HASS Semester 2 Test
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

73 Terms
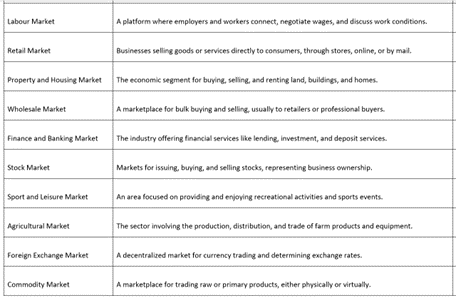
Labour Market
A platform where employers and workers connect, negotiate wages, and discuss work conditions.
Retail Market
Businesses selling goods or services directly to consumers, through stores, online, or by mail.
Property and Housing Market
The economic segment for buying, selling, and renting land, buildings, and homes.
Wholesale Market
A marketplace for bulk buying and selling, usually to retailers or professional buyers.
Finance and Banking Market
The industry offering financial services like lending, investment, and deposit services.
Stock Market
Markets for issuing, buying, and selling stocks, representing business ownership.
Sport and Leisure Market
An area focused on providing and enjoying recreational activities and sports events.
Agricultural Market
The sector involving the production, distribution, and trade of farm products and equipment.
Foreign Exchange Market
A decentralized market for currency trading and determining exchange rates.
Commodity Market
A marketplace for trading raw or primary products, either physically or virtually.
Advertisement
A message that tries to persuade people to buy a product or service.
Allocation and markets
The connection between market prices and demand and supply is called the price mechanism.
Budget
A plan for managing money, showing income and expenses.
Business
An organisation that produces or sells goods and services to make a profit.
Capital
Money or equipment used to start or grow a business.
Career
A job or profession followed for a long period of a person's life.
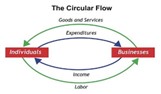
Circular flow model
A diagram showing how money, goods, and services move in an economy.
Competitive advantage
Something that makes a business better than others in the same market.
Consumer
A person who buys goods and services.
Credit
Money borrowed that must be paid back later, usually with interest.
Economic performance and living standards
How well the economy is doing and the quality of life of people.
Economic problem
The issue of having limited resources to meet unlimited wants.
Economics
The study of how people use resources to produce and consume goods and services.
Economy
The system of making and exchanging goods and services in a country.
Employee
A person who works for a business or organisation.
Employer
A person or business that hires employees.
Employment
Having a paid job.
Enterprise
The fourth of the factors of production that brings the other three together to produce a product.
Entrepreneurship
The act of starting and running a business.
Export
Goods or services sold to another country.
Factors of production
Resources used to produce goods and services: Land, Capital, Labour and enterprise.
Financial institutions
Businesses like banks that deal with money and finance.
Goods
Physical items that can be bought or sold.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The total value of all goods and services produced in a country in a year.
Import
Goods or services bought from another country.
Income
Money received from work or investments.
Inflation
The rise in prices of goods and services over time.
Innovation
Creating new ideas, products, or ways of doing things.
Interdependence
When people or businesses rely on each other to satisfy wants and needs.
Interest
Money paid for borrowing money or earned from saving money.
Investment
Putting money into something to earn a profit in the future.
Labour
Work done by people to produce goods and services.
Land
Natural resources used to make goods and services.
Making choices
Deciding between different options when resources are limited.
Market
Where buyers and sellers come together to trade goods and services.
Marketing
Promoting and selling products or services.
Money
A way to exchange goods and services and measure value.
Needs
Things people must have to live, like food, water, and shelter.
Opportunity cost
The value of the next best choice that you give up when making a decision.
Packaging
Materials used to protect and present products.
Oversupply
Too much of a product or service, effecting market price.
Pension
Money paid to a person after retirement.
Producer
A person or business that makes goods or provides services.
Profit
The money left after all business expenses are paid.
Relative scarcity
The limited nature of resources compared to people's wants.
Resources
Things used to produce goods and services.
Retirement
The time in life when someone stops working full-time.
Salaries
Fixed regular payments to employees for their work. Different from wages, because it is a set amount, not determined by hours worked.
Saving
Putting money aside for future use.
Scarcity
When there are not enough resources to meet all wants.
Services
Non-physical activities done for others, like teaching or hairdressing.
Specialisation and trade
Focusing on what one does best and trading with others.
Strategy
A plan of action to achieve a goal.
Superannuation
Money saved during working life for use in retirement. Compulsory in Australia for anyone working.
Survey
A method of collecting information by asking people questions.
Tariff
A tax on imports from other countries.
Tax
Money paid to the government to fund services and infrastructure.
Unemployment rate
The percentage of people who want work but cannot find a job.
Wage
Money paid to workers for the hours they work. Australia has minimum wages.
Wants
Things people would like to have but don't need to survive.
Work
Activity involving effort done to earn money or achieve a purpose.
Market Types
Circular Flow of Income