genetic diversity
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
what different ways can genetic variation be introduced
meiosis
mutations
random fertilisation
meiosis
creates genetically different gametes
results in 4 haploid daughter cells
what are haploids and diploids
haploids (n) - one copy of each chromosome
diploids (2n) - 2 copies of each chromosome
2 key processes in meiosis
independent segregation of homologous chromosomes
crossing over of homologous chromosomes
what happens in interphase
DNA and organelles double
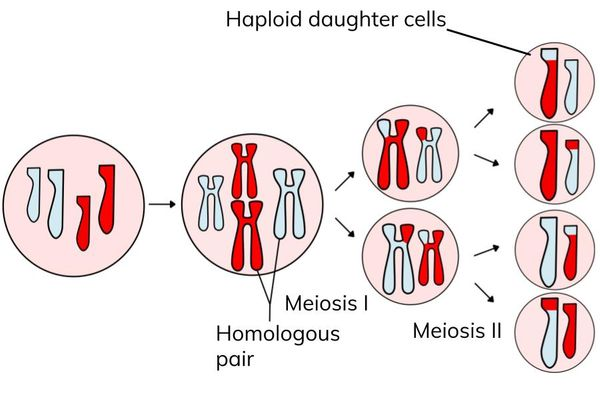
stages of meiosis
2 nuclear divisions; meiosis 1 and meiosis 2
both include prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase and cytokinesis
diagram
what is crossing over
occurs in meiosis 1 when homologous pairs line up opposite each other at the equator and parts of chromatids become twisted
puts tension on the bonds causing pairs of chromatids to break
broken parts chromatid recombine with another chromatid
results in a new combination alleles in the gametes
what is independent segregation
when chromosomes line up it is random which side the paternal and maternal chromosomes lie
pairs are seperated so one of each homologous pair ends up in each daughter cell
creates a large number of possible combinations of chromosomes in daughter cells produced
formula to calculate possible combinations of chromosomes
2n
n = number of homoglous pairs
process of meiosis
prophase 1 homologous chromosomes pair up and cross over (exchange of genetic material)
metaphase 1 paired homologous chromosomes line up along equator
anaphase 1 chromosomes separation and pulled to opposite poles
telophase 1 cell divides resulting in 2 daughter cells, each haploid set of chromosomes
metaphase 2 sister chromatids line along cell’s equator
anaphase 2 sister chromatids separated and pulled to opposite polices
telophase 2 cells divides again resuling in 4 haploid daughter cells
what is a gene mutation
change in the base sequence of DNA that randomly occur during DNA replication
what factors makes gene mutations more likely to occur
mutagenic agents;
○ high energy radiation
○ ionising radiation (X rays etc)
○ chemical carcinogens etc cigarette smoke
different gene mutations
substituted or deleted
silent mutation
when the new base/codon still codes for the same amino acid
deleted mutation
the removal of one base changes all of the codons
means that multiple amino acids may be incorrectly coded for
non overlapping
each base is only part of one triplet
universal
same sequence of bases codes for the same amino acids in all organisms
degenerate
each amino acid is coded for by more than one triplet
eg. proline coded for by; CCC, CCA, CCT, CCG
how do chromosome mutations occur
non disjunction during meiosis
when chromosomes or chromatids do not split equally during anaphase
2 forms of chromosome mutations
changes in the whole sets of chromosomes (polyploidy)
changes in the number of individual chromosomes (aneuploidy)
polyploidy
changing in whole set of chromosomes
occurs when organisms have three or more sets of chromosomes rather than usual 2
mainly occurs in plants
aneuploidy
change in the number of indivdiual chromosomes
when chromosomes fail to separate during meiosis - called non disjunction and results in gamete having one more or one less chromosome
EG. down syndrome caused by 3 copies of chromosome 21