Unit 6 Cities & Urban Land Use Patterns and Processes
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/49
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
1
New cards
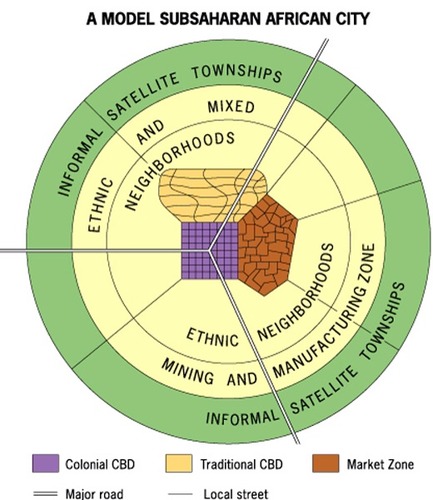
African City Model
Model that suggests that African cities have more than one CBD, which is due to colonialism.
2
New cards
basic sector
the products or services of an urban economy that are exported outside the city itself by a business, earning income for the community, the part of a city's economy that is producing exports, these types of businesses are attractive to cities because they bring IN money and lead to job creation in multiple industries
3
New cards
Block busting (panic peddling)
To profit from inducing any person to sell or rent dwellings by representing entry of certain minority group(s) into a neighborhood.
4
New cards
Boomburbs
rapidly growing city in the US that remains suburban in character, even as it reaches higher populations
5
New cards
Brownfields/brownfield remediation
Abandoned polluted industrial sites in downtown areas, many of which are today being cleaned and redeveloped into parks, business, or entertainment centers (ex: Discovery Green)
6
New cards
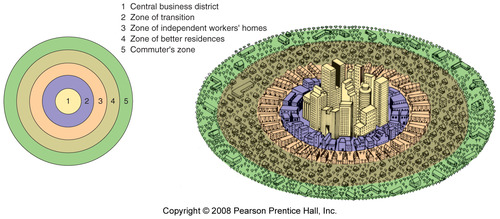
Burgess Concentric Zone Model
This model was devised in the 1920s by Ernest Burgess to predict and explain the growth patterns of North American urban spaces. Its main principle is that cities can be viewed from above as a series of concentric rings; as the city grows and expands, new rings are added and old ones change character. Key elements of the model are the central business district and the peak land value intersection.
7
New cards
Central Business District (CBD)
The downtown or nucleus of a city where retail stores, offices, and cultural activities are concentrated; building densities are usually quite high; and transportation systems converge.
8
New cards
Christaller's Central Place Theory
Developed in the 1930s by Walter Christaller, this model explains and predicts patterns of urban places across the map. In his model, Christaller analyzed the hexagonal, hierarchical pattern of cities, villages, towns, and hamlets arranged according to their varying degrees of centrality, determined by the central place functions existing in urban places and the hinterlands they serve.
\
Assumptions:
\- Flat plane with uniform geography and nature
\- Uniform population
\- single mode of transportation
\- evolution towards the growth of cities
\- all persons have a similar income
\- all persons have similar consumption patterns
\
Assumptions:
\- Flat plane with uniform geography and nature
\- Uniform population
\- single mode of transportation
\- evolution towards the growth of cities
\- all persons have a similar income
\- all persons have similar consumption patterns
9
New cards
de facto segregation
Racial, ethnic, or other segregation resulting from societal differences between groups, as socioeconomic or political disparity, without institutionalized legislation intended to segregate.
10
New cards
Disamenity Sector
A relatively stable slum area that radiates from the central market to the outermost zone of peripheral squatter of settlements and consists of high-density shantytowns, typically seen in semi-periphery and periphery countries
11
New cards
ecological footprint
The impact of a an entity (person, business, or community) on the environment, expressed as the amount of land required to sustain their use of natural resources.
12
New cards
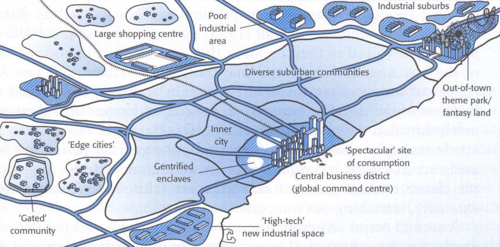
Edge City (Galactic City)
A term introduced by the American journalist Joel Garreau in order to describe the shifting focus of urbanization in the United States away from the CBD toward a new concentrations of economic activity at the urban fringe.
\
An area becomes an edge city when there is a concentration of firms, and entertainment and shopping centers, usually along a highway intersection in a previously known rural or residential area.
\
An area becomes an edge city when there is a concentration of firms, and entertainment and shopping centers, usually along a highway intersection in a previously known rural or residential area.
13
New cards
exurb
An exurb is an area outside the suburbs of a metropolitan area, which has an economic and commuting connection to the metro area, low housing density, and growth.
14
New cards
Farmland Protection Program
Help state, county, and local governments protect farmland in danger of being paved over or otherwise developed.
15
New cards
Gentrification
A process of converting an urban neighborhood from a predominantly low-income renter-occupied area to a predominantly middle-class owner-occupied area
16
New cards
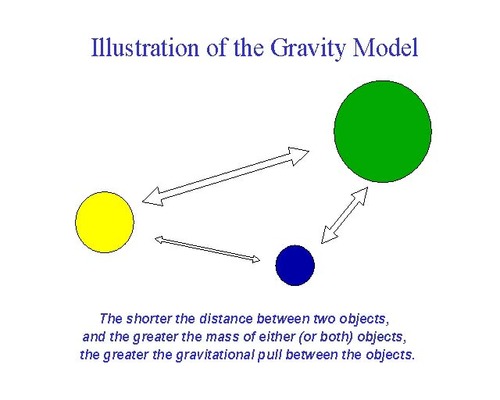
Gravity Model
A model that holds that the potential use of a service at a particular location is directly related to the number of people in a location and inversely related to the distance people must travel to reach the service.
17
New cards
green belt
A ring of land maintained as parks, agriculture, or other types of open space to limit the sprawl of an urban area.
18
New cards
Multiple Nuclei Model
Type of urban form wherein cities have numerous centers of business and cultural activity instead of one central place.
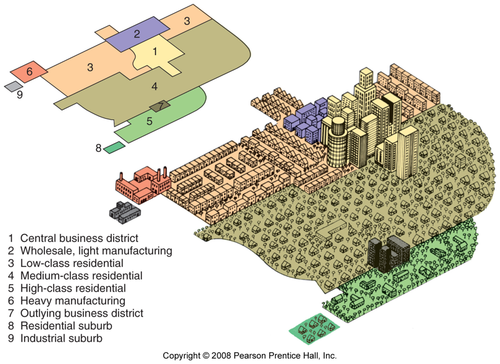
19
New cards
housing discrimination
The illegal practice of denying an individual or group the right to buy or rent a home based on race, color, religion, national origin, sex, disability or family status.
20
New cards
Hoyt Sector Model
Focuses on residential patterns explaining where the wealthy in a city choose to live. He argued that the city grows outward from the center, so a low-rent area could extend all the way from the CBD to the city's outer edge, creating zones which are shaped like pieces of a pie.
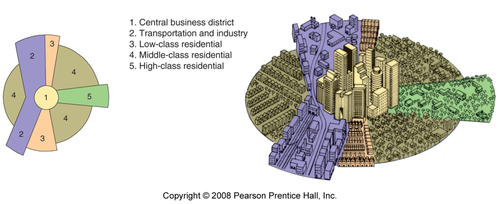
21
New cards
Inclusionary Zoning
Zoning that encourages affordable housing, often through a density bonus. To get the additional density, new construction must include a set percentage of affordable housing units (or make a payment into a fund to support the development of nearby affordable housing).
22
New cards
affordable housing
Housing that has a sale price
or rental amount that is within the means of a household that may occupy middle-, moderate-, or low-income housing. In the case of dwelling units for sale, housing that is affordable means housing in which mortgage, amortization, taxes,
insurance, and condominium or association fees constitute no more than 28% of gross annual household income. In the case of dwelling units for rent, housing that is affordable means housing for which the rent and utilities constitute no more than 30% of gross annual income.
or rental amount that is within the means of a household that may occupy middle-, moderate-, or low-income housing. In the case of dwelling units for sale, housing that is affordable means housing in which mortgage, amortization, taxes,
insurance, and condominium or association fees constitute no more than 28% of gross annual household income. In the case of dwelling units for rent, housing that is affordable means housing for which the rent and utilities constitute no more than 30% of gross annual income.
23
New cards
Infilling
The process by which population density in an urban center is increased by building on waste land or underused land.
24
New cards
land tenure
how property rights to land are allocated within societies, including how permissions are granted to access, use, control, and transfer land.
25
New cards
Latin American City Model
Developed by Ernst Griffin and Larry Ford. Blends traditional Latin American culture with the forces of globalization. The CBD is dominant; it is divided into a market sector and a modern high-rise sector. The elite residential sector is on the extension of the CBD in the "spine". The end of the spine of elite residency is the "mall" with high-priced residencies. The further out, less wealthy it gets. The poorest are on the outer edge.
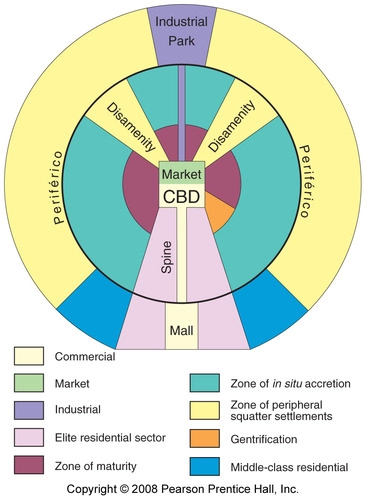
26
New cards
Megacities
Cities with more than 10 million people, most growth of these cities is occurring in less-developed countries.
27
New cards
metacities
Agglomerations of several cities, towns, and suburbs that have expanded so that they coalesce into a single, sprawling urban mass of more than 20 million people.
28
New cards
mixed land use/mixed-use development
an urban design initiative in which land development contains two or more major types of uses (such as residential, commercial, office, and institutional), each of which should attract a significant market share in its own right, such as a condominium that has residential and commercial units.
29
New cards
New Urbanism
A movement in urban planning to promote mixed use commercial and residential development and pedestrian friendly, community orientated cities. New Urbanism is a reaction to the sprawling, automobile centered cities of the mid twentieth century.
30
New cards
Primate City Rule
The largest city has more than twice as many people as the second-ranking city.
31
New cards
rank-size rule
A pattern of settlements in a country, such that the nth largest settlement is 1/n the population of the largest settlement.
32
New cards
redevelopment
Where old buildings and land are replaced by new buildings.
33
New cards
red lining
A process by which banks draw colored lines on a map ranking neighborhoods by lending approval. Banks would refuse to lend money for purchase or improve property within the red colored boundaries. This practice was declared illegal in 1968
34
New cards
Slow-growth cities
Urban communities where the planners have put into place smart growth initiatives to decrease the rate at which the city grows horizontally to avoid the adverse affects of sprawl.
35
New cards
Smart Growth Principles
1\. Mixed land use
2\. Range of housing (socioeconomic)
3\. Walk-able neighborhoods
4\. Community and stakeholder collaboration
5\. Compact building design
6\. Communities with a strong sense of place
7\. Preservation of land
8\. Transportation (community based versus auto based)
9\. Development of existing communities
10\. Predictable and cost effective development decisions
2\. Range of housing (socioeconomic)
3\. Walk-able neighborhoods
4\. Community and stakeholder collaboration
5\. Compact building design
6\. Communities with a strong sense of place
7\. Preservation of land
8\. Transportation (community based versus auto based)
9\. Development of existing communities
10\. Predictable and cost effective development decisions
36
New cards
Southeast Asian City Model
Developed by T.G McGee. The focal point of the city is the colonial port zone combined with the large commercial district that surrounds it. McGee found no formal CBD but found seperate clusters of elements of the CBD surrounding the port zone: the government zone, the Western commercial zone, the alien commercial zone, and the mixed land-use zone with misc. economic activities.
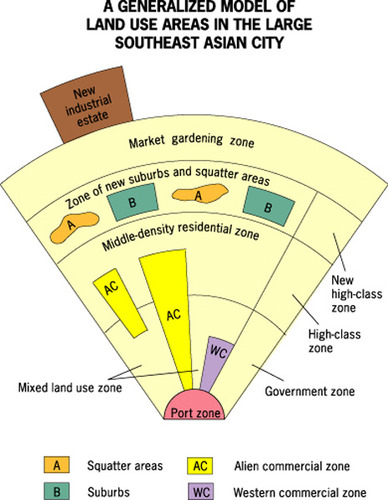
37
New cards
Squatter Settlement
An area within a city in a less developed country in which people illegally establish residences on land they do not own or rent and erect homemade structures.
38
New cards
Suburbanization/Sprawl
The process of population movement from within towns and cities to the rural-urban fringe. The development of undeveloped land.
39
New cards
Sustainable Design Initiatives
Communities that use smart growth and green building techniques to create neighborhoods that are economically thriving and environmentally responsible.
40
New cards
Tenements
Urban apartment buildings that served as housing for poor factory workers. Often poorly constructed and overcrowded.
41
New cards
transportation-oriented development
The exciting fast growing trend in creating vibrant, livable, sustainable communities. Also known as TOD, it's the creation of compact, walkable, pedestrian-oriented, mixed-use communities centered around high quality train systems. This makes it possible to live a lower-stress life without complete dependence on a car for mobility and survival.
42
New cards
urban decentralization
metropolitan areas sprawl in all directions and suburbs take on many of the characteristics of traditional down-towns with a high concentration of services, businesses, and entertainment
43
New cards
Urban function
Services that are provided in a certain metropolitan area such as police, fire, public libraries, transportation....
44
New cards
Urban Growth Boundary (UGB)
A line used by city planners to separate areas that will remain urban from areas that will remain rural.
45
New cards
urban hierarchy
A ranking of settlements (hamlet, village, town, city, metropolis) according to their size and economic functions.
46
New cards
Urbanization
An increase in the percentage and in the number of people living in urban settlements.
47
New cards
urban renewal
Program in which cities identify blighted inner-city neighborhoods, acquire the properties from private members, relocate the residents and businesses, clear the site, build new roads and utilities, and turn the land over to private developers.
48
New cards
Urban sustainability
The goal of improving the social and economic conditions of an increasingly urbanized population while maintaining environmental quality.
49
New cards
world city (global city)
City that plays an especially important role in global business services. (Ex. New York City, London, Tokyo)
50
New cards
zone of abandonment
areas that have been deserted in a city for economic or environmental reasons.