Anti-histamines
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What type of hypersensitivity reaction leads to the release of histamines?
Type 1
What cell or antibody is involved with Type I hypersensitivity reactions?
IgE
What leads to IgE antibody production?
Repeat exposure to allergens
What cells release histamine?
Mast cells.
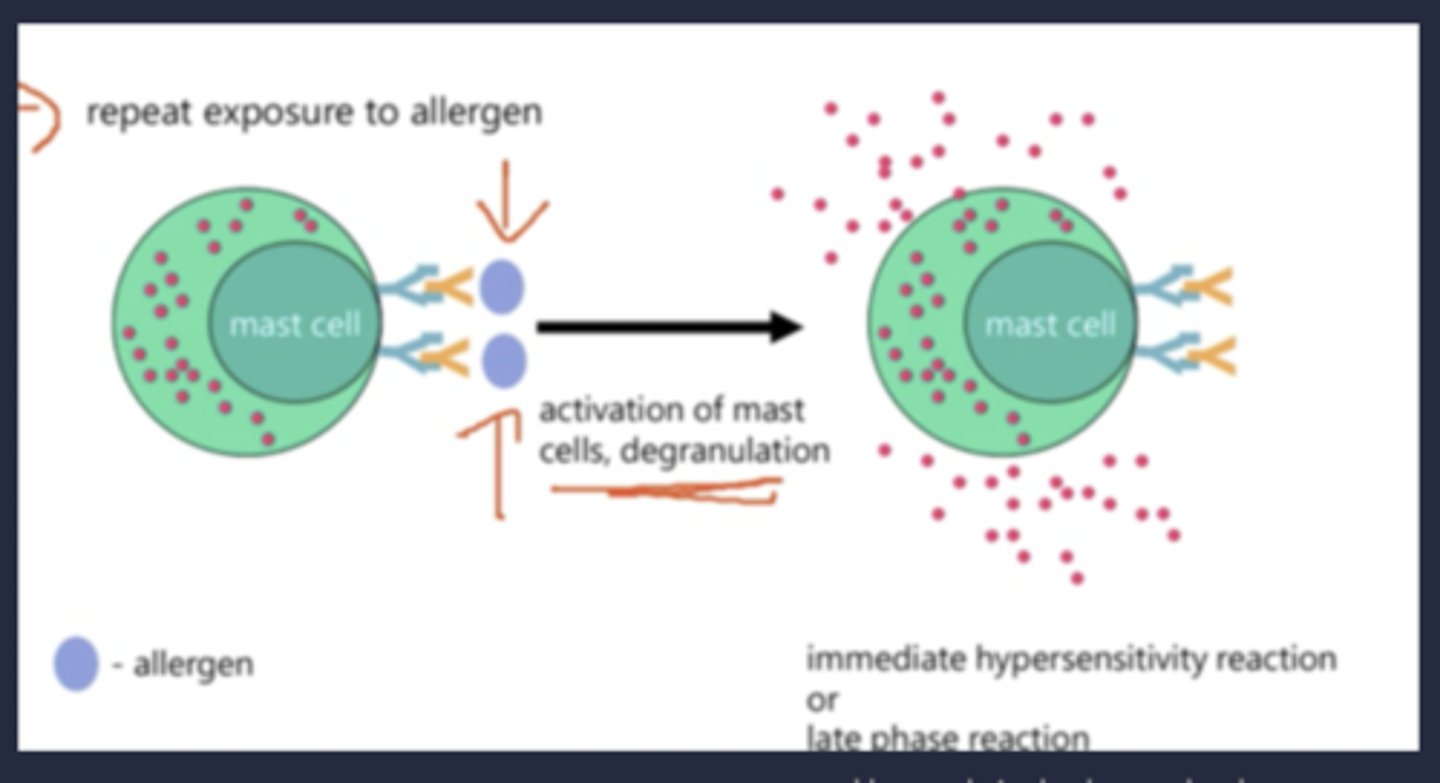
Describe type 1 hypersensitivity reaction.
- Mast cells contain granules containing histamines in the cytoplasm as well IgE receptors on their surface.
- IgE antibodies bind to the IgE receptors however nothing will take place if the IgE antibodies are not exposed to allergens whilst attached to the mast cell.
- This activates of mast cells which leads to degranulation where histamine is released.
- The immediate hypersensitivity reaction/allergic reaction or a late phase reaction take place.
What are the types of histamine receptor antagonists/antihistamines?
First generation and second generation
What are 1st Gen histamine receptor antagonists/antishistamines?
- Can be used on allergic reactions and for motion sickness.
- Very lipophillic so can cross blood brain barrier.
- Short duration of action.
What are 2nd Gen histamine receptor antagonists/antishistamines?
- Can be used on allergic reactions.
- Not lipofillic so cannot cross blood brain barrier.
- Long duration of action.
What effects does being lipophillic have on 1st gen anti-histamines?
- They have lots of effects on the CNS such as causing a sedative effect.
- Also allows them to have an anticholinergic effect which has some side-effects.
- This allows them to effective motion-sickness drugs.
What effects do antihistamines have that are not related to H1 receptors?
- Anticholinergic effects
- Effect the CNS
Describe the anticholinergic effect of antihistamines.
- Many 1st gen antihistamines can inhibit responses to muscarinic receptors e.g., acetylcholine cannot work.
- Can lead to side effects of dry mouth, blurred vision and constipation.
Describe the effects of antihistamines on the CNS.
- Most 1st gen antihistamines have a sedative effect.
- They can have an excitatory effect rather than a sedative effect e.g., convulsions.
- Some 1st gen can prevent motion sickness.
What are the essential groups for 1st gen anti-histamines activity towards H1 receptors?
- Tertiary amine with 2 R groups.
- X group being a C, O or an N.
- 2 aromatic groups on X group.
- 2 or 3 carbons in between tertiary amine and X group.
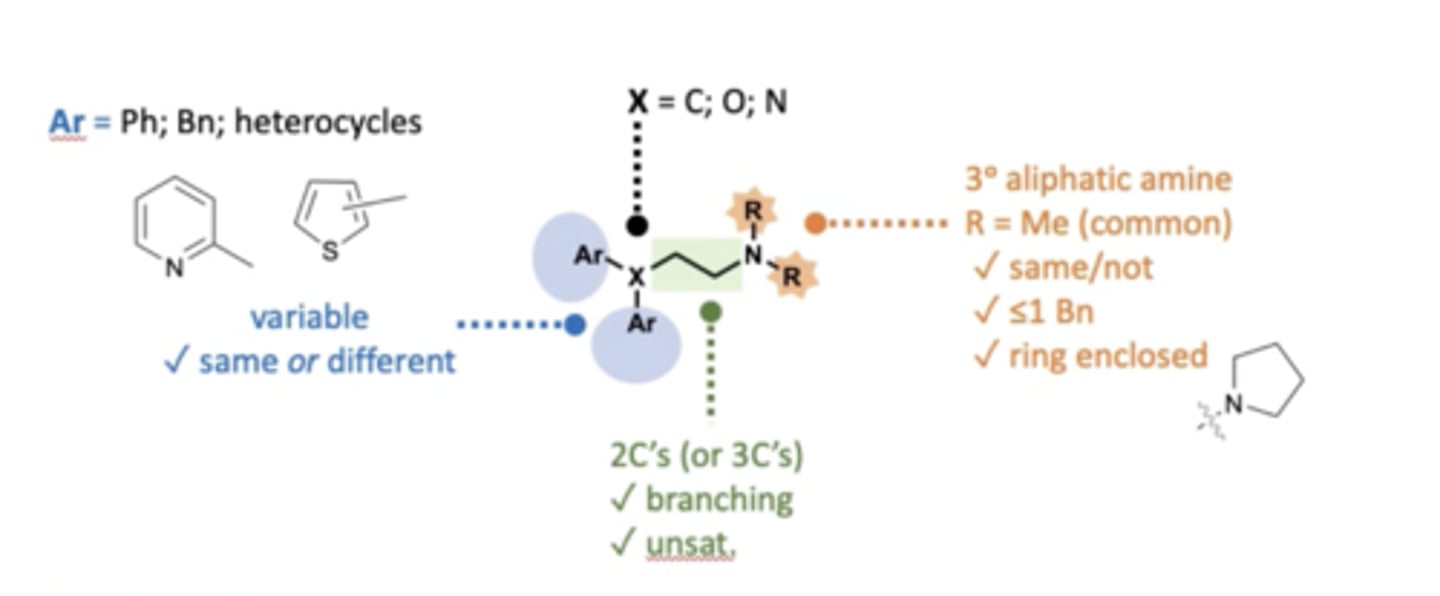
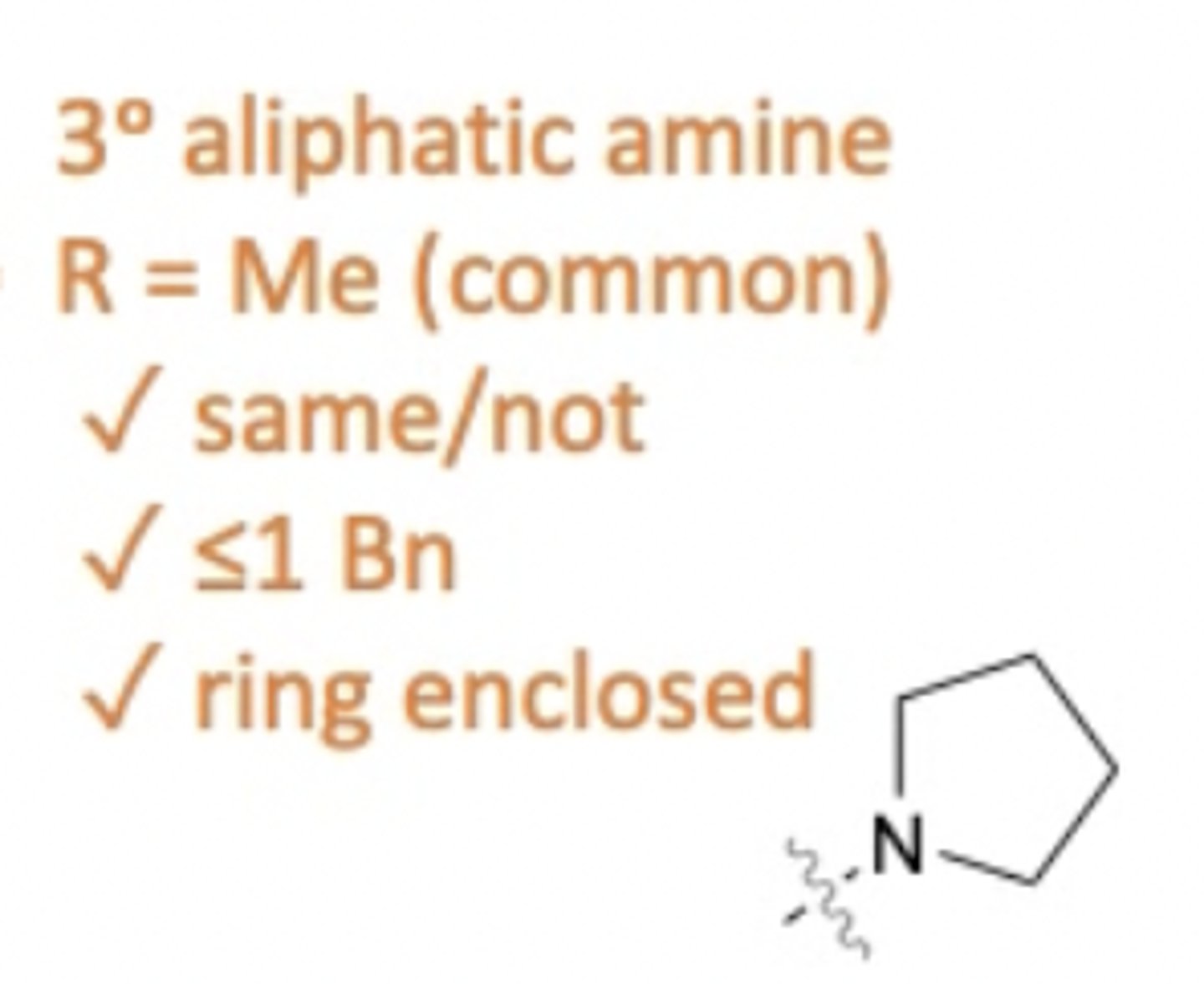
What 2 R groups can be present on the tertiary amine of a 1st gen anti-histamine?
- Most common is 2 methyl groups.
- Can be 2 different groups.
- No more than 1 benzene group.
- Can be a closed ring around nitrogen.
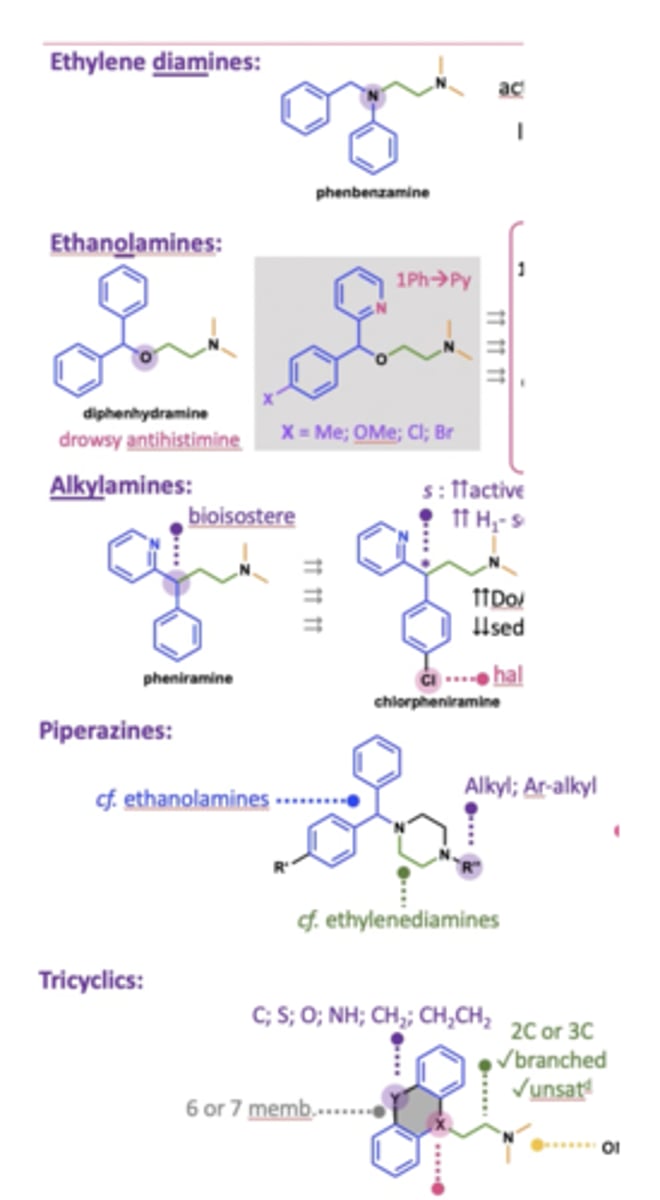
What are the types of 1st gen anti-histamines?
- Ethylene diamines
- Ethanolamines
- Alkylamines
- Piperazines
- Tricyclics
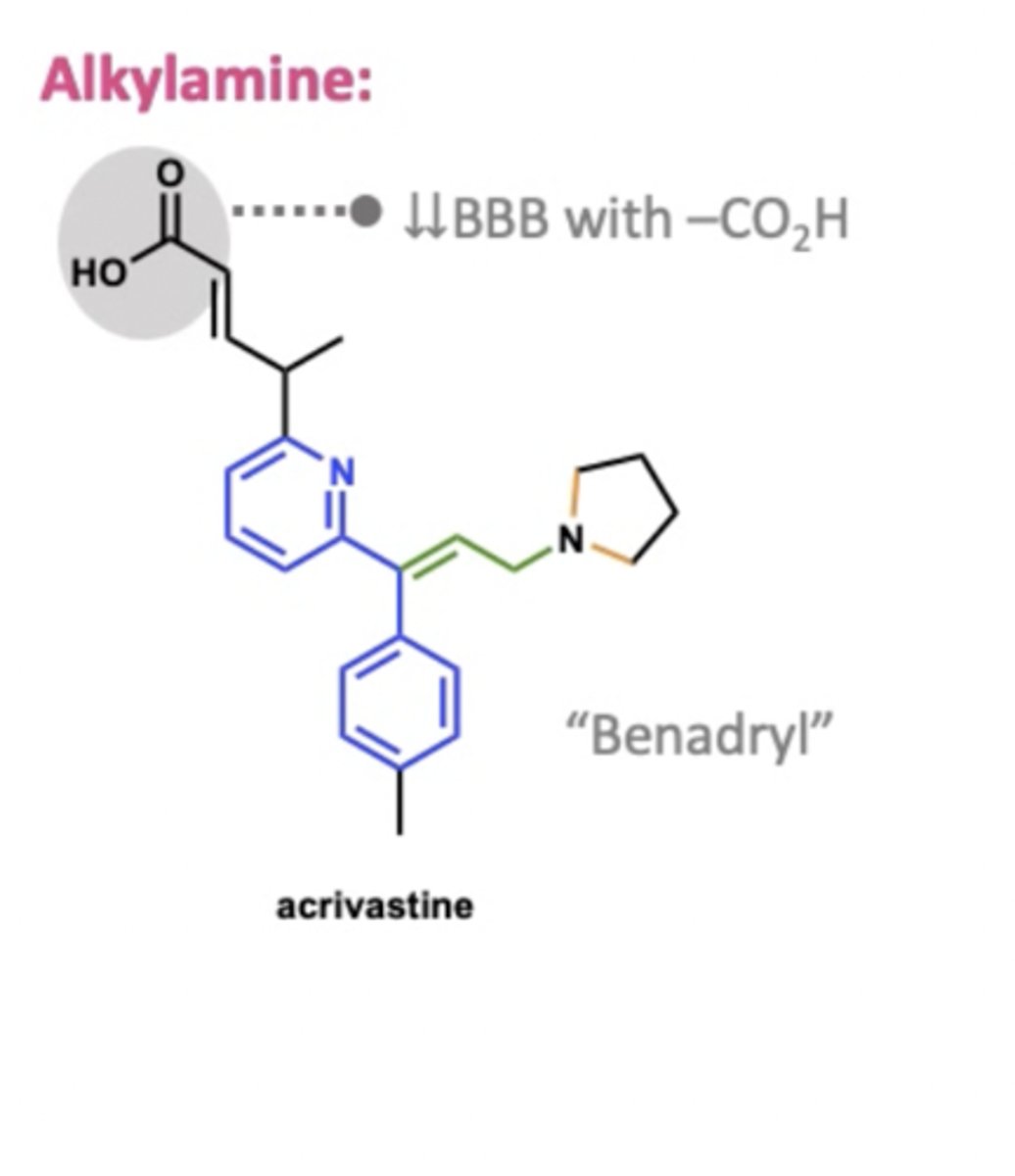
Why do 2nd gen anti-histamines work in the periphery (not in the brain)? (relate to structure)
They have an additional negative polar group like a carboxylate that prevents it from passing through blood brain barrier.
What is an antihistamine for asthma and what is the dosage?
Fexofenadine, up to 240mg daily