Labor and Delivery: First Half
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
cervical, irregular, bloody, contractions
Labor: Definitions
-Labor → regular uterine contractions with _______ changes
-Prodromal or “false” labor → ________ contractions and no cervical change
-Other potential signs of labor → maternal discomfort, ______ show, nausea/vomiting, and palpable ____________
childbirth, labor, baby, placenta, recovery
Phases of Parturition
-Parturition → __________, broken up into 3 phases
-Phase 0 → prelude to parturition, aka pregnancy
-Phase 1 → preparation for _____, aka late pregnancy
-Phase 2 → process of labor, broken into 3 stages
Stage 1 → labor, broken down into early/latent and active labor
Stage 2 → delivery of ____
Stage 3 → delivery of _________
-Phase 3 → parturition ________, aka postpartum
inactivity, conception, relaxes, progesterone
Phase 0: Prelude to Parturition
-Uterine quiescence → ________
-From ___________ to initiation of parturition
-Uterine smooth muscle ________, unresponsive to stimuli
-Myometrial contractility is suspended
-Mediators → __________, prostacycline, relaxin
preparation, ripening, softening, oxytocin, stretch, estrogen
Phase 1: Preparation for Labor
-Activation, from initiation of parturition to onset of labor
-Uterine __________ for labor
-Cervical ___________ → changes in extracellular matrix/cervical collagen leads to ___________
-Mediators → prostaglandin synthesis, _________ receptor expression, gap junction receptors in myometrium, uterine _______, and _________/progesterone
delivery, contractions, expulsion, labor, placenta, oxytocin
Phase 2: Process of Labor
-Stimulation, from onset of labor to _________
-Uterine ____________, cervical dilation, fetal and placental ___________
-Stages of labor → _____, delivery of baby, delivery of ________
-Mediators → fetal cortisol, DHEAS, placental estriol, _________, prostaglandins
shrinkage, fertility, breastfeeding, contractions
Phase 3: Parturient Recovery
-Uterine involution → _________ of the uterus to normal pre-pregnancy size
-From delivery to restoration of ______
-Return to pre-pregnancy physiology and anatomy
-Involution, cervical repair, ____________
-Mediators → oxytocin, which stimulates smooth muscle uterine ____________
opening, internal, shortening, ischial spine, posterior
Cervical Exam
-Dilation → _______ of cervix, specifically ________ os (0-10 cm)
-Effacement → __________/thinning of cervix (0-100%)
-Station → location of presenting part in relation to _______ _______ (-5 to 5+)
-Consistency → firm, medium, soft
-Position → ________, mid, anterior
favorable, higher, successful, effacement, predictive, 6, induction, ultrasound
Bishop Score
-Indicates how ________ the cervix is
-Higher the number, _________ the chance of a ___________ vaginal delivery
-Used to take dilation, effacement, station, consistency, and position into account. Now often just use dilation, _____________, and station only
These are the most _________ factors
-<5 points = cervix unfavorable → use ripening agents
- >6 points = cervix favorable → proceed with _____________
-Cervical length by ____________ can also supplement or replace effacement in some practices
regular, 6, slow, induced, 10, intense, rapid, oxytocin
Stage 1: Labor
-Phase 1 → Early/latent labor
_________ contractions until _ cm cervical dilation
____ cervical dilation / longest stage
Longer in _________ labors compared to spontaneous; longer in obese patients
-Phase 2 → Active labor
6 cm to __ cm dilation (complete)
More frequent/________ contractions and rapid cervical dilation
Primipara = 1.2 cm/hr and multipara 1.5 cm/hr
Similar between induced and spontaneous labor
-May consider augmentation with __________ or membrane rupture
pushing, pushing, delivery, anesthesia
Stage 2: Pushing and Delivery
-Fully dilated and ________, completed with delivery of baby
-2 phases
Passive → complete dilation until patient begins ________
Active → beginning of maternal pushing to ________
-Length affected by parity and regional ____________
after, placenta, 30, oxytocin, fundal, lengthening, blood, rebound
Stage 3: Delivery of Placenta
-Begins ______ delivery of baby, and completed with delivery of _________
-Usually 5-10 minutes, up to __ minutes is normal
Try manual extraction after 30 minutes
-________ infusion to help uterus contract
-______ massage
-Signs of placental separation → cord ________, gush of ______, and uterine fundal _________
involution, vitals, hemorrhage
Initial Hours Postpartum
-First 1-2 hours after delivery
-Uterine _________ begins
-Monitor maternal _______ signs
-Monitor for postpartum ____________
pelvis, engaged
Cardinal Movements of Fetus: Engagement (1)
-Fetal presenting part enters the ______ and becomes __________
-”Lightening” or “dropping”
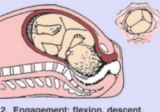
descent, head, pelvis, contraction
Cardinal Movements: Descent (2)
-________ of the vertex will occur as fetal _____ passes down into the ______
-Influenced by shape of maternal pelvis and uterine ____________ strength
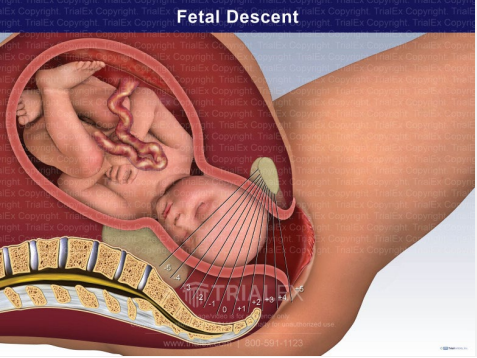
flexion, smallest
Cardinal Movements: Flexion (3)
-Head undergoes _______ which allows ____________ diameter to present into the pelvis
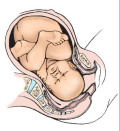
internal, sagittal, anteroposterior, pelvis
Cardinal Movements: Internal Rotation
-Upon descent into the midpelvis, the fetal vertex undergoes ________ rotation from a transverse position so that the ________ suture is parallel to the ______________ diameter of the pelvis (OA or OP)
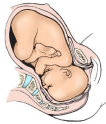
beneath, pubic, deliver
Cardinal Movements: Extension
-As the vertex passes _________ and beyond the _____ symphysis, it will extend to _______
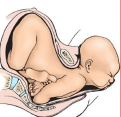
head, external, shoulders, body
Cardinal Movements: External Rotation
-Once the ____ delivers, _________ rotation by which the head turns back to prior transverse position occurs and the __________ may be delivered followed by fetal ____
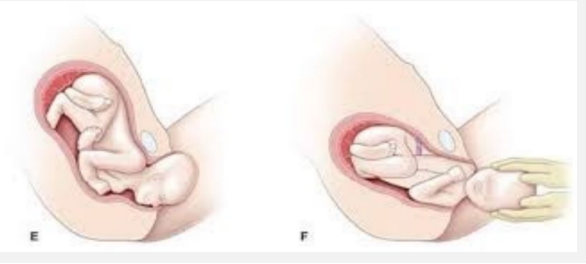
perineum, flex, anterior, body
Normal Spontaneous Vaginal Delivery
-As fetal head is crowning, place one hand on the __________ to protect it
-Other hand is used to ____ head and keep it from extending too far
-Followed by delivery of ________ shoulder, posterior shoulder, and fetal ____
non-laboring, membrane, ripening, mechanical, oxytocin
Induction of Labor: Background
-Attempt to commence labor in a ___-_________ patient
-Methods
__________ stripping/sweep
Prostaglandins → misoprostol and cervidil, which are cervical ________ agents that reduce overall length of induction
Foley balloon for __________ dilation
Laminaria
___________
Artificial rupture of membranes
diabetes, hypertension, age, demise, PROM
Indications for Induction of Labor
-Elective/Term → 39 to 39+6 weeks preferred time frame
-Post-term pregnancy
-Pre-gestational/gestational _________
-Chronic ____________ or pregnancy-induced hypertension
-Advanced maternal ___
-Poor fetal tracing
-Intrauterine fetal ________
-Intrauterine growth restriction/placental insufficiency
-Prelabor rupture of membranes (____)
-Oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios
-Cholestasis
-Chorioamniotis
malpresentation, breech, herpes, cesarean, myomectomy
Contraindications for Induction of Labor
-Fetal ______________ or cephalic disproportion → _____, transverse, funic
-Placenta previa/vasa previa
-Active genital _______ outbreak
-History of uterine scar
2 or more prior low transverse __________ deliveries
Prior classic cesarean delivery
Prior ___________ for removal of uterine fibroid
advance, strength, oxytocin, slower, cessation, coupled
Labor Augmentation
-Help labor ________ and move along
-Increase contraction frequency/________
-Methods
Ambulation
________ → considered as a treatment for protraction disorders, which is when labor progresses _______ than normal. Arrest disorders are a complete ___________ of progress
-Amniotomy/artificial rupture of membranes → more beneficial when _______ with oxytocin
fluid, pooling, infection, pH, basic, acidic, ferning
Rupture of Membranes: Diagnosis
-History and Physical Exam
History of gush or persistent ____ leaking
Sterile speculum exam → may see pooling
Digital cervical exam → limit frequency to reduce _________
__ test of vaginal fluid → amniotic fluid is _____, while vaginal fluid is ______
________ test → look at fluid under microscope, let dry, see “ferning”
Ultrasound for AFI
Tampon test
prelabor, preterm, age, infection, induce
Prelabor Rupture of Membranes: PROM
-_______ Rupture of Membranes
PROM → at term
PPROM → _______ (<37 weeks)
Periviable PROM → < 24 weeks
-Management influenced by gestational ___ and presence of complicating factors (________, placental abruption, labor, abnormal FHR)
PROM → if no spontaneous labor, then ______
PPROM → give birth within 1 week
age, strep, infection, abnormal, bleeding, induction, observation
Management of PROM
-Consider gestational ___, fetal presentation, fetal well being, infection
-Collect group beta _____ screen
-Indications for delivery → intra-amniotic _______, ________ fetal testing, vaginal _________
-Most often proceed with _________ of labor
-May consider __________ for 12-24 hours to await spontaneous labor onset
20, 37, late, 33, 32, 28, higher
Preterm Birth
-Delivery occurring at or after __ weeks and before __ weeks
____ preterm infants → between 34 weeks and 36 weeks and 6 days
Moderate preterm infants → between 32 weeks and __ weeks and 6 days
Very preterm infants → <__ weeks
Extremely preterm infants → <__ weeks
-Non-Hispanic Black and Indigenous women have much ______ rates than white/Asian/Hispanic populations
preterm, short, low, multiple, UTI
Preterm Birth Risk Factors
-History of _______ birth/PPROM
-_____ cervix
-____ maternal pre-pregnancy weight
BMI < 18.5
-Tobacco use
-Substance use
-Short inter-pregnancy interval
-________ gestation
-Vaginal bleeding
-___/genital tract infections
age, abnormal, antibiotics, steroids, magnesium sulfate, steroids
Management of PPROM
-Plan is very dependent on gestational ___
-Deliver if _______ fetal testing, infection, or placental abruption
-Try to manage expectantly if before 34 weeks
Latency _______
_______ for fetal lung maturity
Collect GBS
Treat intra-amniotic infection is present
__________ _______ for neuroprotection if < 32 weeks
Periodic non stress tests and growth ultrasounds
-If 34-36 weeks, expectant management vs delivery
______ for fetal lung maturity/decrease respiratory morbidity
prolongs, infections, ampicillin, amoxicillin
Latency Antibiotics for PPROM
-_______ pregnancy
-Reduces maternal/neonatal __________
-Reduces gestational age dependent morbidity
-If less than 34 weeks → 7 day course of IV _______ + erythromycin x 48 hours followed by PO ________ and erythromycin or azithromycin
length, 2, progesterone, shortening, cerclage
Managing Patient with a History of Preterm Birth
-Serial cervical _______ screening every _ weeks from 16-24 weeks
-Offer ___________ supplementation if cervical __________ noted
Endometrin → vaginal progesterone
-Consider cervical ________
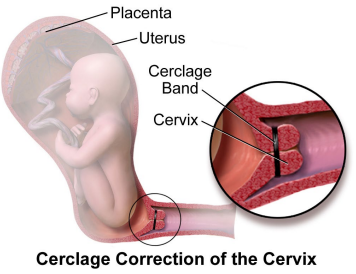
fibronectin, endometrium, increased, TVUS, hydration, nifedipine, steroids, admit
Concern for Patient with Threatened Preterm Labor
-History and physical
-Speculum and pelvic exam
Fetal _________ sampling → fetal fibronectin is a protein made during pregnancy that is found between the ________ and amniotic sac. Positive testing indicates an _________ risk of premature labor
-____ for cervix length
-Continuous electronic fetal monitoring
-Ensure adequate ___________
-Consider tocolytics such as _______ or terbutaline
-Consider _______ for fetal lung maturity
-Observe or _____ if persistent UCs or cervical change
-Inform NICU
death, breathing, sepsis, jaundice, increased
Complications for Preterm Baby
-Increased risk of morbidity and _____ throughout childhood, especially during 1st year of life
-Anemia
-_________ problems → apnea of prematurity, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, respiratory distress syndrome
-Infections or neonatal _____
-Newborn ________
-Intraventricular hemorrhage
-PDA
-Necrotizing enterocolitis
-Retinopathy of prematurity
-___________ risk developmental challenges
nulliparous, cesarean, slower, active, cessation, 6, contractions
Abnormal Labor Patterns
-Affects ~20% of all labors ending in live birth
-Highest risk in term _____________ patient
-Most common reason for primary intrapartum _________ delivery
-Protraction disorders → ______ than normal progress or abnormally long ______ phase
-Arrest disorders → complete ________ of progress or descent
Cervix > _ and ruptured membranes
No change > 4 hours with adequate ____________
No change > 6 hours with inadequate contractions
pelvic, fetal, malposition, uterine, strong, effort, anesthesia
Abnormal Labor Pattern Risk Factors
-Also called “labor dystocia”
-Passage → _____ dystocia
Abnormally shaped pelvis
Cephalopelvic disproportion
Inadequate pelvis
-Passenger → _____ dystocia
Macrosomia
Fetal malformation or ___________
-Power → _____ dystocia
Contractions are not adequate/______ enough
Poor maternal ______
Neuraxial __________
older, obesity, short, macrosomia
Factors Associated with Protracted Labor
-Uterine Factors (Hypocontractile Uterine Activity)
_____ maternal age, uterine abnormality, maternal ________, neuraxial anesthesia, nulliparity, tocolytics, uterine relaxants, infection
-Pelvic Factors
Contracted pelvis/prominent sacrum, _____ stature, high station at full dilation
-Fetal Factors
Fetal anomaly resulting in CPD, non occiput anterior, LGA/__________
first, strong, coordinated, fetus
Hypocontractile Uterine Activity
-Most common risk factor for protraction/arrest disorder in _____ stage of labor
-Uterine activity not sufficiently _____ or not appropriately ___________ to dilate cervix or expel _____
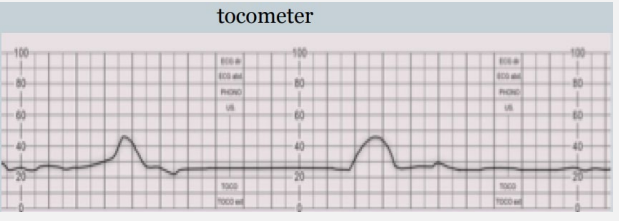
frequent, ret, recover, pitocin, nifedipine
Hypercontractile Uterine Activity
-Tachysystole/Uterine hyperstimulation
-Contractions too _______, > 5/10 minute
-Uterus cannot ____
-Fetus may not have time to ________ between contractions
-Consider decreasing/turning off ______ or give tocolytics such as terbutaline or _______
palpation, pressure, 200
Monitoring Uterine Activity
-Qualitative → _______, external tocodynamometry
-Quantitative → intrauterine _______ catheter (IUPC) to monitor montevideo units
MVUS < ___, not adequate
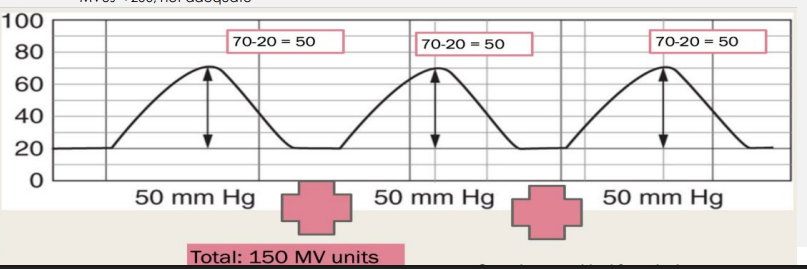
endometritis, hemorrhage, operative, urinary
Maternal Complications of Abnormal Labor
-Infection → chorioamnionitis or __________
-Exhaustion
-Postpartum ___________
-Trauma
Increased risk ________ delivery (vacuum or forceps vs cesarean)
Increased risk of episiotomy
Increased risk of perineal lacerations
-_______ retention
decelerations, variability, NICU, sepsis
Fetal Complications of Abnormal Labor
-Fetal distress
Repetitive late _____________
Bradycardia
Tachycardia
Loss of _________
-Meconium
-Increased risk of admission to _____
-Respiratory distress syndrome
-Neonatal ______