APD Introduction to Organs of the Endocrine System (Lecture 19)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/128
Last updated 6:39 PM on 4/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
1
New cards
1. Autocrine
2. Paracrine
3. Endocrine
What are the 3 mechanisms for hormonal control?
2
New cards
autocrine
What mechanism of hormonal control causes the cell to release substances that **act on the releasing cell?**
3
New cards
endocrine
What mechanism of hormonal control causes the cell to release substances **into the blood** to reach target organs?
4
New cards
paracrine
What mechanism of hormonal control causes the cell to release substances **into connective tissue** to reach **nearby cells**?
5
New cards
True
True/False: Hormonal feedback may be positive or negative.
6
New cards
1. Corticosteroid binding protein
2. Androgen binding protein
What are 2 examples of specific carrier proteins of hormones?
7
New cards
1. Cell surface receptors
2. Intracellular receptors
What are the 2 signaling pathways of hormones?
8
New cards
intracelullar receptors
What type of signaling pathway for hormones go into the cell & modifies genes?
9
New cards
1. Steroids & thyroid hormone
2. Vitamin D
What are 2 examples of intracellular receptors?
10
New cards
albumin
Most hormones can travel bound to ____________.
11
New cards
1. Second messenger systems
2. Tyrosine kinases
What are 2 examples of cell surface receptors of the hormone signaling pathway?
12
New cards
phototransduction
What important process in eye is considered to involve a secondary messenger system?
13
New cards
Metarhodopsin II
In phototransduction diagrams, what does “R\*” stand for?
14
New cards
sodium; 11-cis; all-trans; transducin; cGMP; GMP; sodium
In the pathway of phototransduction, before light hits rhodopsin, ________ enters through cGMP gated channels (depolarized in the dark). When light hits rhodopsin, ________ retinal converts to ________ retinal and rhodopsin is activated. Activated rhodopsin activates _____ who activates phosphodiesterase. Phosphodiesterase breaks down _____ to _________. With no cGMP bound to channels, _________ entry stops (hyperpolarized).
15
New cards
insulin receptor
What is an important example of tyrosine kinase signaling?
16
New cards
nuclear receptors
What type of receptors regulate transcription and are also known as intracellular receptors?
17
New cards
1. Steroids
2. Thyroid hormone
3. Vitamin D
What are the 3 main ligands of nuclear receptors?
18
New cards
vitamin D; thyroid hormone
During intracellular receptor signaling, what binds inside the cell to increase calcium absorption? What binds inside the cell to ultimately increase heat generation & basal metabolic rate?
19
New cards
1. Steroid hormones
2. Small (poly)peptides & proteins
3. Amino acids & arachidonic acid analogs
What are the 3 main types of hormones?
20
New cards
1. Melanin
2. T3 & T4
3. Catecholamines
Tyrosine becomes what 3 things?
21
New cards
seratonin
What does tryptophan become?
22
New cards
steroid hormones
What are cholesterol-derived hormones?
23
New cards
amino acids & arachidonic acid analogs
What type of hormone includes catecholamines, prostaglandins, seratonin, leukotrienes, and T3 & T4?
24
New cards
1. Hypothalamus
2. Pituitary gland
3. Pineal gland
What are the 3 classic endocrine organs?
25
New cards
infundibulum
What connects the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland?
26
New cards
tuber cinereum
What is the most dorsal portion of the hypothalamus?
27
New cards
median eminence
What part of the hypothalamus is part of the tuber cinereum and connects to the infundibulum?
28
New cards
1. Mammillary bodies
2. Optic chiasm
The tuber cinereum is the section between what 2 structures?
29
New cards
1. Median eminence
2. Mammillary bodies
3. Optic chiasm
4. Tuber cinereum
In the image of the hypothalamus, what is indicated by the following colors:
1. Purple
2. Pink
3. Green
4. Blue (includes part of the purple in the center)
1. Purple
2. Pink
3. Green
4. Blue (includes part of the purple in the center)
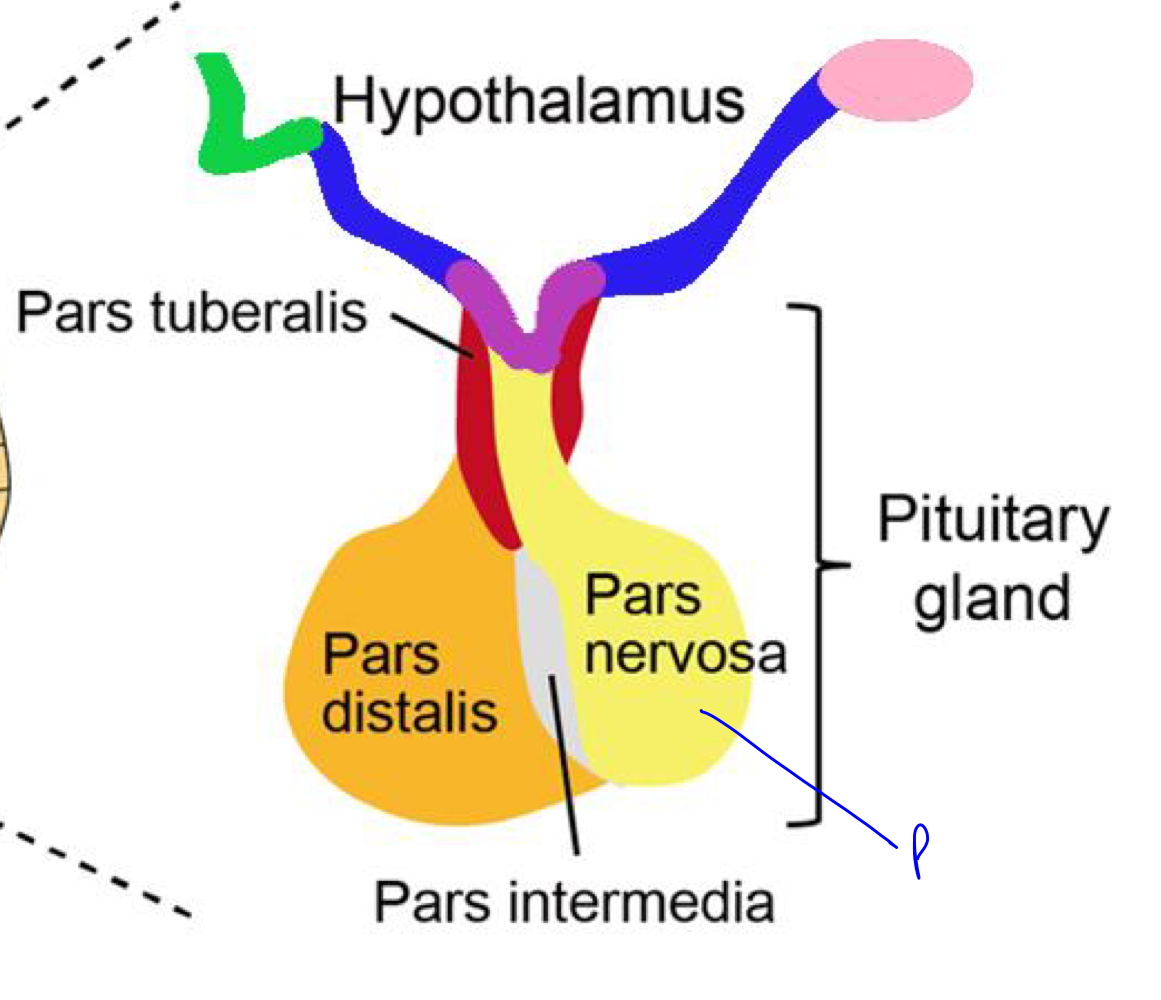
30
New cards
posterior pituitary
What part of the pituitary is made of axons and does not produce hormones?
31
New cards
Hypothalamic-pituitary axis
What important function of the hypothalamus controls release of anterior pituitary hormones and synthesizes & stores posterior pituitary hormones?
32
New cards
hypothalamus
What organ regulates almost all body functions, largely through pituitary hormones?
33
New cards
hypothalamus
Releasing & inhibiting hormones come from what organ location?
34
New cards
1. Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
2. Corticotropin __releasing__ hormone (CRH)
3. Gonadotropin __releasing__ hormone (GRH)
4. Growth hormone __releasing__ hormone (GHRH)
5. Growth hormone __inhibiting__ hormone (somatostatin)
6. Oxytocin
7. Prolactin __inhibiting__ hormone (dopamine)
8. Prolacting __releasing__ hormone (PRH)
9. Thyrotropin __releasing__ hormone (TRH)
What are the 9 hormones synthesized in the hypothalamus?
35
New cards
1. Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
2. Oxytocin
What 2 hormones synthesized in the hypothalamus are released in the posterior pituitary?
36
New cards
releasing
Excitatory anterior pituitary control involves (releasing/inhibitory) hormones.
37
New cards
**R**eleasing
**O**xytocin
**A**nti-diuretic hormone
**D**opamine
**S**omatostatin
**O**xytocin
**A**nti-diuretic hormone
**D**opamine
**S**omatostatin
What is the pneumonic for remembering what is made in the hypothalamus?
38
New cards
dopamine
What inhibitory anterior pituitary control hormone inhibits prolactin release?
39
New cards
1. Dopamine
2. Somatostatin
What 2 hormones are inhibitory hormones that are under anterior pituitary control?
40
New cards
1. Arcuate nucleus
2. Paraventricular nucleus
3. Preoptic area/Periventricular area
4. Supraoptic nucleus
5. Suprachiasmatic nucleus
6. Lateral Hypothalamic area
7. Ventromedial nucleus
What are the 7 hypothalamic nuclei?
41
New cards
1. Growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH)
2. Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH)
3. Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH)
4. Dopamine
What 4 hormones are made in the arcuate hypothalamic nucleus?
42
New cards
1. Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH)
2. Somatostatin
What hormones are made in the preoptic area of the periventricular region of the hypothalamus?
43
New cards
1. Arcuate nucleus
2. Preoptic/Periventricular region
In what 2 nuclei of the hypothalamus is gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) made?
44
New cards
1. Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
2. Oxytocin
3. Corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH)
What 3 hormones are synthesized in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus?
45
New cards
1. Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
2. Oxytocin
What 2 hormones are synthesized in the supraoptic nucleus of the hypothalamus?
46
New cards
1. Paraventricular nucleus
2. Supraoptic nucleus
What 2 nuclei within the hypothalamus are responsible for synthesizing ADH & oxytocin?
47
New cards
suprachiasmatic nucleus
What nucleus of the hypothalamus is responsible for circadian rhythm control?
48
New cards
1. Arcuate nucleus
2. Preoptic/periventricular area
What 2 hypothalamic nuclei are part of the anterior pituitary axis ONLY?
49
New cards
Supraoptic nucleus
What hypothalamic nucleus is part of posterior pituitary release only?
50
New cards
Paraventricular nucleus
What hypothalamic nucleus partakes in both posterior pituitary release and the anterior pituitary axis?
51
New cards
1. Suprachiasmatic nucleus
2. Lateral hypothalamic area
3. Ventromedial nucleus
What are the 3 non-pituitary nuclei of the hypothalamus?
52
New cards
lateral hypothalamic area
What hypothalamic nuclei controls your hunger and is a target for ghrelin?
53
New cards
ventromedial nucleus
What hypothalamic nuclei controls how full you feel and targets ghrelin & leptin?
54
New cards
adenohypophysis
What is another term for anterior pituitary?
55
New cards
6
The anterior pituitary synthesizes and releases ___ main hormones.
56
New cards
1. Neurohypophysis
2. Pars nervosa
What is are 2 other terms for posterior pituitary?
57
New cards
hypothalamus
The posterior releases hormones made by the __________.
58
New cards
False--axons & support tissue
True/False: The posterior pituitary is made up of gland tissue.
59
New cards
Pars distalis
What is the main portion of the anterior pituitary, anatomically?
60
New cards
1. Pars distalis
2. Pars tuberalis
What are the 2 parts of anterior pituitary?
61
New cards
1. Corticotrophs
2. Gonadotrophs
3. Lactotrophs
4. Somatotrophs
5. Thyrotrophs
What are the 5 cell types via immunocytochemistry of the pars distalis (anterior pituitary)?
62
New cards
1. Corticotrophs
2. Lactotrophs
3. Gonadotrophs
4. Thyrotrophs
5. Somatotrophs
6. Gonadotrophs
7. Corticotrophs
Identify which cells of the pars distalis are responsible for releasing the following hormones.
1. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
2. Prolactin (PRL)
3. Luteinizing hormone (LH)
4. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
5. Growth hormone (GH)
6. Follicular stimulating hormone (FSH)
7. Endorphins
1. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
2. Prolactin (PRL)
3. Luteinizing hormone (LH)
4. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
5. Growth hormone (GH)
6. Follicular stimulating hormone (FSH)
7. Endorphins
63
New cards
**F**ollicle stimulating hormone
**L**uteinizing hormone
**A**drenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
**T**hyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
**P**rolactin
**E**ndorphins
**G**rowth hormone
**L**uteinizing hormone
**A**drenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
**T**hyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
**P**rolactin
**E**ndorphins
**G**rowth hormone
What is the pneumonic to remember what the anterior pituitary makes?
64
New cards
capillary plexus
The _________________ supplies the pars distalis with hypothalamic hormones.
65
New cards
From hypothalamus; autonomic nervous system
What is the nerve supply for the posterior pituitary? Anterior pituitary?
66
New cards
portal; 2
The blood supply of the pituitary gland is a _______ system where there are ___ capillary beds BEFORE reaching the heart.
67
New cards
anterior
Blood draining from the hypothalamus carries hypothalamic releasing or inhibitory hormones to ________________ pituitary.
68
New cards
posterior pituitary
What pituitary gland contains unmyelinated axons of cell bodies located in the hypothalamus?
69
New cards
1. Supraoptic nuclei
2. Paraventricular nuclei
What 2 nuclei make up the posterior pituitary gland?
70
New cards
False
True/False: ADH & oxytocin have pituitary nuclei.
71
New cards
1. Follicular stimulating hormone (FSH)
2. Luteinizing hormone (LH)
3. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
4. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
5. Growth hormone (GH)
Releasing hormones of the hypothalamus & pituitary are pro-release for what 5 anterior pituitary hormones?
72
New cards
prolactin
Dopamine inhibits the release of what anterior pituitary hormone?
73
New cards
growth hormone (GH)
Somatostatin inhibits release of what anterior pituitary hormone?
74
New cards
1. Arcuate nuclei
2. Preoptic/Periventricular area
3. Ventromedial nuclei
What 3 hypothalamic nuclei regulate secretion of the ANTERIOR pituitary?
75
New cards
1. Supraoptic nucleus
2. Paraventricular nucleus
What hypothalamic nuclei have axons that project into the posterior pituitary?
76
New cards
1. Zona glomerulosa
2. Zona fasciculata
3. Zona reticularis
What are the 3 layers of the adrenal cortex?
77
New cards
Zona glomerulosa; Zona fasciculata; Zona reticularis
What layer of the adrenal cortex is responsible for salt? Sugar? Sex?
78
New cards
sympathetic
Adrenal medulla involves (parasympathetic/sympathetic) functions.
79
New cards
1. Epinephrine
2. Norepinephrine
What 2 hormones come from chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla?
80
New cards
1. Zona glomerulosa
2. Zona reticularis
3. Zona fasciculata
Identify which layer of the adrenal cortex each hormone is made.
1. Mineralocorticoids
2. Androgens/gonadocorticoids
3. Glucocorticoids (mainly synthesized)
1. Mineralocorticoids
2. Androgens/gonadocorticoids
3. Glucocorticoids (mainly synthesized)
81
New cards
Aldosterone
What is an example of mineralcorticoid?
82
New cards
cortisol
What is an example of a glucocorticoid?
83
New cards
DHEA
What is an example of an androgen/gonadocorticoid?
84
New cards
1. Capsule
2. Zona glomerulsa
3. Zona fasciculata
4. Zona reticularis
5. Medulla
Identify the following areas/structures in the image of a microscopic section of the adrenal gland.
1. Red section
2. Blue section
3. Orange section
4. Green section
5. Purple section
1. Red section
2. Blue section
3. Orange section
4. Green section
5. Purple section
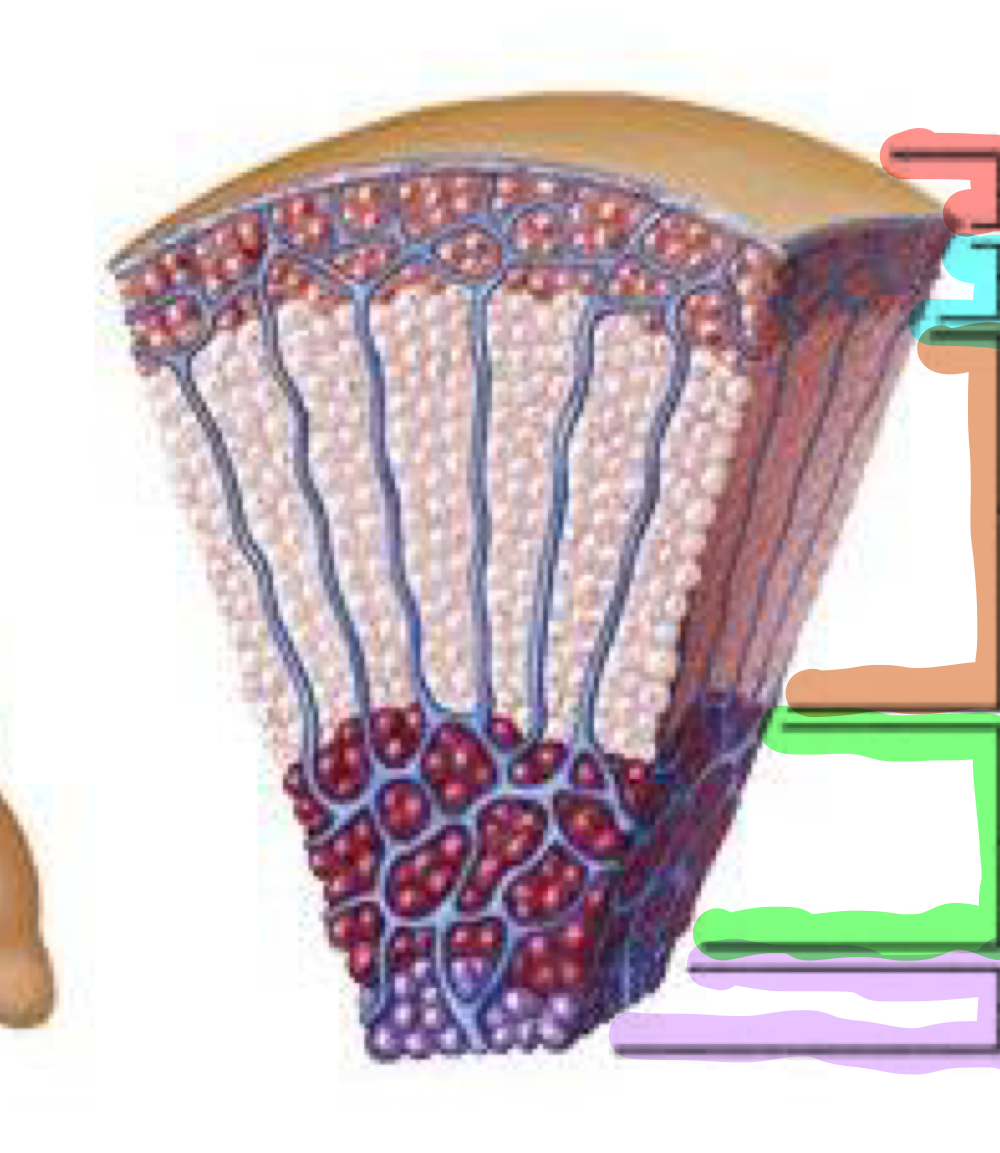
85
New cards
fenestrated sinusoidal capillaries
What principal distribution of blood supply of the adrenal gland supplies the cortex and sinusoids of the adrenal medulla?
86
New cards
medulla
Hormones from the adrenal cortex drain into the adrenal _____________.
87
New cards
Chromaffin cells
What are the main cells of the adrenal medulla?
88
New cards
1. Epinephrine
2. Norepinephrine
What 2 hormones are made from chromaffin cells?
89
New cards
1. T3 (triiodothyoronine)
2. T4 (tetraiodothyronine)
Follicular cells of the thyroid gland synthesize what 2 components?
90
New cards
parafollicular cells
What cells of the thyroid gland __secrete__ calcitonin?
91
New cards
False
True/False: You can live without parathyroid hormone.
92
New cards
follicular cells
What cells of the thyroid make thyroid hormones?
93
New cards
calcitonin (parafollicular cells)
The cells surrounding follicular cells make ___________.
94
New cards
2
There are ____ pairs of parathyroid glands on each thyroid lobe.
95
New cards
1. Principal (chief) cells
2. Oxyphil cells
What are the 2 cell types present in the parathyroid gland?
96
New cards
principal (chief) cells
What cells of the parathyroid gland secrete parathyroid hormone?
97
New cards
parathyroid hormone
What hormone is basically opposite calcitonin?
98
New cards
True
True/False: Parathyroid glands are on the thyroid gland.
99
New cards
Retinohypothalamic tract
What tract present in the pineal gland contains ganglion cells (with melanopsin) that communicates with light levels?
100
New cards
suprachiasmatic nucleus; secretion of melatonin by pineal gland
What nucleus of the hypothalamus communicates with the pineal gland? What does this result in?