Chapter 29 Fungi Biological Diversity
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Fungi
A lineage of eukaryotes that typically have a filamentous body (mycelium) and obtain nutrients by absorption.
Mycelium
A mass of underground filaments (hyphae) that form the body of a fungus.
Hyphae
One of the long, branching strands of a fungal mycelium (the mesh-like body of a fungus).
Mutualists
An organism that is a participant and partner in a mutualistic relationship.
Mycorrhizal
Describes a fungus that lives symbiotically with roots of vascular plants.
Mycorrhizae
A mutualistic association between certain fungi and the roots of most vascular plants.
Ectomycorrhizal fungi
Fungi whose hyphae form a dense network that covers their host plant’s root but do not enter the root cells.
Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
Fungi from the glomeromycotan lineage whose hyphae enter the root cells of their host plants.
Saprophyte
An organism that feeds primarily on dead plant material.
Yeasts
Any fungus growing as a single-cell form.
Lichens
A mutualistic association of a fungus and a photosynthetic alga or cyanobacterium.
Extracellular Digestion
The process of breaking down food outside of a cell, typically in the gut, to make nutrients available for absorption.
Lignin Degradation
The process of breaking down lignin, a complex chemical compound that protects wood cell walls from microorganisms.
Cellulose Digestion
The breakdown of cellulose, a complex carbohydrate found in plant cell walls, into smaller sugar molecules.
absorbing
how do fungi intake nutrients?
decomposers
fungi are used for decaying matter and recycling back into the earth, what is the term?
animals
what are fungi closely related to?
false
True or False: Fungi photosynthesize and have chloroplasts
Parasitic Fungi
Fungi that absorb nutrients from living organisms
Saprophytic Fungi
fungi that feed on dead material
Mycorrhizal Fungi
fungi that have extensive networks in soil that increase plant growth
False
True or False: fungi are not important for the carbon cycle
Hyphae
the smallest unit of fungi
Mycelia
multicellular weblike bodied fungi
Yeasts
unicellular fungi
hyphae
what are the reproductive structure and mycelium made of
septa
cross walls that divide the hyphae into individual cells
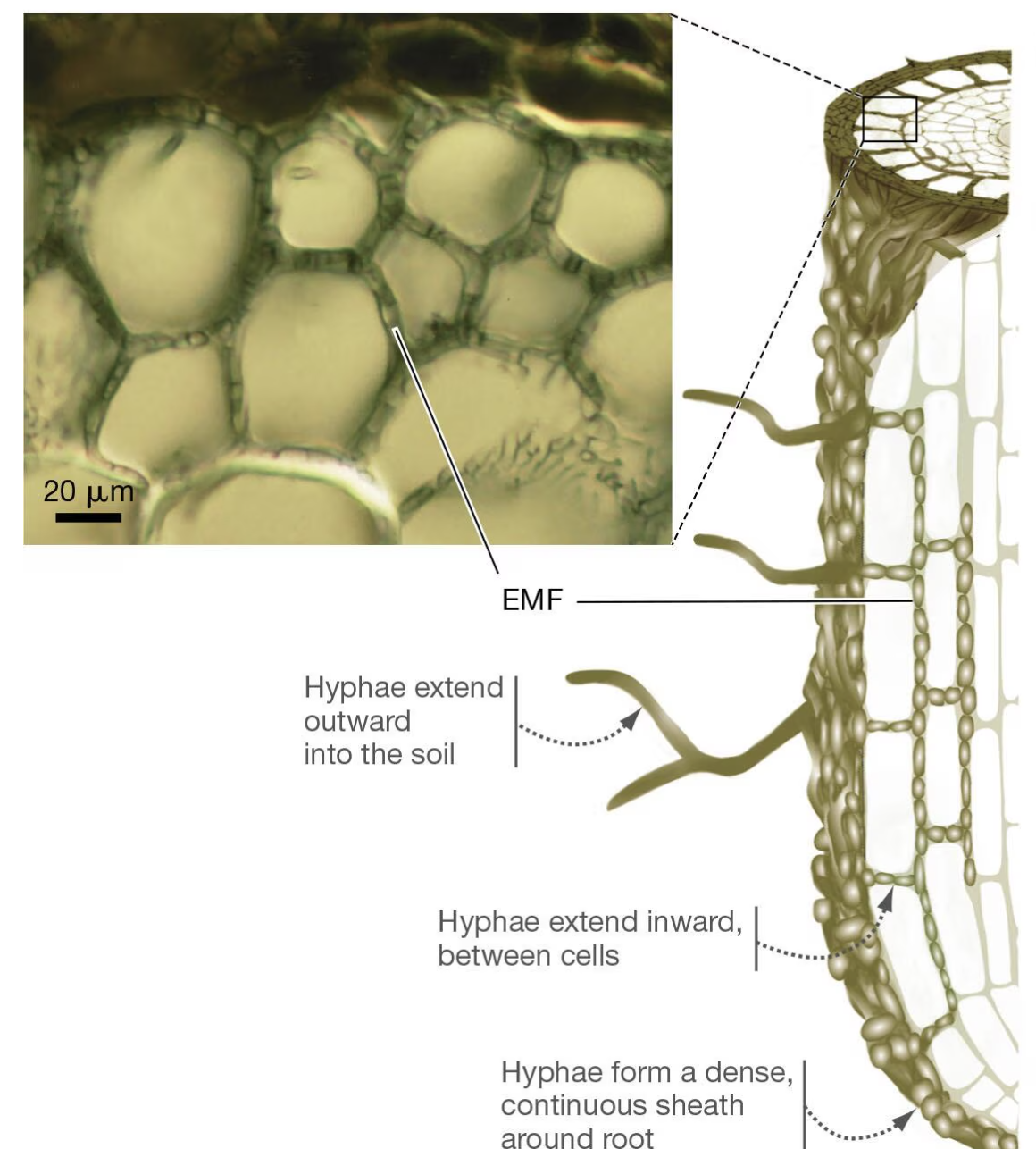
EMF Ectomycorrhizal
form sheaths around roots and penetrate between root cells
organic carbon (glucose)
plants provide fungi with ______
mutualistic
fungi returning phosphorus and nitrogen to plants is an example of what kind of relationship?
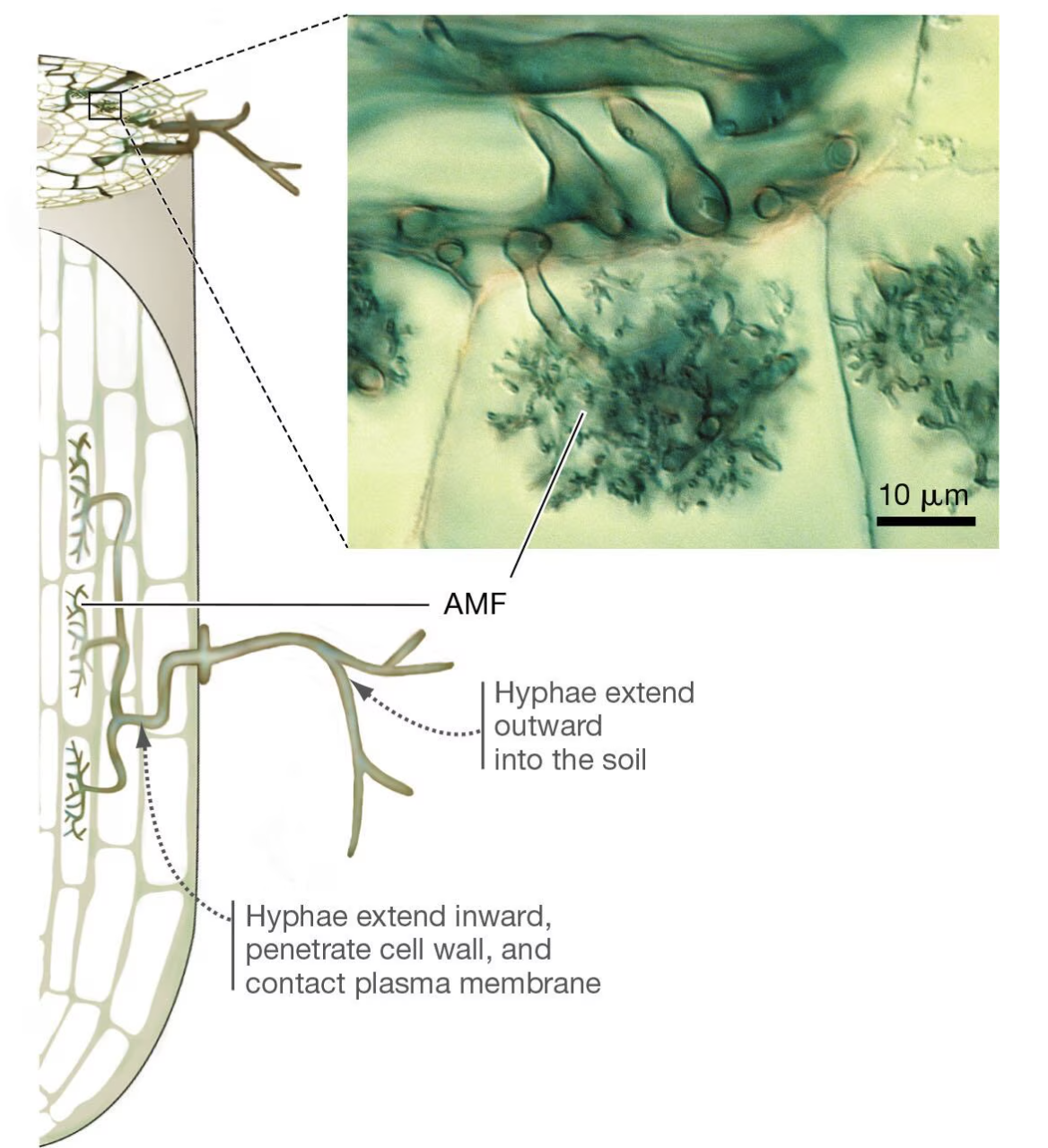
AMF arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
contact plasma membranes of root cells
lichens
the symbiosis between fungi and algae
penicillin
an example of medication that derived from fungi
saprophytic fungi
connects the two parts of the carbon cycle
zygosporangia
haploid hyphae (means of reproduction)
basidia
spore producing structure (means of reproduction)
Asci
sac-like cells at the tips of hyphae (means of reproduction)
Endophytes
“inside plant” organisms that live between and within plant cells
Glomeromycota
a group with species that form arbuscular mycorrhizal associations
Basidiomycota
contains species of mushrooms eaten as foods, some species are ectomycorrhizal
Ascomycota
some species are eaten (morels, truffles), group contains yeasts, some form mutualistic associations with photosynthetic algae or bacteria to form lichen, some are ectomycorrhizal