Protozoan
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms

what is this Protozoan?
Balantidium coli.
what is the motility of Balantidium coli
This protozoan is motile primarily by cilia.
How is transmission of Balantidium coli.
Transmission occurs through the fecal-oral route.
what is the animal reservior for Balantidium coli
The primary animal reservoir for Balantidium coli is pigs, which can carry the organism in their intestines.
what disease does Balantidium coli cause?
It causes balantidiasis, an intestinal infection characterized by diarrhea, abdominal pain, and dysentery.
Exhibits both trophozoite and Cyst form
Infective Form: Cyst.
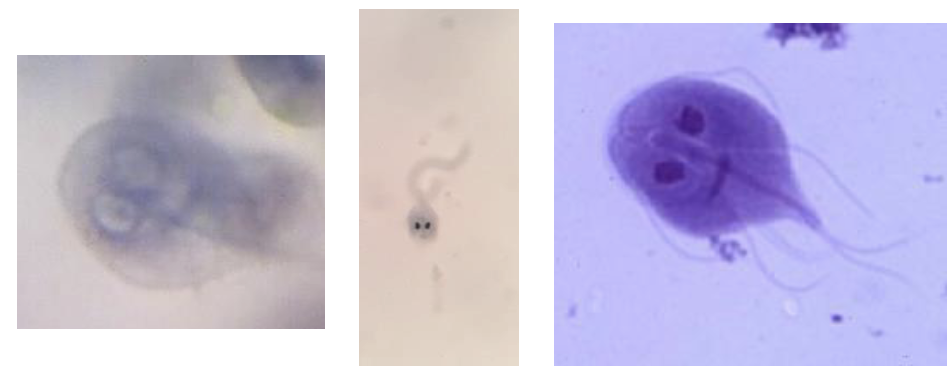
What is this protozoan?
Giardia lamblia
What is the molity of Giardia lamblia
Giardia lamblia exhibits flagellar motility.
what is the transmission of Giardia lamblia
Giardia lamblia is transmitted through the fecal-oral route.
what disease does Giardia lamblia cause?
Giardia lamblia causes giardiasis, an intestinal infection that leads to diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss.
Most frequently diagnosed intestinal parasitic
disease in the USGreen diarrhea and H2S
Does Giardia lamblia exbibith both trophozoite and cyst stages?
Yes, Giardia lamblia has both trophozoite and cyst stages in its life cycle.
Infective form: Cyst

what is this protozoan?
Trichomonas vaginalis
what is Trichomonas vaginalis molitlity?
Trichomonas vaginalis exhibits a motile behavior primarily through its flagella.
How is Trichomonas vaginalis contracted?
Trichomonas vaginalis is contracted primarily through sexual intercourse with an infected partner.
Most common curable STD.
What disease does Trichomonas vaginalis cause?
Trichomonas vaginalis causes trichomoniasis, a sexually transmitted infection characterized by vaginal discharge, irritation, and discomfort.
Does it for infective form of Trophozoite?
The infective form of Trichomonas vaginalis is the trophozoite
exhibits only the trophozoite stage.

What is this protozoan?
Trypanosoma spp.
How many type of Trypanosoma spp. are there?
There are several types of Trypanosoma spp., notably Trypanosoma brucei and Trypanosoma cruzi, which are responsible for African sleeping sickness and Chagas disease, respectively.
What is Trypanosoma brucei?
A protozoan parasite that causes African sleeping sickness, transmitted by tsetse fly bites.
Symptoms included fever, headaches, joint pain, and, in advanced stages, neurological issues.
What is Trypanosoma cruzi?
A protozoan parasite that causes Chagas disease, primarily transmitted by Cone-nosed “Kissing” Bug. Symptoms can range from acute inflammation to chronic cardiac and gastrointestinal complications.
Infective trypomastigote transmitted during cone-nosed
bug’s blood meal through their feces.

What is this protozoan?
Plasmodium spp.
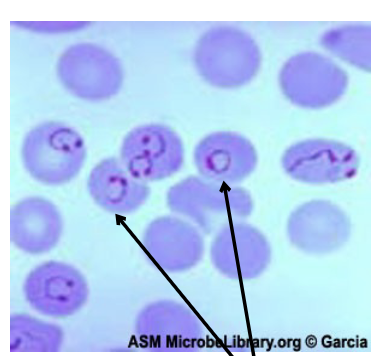
what are thing inside of the cell called?
Signet Rings
What disease does Plasmodium spp. cause?
Plasmodium spp. are responsible for malaria.
infect red blood cells ( erythrocytes)
Different strains cause varying degrees of illness
What vector is responsible for malaria?
The mosquito Anopheles is responsible for transmitting malaria.
The infective sporozoite is introduced by the female
Anopheles mosquito bite

What is this protozoan?
Toxoplasma
What disease is caused by Toxoplasma?
Toxoplasmosis is caused by Toxoplasma, a protozoan that can infect humans and various animals.

What is the host for Toxoplasma?
The host for Toxoplasma is the cat.
A cat is required to complete the sexual phase of the life cycle
Other animals may serve as intermediate hosts, but are dead ends for the organism unless eaten
What are cysts in toxoplasma
Infective form: cysts and oocysts
Tissue cysts can be consumed in undercooked meat
Does Toxoplasma cause harm to pregnant harm?
Yes, Toxoplasma can harm pregnant women by infecting the fetus, potentially leading to serious developmental issues or miscarriage.

What are the arrow pointing at?
Trophozoites, which are the active, motile feeding stage of protozoa, responsible for growth and reproduction.
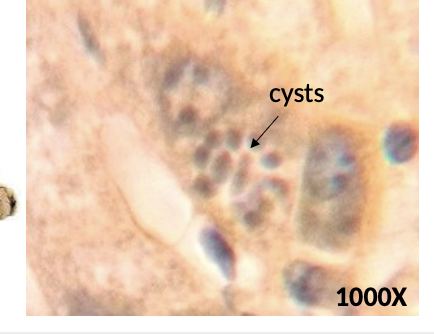
what is the arrow pointing at?
cysts in Toxoplasma, which are dormant forms that can survive in harsh environments.

What is this protozoan?
Leishmania donovani
What disease does Leishmania donovani cause?
Leishmaniasis/ Kala-Azar
Infection of the skin and mucosal membranes, may also be infection of the organs
Infection starts with parasites infecting macrophages, multiplying, and causing macrophages to burst and release more parasites.
What vector is responsible for the Leishmaniasis/ Kala-Azar?
The vector is sand flies( Phlebotomus or Lutzomyia).
Who is the host for Leishmania donovani?nia donovani
Humans and other mammals
what is the lifecyle of Leishmania donovani?
Lifecycle stages in humans are amastigote (very small) and
flagellated promastigote.
May cause death if not treated.