Cell Biology Test Bank Questions
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
The central dogma describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein
Chromosomes are comprised of DNA, which serves as the cell’s genetic material
Through transcription, this DNA is used as a template to synthesize a complementary RNA molecule
The RNA is then translated to produce proteins
Proteins carry out most cellular functions and contribute to cell structure and movement
Explain in at least 3 sentences, not more than 6 sentences, to describe the relationship between cells, chromosomes, DNA, RNA, and proteins. List your points by number or bullet points
A. intermediate filaments
B. actin filaments
D. microtubules
The cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells are responsible for directed cell movements. Which of the following make up the cytoskeleton. Hint: Multiple answer question.
A. intermediate filaments
B. actin filaments
C. intermediate tubules
D. microtubules
A. Chloroplasts absorb light and generate oxygen and electrons
C. Chloroplasts are thought to have originated from bacteria
D. Chloroplasts contain their own DNA
Which of the following statements are TRUE of chloroplasts? Hint: multiple answer question
A. Chloroplasts absorb light and generate oxygen and electrons
B. Chloroplasts are present in essentially all eukaryotic cells
C. Chloroplasts are thought to have originated from bacteria
D. Chloroplasts contain their own DNA
A. has one of the largest genome in plant kingdom
These are all the reasons why arabidopsis has been chosen as a model plant EXCEPT
A. has one of the largest genome in plant kingdom
B. Has relatively small genome
C. the ability to self-fertilize
D. short generation time
A. mitochondria possess ribosomes similar in size to bacterial ribosomes
C. mitochondria contain double membranes resembles that of a bacterial double membrane
D. mitochondria contain DNA arranged in circular chromosome
Mitochondria are thought to have evolved from engulfed aerobic bacteria. Which of the following are evidence that supported the theory of endosymbiosis in eukaryotic cells. Hint: multiple answer question
A. mitochondria possess ribosomes similar in size to bacterial ribosomes
B. mitochondria possess nucleus similar in size to bacterial nucleus
C. mitochondria contain double membranes resembles that of a bacterial double membrane
D. mitochondria contain DNA arranged in circular chromosome
True
True or False? Mitochondria are essentially the same in all eukaryotes, including plants, animals, and fungi.
A. to import extracellular materials
Eukaryotic cells engage in continual endocytosis and exocytosis across their plasma membrane. Why do cells engage in endocytosis?
A. to import extracellular materials
B. They use it to communicate with other cells
C. secrete extracellular materials
D. they use it for mating with other similar cells
True
True or false? Within a developed multicellular organism, NOT all cells have the ability to divide.
D. They are used to study live cells
All of the following are advantages of using electron microscope when compared to light microscope EXCEPT
A. They are used to study viruses
B. They are used to visualize ribosomes
C. They are used to study sub-cellular structures
D. They are used to study live cells
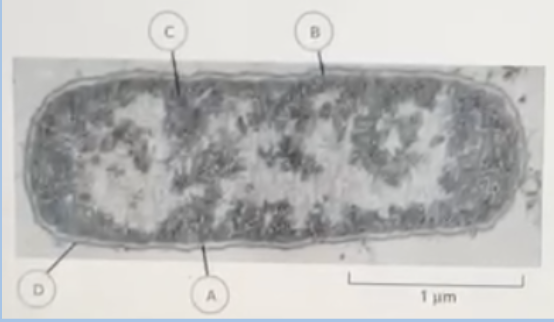
C. Cell wall – inner membrane – cytoplasm – outer membrane
In the electron micrograph below, identify the bacterial cell features labeled A to D respectively. A is pointing to the light shaded area in between
A. Cytoplasm – Cell wall – inner membrane – outer membrane
B. Outer membrane – inner membrane – cell wall – cytoplasm
C. Cell wall – inner membrane – cytoplasm – outer membrane
D. outer membrane – cell wall – inner membrane – cytoplasm
A. The reaction will proceed spontaneously under standard conditions
The ∆G° of a reaction is -350 kcal/mol. Which of the following can be deduced about this reaction?
A. The reaction will proceed spontaneously under standard conditions
B. The reaction will proceed in the presence of another reaction with a positive deltaG value
C. None can be deduced based on the presented information
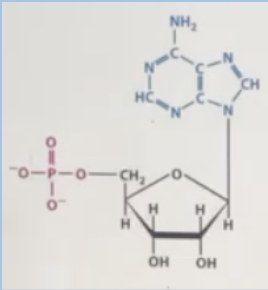
B. It belongs to RNA
F. It is a nucleotide
What can be said about the molecule presented below. Hint: multiple answer question
A. No, it is a plane
B. It belongs to RNA
C. It belongs to one of the non-polar amino acids
D. No, it is a bird
E. It belongs to DNA
F. It is a nucleotide
A. covalent bond
B. van der Waals attraction
C. hydrogen bond
D. ionic bond
Which of the following are types of interactions that help bring molecules together in cells. Hint: multiple answer question
A. covalent bond
B. van der Waals attraction
C. hydrogen bond
D. ionic bond
A. Unlike other eukaryotes, yeast do not have membrane bound nucleus
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of yeast that make them useful model organisms?
A. Unlike other eukaryotes, yeast do not have membrane bound nucleus
B. They can be grown cheaply and quickly
C. They can be haploid or diploid
D. Homologs of yeast proteins are found in nearly all eukaryotes
C. release of water molecules
Peptide bond formation between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another results in
A. release of carbonyl group
B. release of carbon dioxide molecules
C. release of water molecules
D. release of amide group
A. DNA
When comparing liver cells and kidney cells within the same organism, which of the following is the same between the two cells?
A. DNA
B. Lipids
C. RNA
D. Proteins
A. 4
You feed 2 glucose molecules to a yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. How many total numbers of ATP will you expect to recover if the cell decided to ferment the sugars?
A. 4
B. 2
C. 76
D. 10
E. 38
A. NADH can accept electrons from an electron transport system
Which of the following is NOT correct with respect to the redox pair NAD+/NADH?
A. NADH can accept electrons from an electron transport system
B. The nicotinamide ring is a relatively stable aromatic structure
C. The nicotinamide is heteroaromatic because it has a non carbon atom in the 4th position
D. The reduced, nonaromatic ring of NADH is at a higher energy than the aromatic ring of NAD+
A. NADPH is used primarily by plants
Which of the following statements about NADPH and/or NADH is NOT true?
A. NADPH is used primarily by plants
B. NADPH is used in biosynthetic reactions to build energy-rich molecules
C. NADPH is used by both animals and plants
D. NADPH is used in powering the production of ATP
A. It requires oxygen
Which of the following is NOT true of chemiosmosis?
A. It requires oxygen
B. The proton motive force is used to synthesize ATP
C. It produces majority of ATP in the cell
D. ATP synthase generates ATP from ADP and Pi
True
True or false? ATP synthesis by chemiosmosis is similar in bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts.
D. two water molecules
The TCA cycle is capable of generating all of the following products from oxidation of each acetyl-CoA molecule EXCEPT:
A. one ATP molecule
B. two carbon dioxide molecules
C. two FADH2
D. two water molecules
E. 3 NADH molecules
B. ATP synthesis through substrate level phosphorylation
The enzyme pyruvate kinase catalyzes the conversion of PEP to pyruvate. The phosphate group is transferred to ATP to form ATP. This reaction is an example of:
A. ATP synthesis by oxidative phosphorylation
B. ATP synthesis through substrate level phosphorylation
B. Uncoupling proteins (UCPs)
In brown fat of bears, the following transmembrane proteins are used to produce heat during cold season.
A. F0 complex of ATP synthase
B. Uncoupling proteins (UCPs)
C. F1 complex of ATP synthase
D. CoQH2 molecules
True
True or False? Photosynthesis utilizes an electron transport system while Fermentation does not utilize an electron transport system
False
True or false? Fermentation produces more energy than anaerobic respiration.
D. Proton motive force
Production of ATP by ATP synthase directly depends on which of the following factors?
A. Electron carrier force
B. Neutron motive force
C. GTP
D. Proton motive force
A. transfer of electrons from cytosolic NADH across the inner mitochondrial membrane
What is the main purpose of the Malate-Aspartate shuttle to cells?
A. transfer of electrons from cytosolic NADH across the inner mitochondrial membrane
B. Transport of acetyl-CoA from cytoplasm to the mitochondrial matrix
C. transport of pyruvate from cytoplasm to the mitochondrial matrix
D. transfer of electrons from matrix NADH across the inner mitochondrial membrane
A. Both are electron carriers that power the electron transport system
B. Both have the ability to produce similar amount of ATP
D. Both are products of TCA
Which of the following statements is TRUE to both FADH2 and NADH? Multiple answers
A. Both are electron carriers that power the electron transport system
B. Both have the ability to produce similar amount of ATP
C. Both are products of glycolysis
D. Both are products of TCA
D. increase in reduction potential from NADH to O2
Which of the following allows the one way movement of electrons from one complex to the next in ETS?
A. decrease in reduction potential from NADH to O2
B. Presence of more protons in the cytosolic side of the membrane
C. Presence of more protons between the inner and outer membrane of mitochondria
D. increase in reduction potential from NADH to O2
False
True or False? Oxygen is always required for the regeneration of NAD from NADH
C. Proteolysis
Which of the following is NOT a method for controlling protein activity?
A. ATP hydrolysis
B. Phosphorylation can control protein activity by causing a conformational change
C. Proteolysis
D. Catalytic activities of enzymes are often regulated by the product of the reaction
C. hydrogen-bonding between peptide bonds in adjacent strands in a beta sheet
Which of the following does NOT represent covalent interactions?
A. disulfide formation between two antibody subunits
B. disulfide formation during folding of the newly translated protein
C. hydrogen-bonding between peptide bonds in adjacent strands in a beta sheet
D. peptide bond between two amino acids
D. Methionine to Aspartic Acid
Mutations in the nucleic acid sequence of a gene can sometimes direct the substitution of one amino acid for another in the encoded protein. Which amino acid substitution would be most likely to severely disrupt the normal structure of a protein?
A. Tyrosine to Tryptophan
B. Alanine to Glycine
C. Leucine to isoleucine
D. Methionine to Aspartic Acid
D. it involves removal of water molecule
Which of the following is NOT TRUE about the enzyme lysozyme.
A. Its activity increases with increase in substrate concentration
B. It involves addition of water molecule
C. catalyzes the cutting of a polysaccharide substrate molecule
D. it involves removal of water molecule
D. It is made of one large protein subunit
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a hemoglobin molecule?
A. Its ability to deliver oxygen to muscle cells depends on the concentration of carbon dioxide
B. Its function depend on the chemical property of the heme group
C. Its ability to deliver oxygen to muscle cells depends on pH
D. It is made of one large protein subunit
B. amino acid sequence
Which of the following determine how a protein will fold?
A. peptide bond structure
B. amino acid sequence
C. Chaperones
D. Chaperones and peptide bond structure
True
True or false? A competitive inhibitor bound to an enzyme can be overcome by increasing the substrate concentration.
C. Amino group of one amino acid and carboxyl group of the other
Which parts of amino acids are involved in a peptide bond?
A. phosphate of one amino acid and sugar of another
B. carboxyl group of one amino acid and side chain of the other
C. Amino group of one amino acid and carboxyl group of the other
D. Carboxylic acid of one amino acid and fatty acids of the other
A. are strands of polypeptide chain are held together by hydrogen-bonding between peptide bonds in adjacent strands
Beta sheets of proteins
A. are strands of polypeptide chain are held together by hydrogen-bonding between peptide bonds in adjacent strands
B. are formed by hydrogen bonding of the N–H of every peptide bond to the C–O of a neighboring peptide bond four amino acids away
C. are the major components of membrane bound proteins across the lipid bilayer
D. can be either right-handed or left-handed
C. The reaction is associated with a negative change in ∆G°
Which statement is TRUE about the removal of a terminal phosphate from ATP?
A. The reaction is a dehydration reaction
B. The reaction is associated with a positive change in ∆G°
C. The reaction is associated with a negative change in ∆G°
D. The reaction is a condensation reaction
D. speed up reaction by increasing the activation energy
Which of the following is NOT a function of an enzyme?
A. speed up reaction by lowering activation energy
B. bring substrates into close proximity
C. couple favorable and unfavorable chemical reactions
D. speed up reaction by increasing the activation energy
A. polypeptide loops in its variable domains
What determines the specificity an antibody has for its antigen?
A. polypeptide loops in its variable domains
B. polypeptide loops of its heavy chains
C. polypeptide loops in its constant domains
D. polypeptide loops of its light chains
B. Two-dimensional PAGE
Which of the following techniques would you use to separate two proteins with the same size but different isoelectric points?
A. Ion-exchange chromatography
B. Two-dimensional PAGE
C. Antibody affinity chromatography
D. SDS – PAGE
A. Mercaptoethanol
You purified a protein complex with multiple subunits bound together by disulfide bond. Which of the following chemicals would you use to separate the subunits before loading it to polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
A. Mercaptoethanol
B. Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)
C. weak base
D. weak acid
B. liquid chromatography
D. SDS-PAGE
Which of the following can be used for separating different proteins within a sample. Hint: multiple answer question.
A. mass spectrometry
B. liquid chromatography
C. x-ray crystallography
D. SDS-PAGE
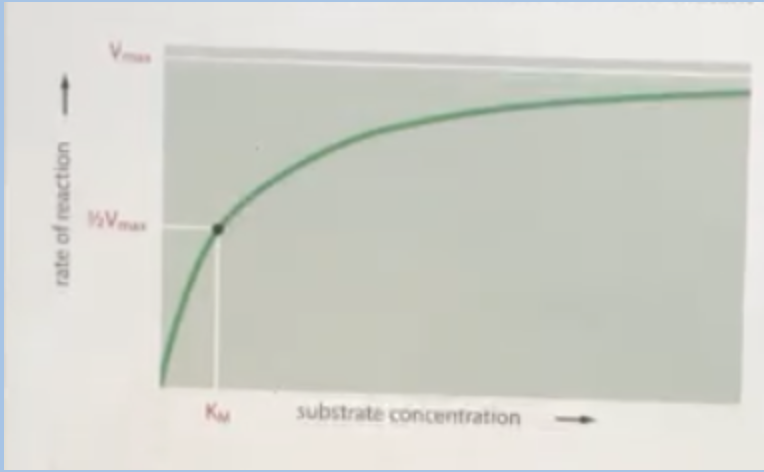
D. The KM would move to the left (decrease)
You are running an experiment to mutate an enzyme in order to increase the enzyme’s ability to bind its substrate. Using the graph as a comparison, what effect would the mutant version of the enzyme likely have on the Km?
A. The KM would move to the right (increases)
B. The KM would not change at all (no effect)
C. The KM would move to the right initially but eventually move to the left
D. The KM would move to the left (decrease)
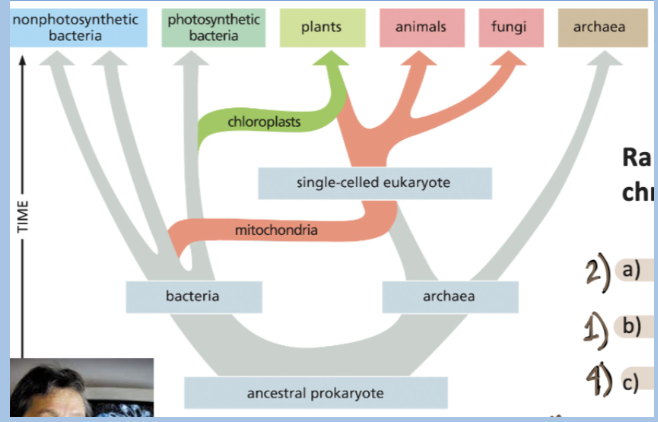
D. C-A-D-B
Rank the following events in chronological order based on the figure below
A. eukaryote and archaea diverged
B. eukaryotes acquired chloroplasts
C. bacteria and archaea diverged
D. eukaryotes acquired mitochondria
Earliest → latest
A. A-B-C-D
B. D-C-B-A
C. A-C-D-B
D. C-A-D-B
1. Regulatory GTP-binding proteins act as on/off switches that control important cell signaling pathways involved in growth and division
2. These proteins are active when bound to GTP and inactive when GTP is hydrolyzed to GDP
3. If a mutation prevents GTP hydrolysis, the protein stays active and continuously sends growth signals
4. An example of a GTP-binding protein is tubulin, which uses GTP to regulate microtubule assembly during cell division
Explain, in at least 3 sentences but not more than 6 sentences, how regulatory GTP-binding proteins can be responsible for human cancer
List your explanation by number or bullet points
Mention at least one example of a protein regulated by GTP-binding
A. Transporters and channels
B. Receptors
C. Enzymes
D. Selective barrier
Plasma membrane proteins provide the following function to the cells. Choose one or more
A. Transporters and channels
B. Receptors
C. Enzymes
D. Selective barrier
E. Energy generation
C. Because of the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids
Why are water-soluble substances unable to freely cross the lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane to enter the cytosol?
A. Because of the hydrophobic outside head group of the membrane
B. Because of the hydrophilic tail of the phospholipids
C. Because of the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids
D. Because of the hydrophilic inside head group of the membrane
A. Composition of the hydrophilic head group
The fluidity of a lipid bilayer in cells is determined by the following ways, EXCEPT
A. Composition of the hydrophilic head group
B. Number of carbons in fatty acid tails
C. Fatty acid saturation
D. Amount of cholesterol
B. phosphoglycerides
C. sphingolipids
D. steroids
Which of the following is/are components of eukaryotic cell membranes. Choose one or more
A. lipopolysaccharides
B. phosphoglycerides
C. sphingolipids
D. steroids
B. increase the proportion of phospholipids with unsaturated fatty acids
How could you increase membrane fluidity?
A. increase the amount of cholesterol present in the membrane
B. increase the proportion of phospholipids with unsaturated fatty acids
C. increase the length of the fatty acid tails in phospholipids
D. increase the proportion of phospholipids with saturated fatty acids
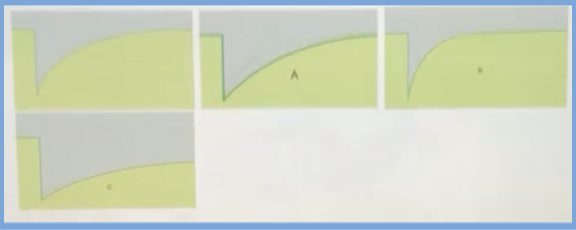
D. B
Shown here are FRAP results for the same membrane proteins after three treatments. The first curve represents untreated protein. The rest of the curves are taken after treating the membrane proteins to increase their membrane mobility. Which frame shows an increase in membrane motility?
A. Both B and C
B. C
C. Both A and B
D. B
E. A
D. A
Shown is a schematic diagram of a membrane phospholipid. Which of the marked segments is different between phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine?
A. B
B. D and E
C. C
D. A

A. decreased amount of cholesterol
D. Polyunsaturated fatty acids
You will expect to find the following in a membrane of a cell that is adapted to function in a very cold temperature. Choose one or more
A. decreased amount of cholesterol
B. saturated fatty acids
C. increased amount of cholesterol
D. Polyunsaturated fatty acids
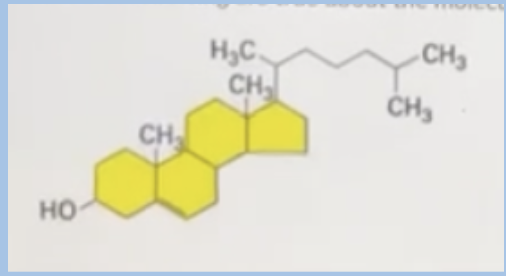
D. It will only interact with the hydrophilic head group of cell membranes
All of the following are true about the molecule below, EXCEPT
A. It is part of a cell membrane in eukaryotes
B. Contains both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions
C. It is responsible for the membrane fluidity cells
D. It will only interact with the hydrophilic head group of cell membranes
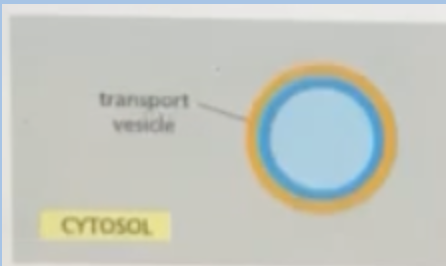
A. Blue side
The following vesicle originated from Golgi apparatus and fuses with the plasma membrane. Which monolayer will face outside (non-cytosolic side)
A. Blue side
B. Sometimes blue and other times orange
C. It will be a hybrid of the two colors
D. orange side
C. expels Na+ from the cell and bring in K+ into the cell
Which of the following is TRUE to all Na+/K+ pump located in the membrane.
A. expels K+ from the cell and brings in Na+ into the cell
B. both Na+ and K+ travel the same direction
C. expels Na+ from the cell and bring in K+ into the cell
D. the movement of Na+ and K+ are driven by their concentration gradient
D. H2O would diffuse out
In one experiment, you create a liposome – a vesicle made of phospholipids – that is filled with distilled water. You placed the liposome in a solution that contains 1mM glucose and 1 mM sodium chloride. What would happen the fastest?
A. NaCl would diffuse in
B. Na+ would diffuse in
C. Glucose would diffuse in
D. H2O would diffuse out
E. Nothing will happen
A. movement of glucose and sodium from the gut lumen to the cell
Absorption of glucose molecules from the gut lumen into the surrounding epithelial cells involves
A. movement of glucose and sodium from the gut lumen to the cell
B. glucose moves from gut lumen to cells at the expense of Na+ moving to opposite direction
C. It involves movement of Na+ against the concentration gradient
D. It involves ATP hydrolysis
B. mainly transport soldiers
Cells contain two classes of membrane transport proteins, transporters, and channels. Which of the following is TRUE to only transporters.
A. only used to transport solutes down their concentration gradient
B. mainly transport soldiers
C. only used to transport solutes actively against their concentration gradient
D. mainly transport ions
C. carbon dioxide, water, glucose
Different molecules pass directly through lipid bilayers at different rates. Which of the following choices presents the correct order, from fastest to slowest?
A. oxygen, sodium ions, glucose
B. water, oxygen, glucose
C. carbon dioxide, water, glucose
D. sodium ions, oxygen, glucose
A. ATP hydrolysis
B. ion gradient
C. light energy
D. concentration gradient of other solutes
Cells use which of the following sources of energy to actively move solutes against their concentration gradient. Choose one or more
A. ATP hydrolysis
B. ion gradient
C. light energy
D. concentration gradient of other solutes
D. the pump moves Ca2+ from extracellular space into the cytosol
Which of the following is FALSE about Ca2+ pump
A. It consumes ATP
B. They are found in plasma membrane of all eukaryotic cells
C. the pump moves Ca2+ from cytosol into the extracellular space
D. the pump moves Ca2+ from extracellular space into the cytosol
True
True or false? Electrochemical H+ gradients drive the transport of solutes in plants, fungi, and bacteria
C. they couple the flow of ions to an energy source to carry out active transport
All of the following are true about ion channels EXCEPT
Move ions down their concentration gradient
B. unlike a transporter an ion channel does not need to undergo conformational changes
C. they couple the flow of ions to an energy source to carry out active transport
D. ion channels are gated
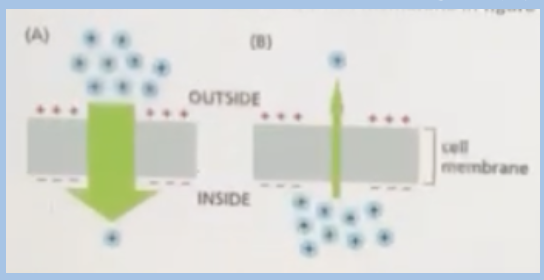
A. both concentration gradient and membrane potential
The movement of ions across the cell membrane in figure (A) below is driven by
A. both concentration gradient and membrane potential
B. membrane potential
C. ATP hydrolysis
D. concentration gradient
A. 350 mV
Calculate the change in reduction potential (∆Eº) for the transfer of electrons from NADH (-320 mV) to ubiquinone (30 mV).
A. 350 mV
B. 1180 mV
C. -350 mV
D. -290 mV
E. 290 mV
D. the transfer of electrons from Ubiquinone to Oxygen is more favorable
What does it mean when the change in reduction potential (∆Eº) is higher when electrons are transferring from Ubiquinone to Oxygen compared to the transfer of electrons from NADH to Ubiquinone during ETS.
A. the transfer of electrons from Ubiquinone to Oxygen in less favorable
B. transfer of electrons from Ubiquinone to Oxygen generates more ATP
C. transfer of electrons from Ubiquinone to Oxygen generate more proton potential
D. the transfer of electrons from Ubiquinone to Oxygen is more favorable
C. generation of ATP by TCA
All of the following processes require a membrane to produce energy, EXCEPT?
A. generation of ATP by photosynthesis in plants
B. generation of ATP by oxidative phosphorylation
C. generation of ATP by TCA
D. generation of energy in mitochondria
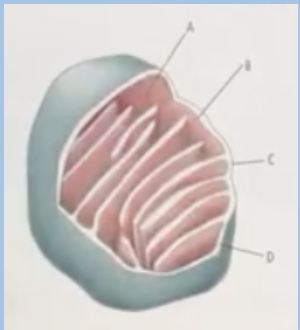
C. 4
In this illustration of the structure of ATP synthase, which of the components is responsible for phosphorylating ADP to ATP?
A. 2
B. 1
C. 4
D. 3
B. produce ATP
When protons move down their electrochemical gradient into the mitochondrial matrix, what do they do?
A. produce NADPH
B. produce ATP
C. consume ATP
D. move electrons through the respiratory chain
B. it is highly favorable
Based on the difference in redox potential between NADH and Oxygen in the ETS, what is true of the transfer of electrons between them?
A. It requires an input of energy
B. it is highly favorable
C. It is highly unfavorable
D. It produces ATP
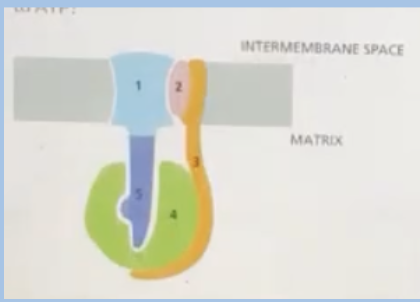
C. D
As a result of ETC proton gradient accumulates in which part of the mitochondrion?
A. B
B. A
C. D
D. C
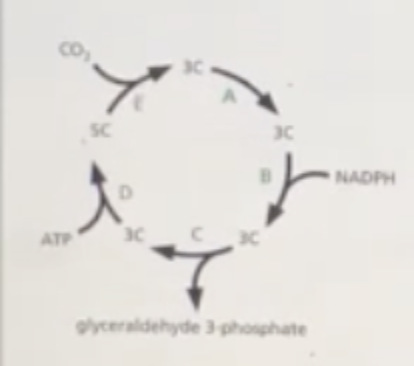
A. A and D. D
In this simplified diagram of the reactions of the carbon-fixation cycle, which step consumes ATP?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
B. an electron carrier that pumps protons out of the stroma into the thylakoid space
The proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis during photosynthesis is generated by which of the following?
A. by an ATP synthase located in the thylakoid membrane
B. an electron carrier that pumps protons out of the stroma into the thylakoid space
C. an electron carrier that removes electrons from water
D. photosystems II and I
B. H2O
When an electron is removed from the reaction center of photosystem II, the missing electron is replaced by an electron from which of the following?
A. light
B. H2O
C. photosystem I
D. NADH
True
True or false? ATP produced during stage 1 of photosynthesis is used to synthesize organic molecules during stage 2 of photosynthesis
D. Dissociation of Ran-GDP from the nuclear import receptor decreases its affinity to proteins in the cytosol
Proteins enter the nucleus through nuclear pores. Which of the following statements is NOT TRUE about transport of proteins into the nucleus.
A. the proteins must contain a nuclear ionization signal
B. GTP hydrolysis drives nuclear transport
C. binding of Ran-GTP to nuclear import receptor decreases its affinity to proteins in the nucleus
D. Dissociation of Ran-GDP from the nuclear import receptor decreases its affinity to proteins in the cytosol
B. Chloroplast D. Mitochondrion
Which of the following organelles are thought to have originated when a bacterium was engulfed by a larger eukaryotic cell. Choose one or more
A. Endosomes
B. Chloroplast
C. Lysosomes
D. Mitochondrion
E. nucleus
True
True or false? All proteins destined to be transported to the nucleus must have a nuclear nuclear localization signal
False
True or false? Proteins made in the cytosol without signal sequence are delivered to the lumen of the ER
A. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) - synthesis of most lipids and proteins
B. Endosomes - sorting of endocytosed material
C. Golgi apparatus - sorting and packing of proteins for transport
Match the organelles with their function
Intracellular degradation
sorting and packing of proteins for transport
Glycolysis
sorting of endocytosed material
synthesis of most lipids and proteins
Oxidative breakdown of toxic molecules
A. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) -
B. Endosomes -
C. Golgi apparatus -
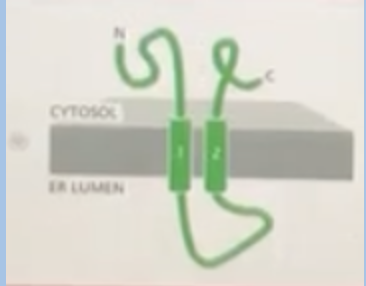
Option B
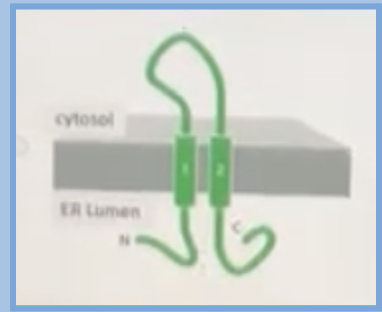
A transmembrane protein normally form a structure shown below. If an ER signal sequence were added to its N-terminus, which structure would the engineered protein adopt?


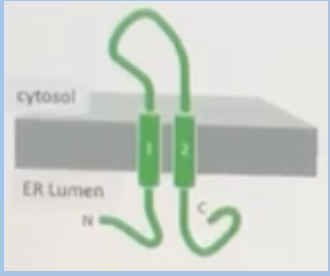
A. endosomes
Which cellular compartment acts as the main sorting station for extracellular cargo molecules taken up by endocytosis?
A. endosomes
B. golgi apparatus
C. lysosomes
D. ER
B. SNAREs
These proteins play a central role in the fusion of a vesicle with a target membrane?
A. clathrins
B. SNAREs
C. Rab proteins
D. adaptins
D. process of ingesting and destruction of infection agent
Phagocytosis
A. it is a process of expelling cholesterol using receptor-mediated exocytosis
B. is a process of cell feeding from intracellular space by the process of endocytosis
C. It is a process of collecting cholesterol using receptor-mediated endocytosis
D. process of ingesting and destruction of infection agent
A. Cargo - Molecules packaged into vesicles
B. Receptor - captures the correct cargo
C. Adaptin - mediates contact between the cargo receptors and clathrin
D. Clathrin - shapes the forming vesicle
Match the following structures used in receptor mediated endocytosis with their functions
shapes the forming vesicle
Molecules packaged into vesicles
mediates contact between the cargo receptors and clathrin
captures the correct cargo
A. Cargo -
B. Receptor -
C. Adaptin -
D. Clathrin -
1. NADH and FADH2 produced from the citric acid cycle donate electrons to the ETC
2. Electrons move through protein complexes in inner mitochondrial membrane toward oxygen
3. NADH gives electrons to Complex I, while FADH2 donates electrons to Complex II, and electrons are passed to ubiquinone and then to Complex III
4. Electrons are carried by cytochrome c to Complex IV, where oxygen is reduced to water
As electrons move through ETC, protons are pumped from mitochondrial matrix to intermembrane space
This proton gradient generates a proton motive force that powers ATP synthase to synthesize ATP form ADP and phosphate
Summarize the process of ATP production using oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria
List each sentence in your summary by number to receive credit
Include information starting from electron carriers to ATP synthesis
Include all major proteins/enzymes for credit
A. Its ability to self-fertilize and support cross-breeding between hermaphrodites and males
What makes Caenorhabditis elegans a notable model organism for genetic studies?
A. Its ability to self-fertilize and support cross-breeding between hermaphrodites and males
B. It is the largest nematode worm in existence
C. It was the last multicellular organism to have its genome sequenced
D. Its incapacity to live outside of laboratory settings
A. Na → Na+ (Na atom → Na+ ion)
C. CH3CH2OH → CH3CHO (ethanol → acetaldehyde)
D. CH3CHO → CH3COO- (acetaldehyde → acetic acid)
In which of the following reactions does the red atom undergo oxidation?
A. Na → Na+ (Na atom → Na+ ion)
B. Cl → Cl- (Cl atom → Cl- ion)
C. CH3CH2OH → CH3CHO (ethanol → acetaldehyde)
D. CH3CHO → CH3COO- (acetaldehyde → acetic acid)
E. CH2=CH2 → CH3CH3 (ethene → ethane)
B. Production of ATP
What features are shared by photosynthesis and respiration?
A. Production of NADH
B. Production of ATP
C. Production of sugar
D. Production of oxygen
A. To transfer electrons from cytosolic NADH across the inner mitochondrial membrane
What is the primary function of the Malate-Aspartate shuttle in cellular metabolism?
A. To transfer electrons from cytosolic NADH across the inner mitochondrial membrane
B. transport of acetyl-CoA from cytoplasm to the mitochondrial matrix
C. Transfer of electrons from matrix NADH across the inner mitochondrial membrane
D. Transport of pyruvate from cytoplasm to the mitochondrial matrix
B. To enhance the availability of resources for rapid growth.
Why do proliferating cancer cells prefer aerobic glycolysis (fermentation), known as the Warburg Effect, despite its lower energy yield compared to oxidative phosphorylation?
A. To generate ATP at a faster rate, even if less ATP is produced per glucose molecule
B. To enhance the availability of resources for rapid growth.
C. To compensate for defective mitochondria incapable of oxidative phosphorylation
D. To minimize reactive oxygen species (ROS) production during rapid proliferation
C. Presence of a membrane-bound nucleus
Which feature distinguishes a eukaryotic cell from a prokaryotic cell?
A. Presence of ribosomes for protein synthesis
B. Ability to carry out metabolic reactions
C. Presence of a membrane-bound nucleus
D. Ability to reproduce by cell division
A. Because it shares a high number of proteins with most eukaryotic cells, reflecting common fundamental processes such as the cell cycle and protein secretion.
Why is Saccharomyces cerevisiae considered an ideal model organism for studying eukaryotic cell processes?
A. Because it shares a high number of proteins with most eukaryotic cells, reflecting common fundamental processes such as the cell cycle and protein secretion.
B. Because it exists only as a diploid organism which simplifies genetic studies
C. Because its cell cycle proteins are completely unique to yeast, making it easier to study mutations
D. Because it does not undergo sxual reproduction, simplifying genetic manipulation
A. Rapid generation time of around 10 days
What characteristic of Drosophila melanogaster makes it an ideal model organism for genetic studies?
A. Rapid generation time of around 10 days
B. Presence of only two life stages
C. Ability to fly
D. Large size
A. Their embryos develop outside the mother and are transparent, allowing for easy observation
Why are zebrafish considered ideal models for studies on vertebrate development?
A. Their embryos develop outside the mother and are transparent, allowing for easy observation
B. They require specialized equipment and care, making observations challenging
C. Zebrafish developmental studies do not provide insights relevant to other vertebrates
D. Development of zebrafish embryos is not visible to the naked eye