EESC 101 Lecture 2: Earth Systems and Internal Structure
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Where did the heat that formed the early Earth come from?
heat from impacts on the forming Earth’s surface
much more prevalent early in Earth’s history, but there are still many (thousands) of small impacts each year
heat from differentiation of the Earth’s layers
mostly spent but density differences still drive Earth’s processes
radioactive materials
again, much stronger early on, but still creates the bulk of internal heat today
Radioactivity: Short Half Lives
Atoms with short half lives are not great for age dating rocks as they are too young
H = 12yrs
C = 20min to 5730yrs
Carbon dating is great for archeological purposes
N = 10min
Cs = 30yrs
I = 13hrs to 15.7mil yrs
Radioactivity: Long Half Lives
Atoms with long half lives are great for age dating in geology
U = 4.468billion yrs
Th = 14.05billion yrs
K = 1.248billion yrs
Layers of the Earth: Magnetosphere
deflects solar winds
caused by Earth’s outer core
not unique to Earth, but causes may be different on other planets/moons
metallic hydrogen
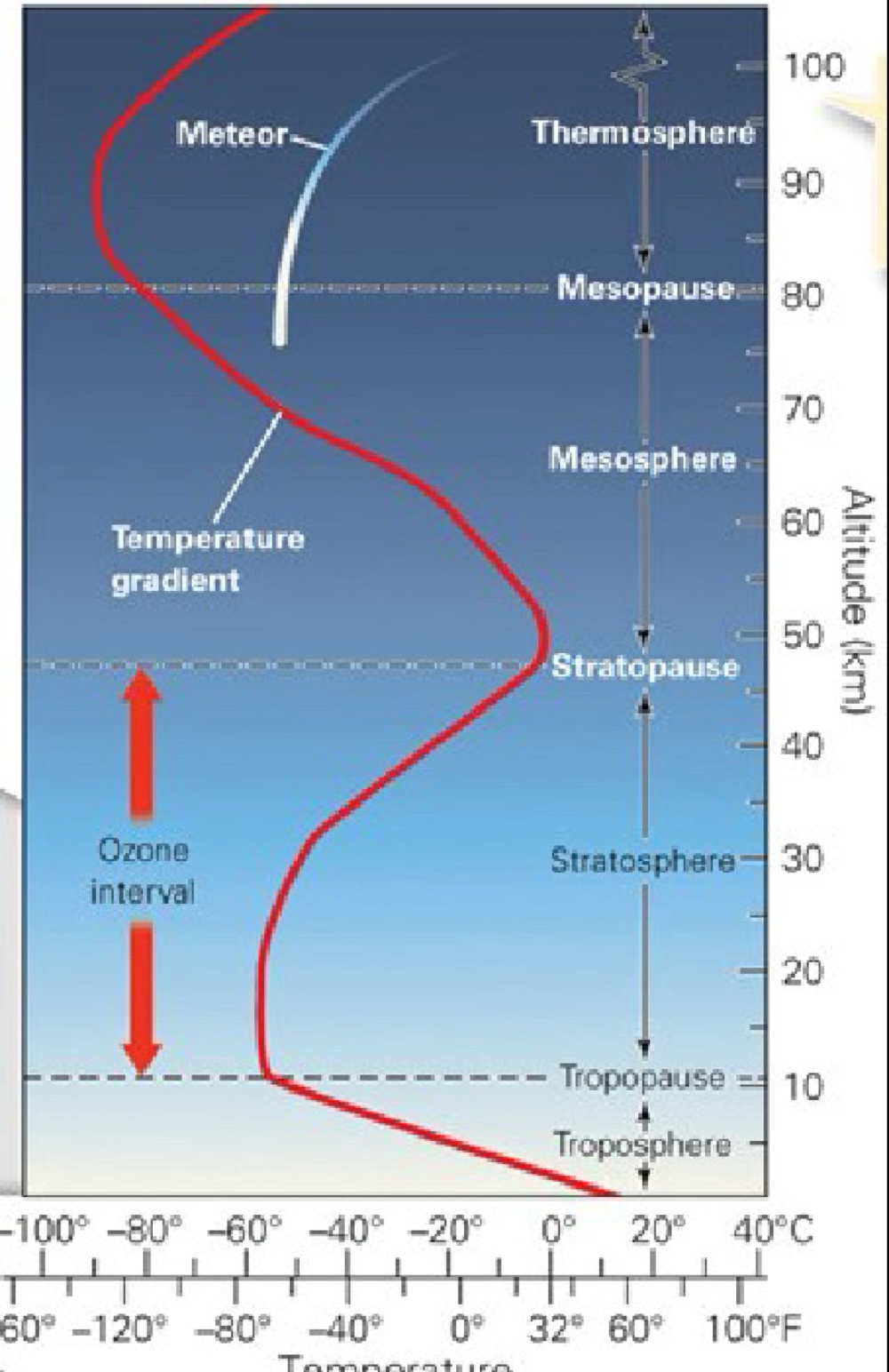
Layers of the Earth: Atmosphere
(78% N, 21% O)
1 atm (unit of pressure) is the amount of pressure exerted by the atmosphere at sea level
all clouds form in the troposphere (lowest level)
all weather is in the troposphere
planes cruse in low stratosphere
the atmosphere’s boundary with space is gradual (700-10,000km)
differences in temperature gradient due to balance of forces
troposphere gets hot from Earth (radiation)
stratosphere absorbs heat from solar radiation (UV rays)
Northern Lights
aurora borealis/aurora australis caused by solar flares
Interactions between atmosphere and magnetosphere
charged particles deflected to poles by magnetic fields
particles interact with molecules in the atmosphere and emit light
Oxygen: yellow/green
Nitrogen: red/violet
occur in narrow bands of latitude
typically within 10-20 deg of the (magnetic) north and south poles
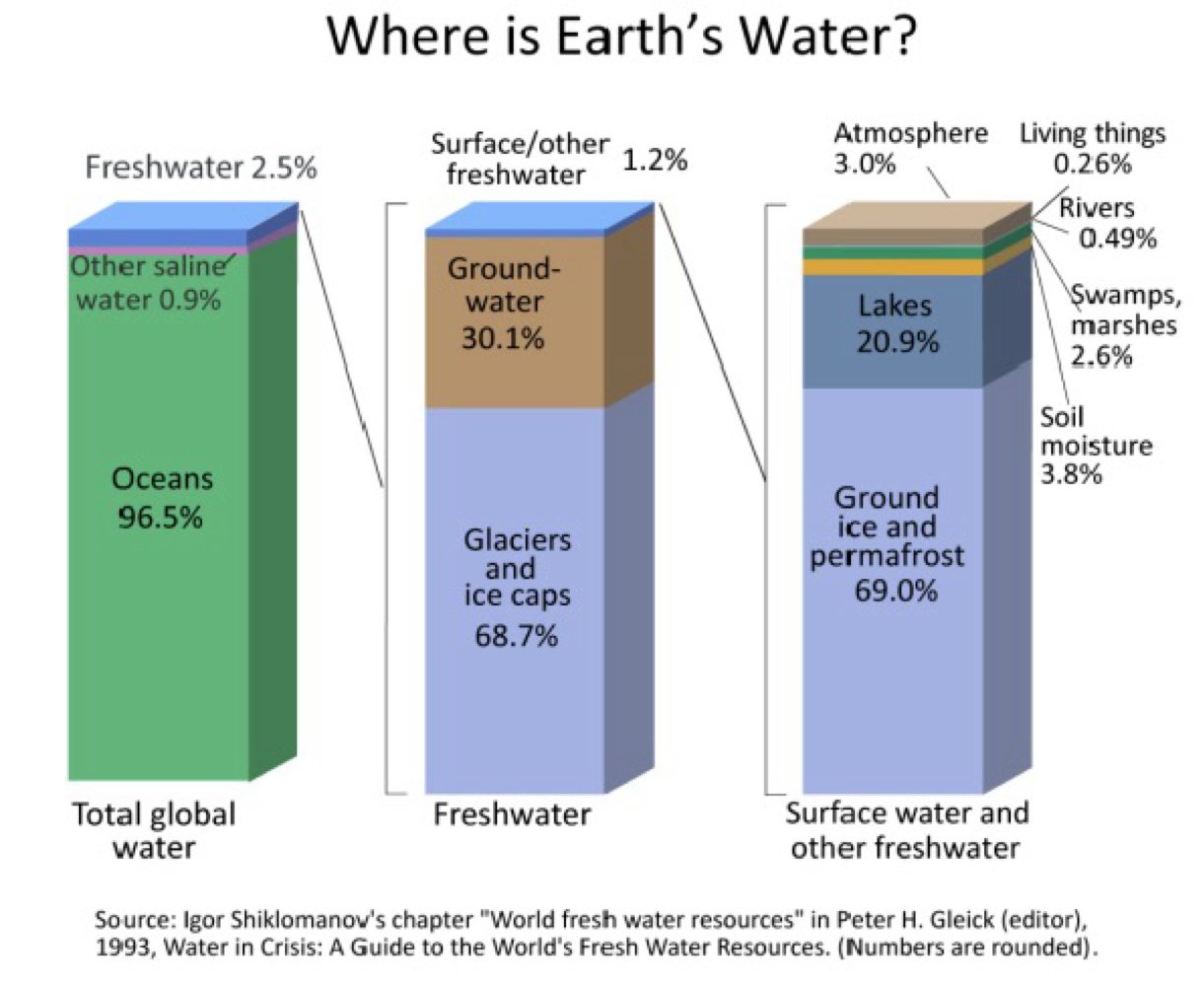
Layers of the Earth: Hydrosphere/Cryosphere
covers 70% of the Earth’s surface
part of what makes the Earth so unique in the solar system
most freshwater is captured in glaciers
last glacial maximum (~20,000 years ago)
lots of ice=lower sea level
migration of land animals (ex. mammoth, horse, camel, people)
Layers of the Earth: Biosphere
combination of all living organisms that occupy the Earth
extends through the lower atmosphere…
kitting spiders found at 16,000 ft above sea level
… to depths of ocean…
6.6 miles below surface
… and into the outermost layer of the Earth
~1 mile underground
plants and humans are the most obvious signs of the biosphere
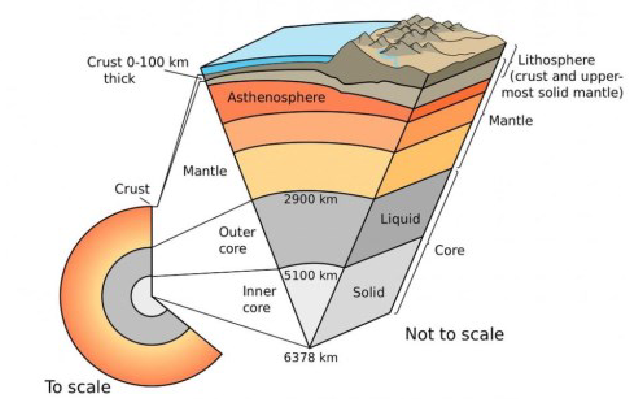
Layers of the Earth: Geosphere
includes the uneven land surface of the Earth and its inner layers
when examining the Earth’s inner structure
made up of meteorites
study of xenoliths (alien-rocks)
theoretical/experimental work simulations
seismic waves
deepest mine : ~2 miles
deepest core : ~7.5 miles
geosphere will include layers of the Earth
Crust (oceanic, continental)
Upper mantle
Lower Mantle
Core (inner/outer)
Crust
upper part of Earth’s solid body
oceanic crust:
7-10km thick
very dense
Fe/Mg rich (mafic)
low viscosity (when melted)
darker in colour
density is ~3 g/cm3
continental crust:
silica rich (felsic)
high viscosity (when melted)
lighter in colour
density is ~2.7 g/cm3
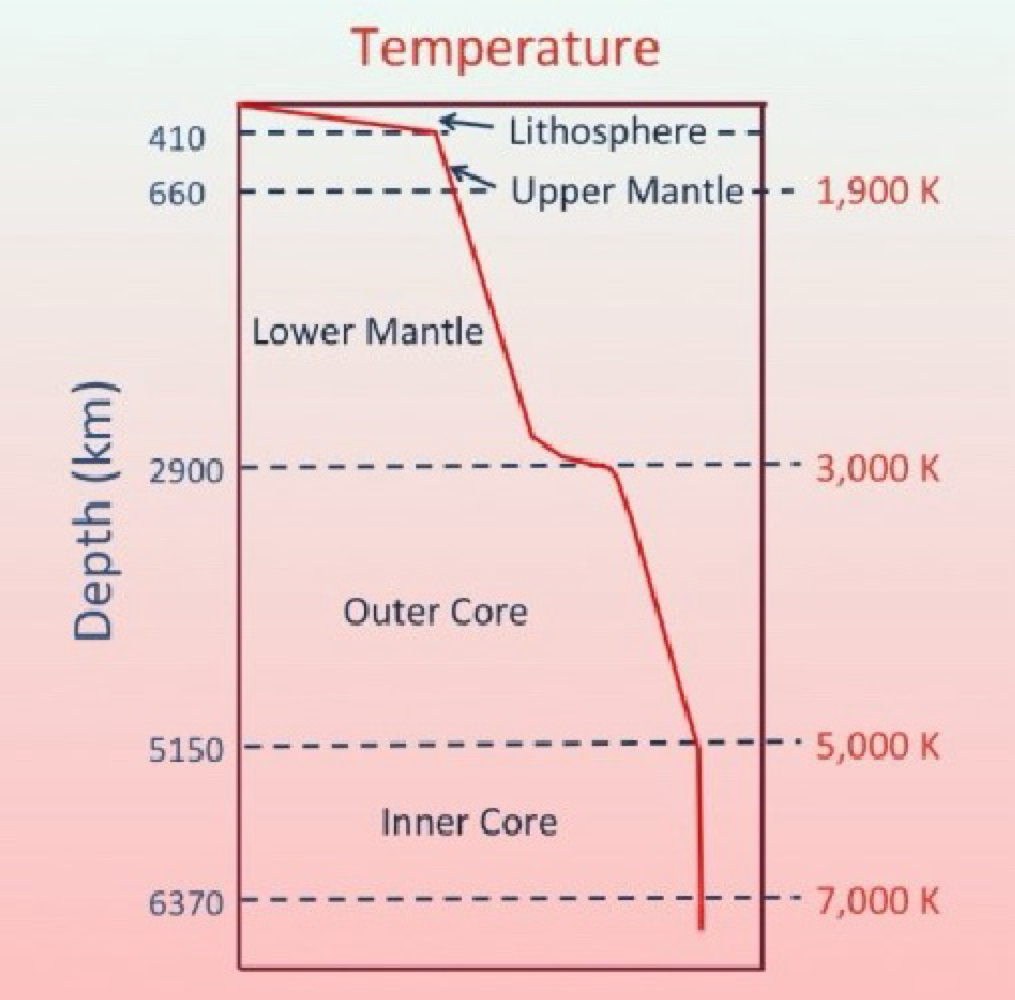
Mantle
makes up the bulk of the Earth by volume
stretches from the base of the crust to 2,900 km
composed mostly of the rock peridotite
silicate minerals (SiO2) with lots of iron and minerals
split into three parts
upper (crust-660km)
lower (660-2,900km)
transition zone (400-660km)
lower mantle is ductile
on long timescales it behaves like a fluid
flows at a rate of 15 cm/yr
three times faster than fingernails
Core
composed primarily of iron, nickel, and other heavy elements
core stats: 4,700 deg C and 3,600,000 atm
Alternate Layers
crust/mantle/core layers defined by compositional differences
another common say to divide Earth’s layers is by density
crust/upper mantle = Geosphere
lower mantle = asthenosphere