programming fundamentals
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
what’s needed to create an algorithm
To create an algorithm, the inputs, processes and outputs must be identified
What is an input?
An input is data or information being entered/taken into a program before it is processed in the algorithm
An input can come from a variety of sources, such as:
User - keyboard, mouse, controller, microphone
Sensors - temperature, pressure, movement
what’s a process
A process is a doing action performed in the algorithm that transforms inputs into the desired output. The central processing unit (CPU) executes the instructions that define the process
examples of process
Comparing two numbers
Calculating an average
What is an output?
An output is the result of the processing in an algorithm and usually the way a user can see if an algorithm works as intended
what are some forms of an output?
An output can take various forms, such as:
Numbers - result of calculations
Text
Images
Actions - triggering events
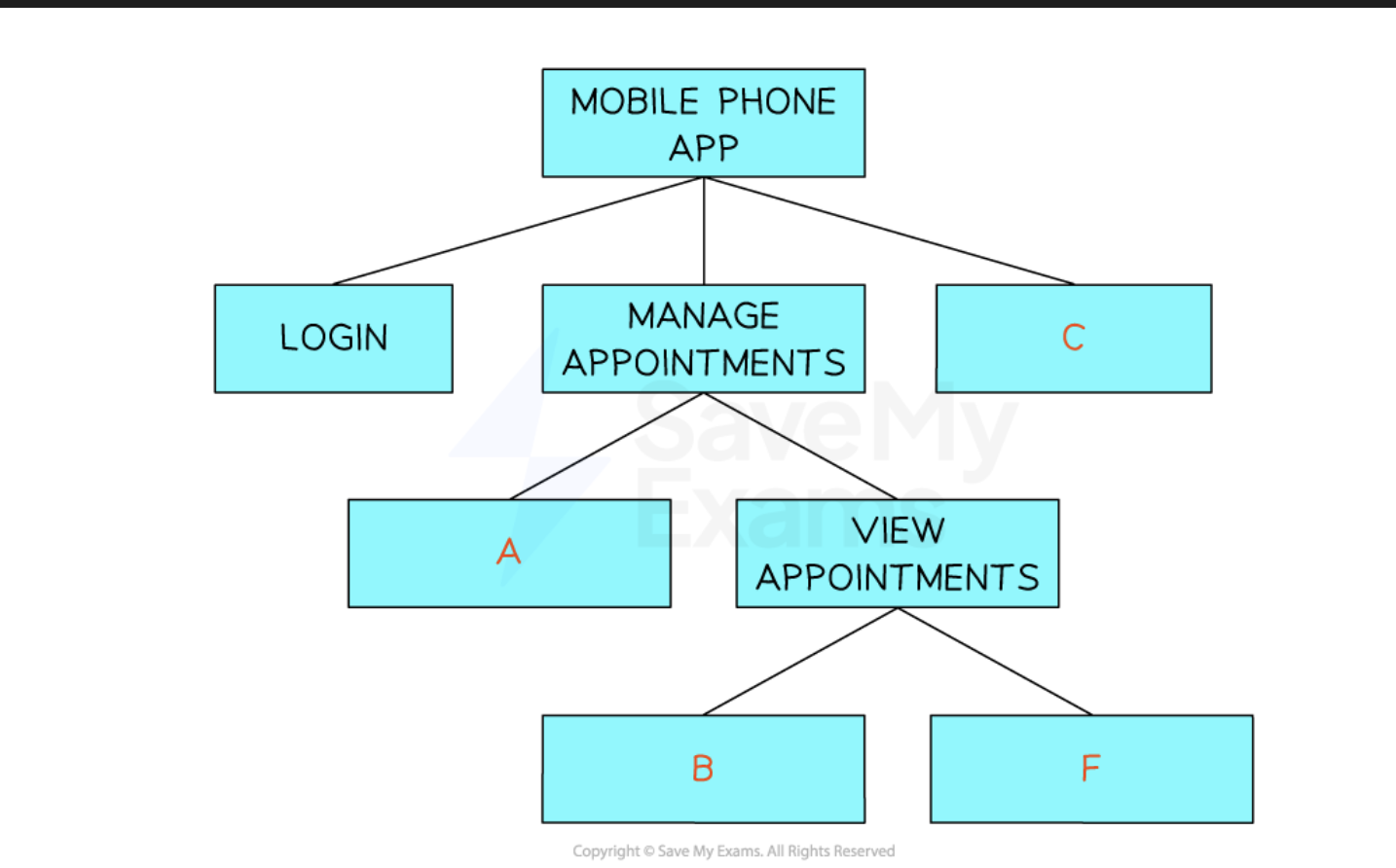
what is a structure diagram?
A structure diagram is a visual representation of problem decomposition
A tool to show how a complex problem can be broken down into more manageable sub problems
A planning tool for developers during the analysis of a problem
symbol for start or end in a flowchart

input/output symbol

process symbol
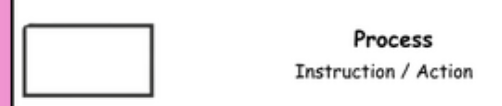
decision symbol

what is a syntax error
A syntax error is an error that breaks the grammatical rules of a programming language and stops it from running
Examples of syntax errors are:
Typos and spelling errors
Missing or extra brackets or quotes
Misplaced or missing semicolons
Invalid variable or function names
Incorrect use of operators
Incorrectly nested loops & blocks of code
What is a logic error?
A logic error is where the program runs/executes but produces an unexpected or undesired output
They do not perform what the programmer intended
Logic errors can be difficult to identify by the person who wrote the program, so one method of finding them is to use 'Trace Tables'
Examples of logic errors are:
Incorrect use of operators (< and >)
Logical operator confusion (AND for OR)
Looping one extra time
what’s a variable
A variable is a named memory location that holds data that during the execution of a program, the data can change
Variables can store a variety of different types of data such as numbers, text or true/false values
What is a constant?
A constant is fixed data that during the execution of a program cannot change
A constant can store a variety of different types of data, similar to variables
what is assignment?
Assignment is the process of storing data in a variable or constant under a descriptive name
What is an operator?
An operator is a symbol used to instruct a computer to perform a specific operation on one or more values
Examples of common operators include:
Arithmetic
Comparison
Boolean (AND, OR and NOT)
What is an input?
An input is a value that is read from an input device and then processed by a computer program
Typical input devices include:
Keyboards - Typing text
Mice - Selecting item, clicking buttons
what’s an output
An output is a value sent to an output device from a computer program
Typical output devices include:
Monitor - Displaying text, images or graphics
Speaker - Playing audio
What is sequence?
Sequence refers to lines of code which are run one line at a time
The lines of code are run in the order that they written from the first line of code to the last line of code
Sequence is crucial to the flow of a program, any instructions out of sequence can lead to unexpected behaviour or errors
What is selection?
Selection is when the flow of a program is changed, depending on a set of conditions
The outcome of this condition will then determine which lines or block of code is run next
Selection is used for validation, calculation and making sense of a user's choices
EG. if... then... else... statements - this is when you test conditions sequentially
What is iteration?
Iteration is repeating a line or a block of code using a loop
Iteration can be:
count controlled - this is when the code is repeated a fixed number of times (e.g. using a for loop)
what are the 4 datatypes
integer : whole number
float : unwhole number
string : letters
boolean : true/false
What is casting?
Casting is when you convert one data type to another data type
string manipulation ?
String manipulation is the use of programming techniques to modify analyse or extract information from a string
What is case conversion?
Case conversion is the ability to change a string from one case to another e.g. lowercase