Corporate Finance Ch3
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
PV of bonds
annuity + discounted PV of final payment
C(1/r - 1/r(1+r)^t) + par/(1+r)^t
or if paid multiple times a year:
where y = yield to maturity (opportunity cost of capital)
n = number of payments each year
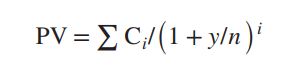
Yield to maturity
THE DISCOUNT RATE THAT EXPLAINS THE BOND PRICE. Opportunity cost of capital. doesnt equal the coupon interest rate; that only represents interest payments, not the difference btwn the par and price.
discount bond
a bond where the price is less than the face value. The yield to maturity exceeds the coupon rate
capital gain
premium bond
a bond that sells above par. yield to maturity < coupon rate
capital loss
par bond
price = par, yield = coupon rate
treasury bonds vs notes vs bills
bonds: 10+ years
notes: <10 years
bills: < 1 year
how are bond prices usually expressed
as a percentage of face value
Do prices and yields move inversely or directly?
INVERSELY
rate of return
(coupon income + price change)/investment
Macaulay Duration
t = # of years until the ith payment
weighted average of the times to each of the cash pyaments. the PV of the cash flow received at that time / cash flow of the bond
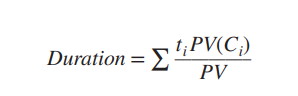
modified duration
duration / (1+yield)
measures the percentage change in bond price for a 1 percentage point change in yield
helpful to assess interest rate risk
term structure of interest rates
the relationship between long and short term interest rates
how to use the spot rate
the individual discount rate at a point in time. To find the yield to maturity, discount each cash flow by the SPECIFIC YEAR’S SPOT RATE and find that present value. Then, set the PV equal to equation using a uniform yield to maturity and solve for it.
stripped bonds/strips
bonds broken down into mini bonds that each pay 1 of the interest payments/principal
to calculate spot rate at a specific year:
Discount Factor at specific year = 1/(1+spot rate at specific year)^specific year set equal to known DF and solve for r
arbitrage
cases where two identical sets of future cash flows sell at different prices.
expectations theory in the bond market
expected returns of a series of short term bonds must return the same as a single long-maturity bond
are prices for short or long-term bondsmore sensitive?
long term
nominal dollars vs real dollars
nominal: the literal cash flow in dollars you will receive
real: discount future cash flow by rate of inflation to show its real purchasing power that you will receive
real cash flow at date t
nominal cash flow at date t / (1+inflation rate)^t
real rate of return
1+rreal = (1+rnominal)/(1+inflation rate)
indexed bonds
make cash payments linked to inflation. real cash flows are fixed instead of nominal cash flows.
Fisher’s theory
a change in the expected inflation rate causes the same proportionate change in the nominal interest rate
own currency debt
if government issues bonds/borrows in its own currency, lower risk because they can just print money to payment
eurozone debt
own currency debt not applicable to EU countries that use euros, because they use the european central bank and do not print their own money.