develop 4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 9:27 PM on 4/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
1
New cards
understanding family as system
Parents influence children but children also influence parents (Reciprocal relationships)
constantly evolving- due to cognitive capacities changing (e.g Parents realizing how completed most of their life is and stressing)
It is complex social system, and you have to look at family the same way a doctor looks at a body- by taking everything that could be affecting it into account
affected by community and culture
Parents influence children directly and indirectly
constantly evolving- due to cognitive capacities changing (e.g Parents realizing how completed most of their life is and stressing)
It is complex social system, and you have to look at family the same way a doctor looks at a body- by taking everything that could be affecting it into account
affected by community and culture
Parents influence children directly and indirectly
2
New cards
Parents directly influence
Physical violent= future violent adults
3
New cards
Parents indirectly influence
watching parents fight= how the children believe a marriage should be
4
New cards
Goal of parenting
Socialization
Long term goal : internalization of self-control or conscience
Long term goal : internalization of self-control or conscience
5
New cards
Socialization
Process by which children acquire the beliefs, values, and behaviors needed to be competent members of groups and their society.
6
New cards
What are the dimensions of parenting
Warmth
Control
Control
7
New cards
no
Is it possible to go overboard with the warmth dimension
8
New cards
Warmth (acceptance-responsiveness)
How warm you are as parents.
Positive reinforcement
Responsiveness
Expression of positive regard
Positive reinforcement
Responsiveness
Expression of positive regard
9
New cards
Positive reinforcement
“You did well, so I will verbally tell you”
\-NOT GIFT GIVING
\-NOT GIFT GIVING
10
New cards
Responsiveness
Helping them solve problems in a developmental way.
“What do you need, I will work with you, but not for you”
“What do you need, I will work with you, but not for you”
11
New cards
Expression of positive emotion
“ I don’t just love you because you did so well on the Exam, I’d love you this much regardless.”
12
New cards
Why aren’t parents warm towards their children
They weren’t raised with warm parents themselves
parents suffering from depression
also thinking that not being warm will toughen them up
parents suffering from depression
also thinking that not being warm will toughen them up
13
New cards
Control (demandingness)
Setting high standards, training children to meet them.
consistent enforcement of rules
open communication- showing kids respect
situation management- don’t put them in a situation where can cause an undesired actions
No power assertion
consistent enforcement of rules
open communication- showing kids respect
situation management- don’t put them in a situation where can cause an undesired actions
No power assertion
14
New cards
Power assertion
Corporal punishment, which is physical punishment, is known as _______ _______
15
New cards
Convention on the rights of the child 1989
to protect children from neglect
provide health care
protect children from abuse
provide health care
protect children from abuse
16
New cards
Development consequences of spanking
the brain does not develop
leads to aggressive behavior
verbal abuse causes stress and health problems
slower learning and less vocab
leads to aggressive behavior
verbal abuse causes stress and health problems
slower learning and less vocab
17
New cards
How parents should discipline children
Try to reward good behavior
time out (as many minutes they are as old)
praise them for being good
explain why a behavior isn’t valued
time out (as many minutes they are as old)
praise them for being good
explain why a behavior isn’t valued
18
New cards
“I was spanked but turned out fine”
It can still be harmful, like how when they use to not have car seats
19
New cards
why is spanking ineffective
teaching them to not get caught rather than not doing it
doesn’t socialize children to have a conscious
teaches children that violence is expectable
modeling: we model behavior.
doesn’t socialize children to have a conscious
teaches children that violence is expectable
modeling: we model behavior.
20
New cards
Parenting styles
Authoritarian
Authoritative
Permissive
Neglectful
Authoritative
Permissive
Neglectful
21
New cards
Authoritarian
Low on warmth and high on control
22
New cards
Authoritative
High in warmth and High in Control
23
New cards
Permissive
high in warmth and low in control
24
New cards
Neglectful
low in warmth and control
25
New cards
Authoritarian outcome
Average academic performance and social skills, conforming. Lower self control
26
New cards
Authoritative outcomes
High self-esteem, academic achievement, social skills, and moral/prosocial concern
27
New cards
permissive outcomes
Poor self-control, academic achievements are poor, more drug use
28
New cards
Neglectful outcomes
Aggressive, selfish, rebellious, more prone to deviant acts (probably for attention)
29
New cards
some factors that influence parenting style
Family stress
Culture and ethnicity
gender isn’t one though
Culture and ethnicity
gender isn’t one though
30
New cards
Family stress model
Economic harships or family economic pressure
= Low income, instable employment, many depts, jobloss
poor families tend to be more authoritarian, controlling style
socialization goal obedience
= Low income, instable employment, many depts, jobloss
poor families tend to be more authoritarian, controlling style
socialization goal obedience
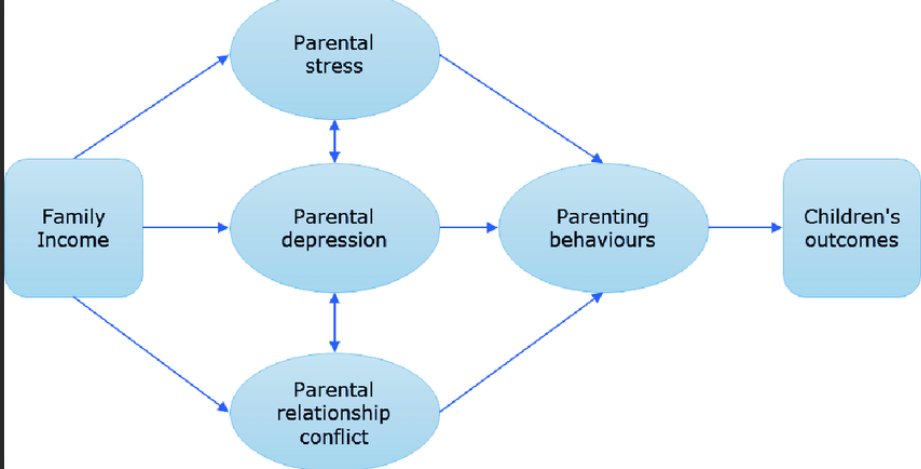
31
New cards
Culture and ethnicity
Authoritative reflects middle class white values
applicable to WEIRD cultures
Authoritative more prevalent European American
applicable to WEIRD cultures
Authoritative more prevalent European American
32
New cards
Asian American parents
Authoritarian, but white people consider them harsh
prenatal desire for obedience= parental concern
“chiao shun”- be moral and respect elders. “guan” to govern (positive)
prenatal desire for obedience= parental concern
“chiao shun”- be moral and respect elders. “guan” to govern (positive)
33
New cards
Emotional expressions
____________ __ Varies by culture. For example weird people are emotional.
34
New cards
School success
\---------- ------- is of great importance because it shows parental investment
35
New cards
Always
Authoritative ------ Associated with positive outcomes (in America)
36
New cards
Authoritarian
Being -------- is more detrimental to EA (white kids)
37
New cards
Mothers are more sensitive?
If they are, it is due to stereotype
No evidence sex chromosome= parenting genes
Mothers do have more time and care for child
No evidence sex chromosome= parenting genes
Mothers do have more time and care for child
38
New cards
Sexual orientation
\------ ------ is not determined by a parent being gay or straight
39
New cards
Golombok and colleagues
Measures: survey’s, observations
parenting: warmth, sensitivity, discipline
child outcomes: externalizing issues, hyperactivity, aggressive behavior
Results: Gay fathers more sensitive and responsive
Gay fathers- less stress, more responsive
anyone can be a good parent
parenting: warmth, sensitivity, discipline
child outcomes: externalizing issues, hyperactivity, aggressive behavior
Results: Gay fathers more sensitive and responsive
Gay fathers- less stress, more responsive
anyone can be a good parent
40
New cards
Short term consequences of divorce
Period of crisis and reorganization
Conduct (Acting out, potty accidents) and relationship with father
School achievements, psychological adjustment, self concept, and go down
Peer relationships not harmed
Conduct (Acting out, potty accidents) and relationship with father
School achievements, psychological adjustment, self concept, and go down
Peer relationships not harmed
41
New cards
Why there is relationship problems with dad after divorce
Usually, mom get the custody, and the dads try to be “cool” and passive and get the kids what ever they want. the mother could be seen as the bad guy
42
New cards
long term consequences of divorce on development
Relationship with mother improves
grades look better and kids go back to how it was
relationship with father improve dramatically over time
poor academic adjustment, psychological, and social norms
grades look better and kids go back to how it was
relationship with father improve dramatically over time
poor academic adjustment, psychological, and social norms
43
New cards
Theories of the impact of divorce
Parental absence causes child to loose emotional and practical support
Economic hardship
Family conflict
Economic hardship
Family conflict
44
New cards
factors associated with impact of divorce
Childs age
child’s gender doesn’t matter
custody
coping strategies
child’s gender doesn’t matter
custody
coping strategies
45
New cards
infant during divorce
they don’t understand/ don’t remember
46
New cards
Child during divorce
sensitive time understanding divorce, might think it is their fault or doesn’t understand why their parent would do this
47
New cards
Adolescents during divorce
They have perspective skills and can realize this divorce has nothing to do with them
48
New cards
Emerging adult during divorce
they are living on their own, so divorce it doesn’t affect them
49
New cards
impact of remarriage on development
Having a parent who isn’t related to them can disrupt the development
50
New cards
age for problems with remarriage
early adolescents (12-13 years) Because of hormonal changes, and it is awkward for them to think about their parent - usually having sex. could also be because they want autonomy and new parent isn’t giving it
51
New cards
tips for step fathers
step lightly
be interested but don’t interfere with established routines
once you’ve established they can trust you, you can make rules
be interested but don’t interfere with established routines
once you’ve established they can trust you, you can make rules
52
New cards
Girls vs. Boys with step father
Boys benefit vs. girls view stepfathers as a threat to relationship with mother
53
New cards
Father-stepmother families
Less common
mother who doesn’t have custody is till seen very often
mothers would also feel like they are getting replaced.
mother who doesn’t have custody is till seen very often
mothers would also feel like they are getting replaced.
54
New cards
Emergence of crowds
Reputation based entities; Stereotypes.
you can be in more than one
1/3 of kids might not fit but 2/3 do
Appearance; activities
they do not have to be friends
Example's (jock, nerds, druggies)
Prestige
socioeconomic status
you can be in more than one
1/3 of kids might not fit but 2/3 do
Appearance; activities
they do not have to be friends
Example's (jock, nerds, druggies)
Prestige
socioeconomic status
55
New cards
Prestige
You might be in a more powerful position if you are in a more prestigious crowd
56
New cards
Status vs. likability
how popular someone is vs. how well liked someone is
57
New cards
consequences of high status
pretty bad long term effects because it is hard for them to understand what worked for them in high school won’t work anywhere else
addictions and bad marriages
addictions and bad marriages
58
New cards
Cliques
Smaller group (2 to 12)
interaction needed
similar interests and characteristics
the have to share at least 3 same values
interaction needed
similar interests and characteristics
the have to share at least 3 same values
59
New cards
Cliques and crowds as we get older
Childhood: same gendered cliques
Middle school: Crowds
High school: crowds gone, couple emerges
Adulthood: Couple becomes more important social unit
Middle school: Crowds
High school: crowds gone, couple emerges
Adulthood: Couple becomes more important social unit
60
New cards
Girls
\---- Are more likely to be in a clique
61
New cards
Cliques
\----- impact on development:
social skills like intimacy, listening, and conflict resolution
social skills like intimacy, listening, and conflict resolution
62
New cards
What is popularity
Perceived/ reputed popularity
real popularity/ sociometric status
real popularity/ sociometric status
63
New cards
Perceived/reputed popularity
Crowds membership, social prestige (status)
64
New cards
Real popularity/Sociometric status
Liked by a lot of peers
social preference
(likability)
social preference
(likability)
65
New cards
self report measure
Name three people you like the most and 3 you like the least.
has two dimensions:
Peer acceptance and Impact/visibility
has two dimensions:
Peer acceptance and Impact/visibility
66
New cards
Peer acceptance
When doing the self report measure, it is the difference between positive and negative nominations
67
New cards
Impact/visibility
When doing the self report measure, it is the adding of positive and negative total nominations
68
New cards
Sociometric status groups
Popular
average
controversial (Many people like them, but many don’t)
rejected (unpopular)
neglected (unpopular, not many nominations but if they get them, their negative)
average
controversial (Many people like them, but many don’t)
rejected (unpopular)
neglected (unpopular, not many nominations but if they get them, their negative)
69
New cards
Popular/average
Characteristics of ------
intelligence, adherence to adult norms, nonjudgmental, and attractiveness is also important
better friendships, adhere to adults social norms. they become financially stable, relationship success
intelligence, adherence to adult norms, nonjudgmental, and attractiveness is also important
better friendships, adhere to adults social norms. they become financially stable, relationship success
70
New cards
Unpopular
characteristics of ------
aggression, withdrawn, or both
hostile attribution bias (they will see everything that is ambiguous as hostile
aggression, withdrawn, or both
hostile attribution bias (they will see everything that is ambiguous as hostile
71
New cards
Rejected vs. neglected
Externalizing problems vs. internalizing problems
72
New cards
Relation aggression
Deliberately damage and manipulate another’s social relationships and social standing.
73
New cards
Piaget
---- view on the importance of friendships for development
Believed that the people you should learn the most from should be from people equal to you.
Behavioral and cognitive equals
important for conflict resolution
Believed that the people you should learn the most from should be from people equal to you.
Behavioral and cognitive equals
important for conflict resolution
74
New cards
Sullivan
---- view on the importance of friendships for development
very Freudian
believed that at different ages we have to have different relationships for self-development
believed in chumship (same age and gender)
important for validation and emotional intimacy
\
believed that all of this results in a healthy sense of self and self esteem
very Freudian
believed that at different ages we have to have different relationships for self-development
believed in chumship (same age and gender)
important for validation and emotional intimacy
\
believed that all of this results in a healthy sense of self and self esteem
75
New cards
Harris
\---- view on the importance of friendships for development
Friends = primary socializing agents
good enough parents
Friends = primary socializing agents
good enough parents
76
New cards
what a friend is
Companion
prosocial behavior
(relative) Absence of conflicts
age difference- concrete vs.. abstract. “We are friends because she like purple like I do vs. she cares about what I have to say and listens”
prosocial behavior
(relative) Absence of conflicts
age difference- concrete vs.. abstract. “We are friends because she like purple like I do vs. she cares about what I have to say and listens”
77
New cards
Childhood and adolescence
During ---- ---- competition/ rivalry are common in childhood because they see their friends as their equal unlike their parents and uses them to gage where they are level wise.
78
New cards
Resolving conflict when younger
More common to Forget about it, renew the friendship, apologizing.
they rarely talk it out, adults compromise
they rarely talk it out, adults compromise
79
New cards
intimacy
\----- is not a characteristic part of friendship
children prefer parents to share their secrets with because little kids are not good at psychologically complex things, like Sullivan says.
children prefer parents to share their secrets with because little kids are not good at psychologically complex things, like Sullivan says.
80
New cards
Narr and colleagues
asked do close friends in adolescence lead to better emotional health in adulthood or is high status more important
method: 15 years old; longitudinal
measures: close friendships (intimacy)
results: Friendship is the most important so they will do better in life and have less social anxiety
method: 15 years old; longitudinal
measures: close friendships (intimacy)
results: Friendship is the most important so they will do better in life and have less social anxiety
81
New cards
Sullivans theory
Intimate friendship= good romantic relationship
positive connection
in early adolescence, boy’s and girl’s friendship are similar in their intimacy
Research: boys don’t have a best friend they just have friends at 15, this is also the time we see suicide
positive connection
in early adolescence, boy’s and girl’s friendship are similar in their intimacy
Research: boys don’t have a best friend they just have friends at 15, this is also the time we see suicide
82
New cards
Socialization
In other countries, men are very intimate with each other and it is not considered a bad thing. This is because of their -------
83
New cards
implications of men not having close friends
20% of men struggling with loneliness, increased risk or early death as well as cardiovascular disease, stroke, and progression of Alzheimer’s
26%-32% increased risk of premature death
26%-32% increased risk of premature death
84
New cards
boys reason for Non close relationships
Betrayal; distrust; maturity
85
New cards
Girls, boys
Stereotype that adolescent---- care more than ---- about being rejected by a friend is accurate
86
New cards
integrating friendships for girls
very trusting with secrets so does not like big group of friends
87
New cards
Rejection and jealousy for girls
Much more upset about bailing on plans
also have a harder time merging new people into the group.
also have a harder time merging new people into the group.
88
New cards
girls
\----- Interact more often with single friend- too many knowing your secrets aren’t good
89
New cards
little
is it a big or little difference in how girls and boys stability in friendships as well as other friendship features?
90
New cards
Teenagers; Young adults; adults
\----- and --- --- have considerably more friends than --- do.
91
New cards
Friendship in adulthood
Social networks shrink- because teens have fewer responsibilities and more time.
92
New cards
social networks
\------ ----- help you find yourself
93
New cards
Sociometric selectivity theory
make better choices who can meet emotional needs
quality over quantity in friends as you get older
quality over quantity in friends as you get older
94
New cards
consequences of friendship in development
higher self-esteem, more cooperative, handle life stresses
95
New cards
older adult and friendship
social support
they are less likely to get sick
they are less likely to get sick
96
New cards
sex
biological difference
97
New cards
gender
social construction
98
New cards
gender binary
there is two sides, and it’s one or the other
99
New cards
gender nonbinary
when you do not identify as the two sides
100
New cards
gender stereotypes
Beliefs about how males and females differ in personality traits interests and behaviors