Connective tissue
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
LSU SVM
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is the function of fibroblasts?
structural support and synthesizes all 3 fibers and extracellular/ground substance
What is the function of adipocytes?
energy storage and thermal insulation
What is the function of mesenchymal stem cells?
embryonic source of all connective tissue cells
What is the function of macrophages?
immune mediated inflammatory response
What is the function of mast cells?
important in allergies to mediate inflammatory response
What is the function of plasma cells?
antibody production
What is the function pericytes?
angiogenesis, vascular integrity, and inflammation
What is another name for mast cells?
mastocytes
What is the most important and abundant connective tissue cell?
fibroblast/fibrocytes
Which connective tissue cell proliferates in the wound healing process of making scar tissues?
fibroblast/fibrocytes
What cell is similar in morphology to fibroblast/fibrocytes?
pericytes
What connective tissue cell is associated with capillaries and endothelial cells?
pericytes
What are unilocular adipocytes?
white; single large fat lipid droplet made of type 4 collagen
What are multilocular adipocytes?
brown; multiple fat lipid droplets in cytoplasm
What connective tissue cells are perivascular?
mast cells
Which of the following does not belong when listing transient/mobile cells?
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, pericytes, lymphocytes, monocytes, plasma cells, and granulocytes.
pericytes
Which of the following does not belong when listing fixed/immobile cells?
fibroblast/cytes, pericytes, adipocytes, plasma cells, macrophage, mast cells, and undifferentiated mesenchymal cells.
plasma cells
What is the main function of collagen fibers?
high tensile strength
What is the main function of reticular fibers?
structural network
What is the main function of elastic fibers?
stretching ability
What are characteristics of collagen fibers?
most abundant protein of white fibers that are eosinphillic; type 1 collagen
What are characteristics of reticular fibers?
type 3 collagen fibers associated with blood vessels and nerve fibers that are too thin for HE stain, better in silver stain
What are characteristics of elastics fibers?
yellow fibers that need to be seen via verhoeff stain as black
What are the classifications of connective-tissue proper?
any tissue that supports, protects and gives structure to other tissues and organs in the body
What is connective tissue proper made up of?
cells and extracellular matrix
What is ground substance composed of?
glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) with sulfated proteoglycans and non-sulfated hyaluronan (hyaluronic acid)
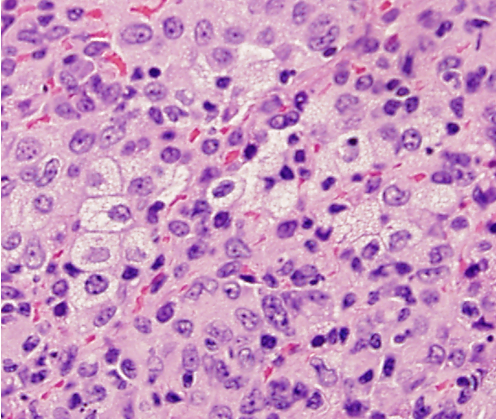
What connective tissue cell is shown in the following image?
macrophages
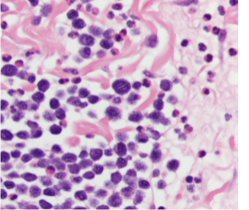
What connective tissue cell is shown in the following image?
mastocytes
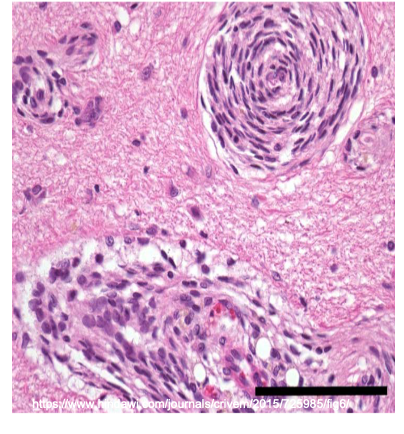
What connective tissue cell is shown in the following image?
pericytes
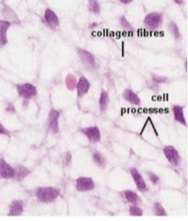
What connective tissue cell is shown in the following image?
mesenchymal stem cells
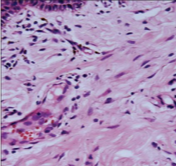
What connective tissue cell is shown in the following image?
fibroblasts/fibrocytes
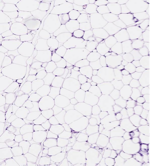
What connective tissue cell is shown in the following image?
unilocular
What connective tissue cell is shown in the following image?
multilocular
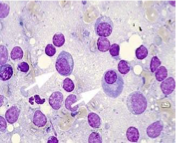
What connective tissue cell is shown in the following image?
plasma cells

What connective tissue fiber is shown in the following image?
collagen
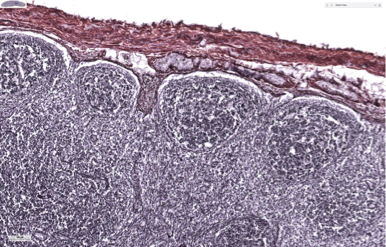
What connective tissue fiber is shown in the following image?
reticular
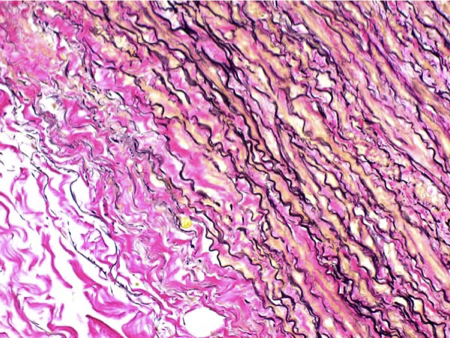
What connective tissue fiber is shown in the following image?
elastic