AP Human Geo Unit 3
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
contagious diffusion
involves the rapid spread of cultural traits directly through personal interactions within a population, regardless of social hierarchy
Distance-controlled spreading of an idea through a local population by contact from person to person.
expansion diffusion
The spread of an idea through a population in a way that the number of those influenced becomes continuously larger. Includes contagious, hierarchical, and stimulus diffusion.
Examples include the spread of Roman culture during the expansion of the Roman Empire and the spread of Western culture during British Imperialism.
hierarchical diffusion
a form of diffusion in which ideas or innovations are spread by passing first among the most connected places or people
stimulus diffusion
A form of diffusion in which a cultural adaptation is created as a result of the introduction of a cultural trait from another place. In other words, it is the spreading of an underlying principle of an idea when the idea as a whole cannot spread to a particular culture.
relocation diffusion
A form of diffusion where the ideas being diffused are transmitted by their carriers as they relocate to new areas
diffusion
The spatial spreading of a culture element or phenomenon
acculturation
the process in which individuals or groups from one culture adopt the traits and social patterns of another culture while still retaining some aspects of their original culture.
syncretism
when cultural traits from two distinct cultures fuse to form a new cultural trait
ethnocentrism
a judgmental perspective - judge others and their way of life from the perspective of your own culture
cultural relativism
a non-judgmental perspective - judge others and their way of life through the eyes of the people who live that way
cultural convergence
when two or more cultures influence each other and become similar with increased contact.
cultural divergence
when cultures become less alike over time due to physical and cultural barriers
learned
1 of 6 characteristics/elements of culture
culture is not inherited, not instinctive
universal
1 of 6 characteristics/elements of culture
every human being has a culture
unique
1 of 6 characteristics/elements of culture
no two cultures are exactly alike; vary geographically
integrative
1 of 6 characteristics/elements of culture
cultural traits form a cultural system; a change in one trait influences others
dynamic
1 of 6 characteristics/elements of culture
culture is never static, but some cultures change faster than others
symbolic
1 of 6 characteristics/elements of culture
culture is passed on through generations
popular culture
the set of ideas, practices, beliefs, and objects that are prevalent and widely accepted within mainstream society at a given time
assimilation
the process through which people lose differentiating traits, such as dress, speech patterns, or mannerisms when come into contact with another society or culture
EX:
folk (local) culture
Culture traditionally practiced by a small, homogeneous, rural group living in relative isolation from other groups.
cultural landscape
visible imprint of human activity on landscape
material culture
housing, art, clothing, sports, dances, foods, and other similar items constructed by a group of people
nonmaterial culture
beliefs, practices, aesthetics, and values of a group of people
cultural appropriation
process by which other cultures adopt customs and knowledge and use them for their own benefit
commodification
process through which something that previously was not regarded as an object to be bought or sold becomes an object that can be bought, sold, and traded in the world market
ex: housing
placelessness
loss of uniqueness in the cultural landscape
differences in dialects
spelling
pronunciation
syntax
kurgan theory
proto indo-european diffused from kurgan hearth north of caspian sea about 7000 years ago
horse domestication, acculturation, and warfare helped diffusion of language family from its hearth
anatolian hearth theory
indo-european originated in turkey before the kurgans and diffused through agricultural expansion
caucasus mountains
greatest linguistic fragmentation
between Iran and Russia
lingua franca
2 people(s) with different native languages use a lingua franca to communicate with each other; english is a lingua franca (historically because of british imperialism and literature)
architecture
refers to the art and science of designing and constructing buildings and other physical structures.
artifacts
An object made by human beings; often refers to a primitive tool or other relic from an earlier period
branch (religion)
a large and fundamental division within a religion
denominations
a division of a branch that unites a number of local congregations
sect
a relatively small group that has broken away from an established denomination
adherents
A person who supports a certain religion.
caste system
a division of people into distinct groups based on occupation or lineage
creole or creolized language
A language that results from the mixing of colonial and indigenous languages. One forms grammar and syntax and the other forms vocab. Can have many layers because of multiple conquests. A pidgin language has no native speakers (it is acquired), and a creole language has native speakers and standardized structure.
Haitian creole: French + West African
Bislama: English + Melanesian
cultural trait
individual element that makes up a culture, including beliefs, practices, symbols, and values shared by a group of people
culture
shared beliefs, values, norms, customs, and practices of a group of people, shaping their worldview and lifestyle
the sum total of the knowledge, attitudes, and habitual behavior patterns shared and transmitted by the members of a society
dialect
A regional variety of a language distinguished by syntax, spelling, and pronunciation.
ethnic religion
A religion that is particular to one, culturally distinct, group of people. Unlike universalizing religions, adherents of ethnic religions do not actively seek converts through evangelism or missionary work.
A religion with a rather concentrated distribution whose principles are likely to be based on the physical characteristics of the particular location where its adherents are located. This is important because most religions start off as a Ethnic Religion!
Example: Judaism, hinduism in the Caribbean
ethnicity
common origins with ties to culture, religion, language, or nationality
ethnic neighborhoods
a small area within a large city with a strong clustering of a specific ethnic group in which the people living there have a similar ethnic culture and background. This is referred to as an ethnic enclave and has resulted in the creation of specfic ethnic neighborhoods like Chinatown in San Francisco or Little Havana in Miami.
Relocation Diffusion has helped in the growth of ethnic neighborhoods as many people from the same ethnic background continue to migrate into the specific area of the city, the ethnic neighborhood continues to grow as much of the cultural elements are brought over to ethnic neighborhoods like specific ethnic food, ethnic language, ethnic religion which help to transform the area and welcome new immigrants.
gender
A culture's assumptions about the differences between men and women including their characters and the roles they play in society.
cultural hearth
Heartland, source area, innovation center; place of origin of a major culture.
indigenous language
a language that is native to a particular region or people, often spoken by the original inhabitants of an area
indigenous people
groups of people who have historical ties to a particular territory, often predating colonial or outside influences
language extinction (endangered languages)
Language extinction refers to the process by which a language loses its last native speakers, leading to its total disappearance from use and communication.
Endangered languages are those that are at risk of falling out of use, typically because they have few speakers remaining.
language branch
A collection of languages related through a common ancestor that existed several thousand years ago. Differences are not as extensive or old as with language families, and archaeological evidence can confirm that these derived from the same family.
language family
A collection of languages related to each other through a common ancestor long before recorded history.
language group
A collection of languages within a branch that share a common origin in the relatively recent past and display relatively few differences in grammar and vocabulary.
multiculturalism
the coexistence of diverse cultural groups within a society, promoting the recognition, appreciation, and preservation of different cultural identities
post modern architecture
a style that emerged in the late 20th century as a reaction against modernism's perceived lack of context, uniformity, and ornament
Rejection of modernism: Postmodernism is a direct response to the minimalist, functionalist, and "less is more" principles of modern architecture.
Historical references: It reincorporates elements from various historical styles, such as classical or vernacular, often creating a dialogue between past and present.
Contextualism: This approach considers the existing urban and cultural environment, designing buildings that respond to and connect with their surroundings, materials, and local character.
Complexity and contradiction: Postmodern architecture embraces "both-and" over "either-or," using hybrid elements, and a "messy vitality" rather than obvious unity.
Ornamentation and symbolism: It brings back ornament, color, and playful, sometimes exaggerated, forms, rejecting the severe austerity of modernism.
Eclecticism: Postmodern buildings often juxtapose different styles, materials, and symbols, creating a layered and diverse aesthetic.
pilgrimage
a journey undertaken by individuals to a sacred place or shrine, often for religious reasons
revived language
one that having experienced near or complete extinction as either a spoken or written language, has been intentionally revived and has regained some of its former status
What is the difference between a language family, branch and group?
Family - collection of languages related through a common ancestral language
Branch - collection of languages within a family related through a common ancestral language differences are not as significant or old as families
Group - collection of languages within a branch that share a common origin in the relatively recent past and display similar grammar and vocabulary
What is the largest language family?
Indo-European
What is the Origin of English? (use family, branch and group)
Indo-European
Germanic
West Germanic
secularism
the principle of separating religion from political, social, and educational institutions, promoting a society where religious beliefs do not influence public policy or governance
sense of place
the emotions someone attaches to an area based on their experiences
sequent occupancy
refers to the process by which successive groups of people settle in a particular area, leading to layers of cultural influence and change over time
taboo
a cultural or social prohibition that dictates what behavior, practice, or discussion is considered unacceptable or forbidden within a society
toponym
a name given to a place or geographic feature, often reflecting the culture, history, or characteristics of that location
universalizing religion
Religions that attempt to be global, to appeal to all people, wherever they may live in the world, not just to those of one culture or location.

addis ababa, capital of ethiopia
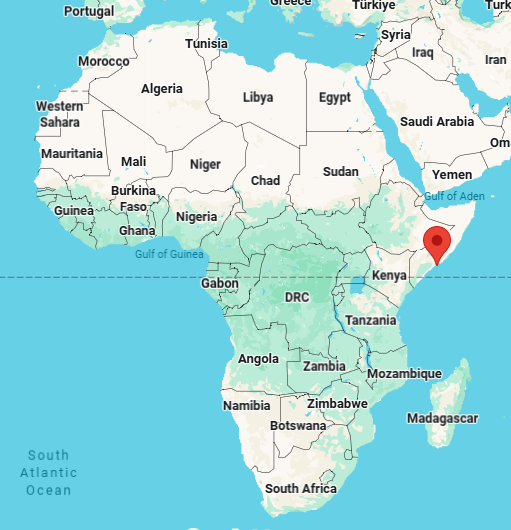
mogadishu, capital of somalia
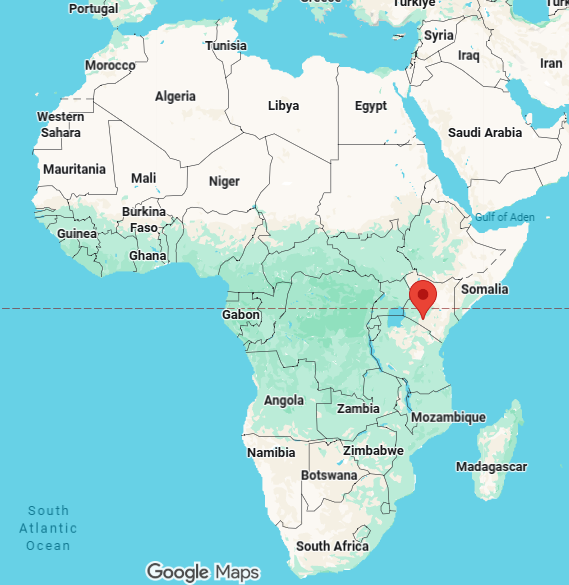
nairobi, capital of kenya
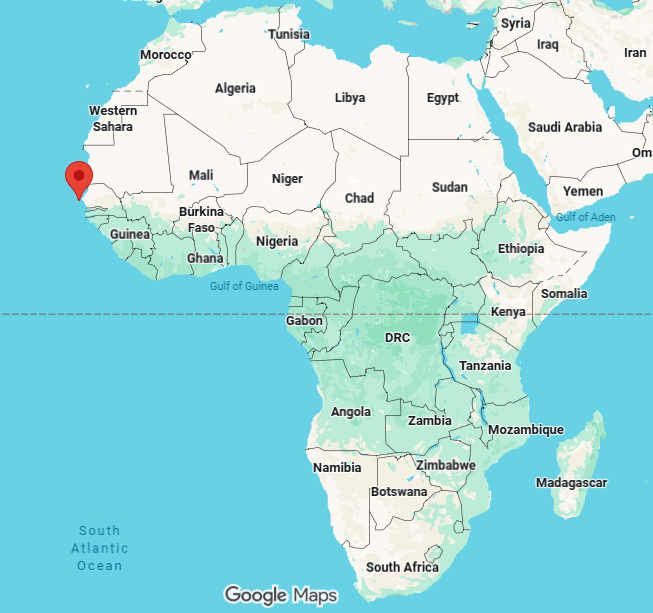
dakar, capital of senegal
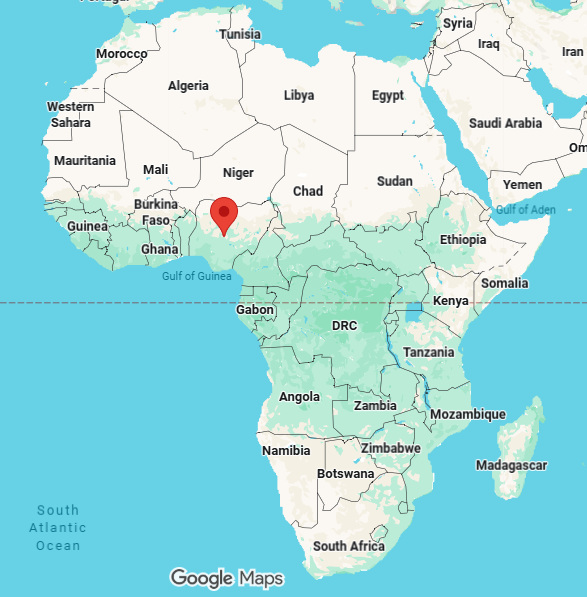
abuja, capital of nigeria
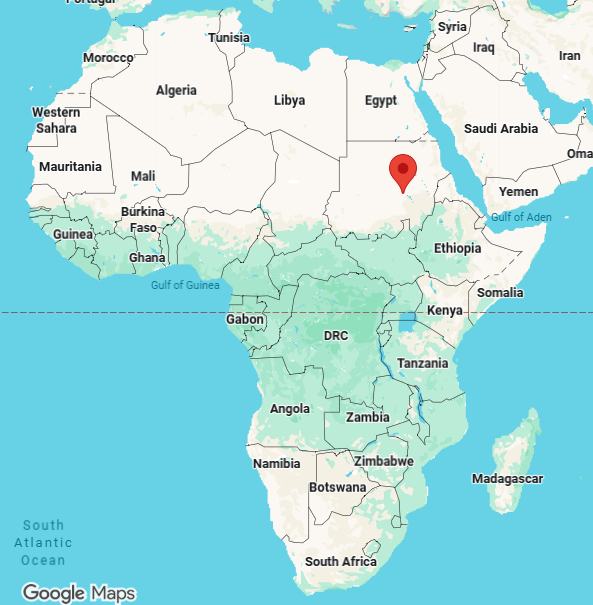
khartoum, capital of sudan
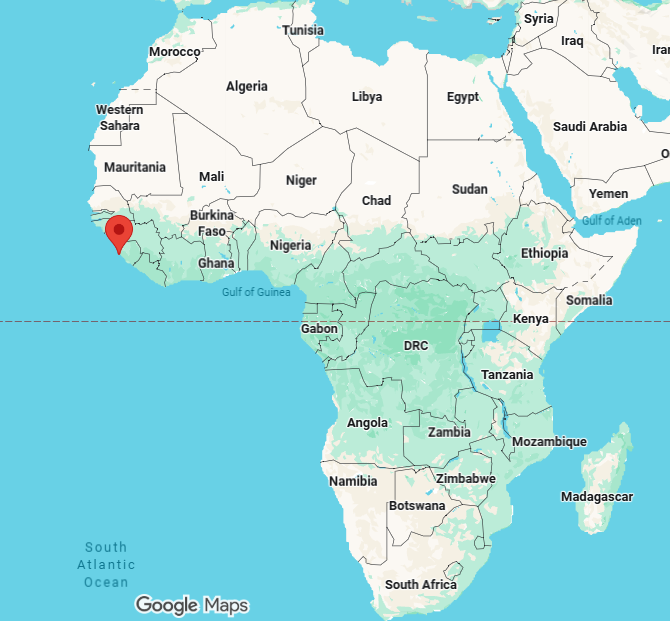
freetown, capital of sierra leone
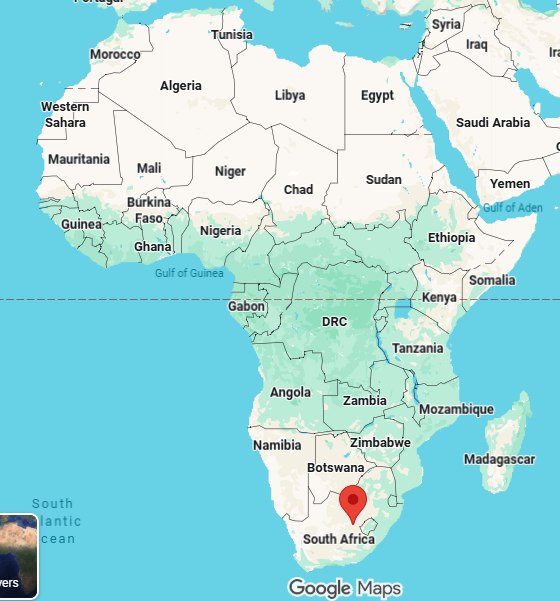
bloemfontein, judicial capital of south africa
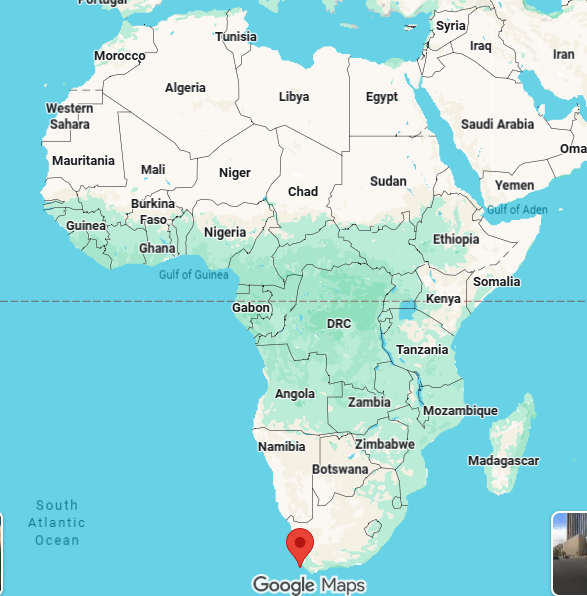
cape town, legislative capital of south africa
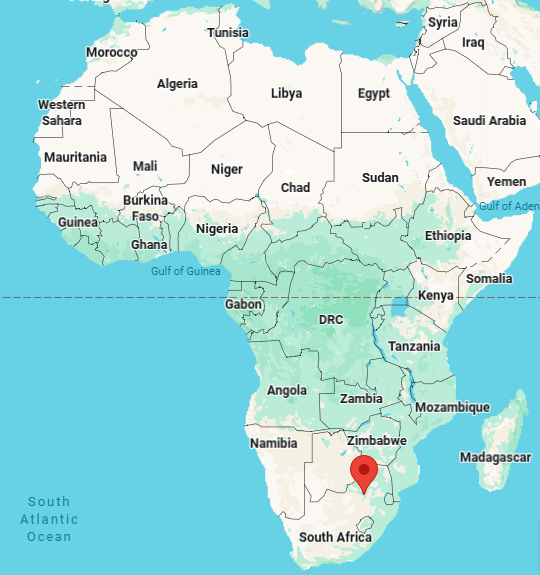
pretoria, administrative capital of south africa