part 1 & 2, chapter 1: the human body and orientation
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Anatomy
Structure
Physiology
Function
Principle of complementary
The structure of a body part is perfectly suited to its function; function is always dependent on structure
Microscopic anatomy
Cannot see with the naked eye
Gross or macroscopic anatomy
Can see with the naked eye
Developmental anatomy
How anatomical structures form and change in an organism, from a single cell, to maturity
Structural organization
Chemical level, cellular level, tissue level, organ level, organ system level, organismal level
Chemical level
Atoms combine to form molecules
Cellular level
Cells are made up of molecules
Tissue level
Tissue consist of similar cell types
Organ level
Organs are made up of different types of tissue
Organ system level
Organ systems consist of different organs that work together closely
Organism level
The human organism is made up of many organ systems
Requirements to maintain life
maintaining boundaries, movement & responsiveness, digestion, metabolism & excretion, and reproduction & growth
Survival needs
Nutrients, oxygen, water, normal body temperature, appropriate atmospheric pressure
Homeostasis
A dynamic state of equilibrium, always adjusting as needed
How does negative feedback maintain homeostasis?
Allow for a variable to go back to its set point
How does positive feedback maintain homeostasis?
Allows for the variable to be strengthen, instead of changing it
Homeostatic imbalance and disease
Aging and destructive positive feedback mechanisms may take over
Anatomical position
Body upright, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward with thumbs pointing away from body
Superior
Toward the head end or upper part of the body
Inferior
Away from the head end or toward the lower part of the body
Anterior (ventral)
Towards the front of the body (in front of)
Posterior (dorsal)
Towards the back of the body (behind)
Medial
Toward or at the midline of the body
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body
Intermediate
Between a more medial and lateral structure
Axial
Head, neck, and trunk
Appendicular
Limbs (legs and arms)
Sagittal
Right and left sections
Proximal
Closer to the origin of the body part
Distal
Farther from the origin of a body part
Superficial (external)
Toward or at the body surface
Deep (internal)
Away from the body surface; more internal
Midsagittal (median) plane
Right down the middle of the body with even halves
Parasagittal plane
Left and right halves but do not pass directly through the midline
Frontal (coronal) plane
Front and back sections (anterior & posterior)
Transverse (horizontal) plane
Upper and lower sections
Dorsal Body Cavity: subdivisions
Cranial cavity and vertebral (spinal) cavity
Cranial cavity
Contains brain
Vertebral cavity
Contains spinal cord
Ventral body cavity: subdivisions
Thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity
Thoracic cavity
Two pleural cavities that contains the right and left lung and the mediastinum which contains the heart
Abdominopelvic cavity
Abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity
Abdominal cavity
Contains digestive viscera
Pelvic cavity
Contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum
Abdominopelvic quadrants and regions
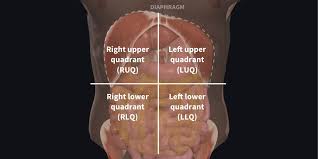
Organs in the right upper quadrant
Liver, gallbladder, right kidney, pancreas, colon, etc
Organs in the right lower quadrant
Appendix, right ovary and fallopian tube (in females), part of the small intestine, cecum, ascending colon
Organs in the upper left quadrant
Stomach, left kidney, pancreas, etc
Organs in the left lower quadrant
Descending colon, sigmoid colon, left ovary and fallopian tubes (in females), part of small intestine, etc
Serous membranes
outer balloon wall: parietal pericardium
air: pericardial spears w/ serous fluid
inner balloon wall: