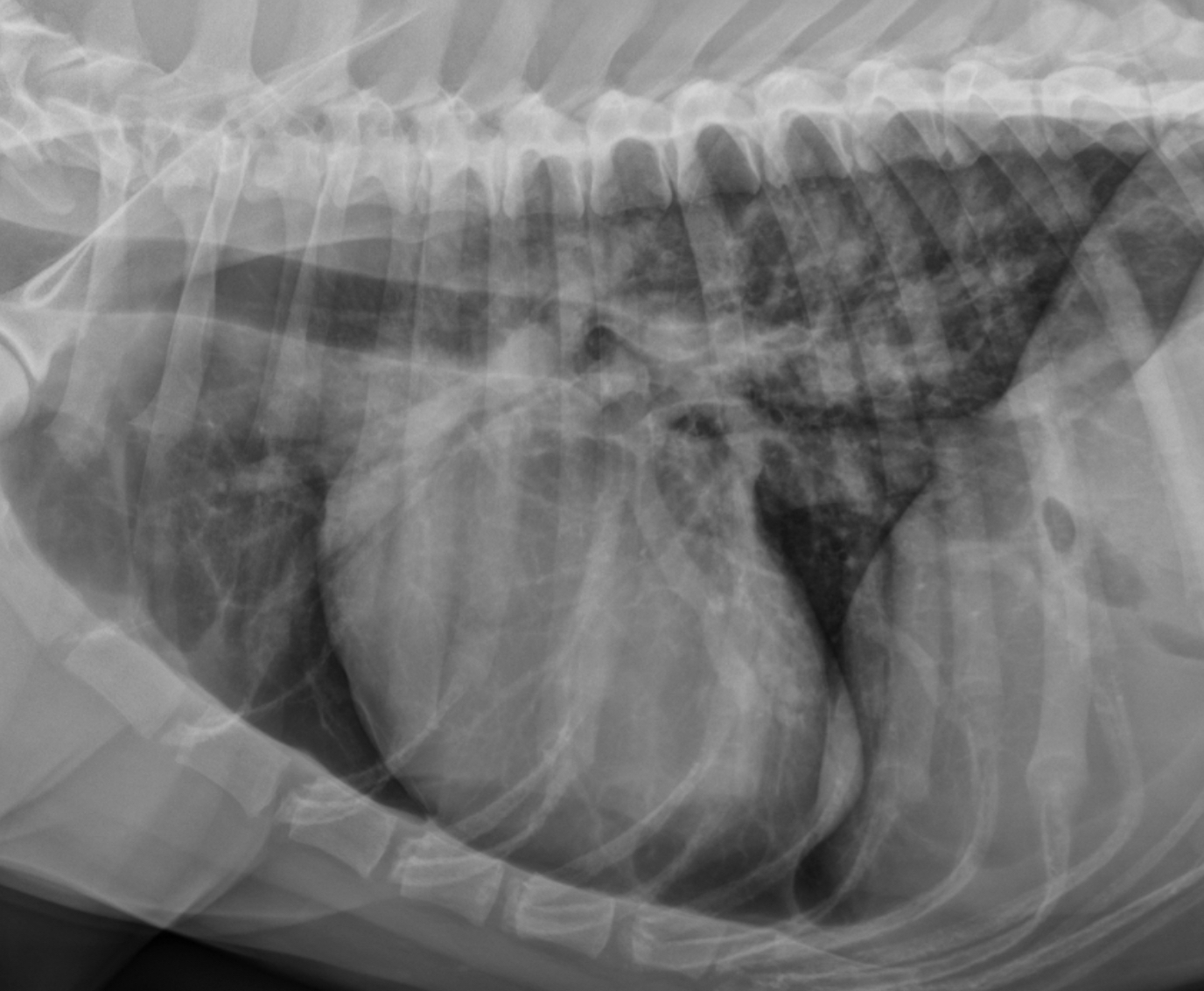
What part of heart is enlarged?
RVE
2 features of RVE on VD
-bulge 5-9 o’clock
-reverse D
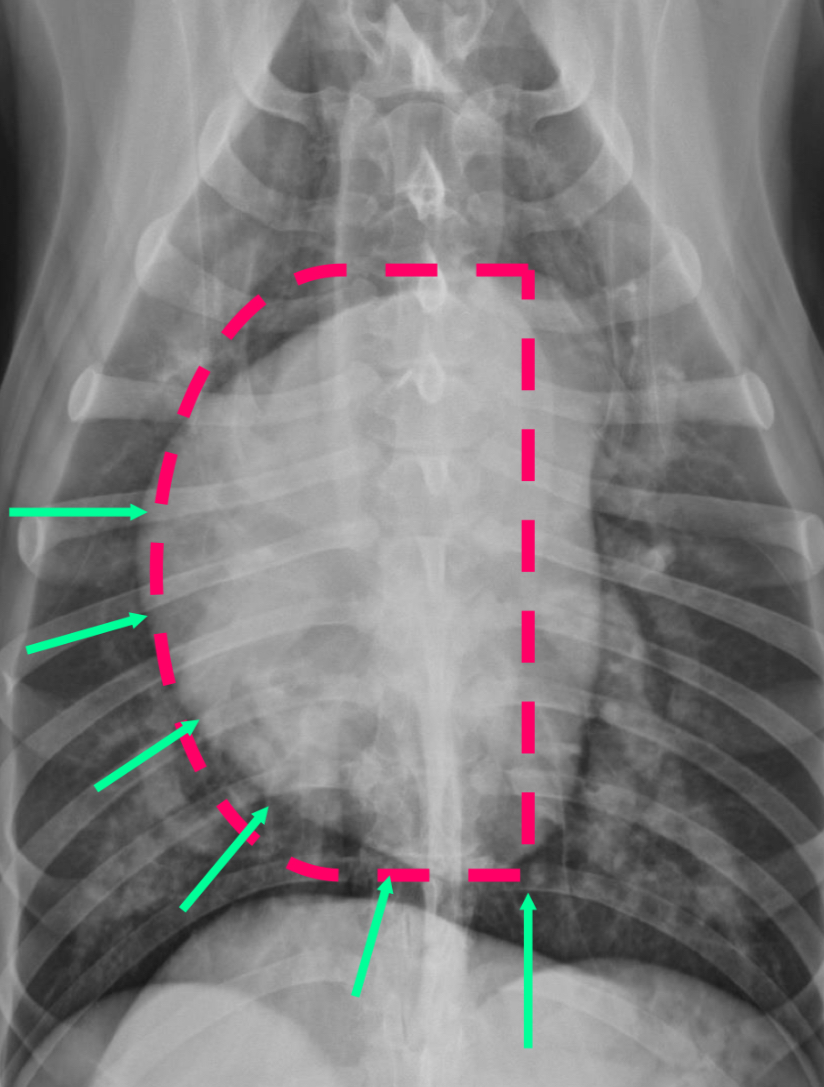
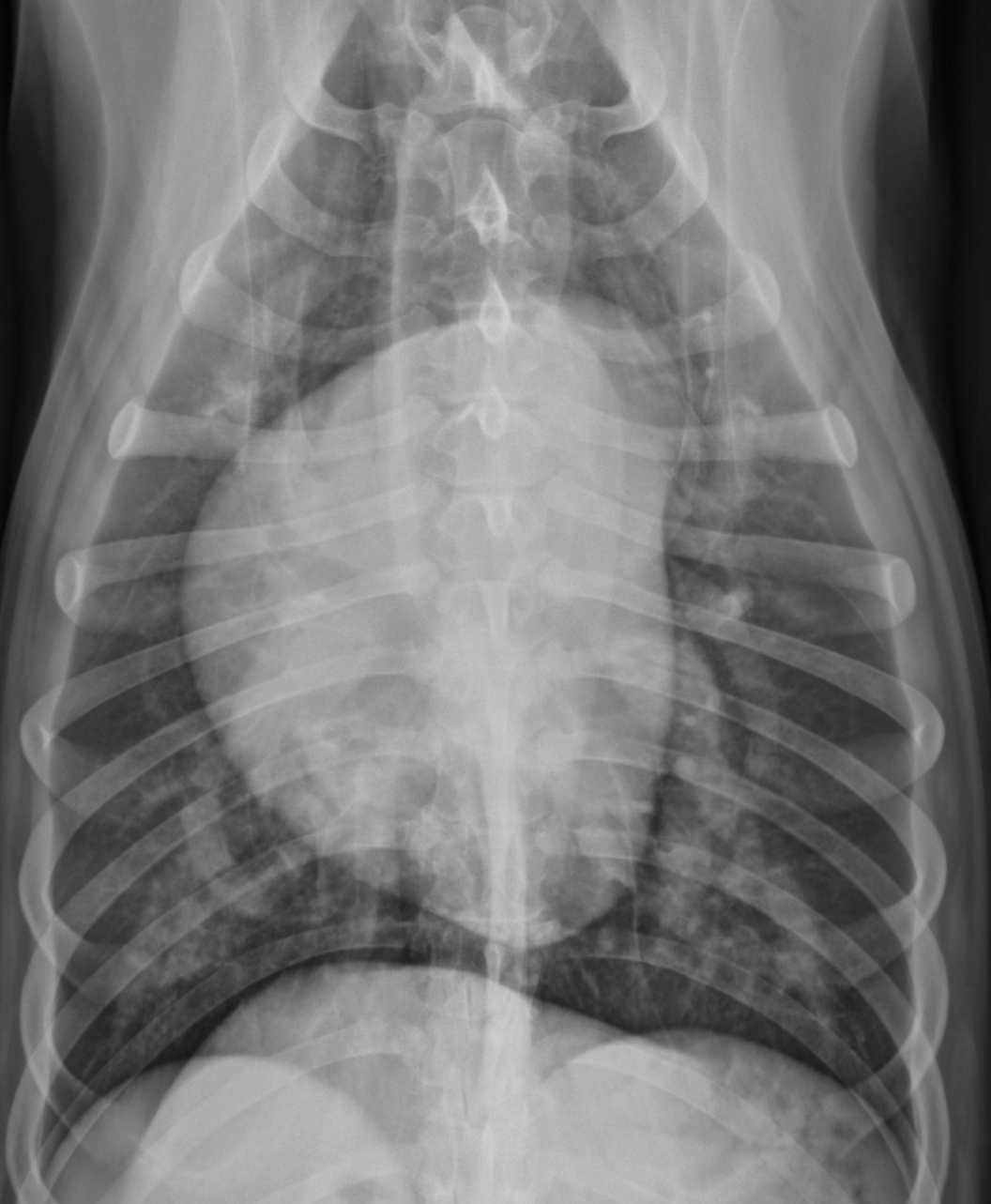
What part of the heart is enlarged
RVE
Features of generalized cardiomegaly in dogs and what disease is associated with this?
-combo roentgen signs involving L and R cardiac chambers
-dogs often get mitral dz which results in both L+R heart enlargement
-tall + wide, sternal contact
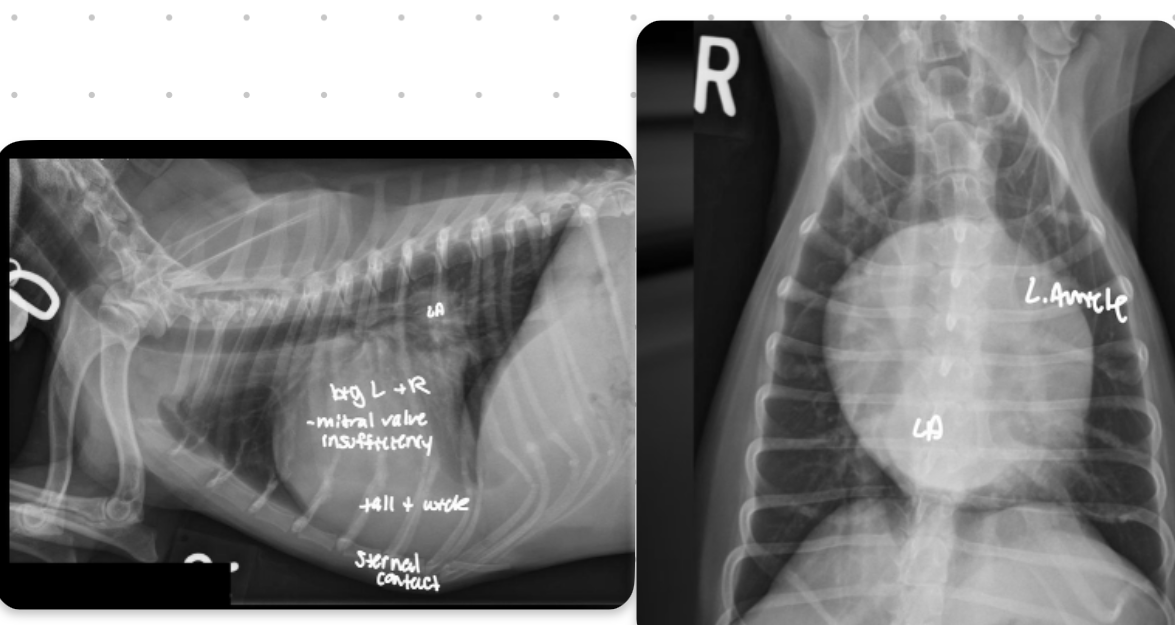
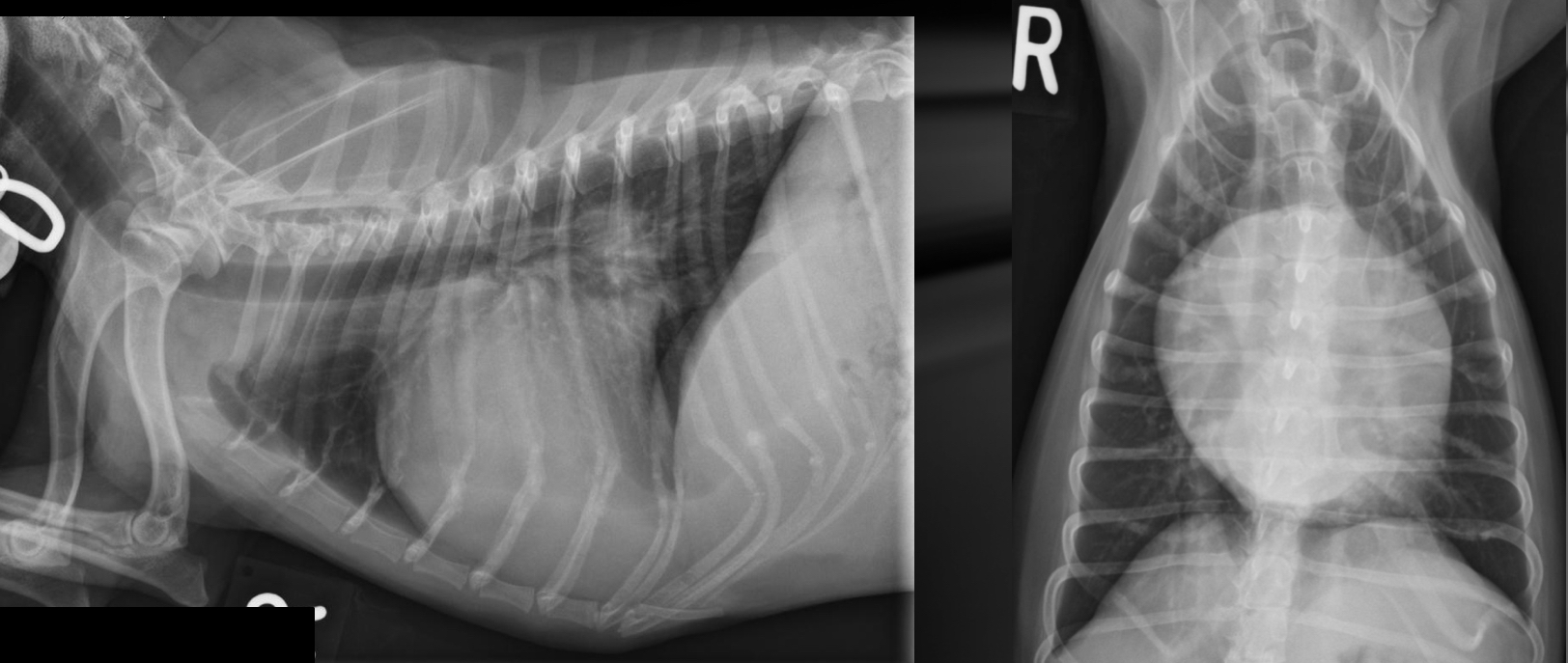
what part of the heart is enlarged in this dog
Generalized (whole thing)
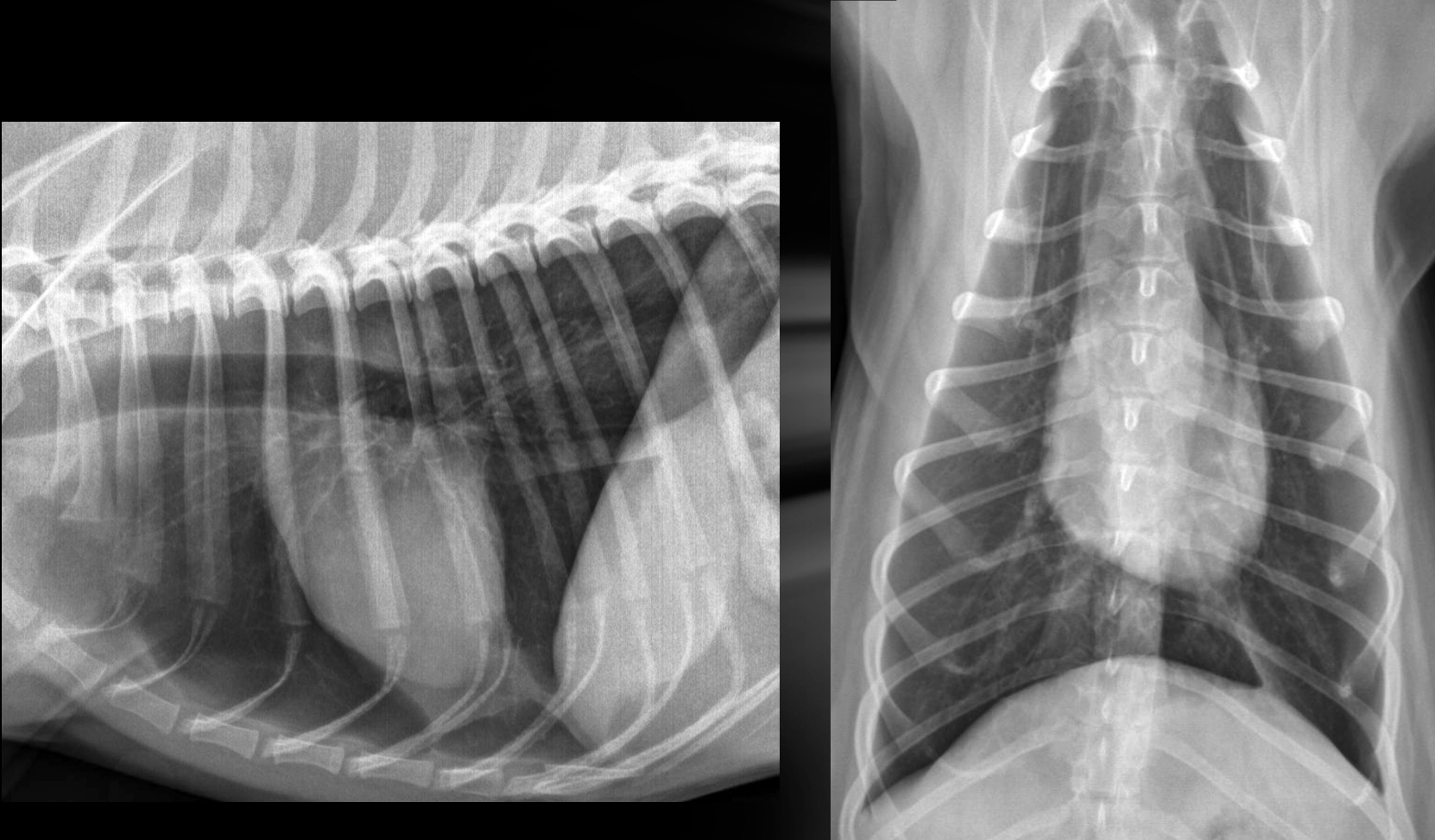
Generalized cardiomegaly in cats features and what disease associated with this
-change in shape = abnormal (hard to tell what chamber affected tho) —> results in valentine shape
-HCM —> big LA and L. Au —> probably baggy left atrium that makes the whole thing look “huge”
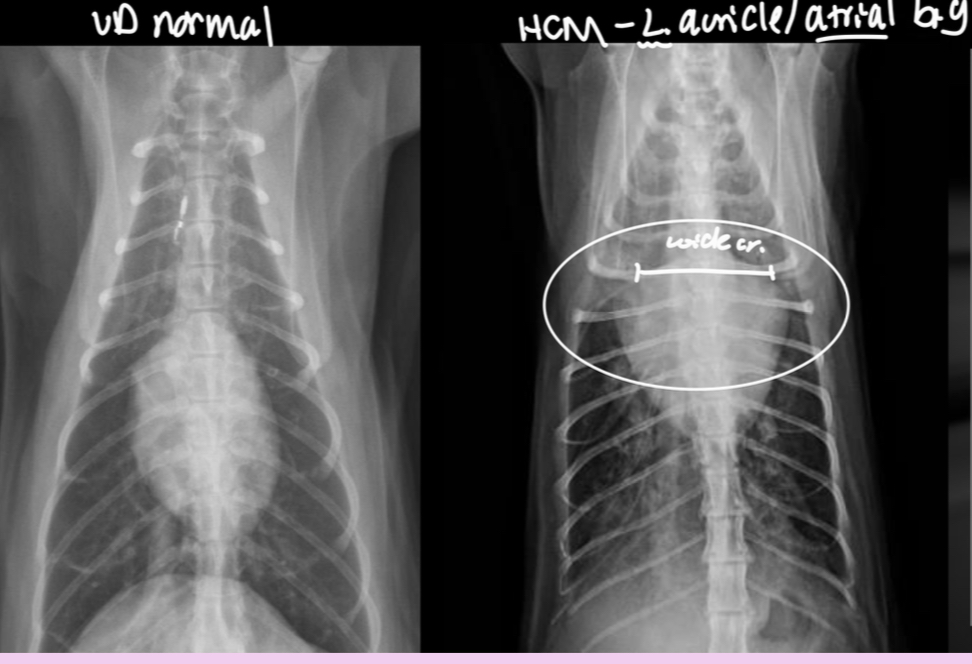
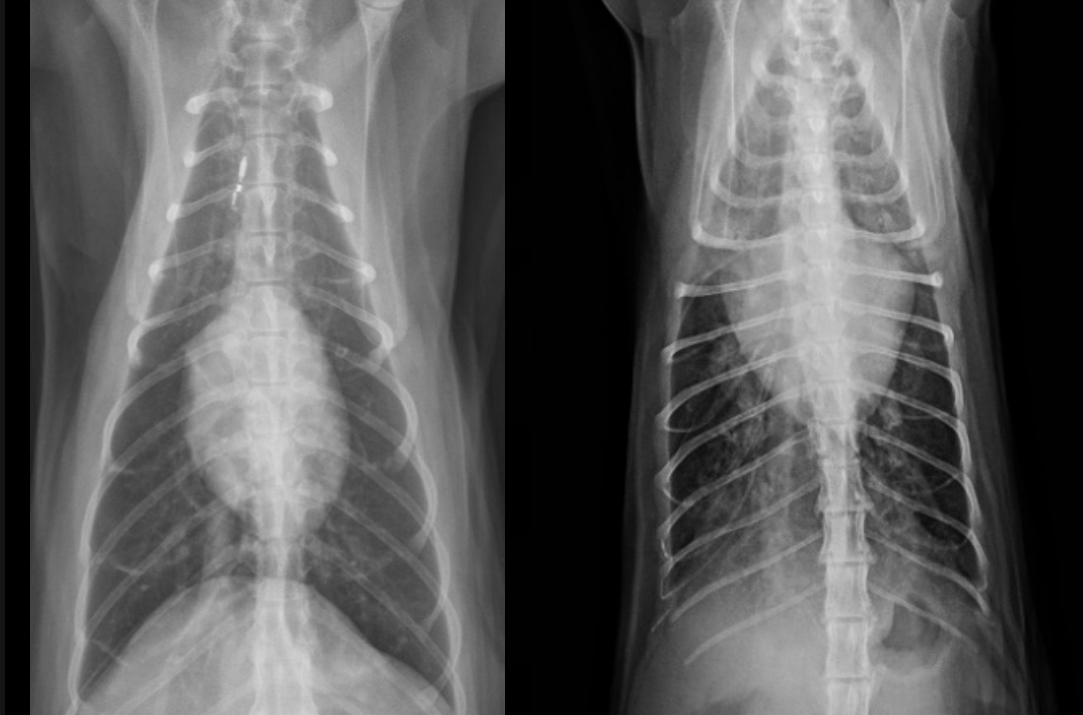
What part of the heart is enlarged in this cat
Generalized (the whole thing)
Microcardia cause
Dehydration, shock, Addisons (electrolyte imbalance)
Microcardia roentgen signs
-small cardiac silhouette (<2 IC in dog, <1.5 IC in cat)
-pulmonary hypoperfusion (small vessels)
-consistently small CdVC
-lung margins visible
-heart elevated off sternum
-still can trace vessels
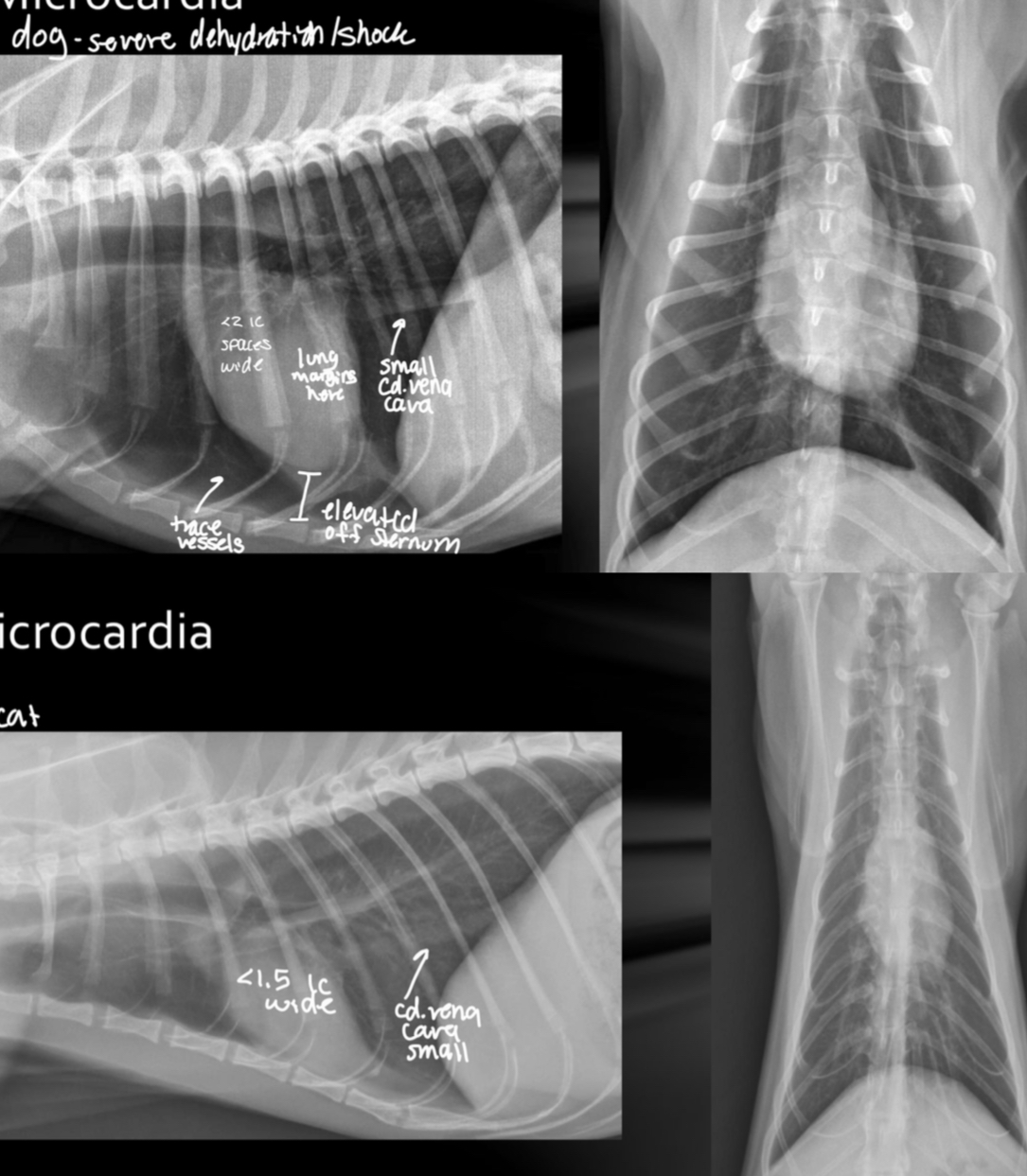
What is going on with this dog heart?
Microcardia
What is going on with this cat heart?
Microcardia
How is heart failure defined radiographically
Rad evidence of inability of heart to adequately handle volume of returning blood
T/F cardiomegaly alone is considered an indicator of heart failure
FALSE, just b/c the heart is big does not mean it can’t handle that blood volume
LHF cannot handle the blood returning from what segment
Pulmonary circulation (lungs)
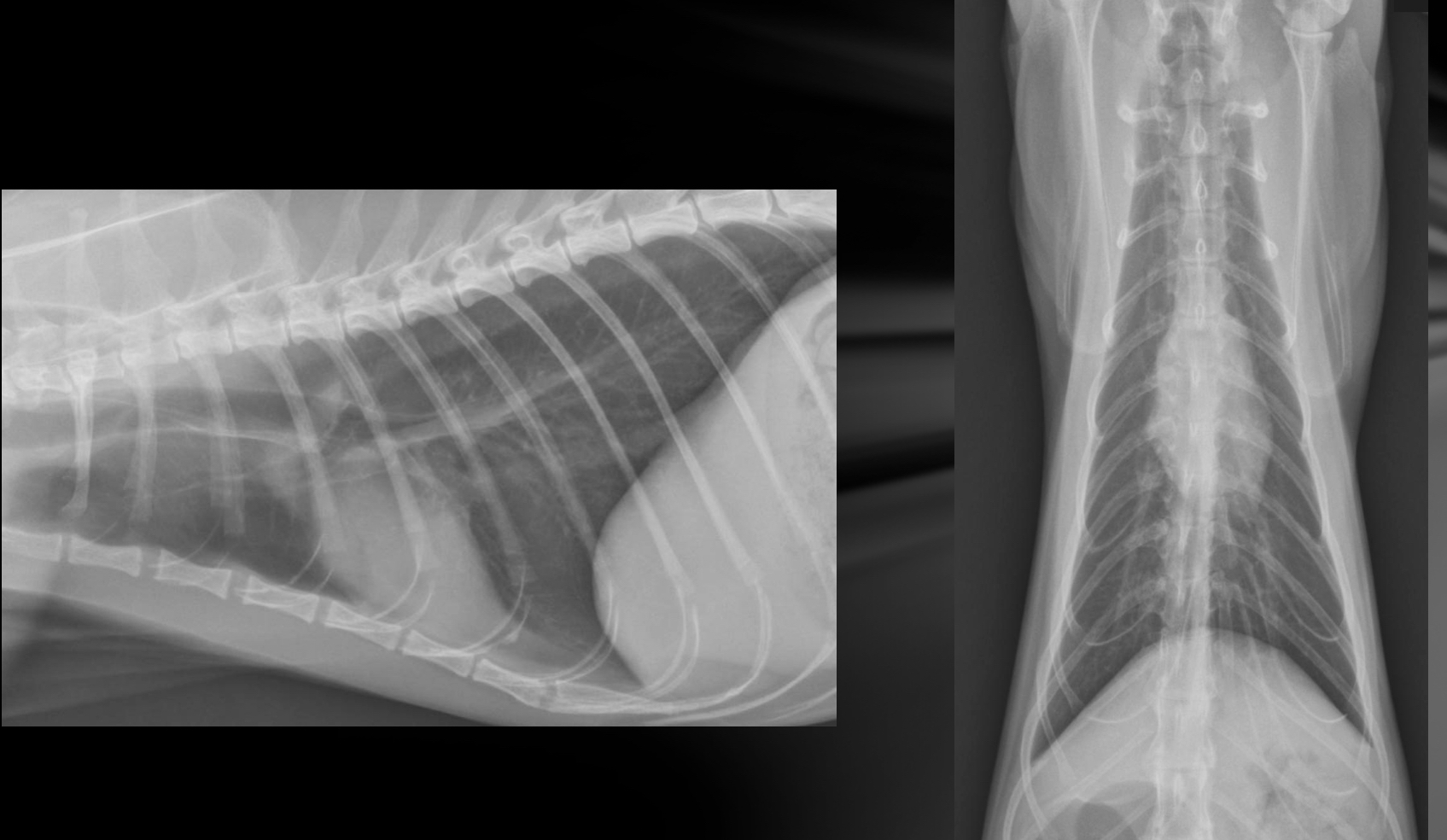
Roentgen signs of LHF Regarding the vasculature
-pulmonary vessel enlargement/congestion
-pulmonary veins > pulmonary arteries
-both arteries and veins are increased in size (esp cats)
Roentgen signs regarding pulmonary edema with LHF
-unstructured interstitial or alveolar infiltrates (perihilar cd.dorsal lung fields)
-multifocal patchy distribution (cats, dobby pinscher, acute tendinae rupture)
-peribronchial cuffing in cats may also cause bronchial pattern
-pleural effusion -cats
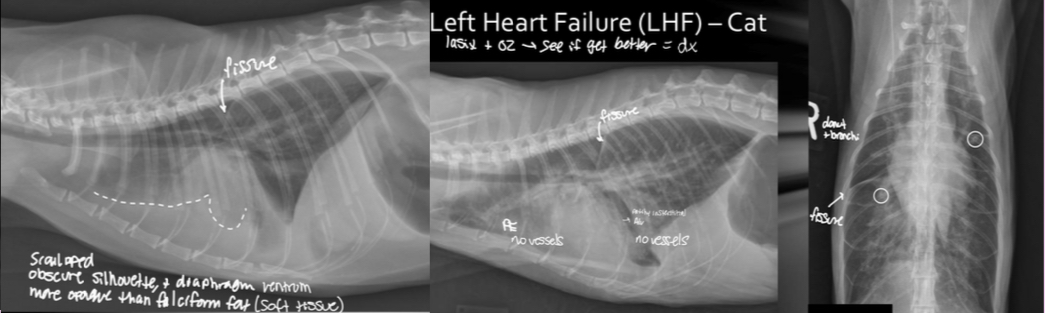
Multifocal patchy lung patterns are often seen in what 3 situations
-cats
-Doberman pinschers
-dogs with acute rupture of chordinae tendinae
What 4 patterns can cats have when LHF and where is it distributed
-unstructured interstitial
-alveolar
-bronchial
-pleural effusion
-distributed everywhere and anywhere
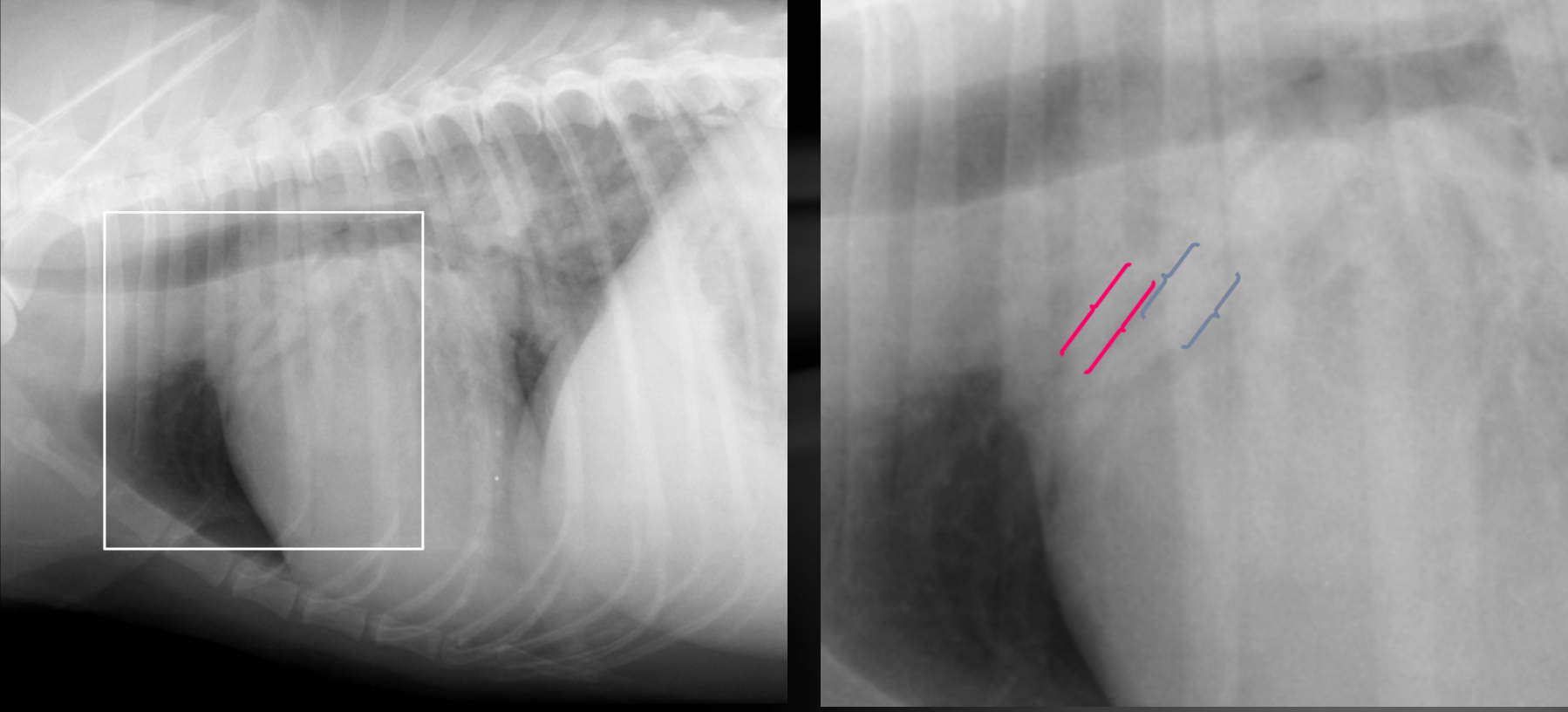
What are the 2 features of pleural effusion that help you differentiate it from other patterns?
-fissures lines with lungs
-no vessels can be traced
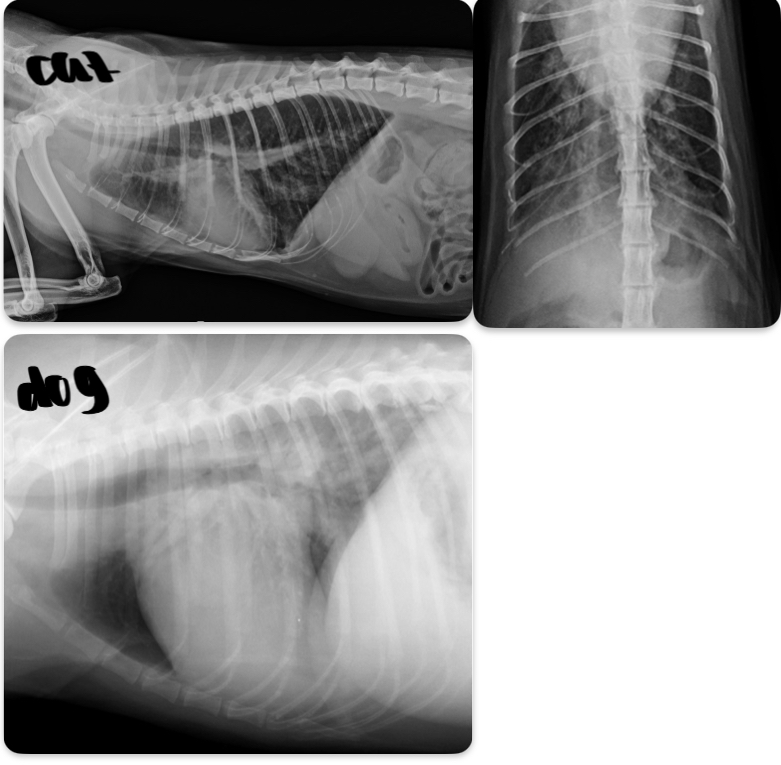
Cat - what sided HF is this
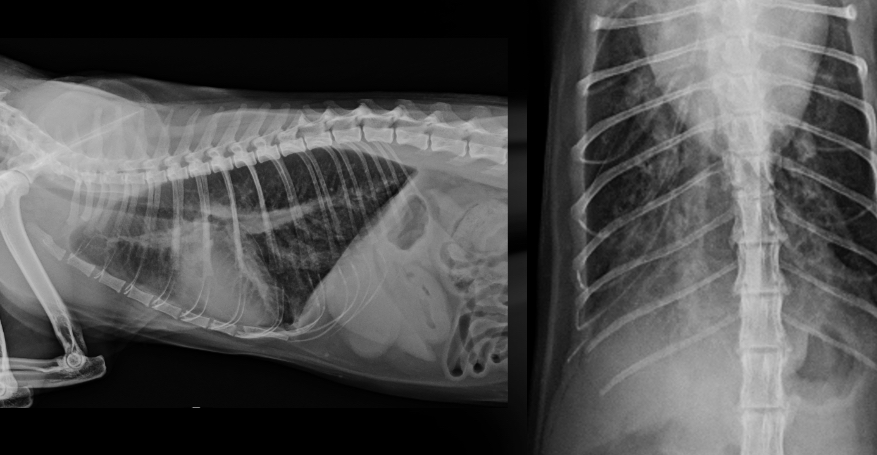
Dog - what sided heart failure is this
LHF
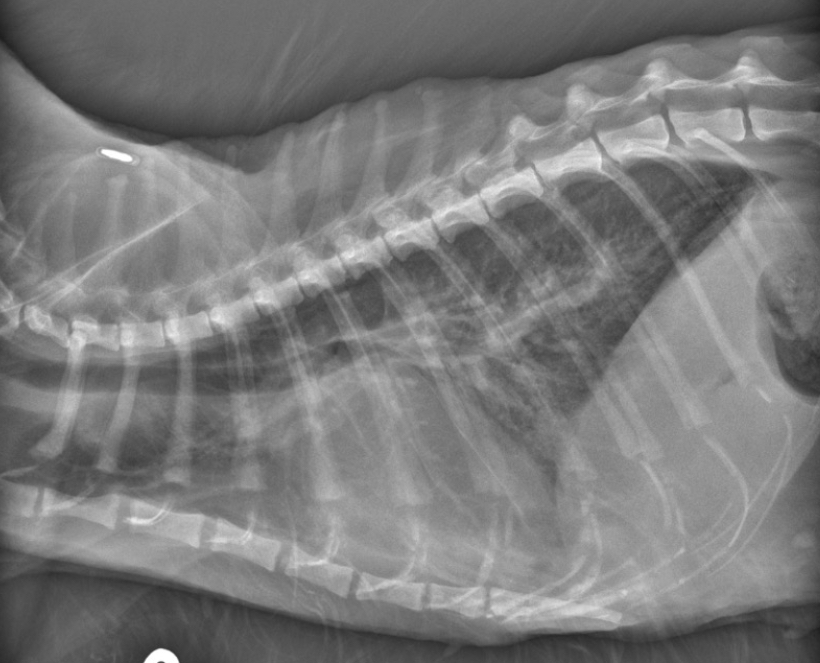
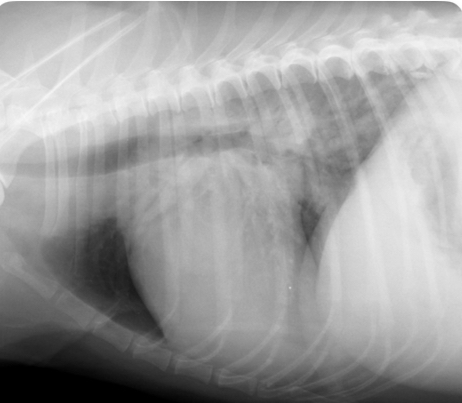
Cat- what sided heart failure
LHF
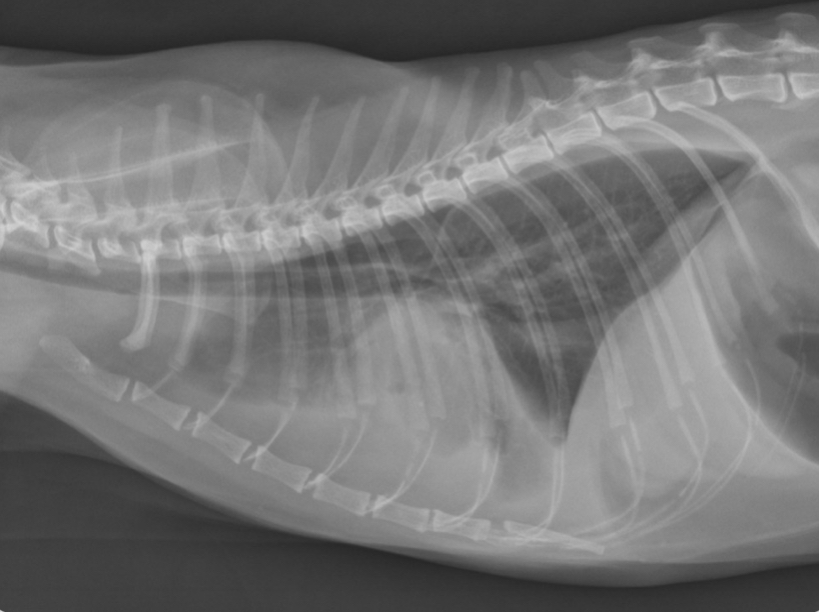
What features of this image screams this cat is in LHF
Pleural effusion
-scalloping and fissure lines present
-vessels are not traceable in cr.ventral thorax
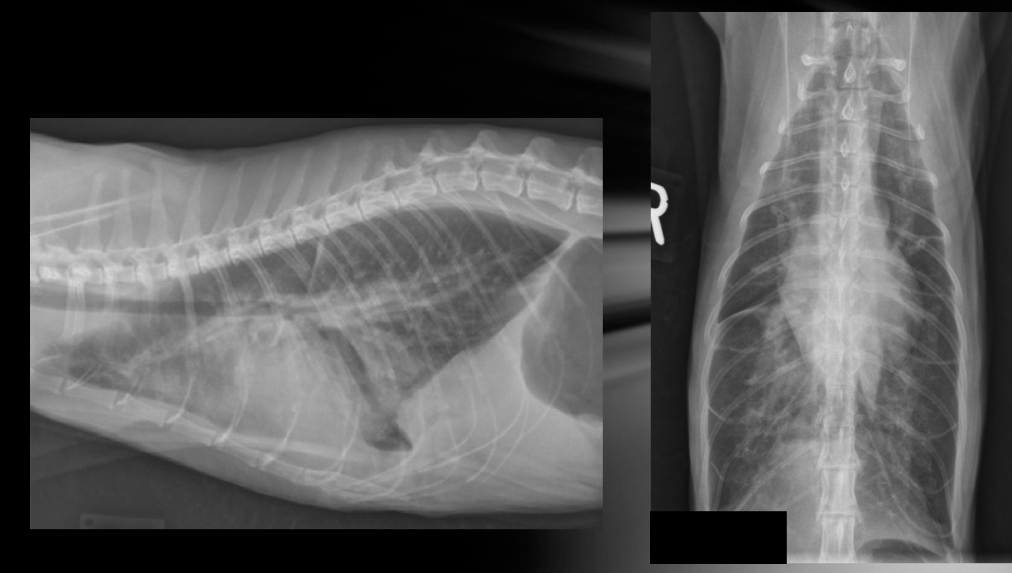
Cat- what kind of heart failure is happening
LHF
RHF cannot handle the blood volume coming from what part of circulation
Systemic circulation
3 Roentgen signs of RHF
-enlarged cd.VC(Venous congestion)
-hepatomegaly (visceral congestion)
-ascites
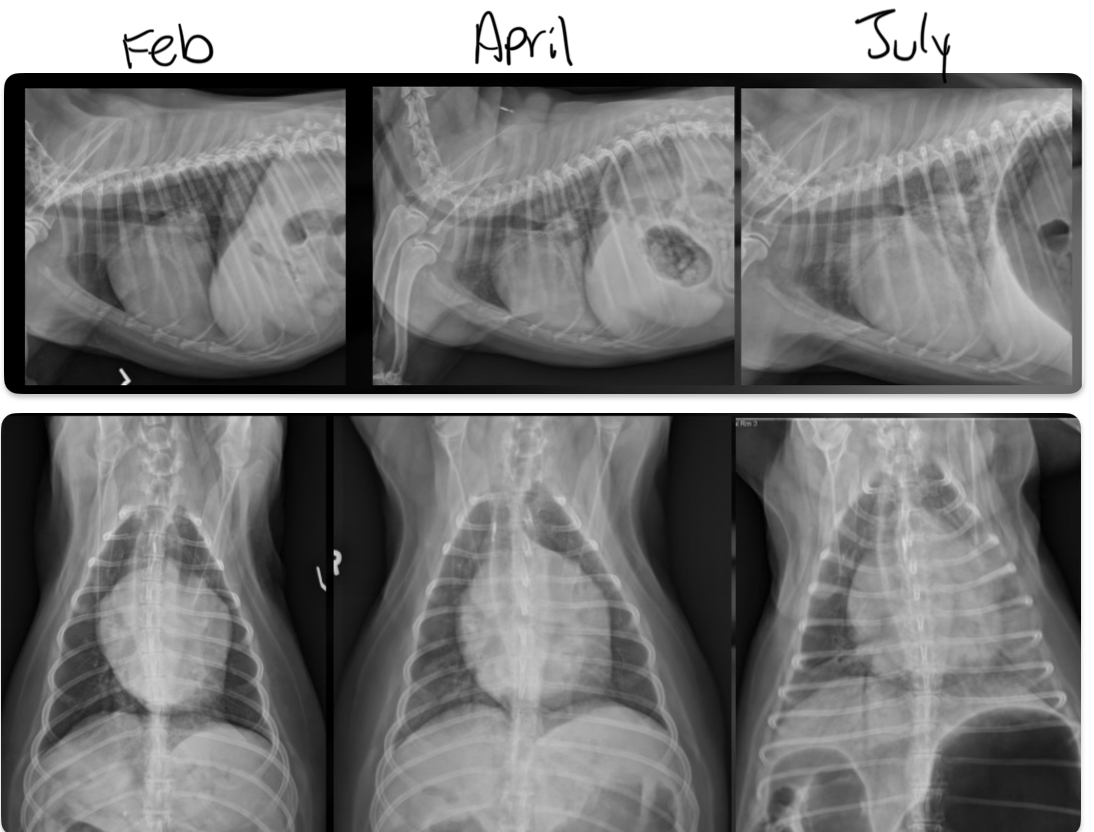
at what point is this dog in heart failure
April - pulmonary vein enlargement and beginning of lung patterns forming
July - alveolar lung patterns, big pulmonary veins
3 congenital heart diseases
-pulmonic stenosis
-Subaortic/aortic stenosis
-PDA
what part of the outflow tract is obstructed in pulmonic stenosis
Right ventricular outflow tract
Pulmonic stenosis happens at what level
-subvalvular or valvular
Valvular is most common
What two breeds inherit pulmonic stenosis
Beagles, keeshonds
Other breeds at risk: English bulldog, mastiff, Samoyed, mini schnauzer, American cocker spaniel, WHWT
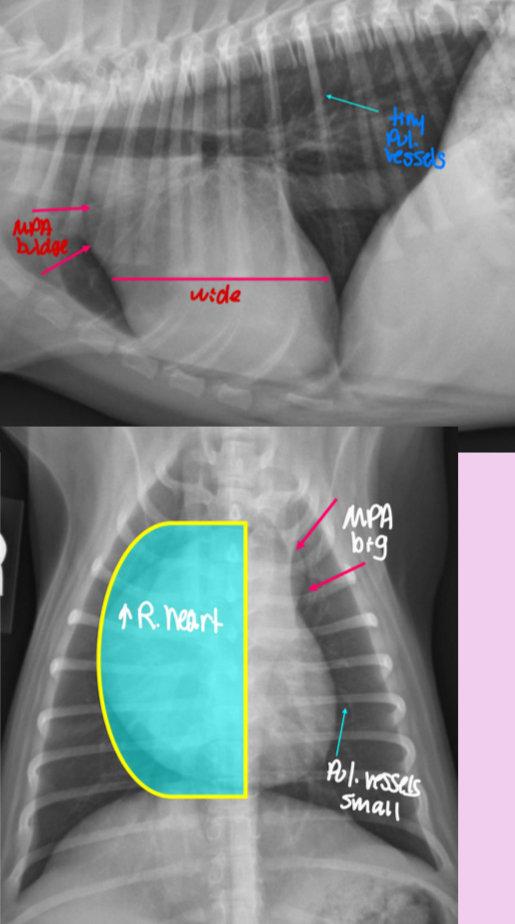
Roentgen signs of pulmonic stenosis
-Right heart enlargement (RVE +/- RAE) d/t PRESSURE OVERLOAD
-MPA enlargement
-Normal to small pulmonary vessels (hypoperfusion)
+/- RHF
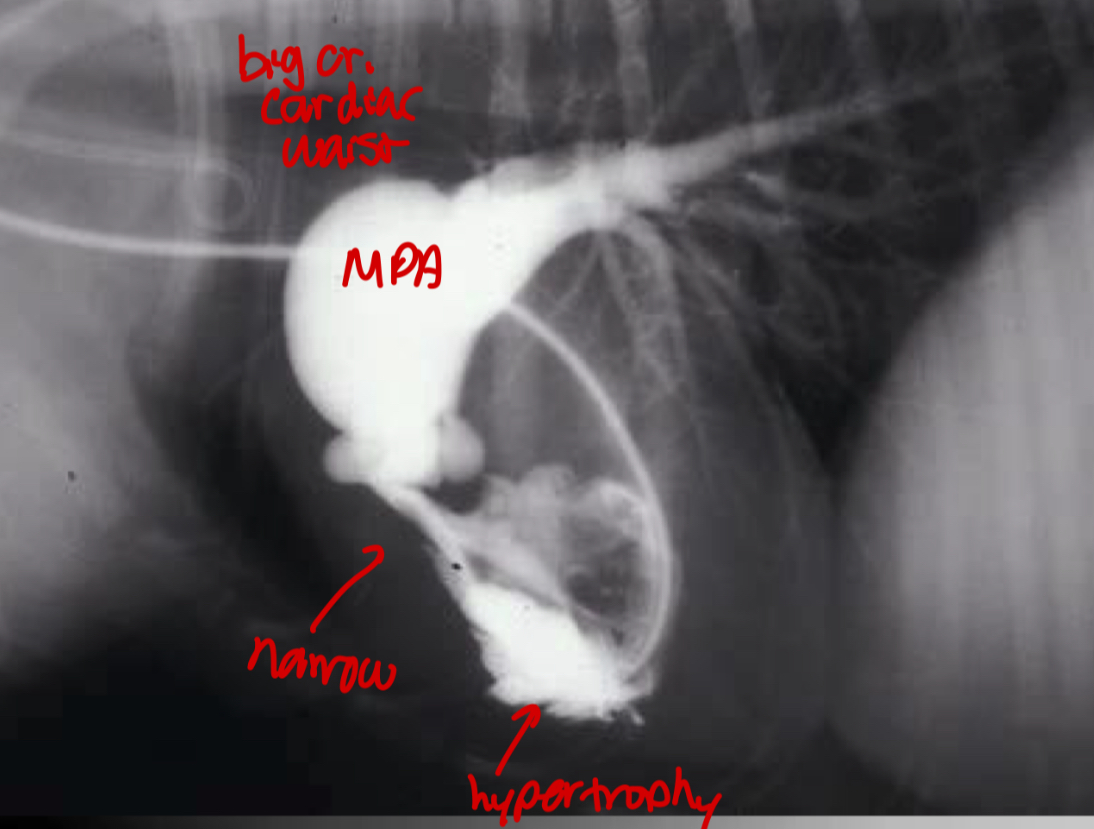
pathogenesis of pulmonic stenosis
1.Narrow pulmonic valve
2.RV hypertrophies to try and muscle the blood through narrow valve
3.dilation of MPA after the stenotic region
What does the angiocardiography highlight in pulmonic stenosis
-RV hypertrophy
-narrowing pulmonary outflow tract
-post-stenotic dilation of MPA segment
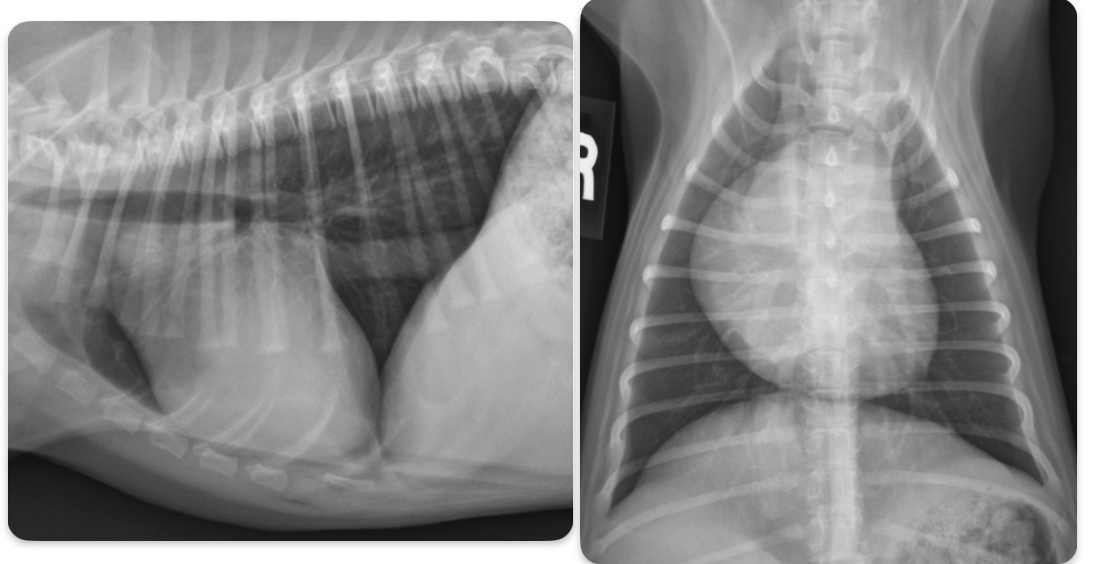
What disease does this dog have
Pulmonic stenosis
What part of the outflow tract is obstructed in aortic stenosis
Left ventricular outflow tract
Aortic stenosis happens at what level
-subvalvular/valvular
Subvalvular (subaortic stenosis)
What breed is aortic stenosis heritable in
Newfoundland dogs
Other breeds: Rottweilers, boxers, golden, GSD (large breeds)
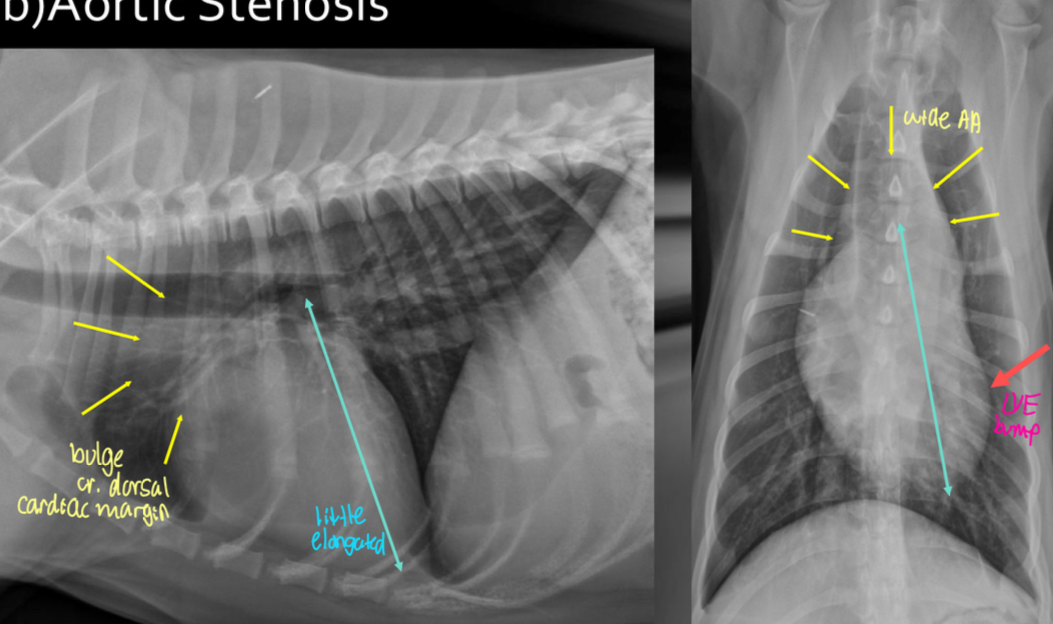
Roentgen signs of aortic stenosis
-survey rads could be NORMAL
-LH enlargement (LVE ± LAE) from PRESSURE OVERLOAD
-elongated cardiac silhouette
-AA bump
-low incidence of LHF
What ends up killing the dogs with aortic stenosis
Sudden death due to ventricular arrhythmias and impaired coronary arteries
Pathogenesis of aortic stenosis
1.subaortic abnormality
2.left ventricular hypertrophy
3.focal dilation of AA
What does the angiocardiography highlight in aortic stenosis
-AA bulge
-increased cardiac waist
-left ventricular hypertrophy
-narrowing of aortic outflow tract
-post stenotic dilation of AA
± mitral regurg
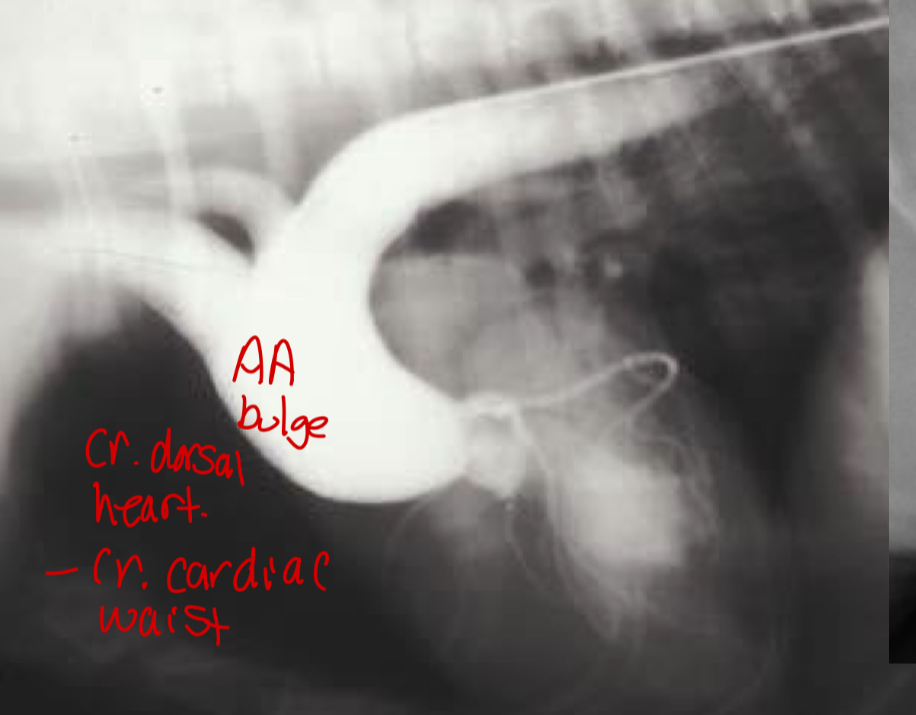
What disease does this dog have
Aortic stenosis
What fails to happen at birth in PDA dogs
Failure of ductus arteriosus to close after birth —> persistent shunt between aorta and MPA
Which direction is the PDA shunt
Left to right (can flip later in disease but don’t worry about that)
Roentgen signs of PDA
-BIG LVE, VOLUME OVERLOAD
-triple bump sign on VD (Prox desc. Aorta, MPA, L.Au)
-normal to large pulmonary vessels (hyperperfusion)
±LHF
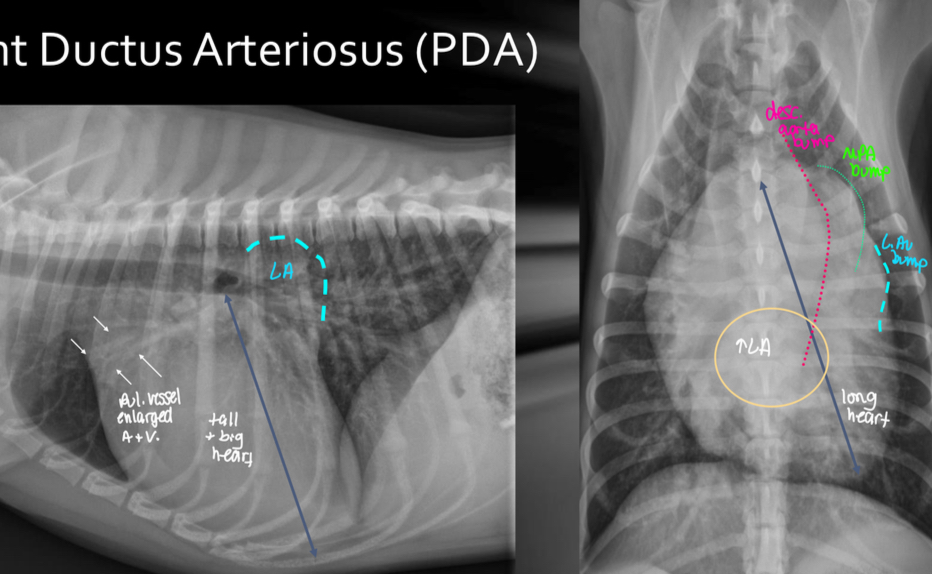
Pathogenesis of PDA
1.shunt connection between aorta and pul artery
2.high pressure blood from aorta to pul artery —> dilate pul artery
3.hyperperfused lungs
4.dumps blood into left heart
5.big LA and LV
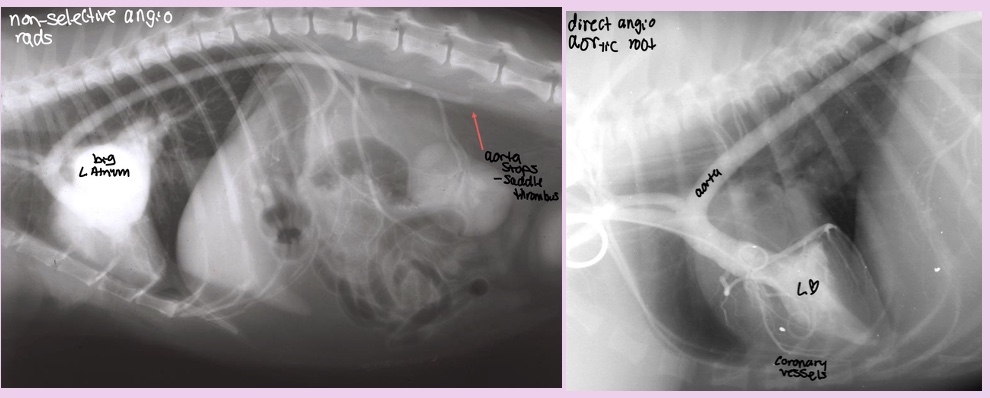
What does the angiocardiography highlight in PDA
-see the shunt
-left ventricular dilation
-opacification of aortic and pulmonary arteries
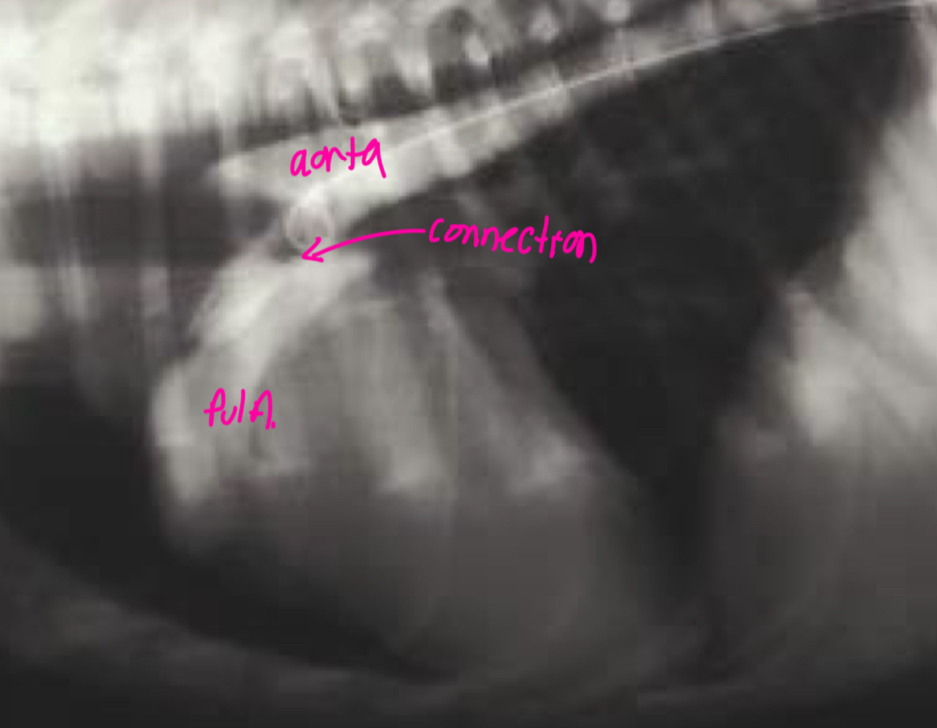
What disease does this dog have
PDA
5 acquired heart diseases
-heartworm
-canine CM
-feline CM
-endocardiosis
-cardiac neoplasia
Roentgen signs of heartworm disease
-RVE, RAE
-big MPA
-big pruned, tortuous pulmonary arteries (big sign in cats)
-pulmonary infiltrates with eosinophilia aka eosinophilia bronchopneumopathy
-mixed pulmonary patterns (unstructured interstitial bronchial, ± alveolar
-evidence of pulmonary thromboembolism (worm in outflow tract)
± RHF
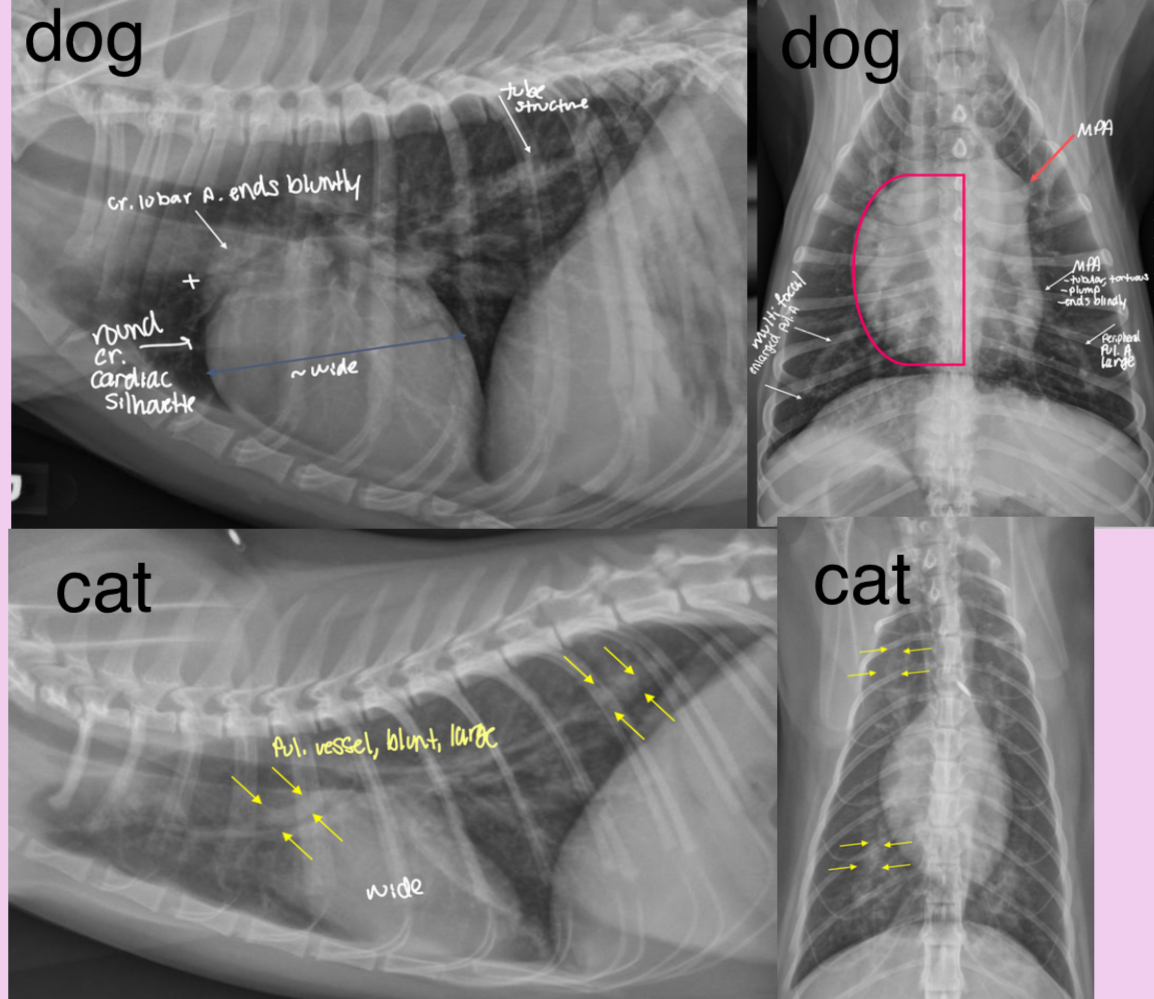
What disease does this dog have
heartworm disease
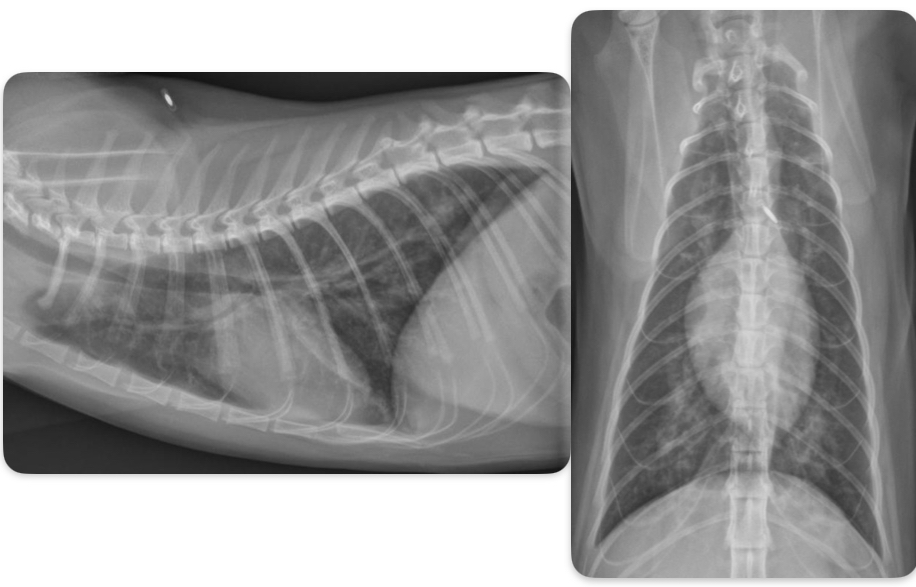
What disease does this cat have
Heartworm disease
What type of CM do dogs most commonly get
DCM - ventricular volume overload —> eccentric hypertrophy
What breeds predisposed to DCM
Doberman, boxer, Great Dane, Labrador retriever (large breed dogs)
Roentgen signs of DCM
-Generalized cardiomegaly
± LHF > RHF or biventricular heart failure
-unstructured interstitial to alveolar in cd.dorsal