Openstax Biology 2E Chapter 4
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/96
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
1
New cards
A Cell is
the smallest unit of a living thing.
2
New cards
What is the order of structure from cell to organism?
\-Cells connect and form tissue
\-Tissue connects to form organs
\-Organs connect to form organ systems
\-Organ systems connect to form organisms
\-Tissue connects to form organs
\-Organs connect to form organ systems
\-Organ systems connect to form organisms
3
New cards
Prokaryotic Cell Components
1. No nucleus or other membrane-bound organelle
2. Nucleoid region
3. Cell wall made of peptidoglycan used to maintain shape and prevent dehydration
4. Capsule made of polysaccharide
5. Flagella used for locomotion
6. Pili used to exchange genetic information during conjugation (genetic transfer through direct contact)
7. Fimbriae used to attach to host cell
8. Ribosome used for protein synthesis
9. Chromosomes (DNA)
10. Size .1-5.0 μm
4
New cards
Eukaryotic Cell Components
1. Size 10 - 100 μm
5
New cards
A microscope is
an instrument that magnifies an object
6
New cards
What is a micrograph?
An photo taken using a microscope
7
New cards
Magnification is
the process of enlarging an object in apperance
8
New cards
Resolving power is
the microscopes ability to distinguish two adjacent objects
9
New cards
Unified Cell Theory
1. One or more cells comprise all living things
2. the cell is the basic unit of life
3. New cells arise from existing cells
10
New cards
Organelle
“little organ”
11
New cards
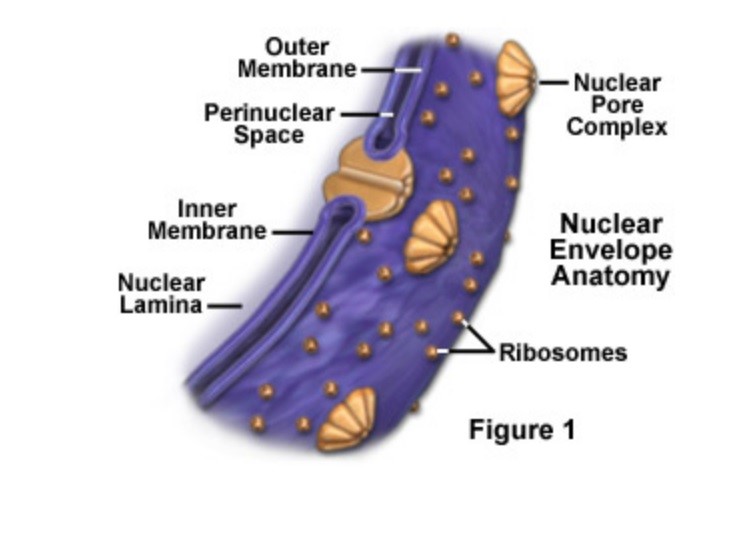
Nuclear Envelope
membrane enclosing the nucleus. Protein lines pores allow material to move in and out. Ch
12
New cards
Chromatin
DNA plus associated proteinsNu
13
New cards
Nucleolus
condensed region where ribosomes are formed
14
New cards
Peroxisomes
metabolizes wastecyt
15
New cards
cytoskeleton microtubules
form the mitotic spindle and maintain cell shape
16
New cards
centrosome
microtubule organizing centerinter
17
New cards
intermediate filaments
fibrous proteins that hold organelles in place
18
New cards
microfilaments
fibrous proteins that form the cellular cortex
19
New cards
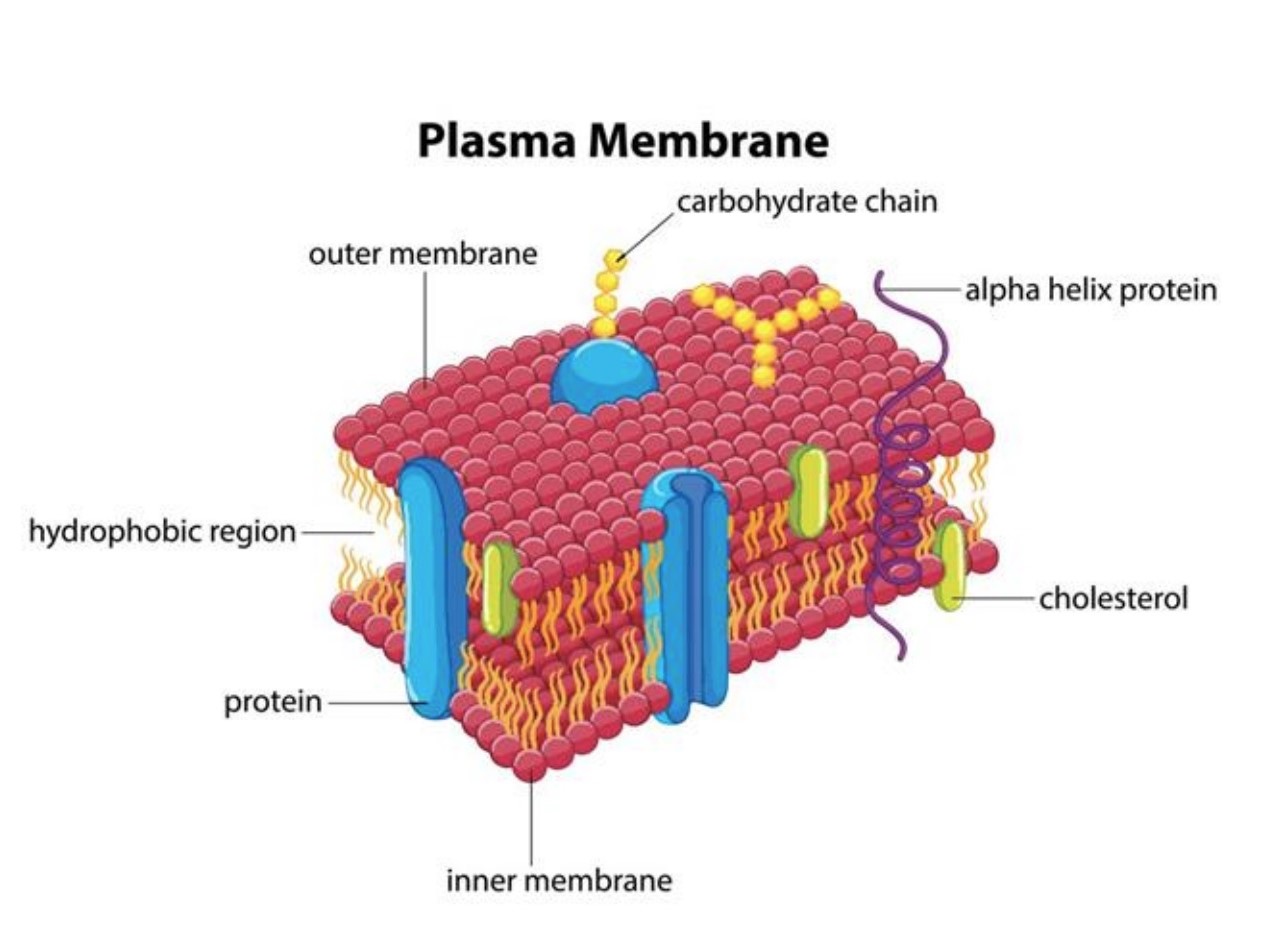
plasma membrane
Phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that separates the internal contents of the cell from its surrounding environment
20
New cards
What is the role of the Lysosome?
* digests food and waste materials
* destroy pathogens using hydrolytic enzymes
* destroy pathogens using hydrolytic enzymes
21
New cards
What is a macrophage?
A group of white blood cells that are part of the body’s immune system.
22
New cards
cytoplasm
23
New cards
mitochondria
produce energy
24
New cards
vacuole
25
New cards
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
associated with ribosomes; makes secretory and membrane proteins
26
New cards
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
27
New cards
Nucleus
Contains chromatin, a nuclear envelope, and a nucleus
28
New cards
Plasmodesmata (plants)
Channels that connect two plant cells
29
New cards
Central Vacuole (plants)
filled with cell sap that maintains pressure against cell wall
30
New cards
Cell Wall (plants)
* Rigid covering that protects the cell, provides structural support and maintains cell shape
* Primary component is cellulose.
* Primary component is cellulose.
31
New cards
Plastid (plants)
Stores pigments
32
New cards
Chloroplast (plants)
site of photosynthesis
33
New cards
Phospholipid
lipid molecule with two fatty acid chains and a phosphate-containing groupGl
34
New cards
Glycolipid
Lipid with carbohydrate attached
35
New cards
Glycoprotein
Protein with a carbohydrate attached
36
New cards
What does the plasma membrane control?
The passage of organic molecules, ions, water and oxygen in and out of the cell, as well as the exit of wastes such as carbon dioxide and ammonia.
37
New cards
Microvilli
projections of the plasma membrane that increase the surface area available for absorption
38
New cards
Cytoplasm
The cell’s region between the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope. 70-80% water, semi-solid consistency,
39
New cards
cytosol
40
New cards
Nucleus
Houses the host cells DNA and directs synethesis of ribosomes and proteins.
41
New cards
Nuclear Envelope
Double membrane structure that constitutes the nucleus’ outermost portion, both the inner and outer membranes are phospholipid bilayers
42
New cards
Nucleoplasm
Semi-solid fluid inside the nucleus
43
New cards
Chromosomes
Structures within the nucleus made up of DNA. Every eukaryotic species has a specific number of chromosomes in the nucleus of each cell.
\
\
44
New cards
Chromatin
The unwound protein-chromosome complexes that makes up chromosomes when condensed and desondensed.
45
New cards
Nucleolus
Aggregates ribosomal RNA with associated proteins to assemble ribosomal subunits.
46
New cards
Ribosomes
* Responsible for protein synthesis.
* Consist of two subunits; large and small
* Attach to: Plasma membranes cytoplasmic side, ER’s cytoplasmic side, nuclear envelope outer membrane.
* Freely float as single units or polyribosomes
* Consist of two subunits; large and small
* Attach to: Plasma membranes cytoplasmic side, ER’s cytoplasmic side, nuclear envelope outer membrane.
* Freely float as single units or polyribosomes
47
New cards
Polyribosomes
clusters of ribosomes
48
New cards
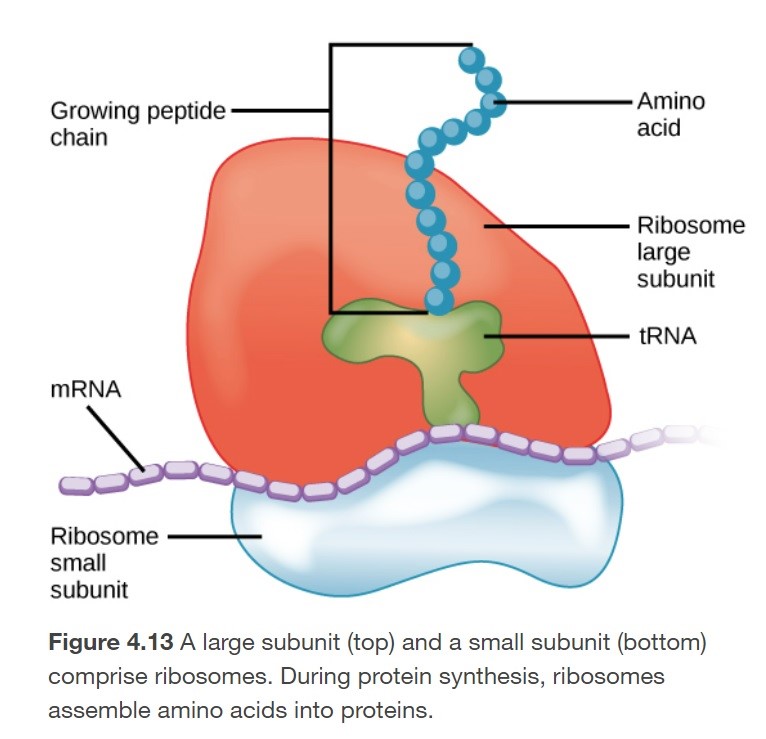
How do ribosomes receive their orders?
1. DNA within the nucleus transcribes into messenger RNA (m-RNA)
2. m-RNA travels to ribosomes which translate the code
3. Ribosomes then assemble amino acids into proteins during protein synthesis
49
New cards
Where are ribosomes particularly abundant?
Cells that synthesize large amounts of protein
* Pancreas - digestive enzymes
* \
* Pancreas - digestive enzymes
* \
50
New cards
Mitochondria
* Responsible for making adenosine triphosphate, the cells main energy carrying molecule
* Oval shaped, double membrane organelles
* Contain separate DNA and ribosomes
* Each membrane is a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins.
* Inner folds called cristae which increase surface area
* Area inside cristae is the matrix
\
* Oval shaped, double membrane organelles
* Contain separate DNA and ribosomes
* Each membrane is a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins.
* Inner folds called cristae which increase surface area
* Area inside cristae is the matrix
\
51
New cards
What is ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)?
The cells main energy carrying molecule. ATP represents the cell’s short term stored energy.
52
New cards
What is cellular respiration?
* The process of making ATP using the chemical energy in glucose and other nutrients.
* Uses oxygen and produces carbon dioxide as a waste product.
* Uses oxygen and produces carbon dioxide as a waste product.
53
New cards
Which cells have a high concentration of mitochondria?
Muscle cells, because muscles require a lot of energy.
54
New cards
What happens when cells don’t get enough oxygen?
They do not produce much ATP, and instead produce lactic acid in the absence of oxygen.
55
New cards
Peroxisomes
* Small round organelles enclosed by single membranes
* Responsible for breaking down fatty acids and amino acids using oxidation reactions
* Detoxify poisons
* Releases hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), but contains enzymes that safely break down H2O2.
* \
* Responsible for breaking down fatty acids and amino acids using oxidation reactions
* Detoxify poisons
* Releases hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), but contains enzymes that safely break down H2O2.
* \
56
New cards
Glyoxysomes
Specialized peroxisomes in plants that convert stored fats into sugars
57
New cards
Vesicles
* Membrane-bound sacs that function in storage and transport
* Does fuse with the membranes of other cellular components
* \
* Does fuse with the membranes of other cellular components
* \
58
New cards
Vacuole
* Membrane-bound sacs that function in storage and transport
* Does not fuse with the membranes of other cellular components
* Does not fuse with the membranes of other cellular components
59
New cards
Centrosome
* The organelle where all microtubules originate
* Microtubule organizing center (MTOC) found near the nuclei of animal cells.
* Contains a pair of centrioles (perpendicular to each other)
* Each centriole is a cylinder of nine triplets of microtubules held together by nontubulin
* Microtubule organizing center (MTOC) found near the nuclei of animal cells.
* Contains a pair of centrioles (perpendicular to each other)
* Each centriole is a cylinder of nine triplets of microtubules held together by nontubulin
60
New cards
Lysosomes
* The cells “garbage disposal”, using enzymes to break down proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids, and worn-out organelles.
* Very acidic 4.5-5pH
* \
* Very acidic 4.5-5pH
* \
61
New cards
What is peptidoglycan?
Primary component of prokaryote cell walls.
62
New cards
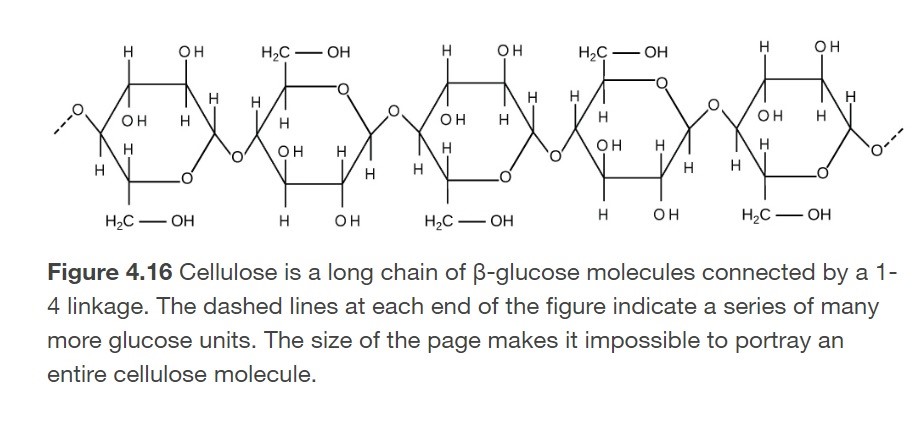
What is cellulose?
A polysaccharide comprised of glucose units.
63
New cards
What is photosynthesis?
A series of reactions that use carbon dioxide, water, and light energy to make glucose and oxygen.
64
New cards
What is an autotroph?
An organism capable of making its own food.
65
New cards
What is a heterotroph?
An organism that must ingest their food.
66
New cards
What is a chloroplast comprised of?
1. Outer membrane
2. Intermembrane space
3. Inner membrane
4. Stroma
5. Granum
6. Thylakoid
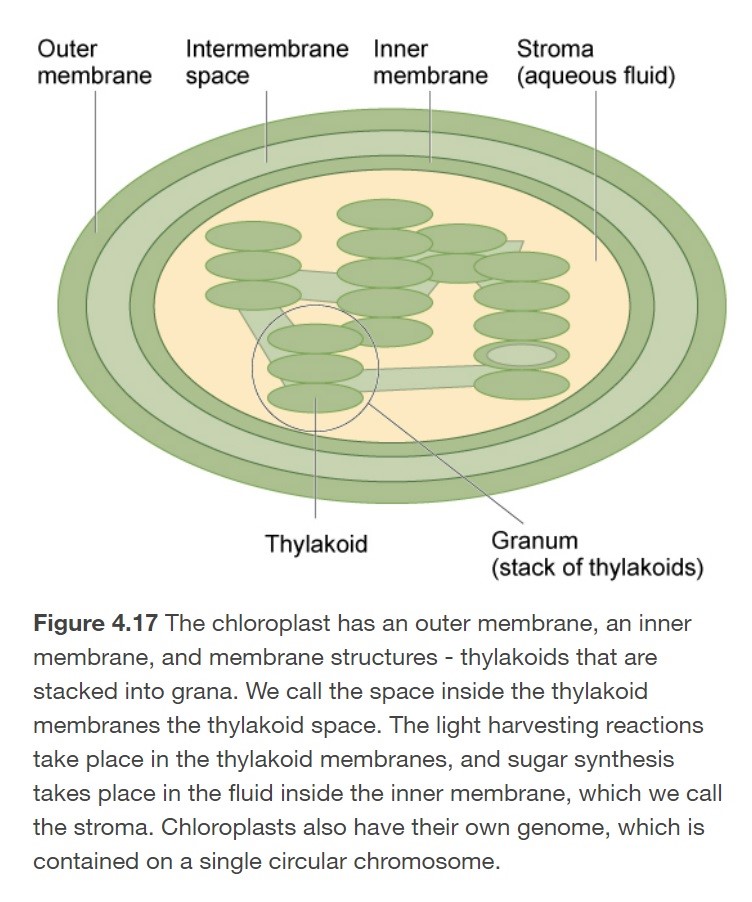
67
New cards
What is a chloroplast responsible for?
Conducting photosynthesis to create the sugars used in cellular respiration to provide ATP energy generated in the plant mitochondria.
68
New cards
What is chlorophyll?
Green pigment that captures light energy that drives the reactions of photosynthesis.
69
New cards
What is endosymbiosis?
A mutually beneficial relationship in which one organism lives inside another.
Example: Microbes in the human gut that produce vitamin K.
Example: Microbes in the human gut that produce vitamin K.
70
New cards
What is symbiosis?
A relationship in which two separate species depend on each other for survival.
71
New cards
What does the Central Vacuole do?
Regulates the cells concentration of water in changing environmental conditions.
72
New cards
What does the endomembrane system do?
A group of membranes and organelles in eukaryotic cells that work together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins.
73
New cards
What makes up the endomembrane system?
1. nuclear envelope
2. lysosomes
3. vesicles
4. endoplasmic reticulum
5. golgi apparatus
6. \*technically the plasma membrane
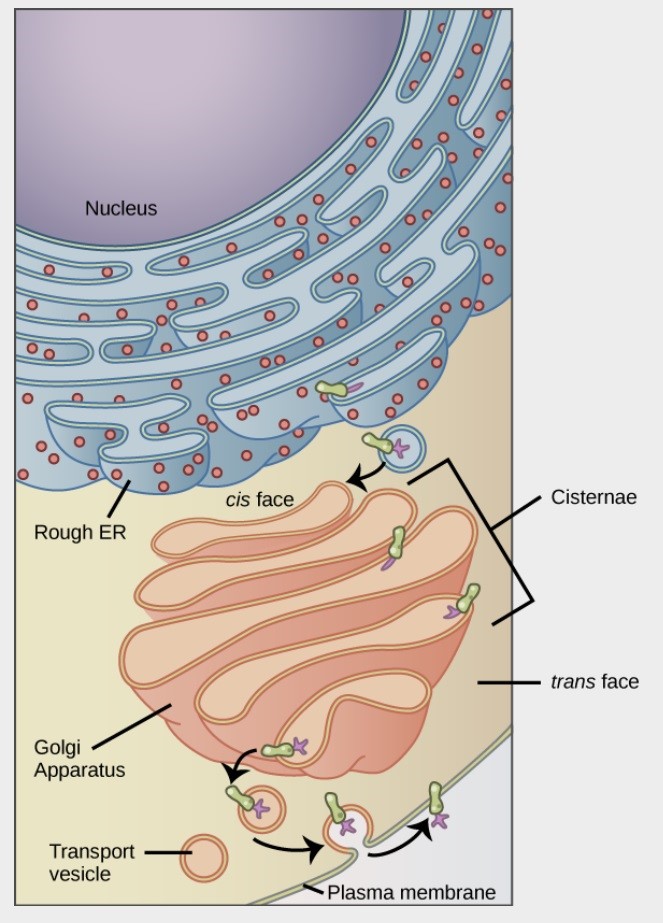
74
New cards
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
A series of interconnected membranous sacs and tubules that modify proteins and synthesize lipids
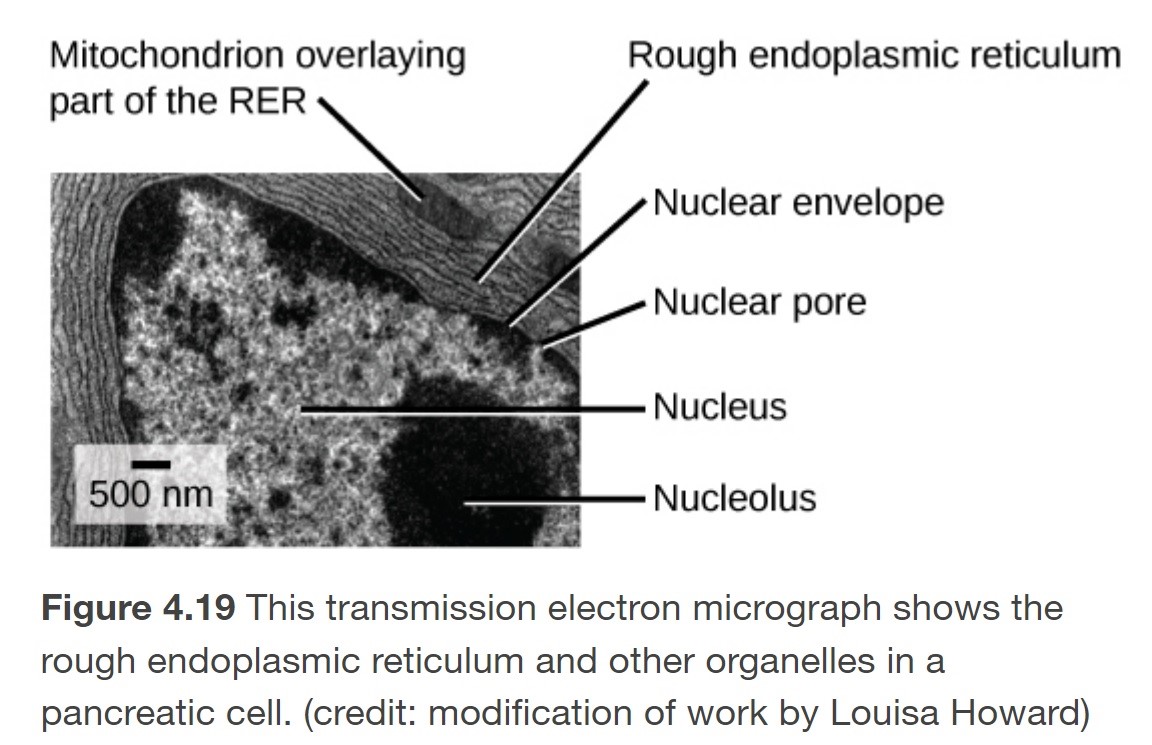
75
New cards
Where does protein synthesis occur?
In the rough endoplasmic reticulum
76
New cards
Where does lipid synthesis occur?
In the smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
77
New cards
What is the ER tubules’ hollow portion?
Lumen or cisternal space
78
New cards
What is the relationship of the ER and the nuclear envelope?
The ER’s membrane is continuous with the nuclear envelope.
79
New cards
What happens to proteins in the RER lumen?
They undergo folding or acquire side chains.
80
New cards
Where is the RER abundant?
In cells that secrete proteins such as the liver?
81
New cards
What is the SER (smooth endoplasmic reticulum) function?
* Synthesis of:
1. Carbohydrates
2. Lipids
3. Steroid hormones
* Detoxification of medications and poisons
* Storing calcium ions
1. Carbohydrates
2. Lipids
3. Steroid hormones
* Detoxification of medications and poisons
* Storing calcium ions
82
New cards
What is the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
A specialized smooth endoplasmic reticulum found in muscle cells responsible for storing calcium ions needed to trigger coordinated contractions.
83
New cards
What is the golgi apparatus?
The organelle that tags, packs, and distributes lipids and proteins.
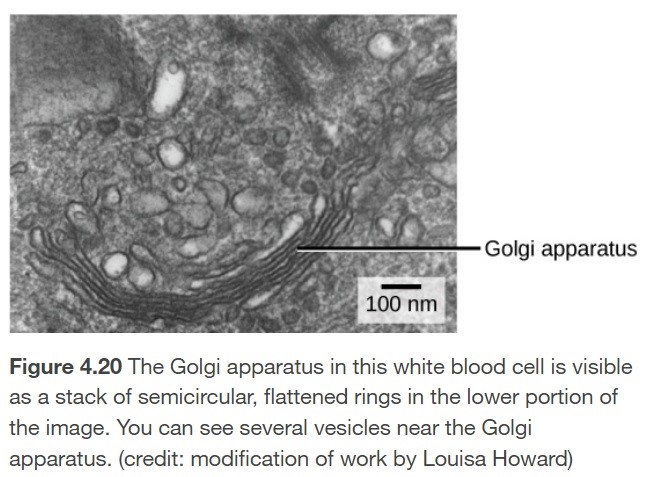
84
New cards
What is the side of the golgi apparatus closer to the ER?
The cis face
85
New cards
What is the side of the golgi apparatus farthest from the ER?
The trans face
86
New cards
What is the most common modificaton that happens in the golgi apparatus?
The addition of short sugar molecule chains
87
New cards
Where are golgi apparatuses most abundant?
* In secretory cells such as salivary gland cells
* In cells that secrete digestive enzymes
* In immune cells that secrete antibodies
\
* In cells that secrete digestive enzymes
* In immune cells that secrete antibodies
\
88
New cards
What is the additional role of the golgie apparatus in plant cells?
Synthesizing polysaccharides
89
New cards
What is the process of phagocytosis?
1. Plasma membrane invaginates (folds in) to engulf a pathogen
2. The invaginated section pinches of and becomes a vesicle inside the macrophage
3. A lysosome fuses to the vesicle and uses hydrolytic enzymes to destroy the pathogen
90
New cards
What is the role of the cytoskeleton?
1. Maintain cell shape
2. secure organelles in position
3. Allow cytoplasm and vesicles to move withing the cell
4. Enables multicellular organisms to move
91
New cards
What three types of fibers make up the cytoskeleton?
1. microfilaments
2. intermediate filaments
3. microtubules
92
New cards
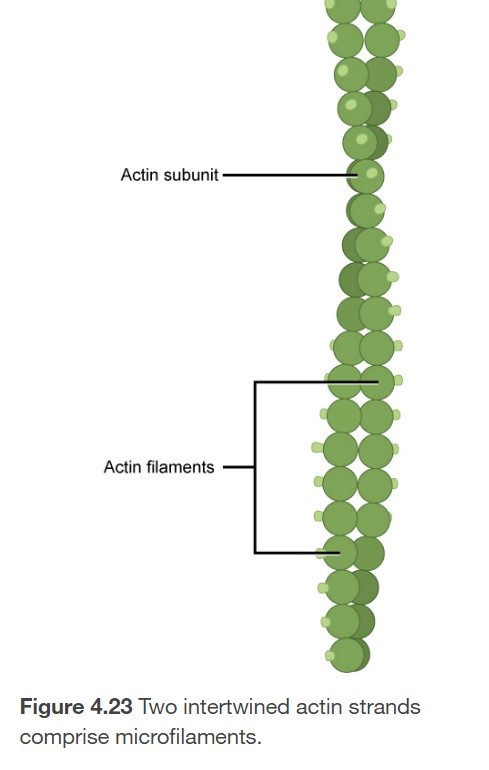
What are the characteristics of Microfilaments (actin filaments)?
1. Narrowest of cytoskeleton fibers
2. Function in cellular movement
3. diameter \~7nm
1. Comprised of 2 globular protein intertwined stands called actin
93
New cards
What is the relationship between actin and myosin?
Actin serves as a track for the motor protein myosin
94
New cards
Where are actin and myosin plentiful?
In muscle cells where they slide past each other
95
New cards
What characteristic of microfilaments enables a cell to change chape and move?
Microfilaments can depolymerize (disassemble) and reform quickly.
96
New cards
What is the role of intermediate filaments?
* Bear tension to maintain cell shape
* Anchor the nucleus and other organelles in place
* Anchor the nucleus and other organelles in place
97
New cards