SNC2DY-a Biology Chapter 3 Test
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
cell specialization
cells develop in different ways to perform a specific function
factors influencing cell specialization
The cytoplasm (organelle distribution), environmental conditions (temperature & nutrients), and neighboring cells (cell interaction).
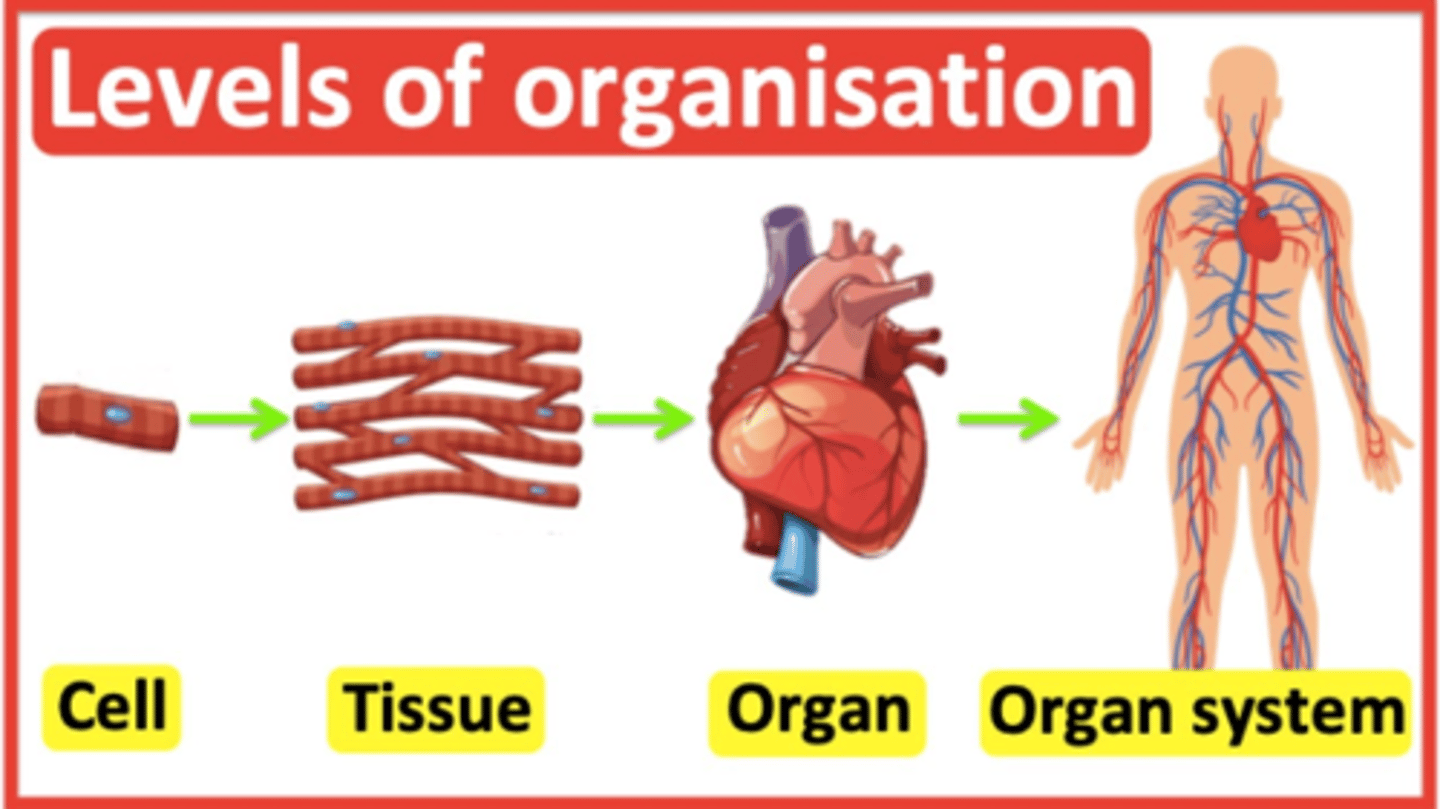
animal body organization
cells, tissues, organs, organ systems
4 types of tissue
epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous
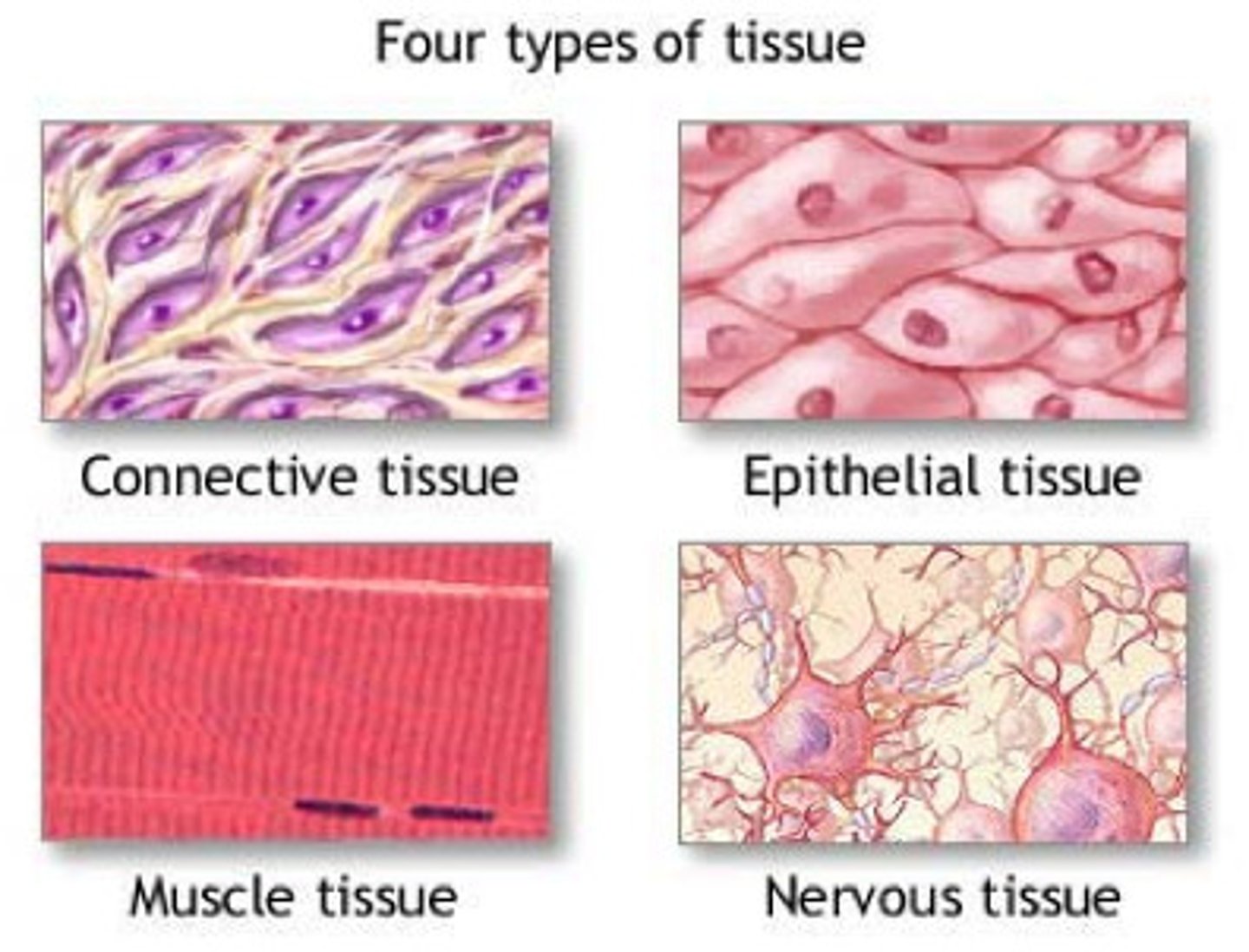
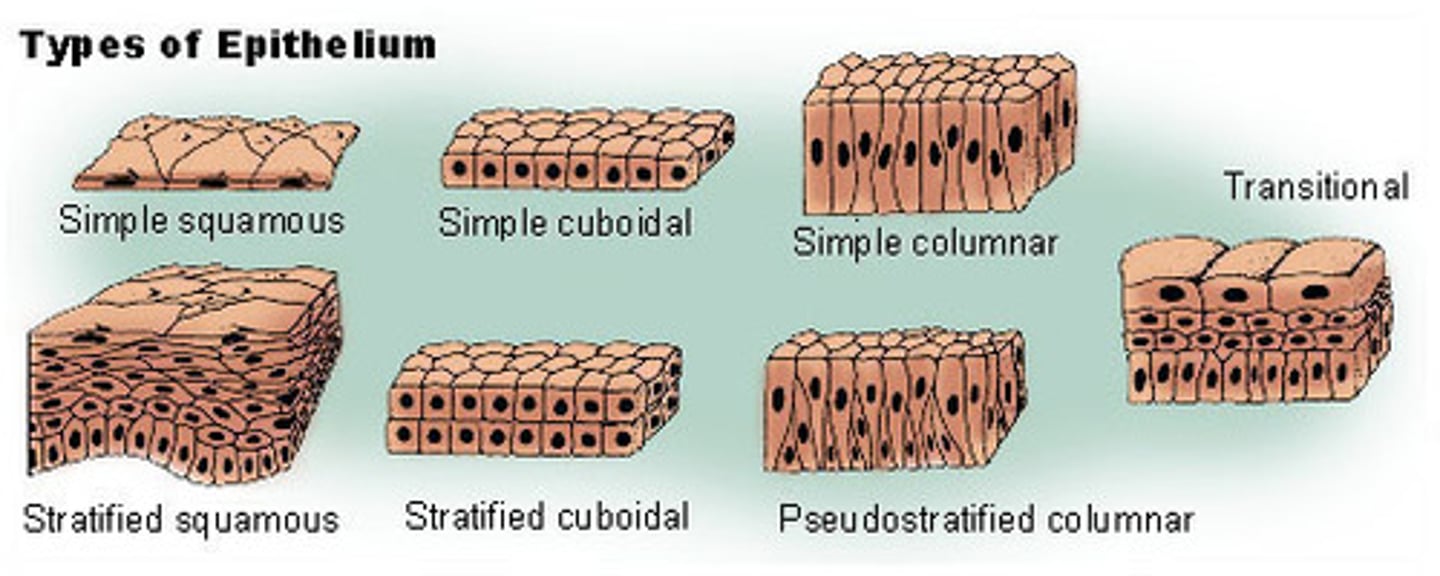
epithelial tissue
tightly packed sheets or columns of cells lining the organ and body
(skin, mouth cavity, digestive organs)
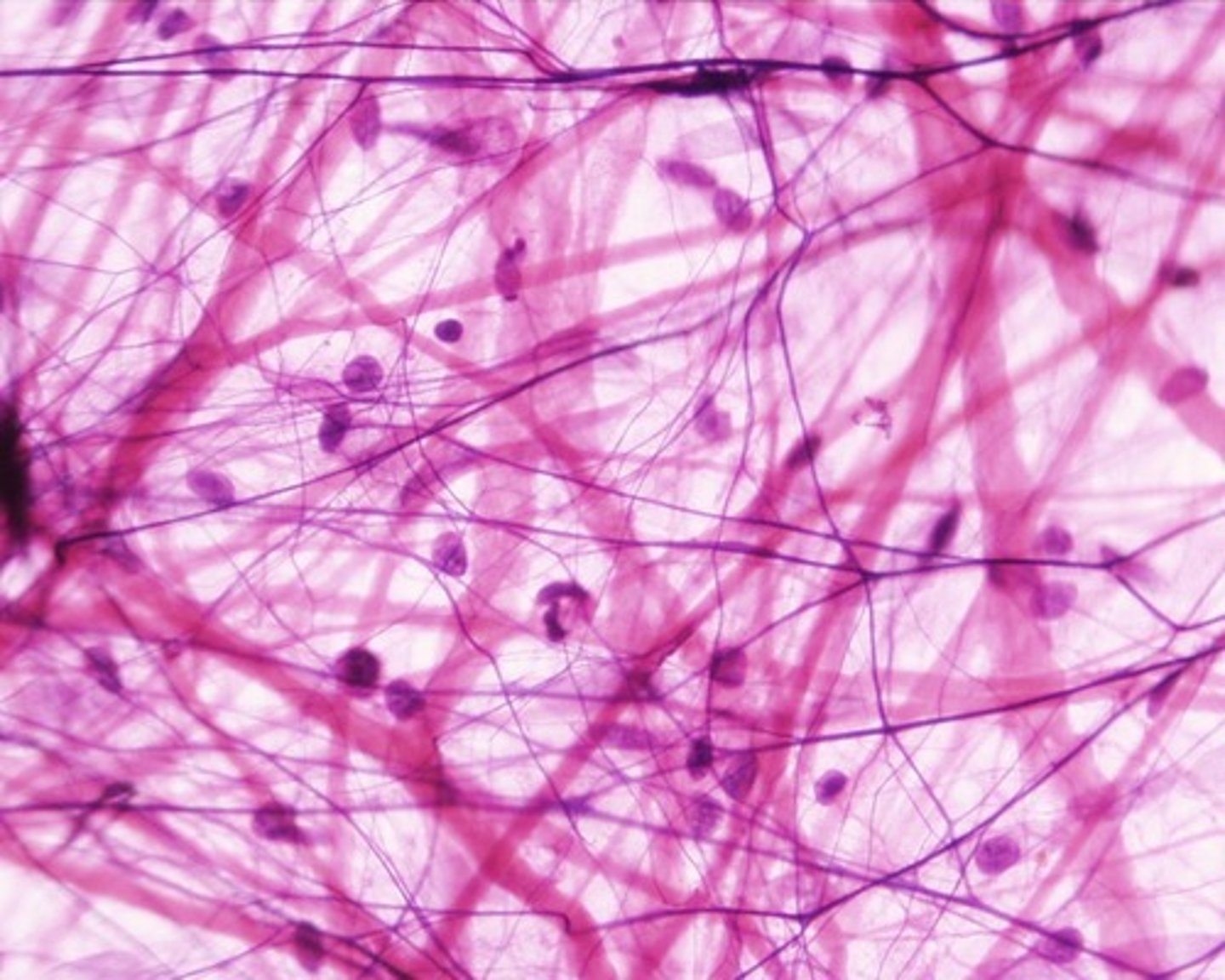
connective tissue
-various types of cells + fibres held together
strengthens, supports + connects cells +tissues
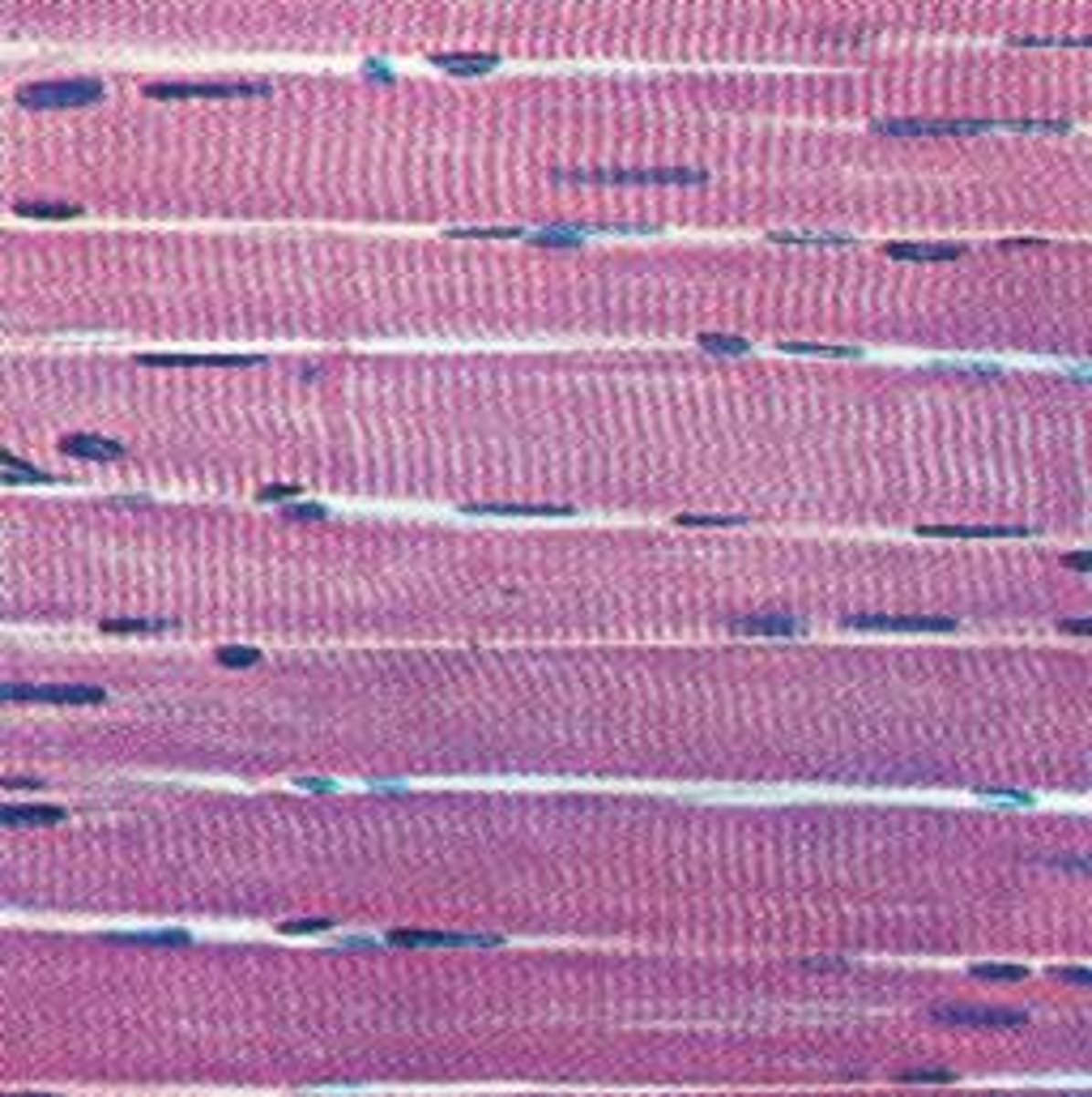
muscle tissue
bundles of muscle fibre containing specialized proteins shortening or lengthening
-skeletal, smooth, cardiac
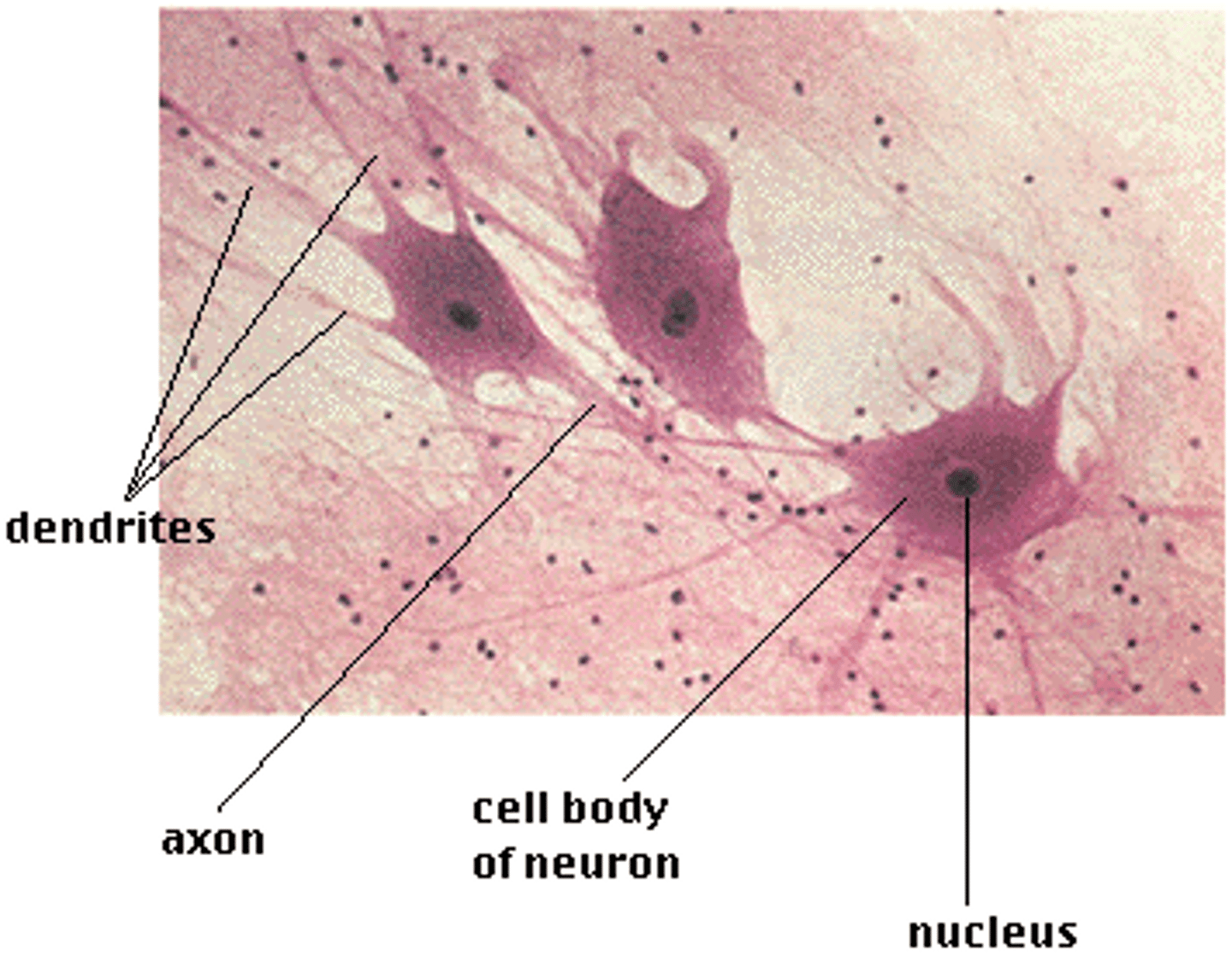
nervous tissue
neurons with fine branches at the end capable of conducting electrical impulses
(brain, nerves)
transmits n stores information and responds to stimuli
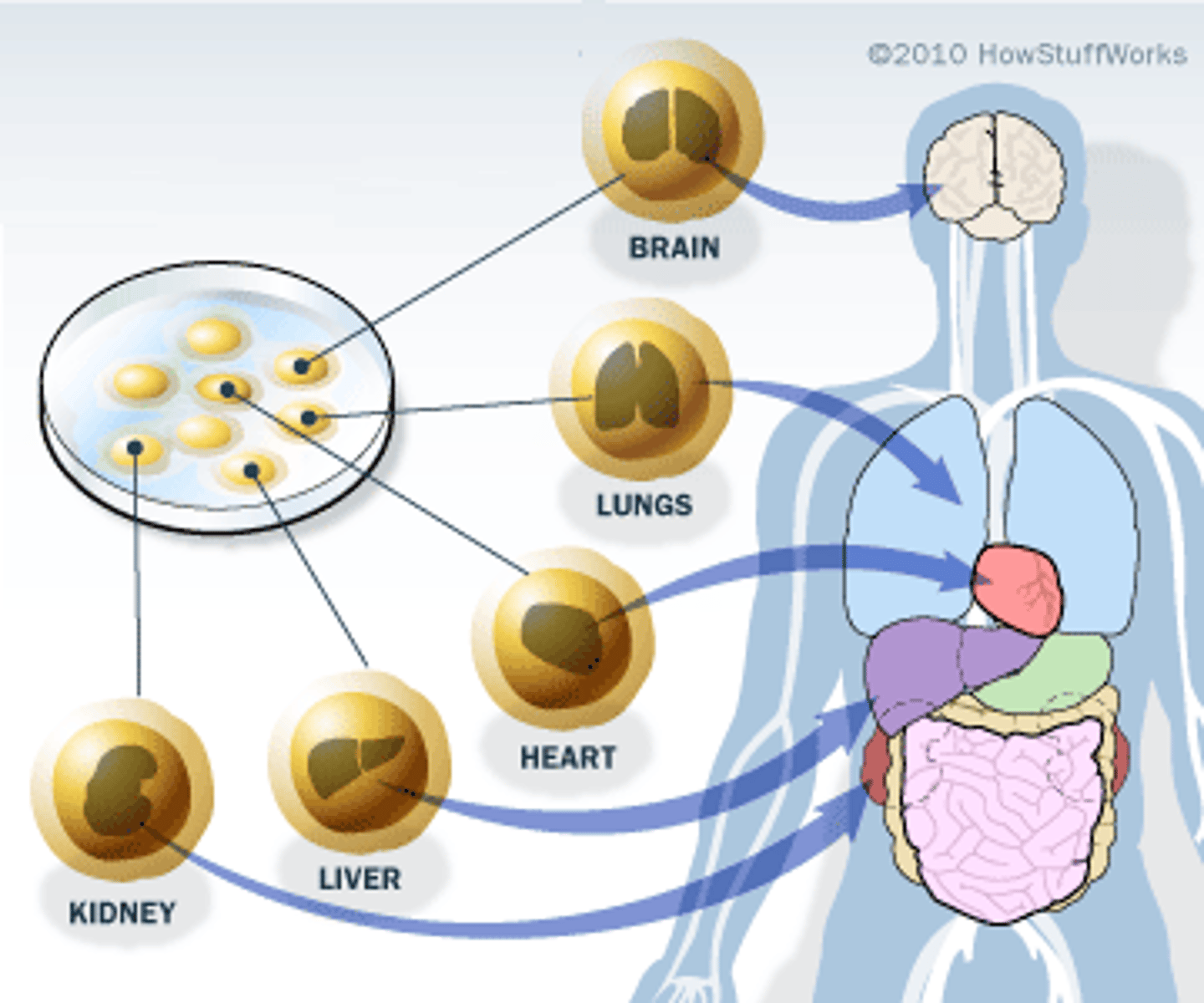
stem cells
unspecialized cells that retain the ability to become a wide variety of specialized cells n divides through mitosis and cytokinesis
embryonic stem cell
A type of stem cell that can differentiate into any kind of cell
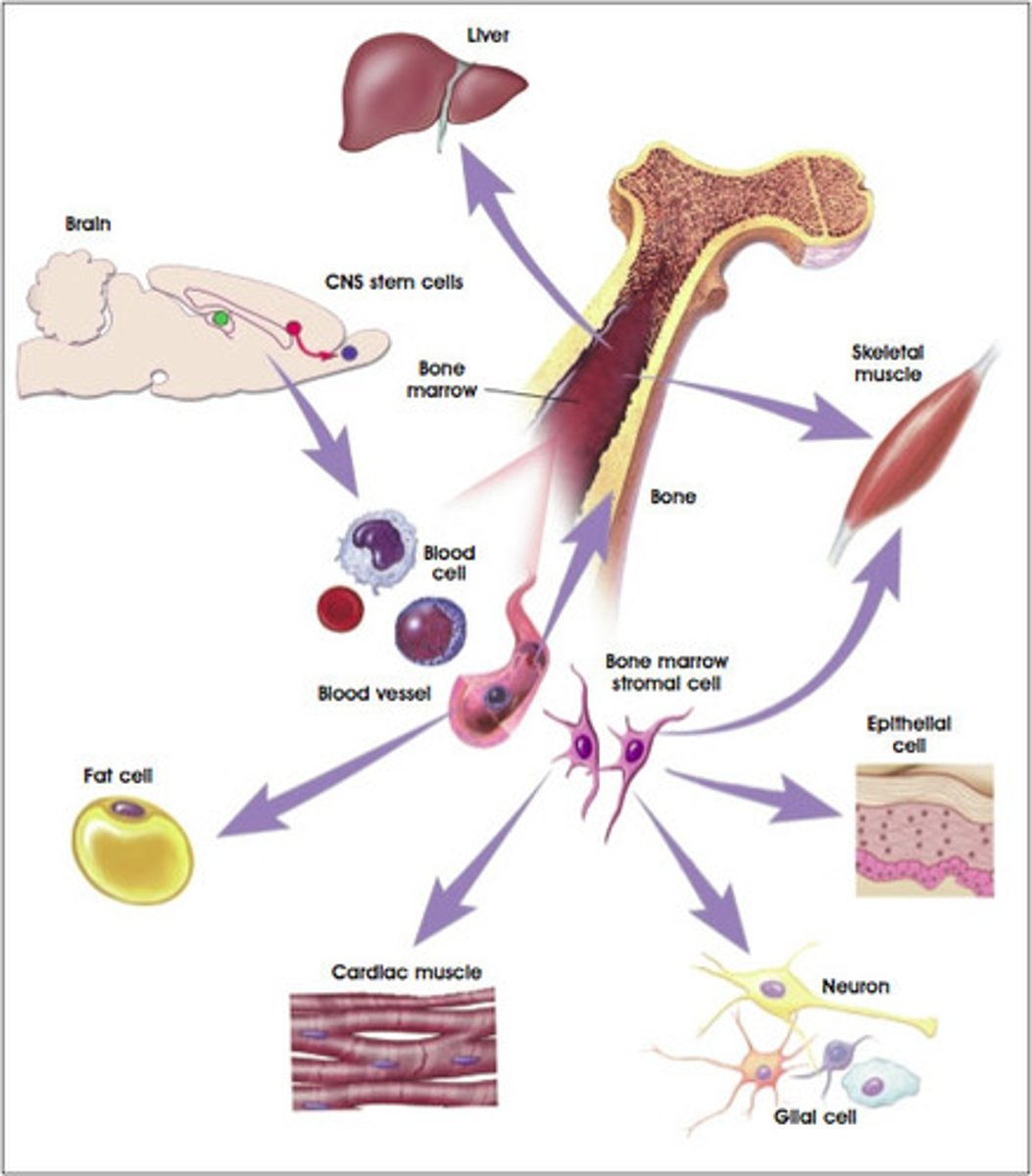
adult stem cell
located in special areas around the body and can only only differentiate depending on location
ie: blood marrow stem cells can b: rbc, wbc, or platelets
umbilical cord
the reproductive system
manufacture cells that reproduce
ovaries testes
endocrine system
manufactures and releases hormones that w nervous system regulate body
glands
urinary system
to filter out excess waste water and nutrients from circulatory
kidneys bladder
lymphatic system
destroy n defend against viruses n bacteria
lymph nodes and white blood cells
skeletal system
provide support, protect delicate organs and attachment site for organs
bones, tendons
muscular system
for movement n controls movement of materials like heart stomach intestine
3 main muscle types
nervous system
relay information n electrical systems, controls and coordinates, brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves
Intergumentary system
waterproof barrier
skin hair nails
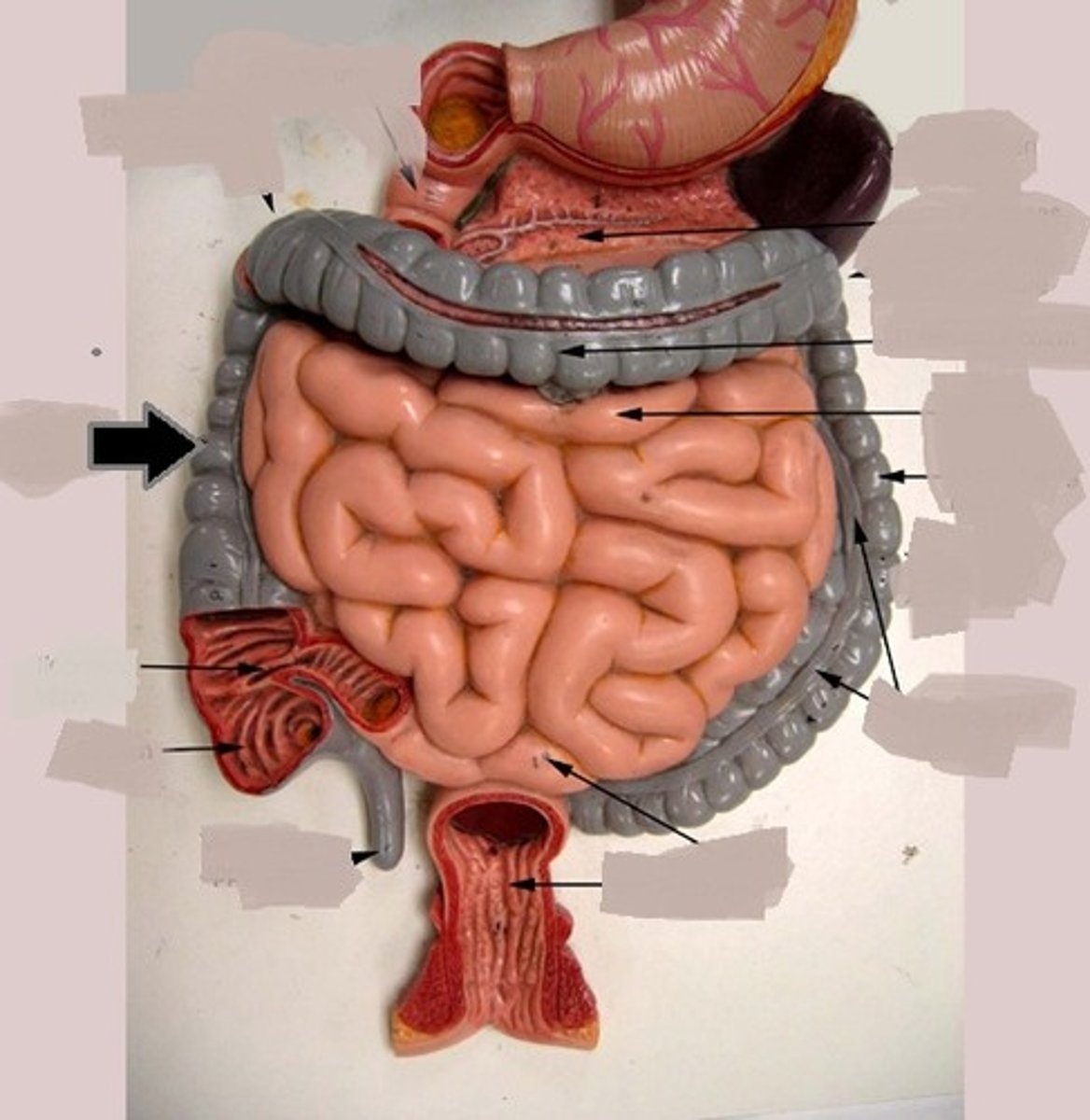
4 phases of digestion
-ingestion, digestion, absorption, egestion
-digestive tract and organs
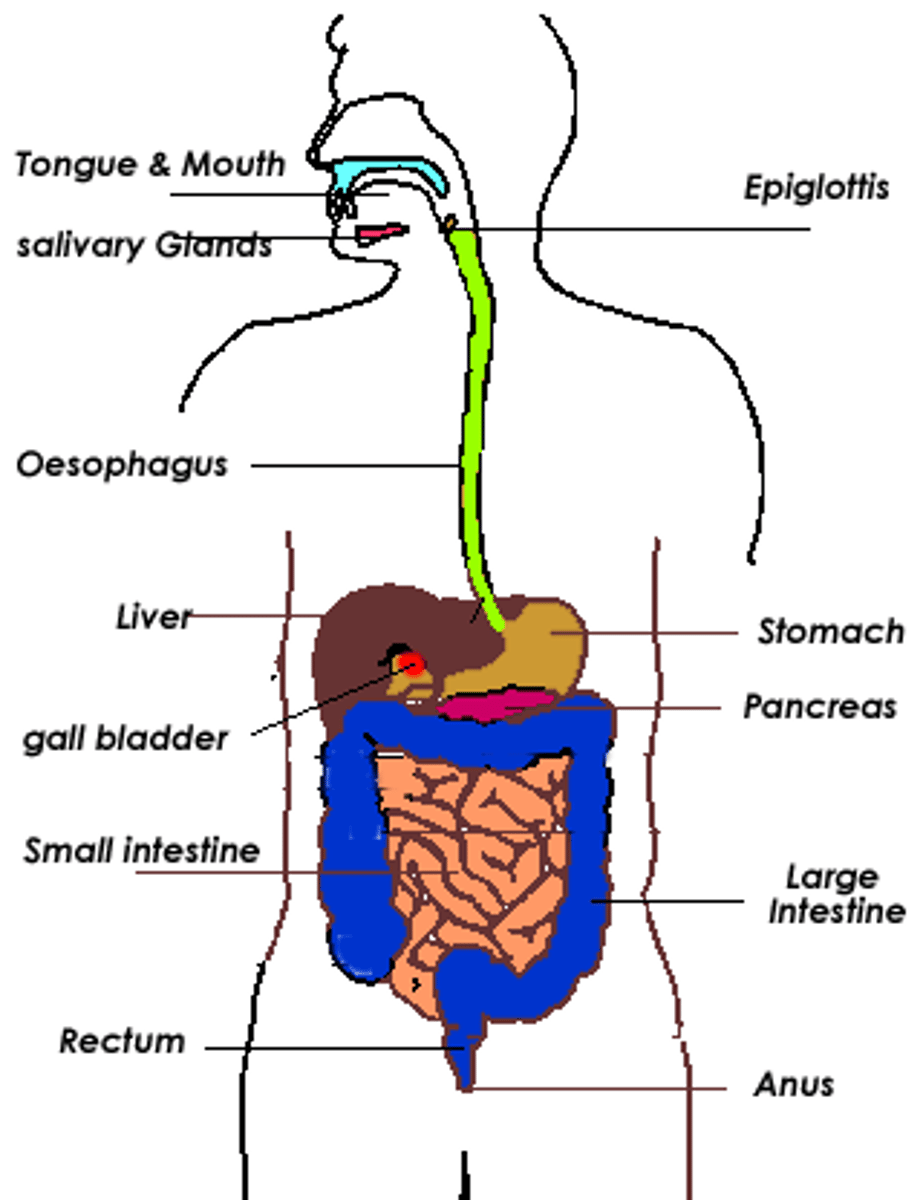
Mouth
-mechanical (teeth and tongue)
-carbs, fats, proteins r digested using enzymes and dig. juices
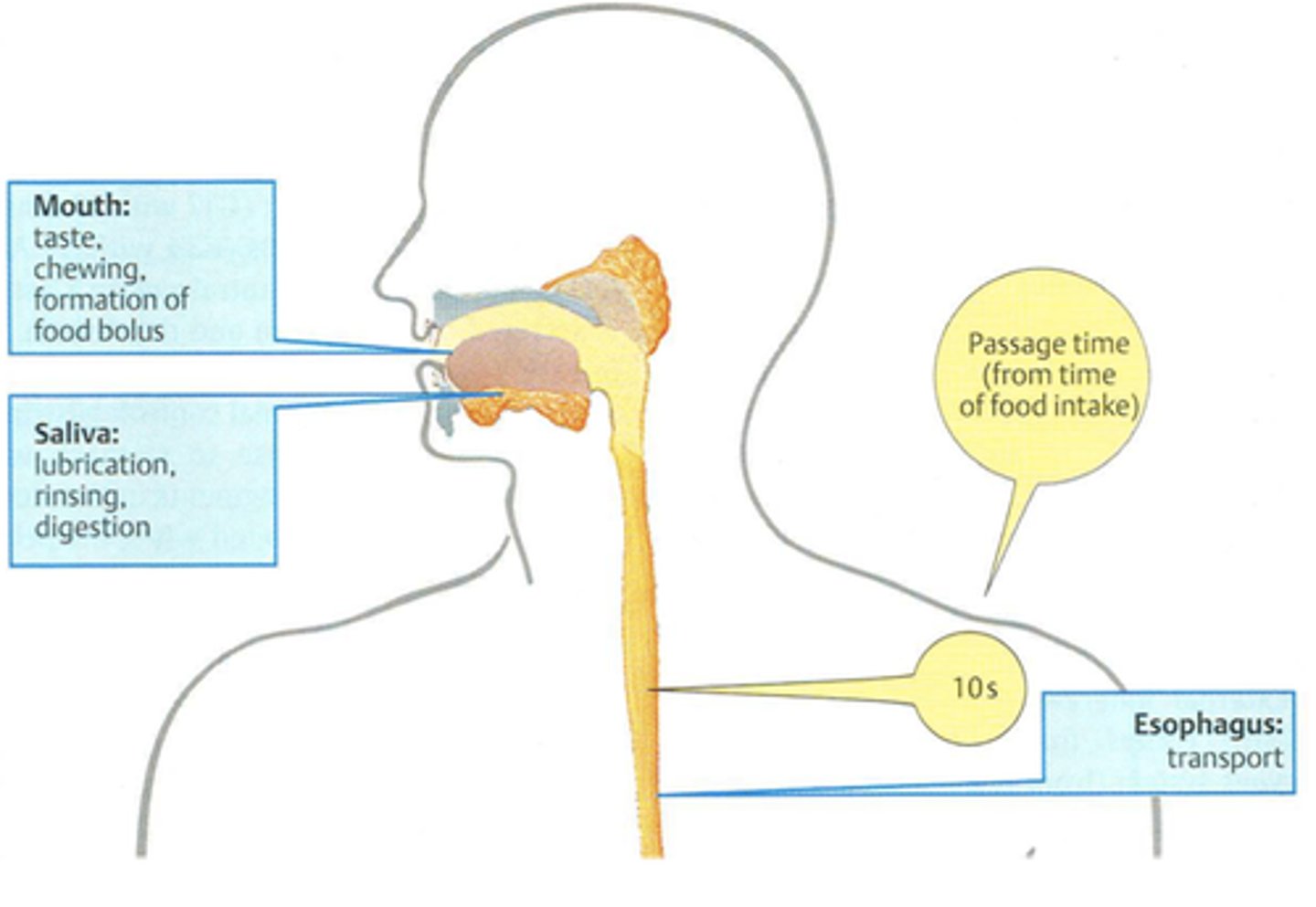
salivary glands
water, mucin (lubricates food), salivary amylase (enzyme that breaks down starch to maltose)
esophagus
muscular tube connecting the mouth to the stomach, smooth muscle tissue contracts n relaxes pushing food (peristalsis)
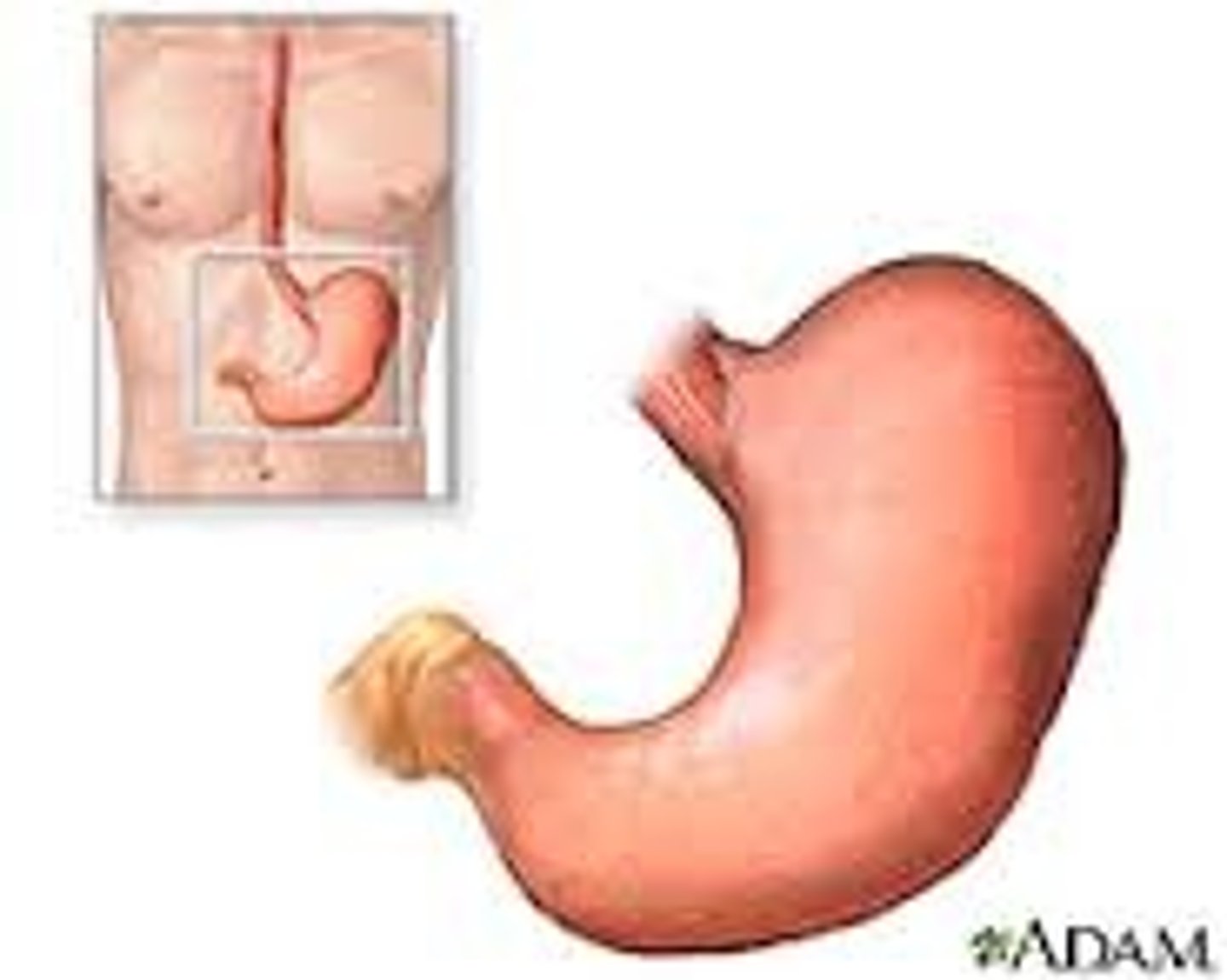
stomach
-mechanical digestion--> churning
-enzymes and hydrochloric acid (epithelial)
-pepsinogen--> pepsin (protein digestion)
-HCl also kills bacteria
-chyme (liquid paste in small intestine)
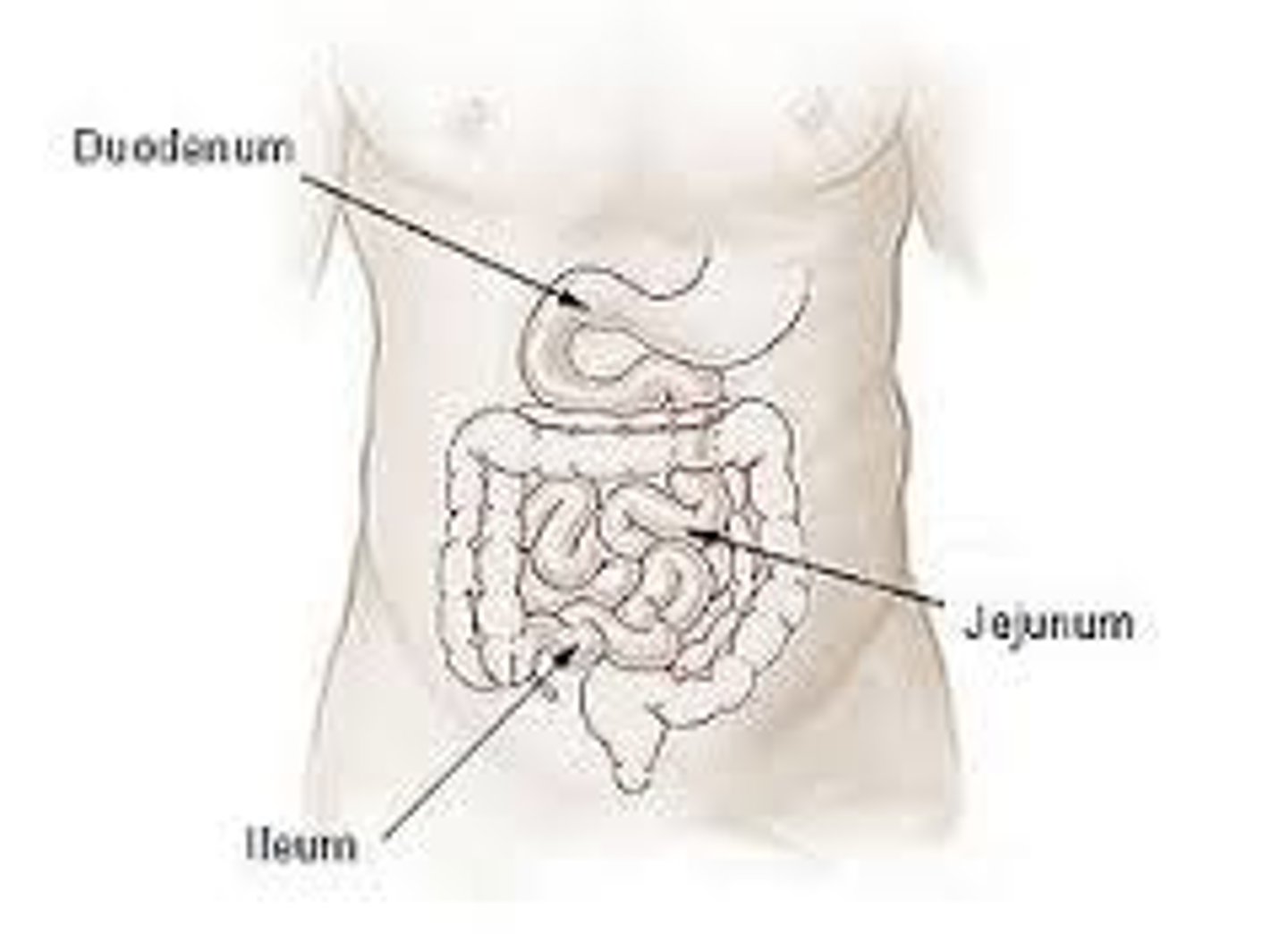
small intestine
duodenum(mech. dig.) jejunum, ileum (absorption)
liver bile globs of fat into small droplets
pancreas enzymes break down 3 macros
amylase: carbs to glucose
protease: proteins to amino acids
lipase: fats into fatty acids
large intestine
Absorbs water and electrolytes and forms feces
holds waste
Respiratory system
-gas exchange between the body and the environment, consisting especially of the nose, nasal passages, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, capillaries.
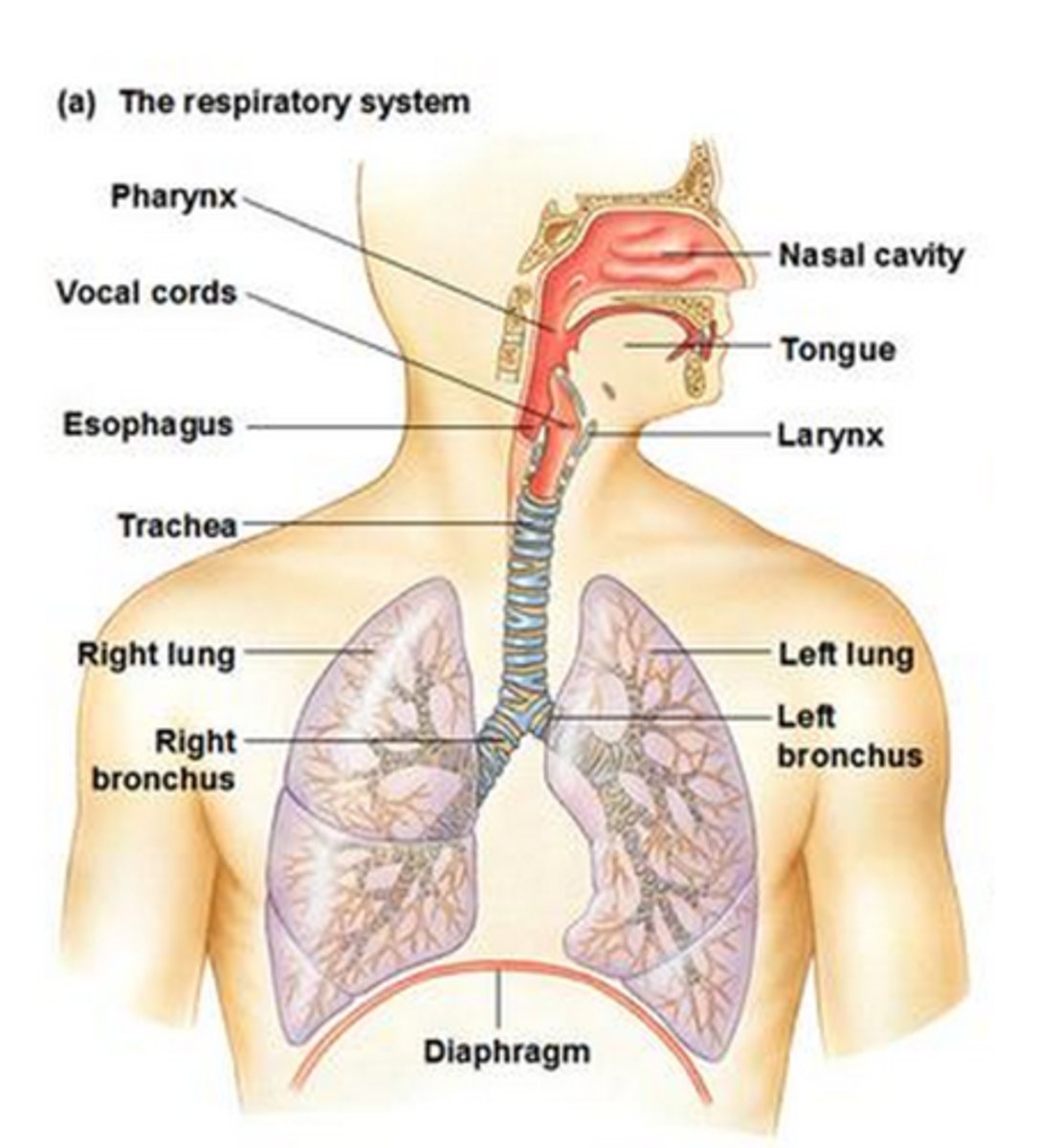
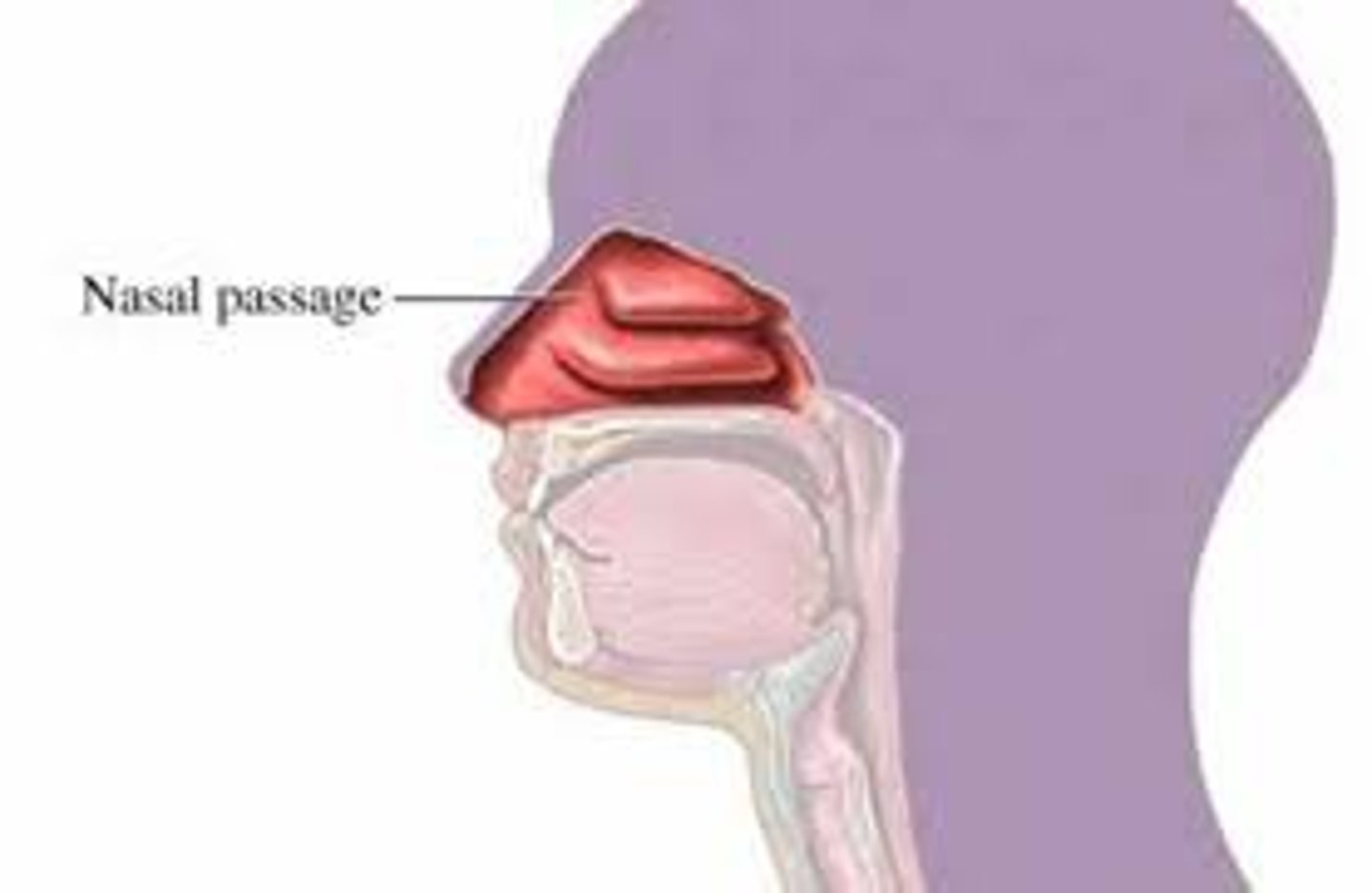
nasal passages
air is warmed and moistened with mucus
have cilia to move mucus upwards
pharynx and larynx
carries air to the trachea and produces sound
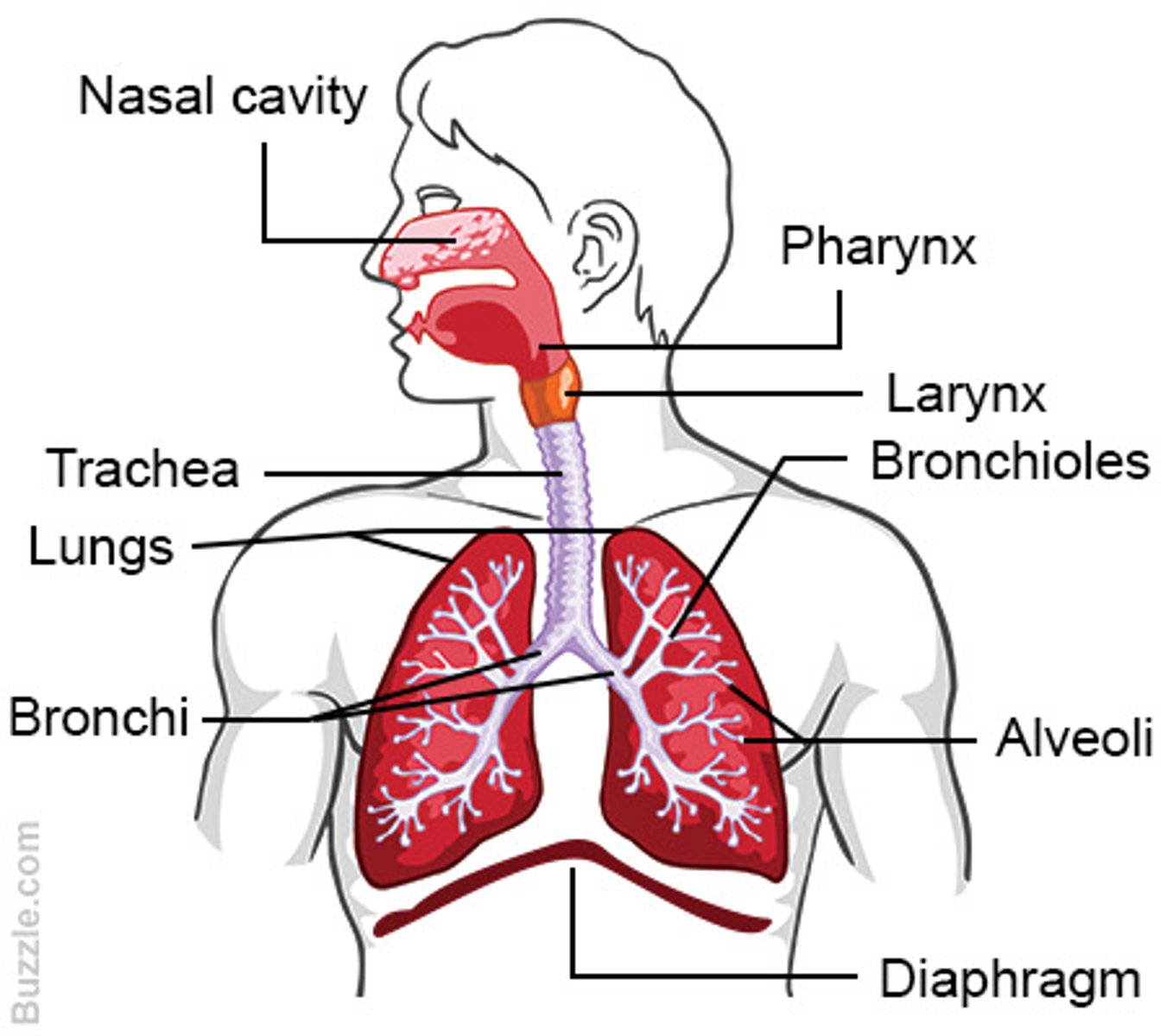
trachea
Allows air to pass to and from lungs
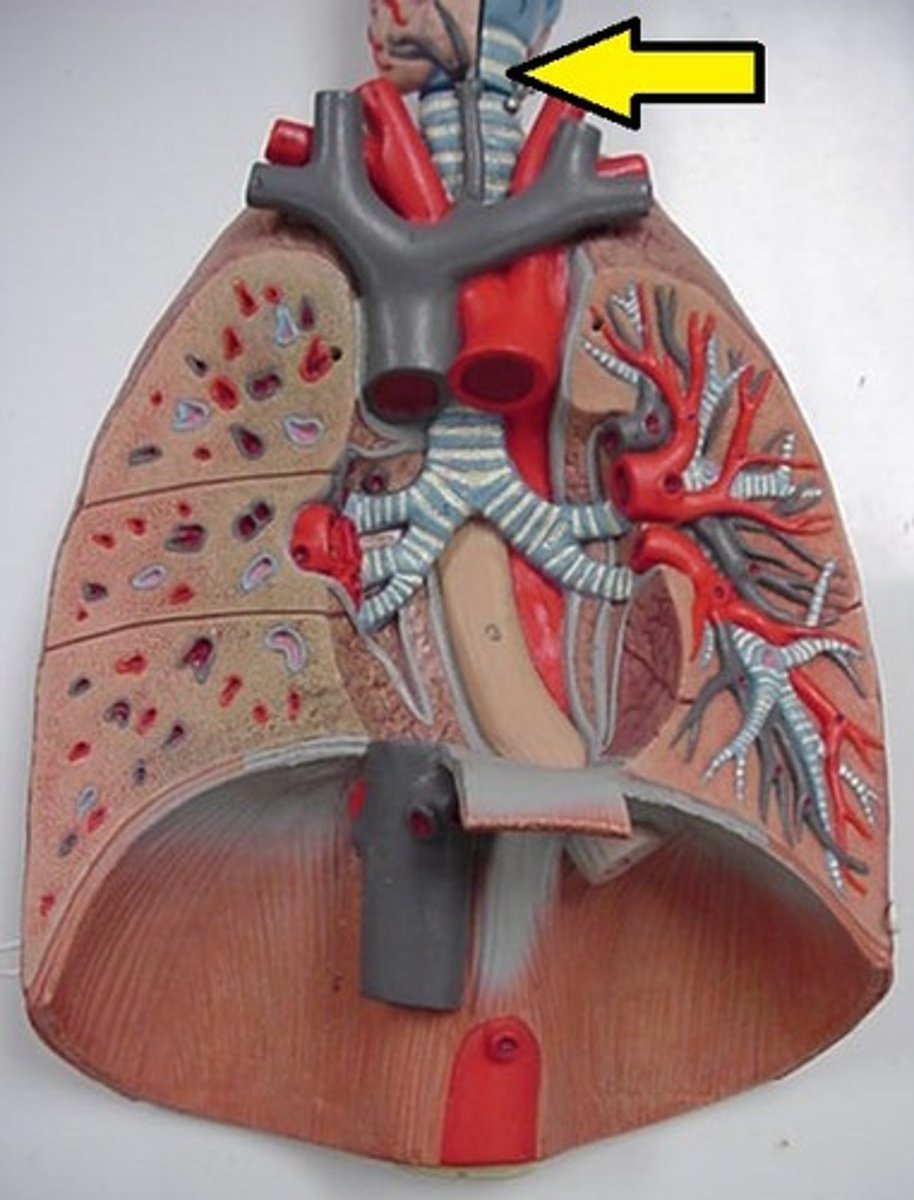
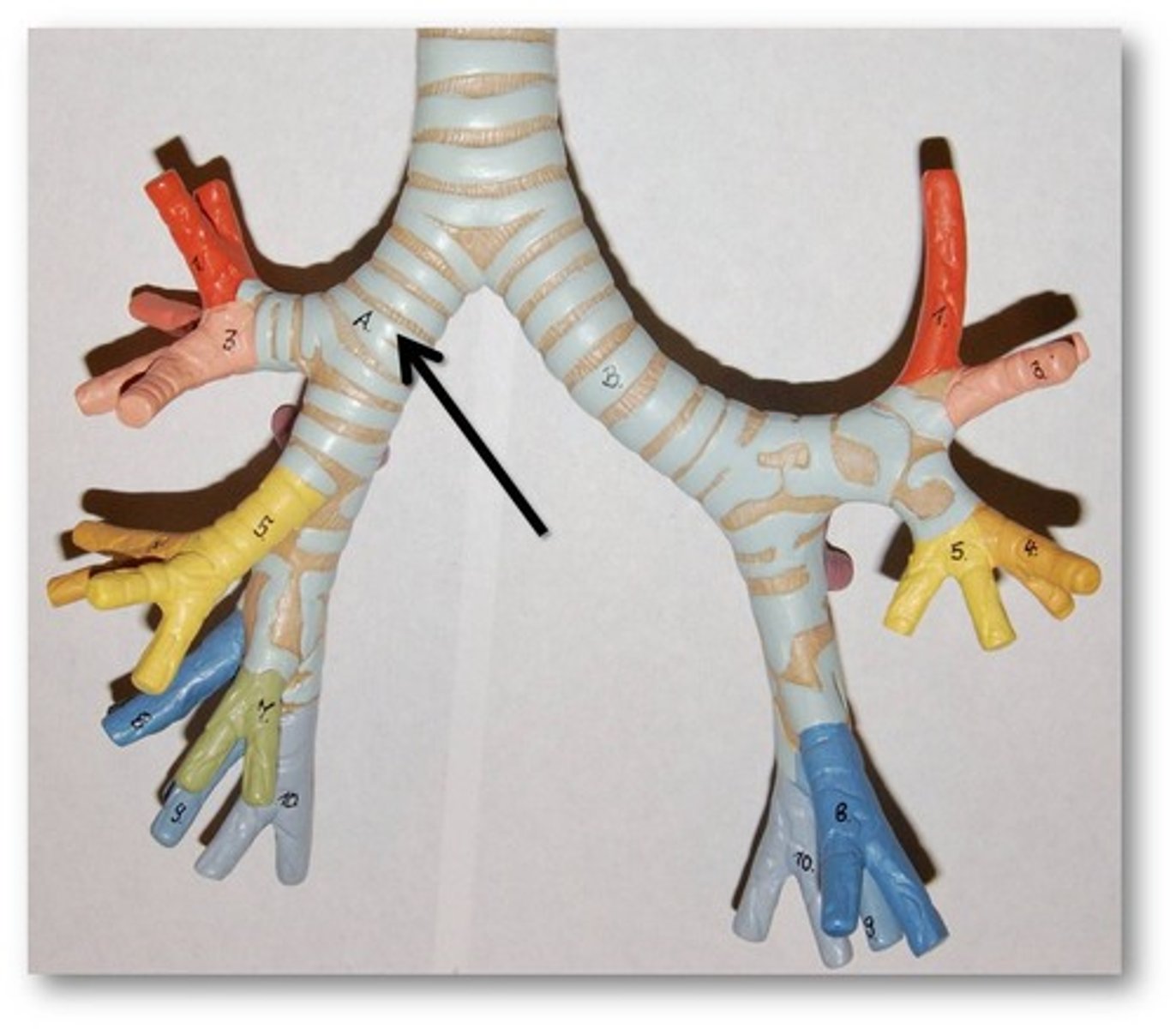
bronchi
two short branches located at the lower end of the trachea that carry air into the lungs.
contains muscle tissue and epithetlial tissue(cartilaginous rings)
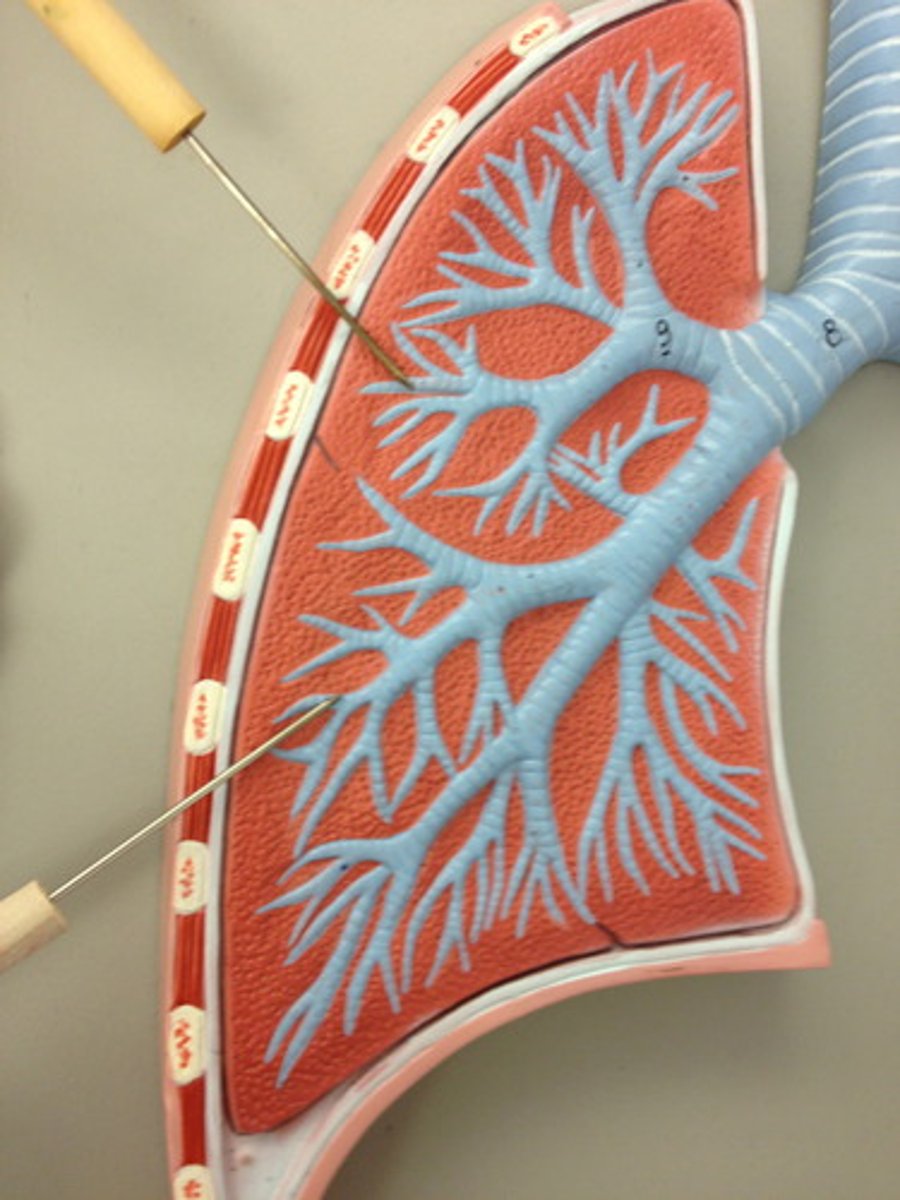
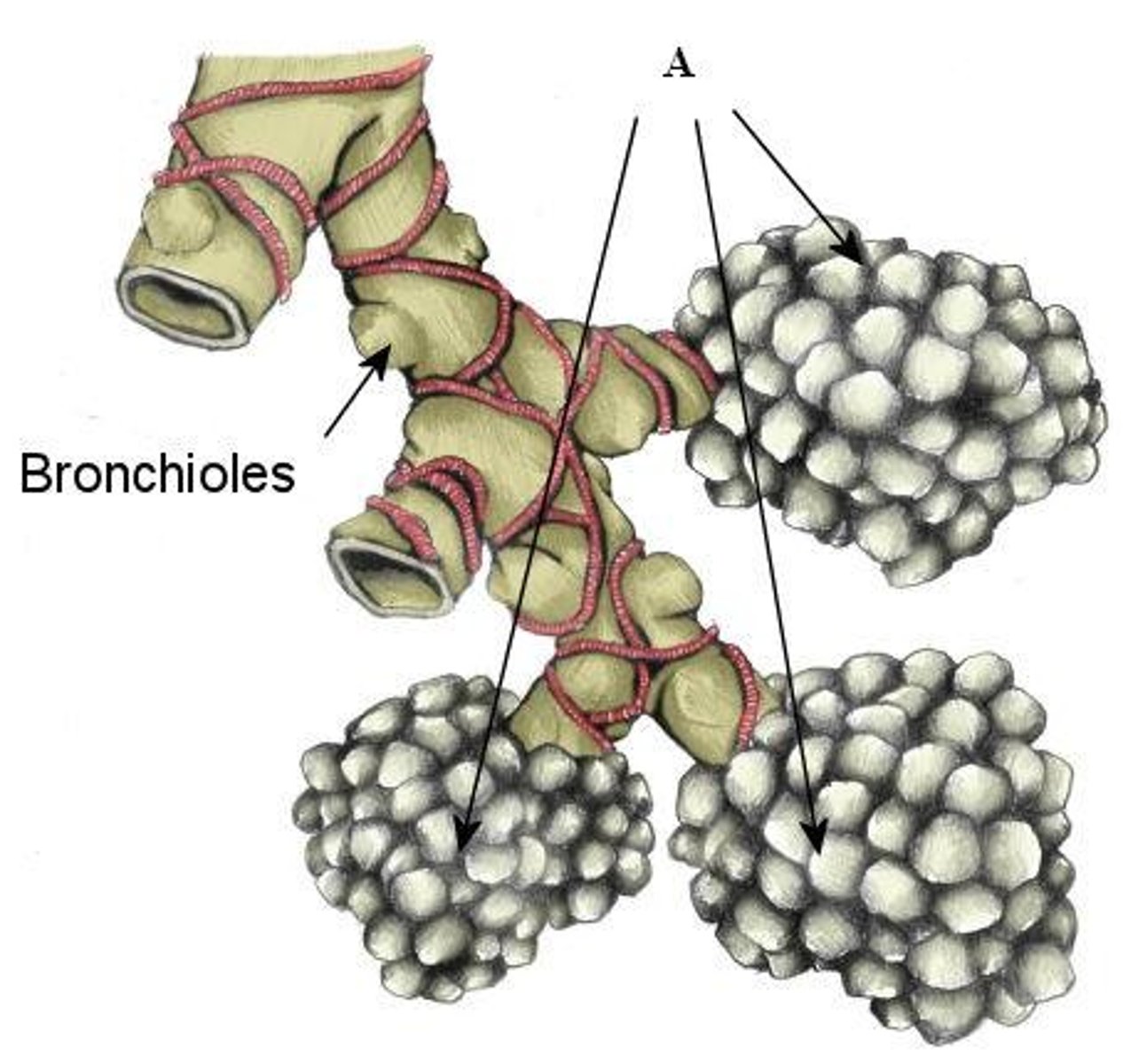
bronchioles
smallest branches of the bronchi
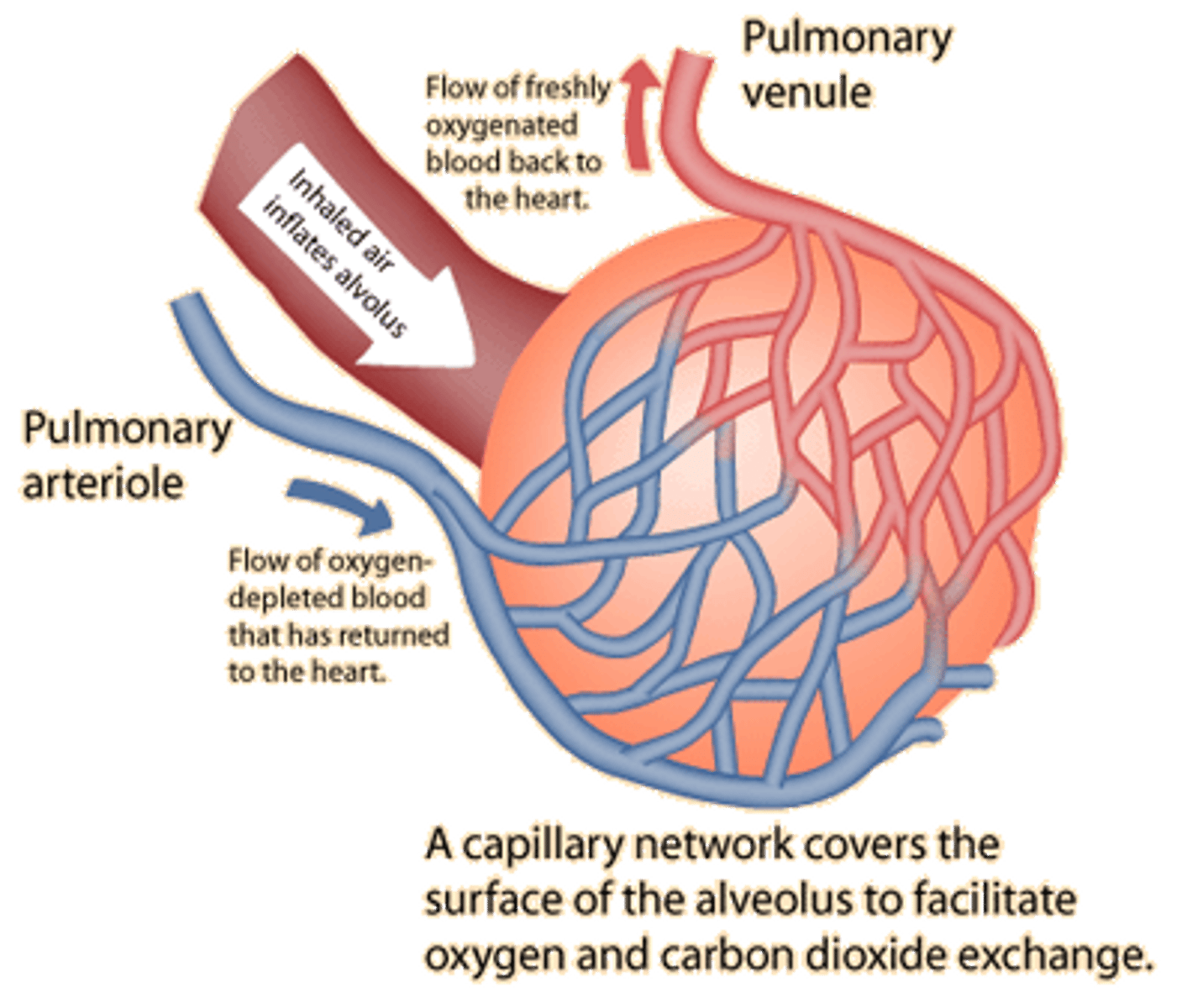
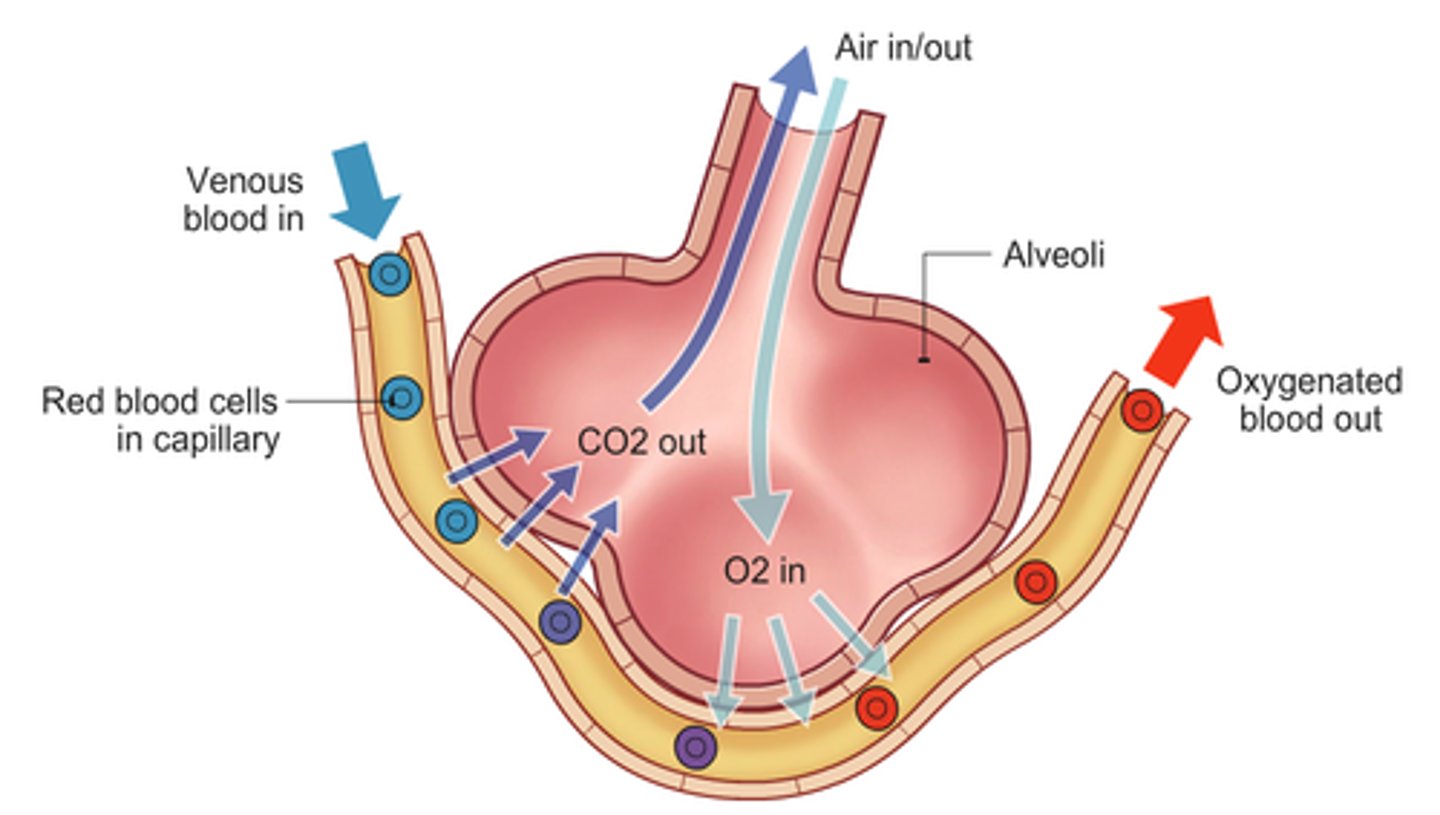
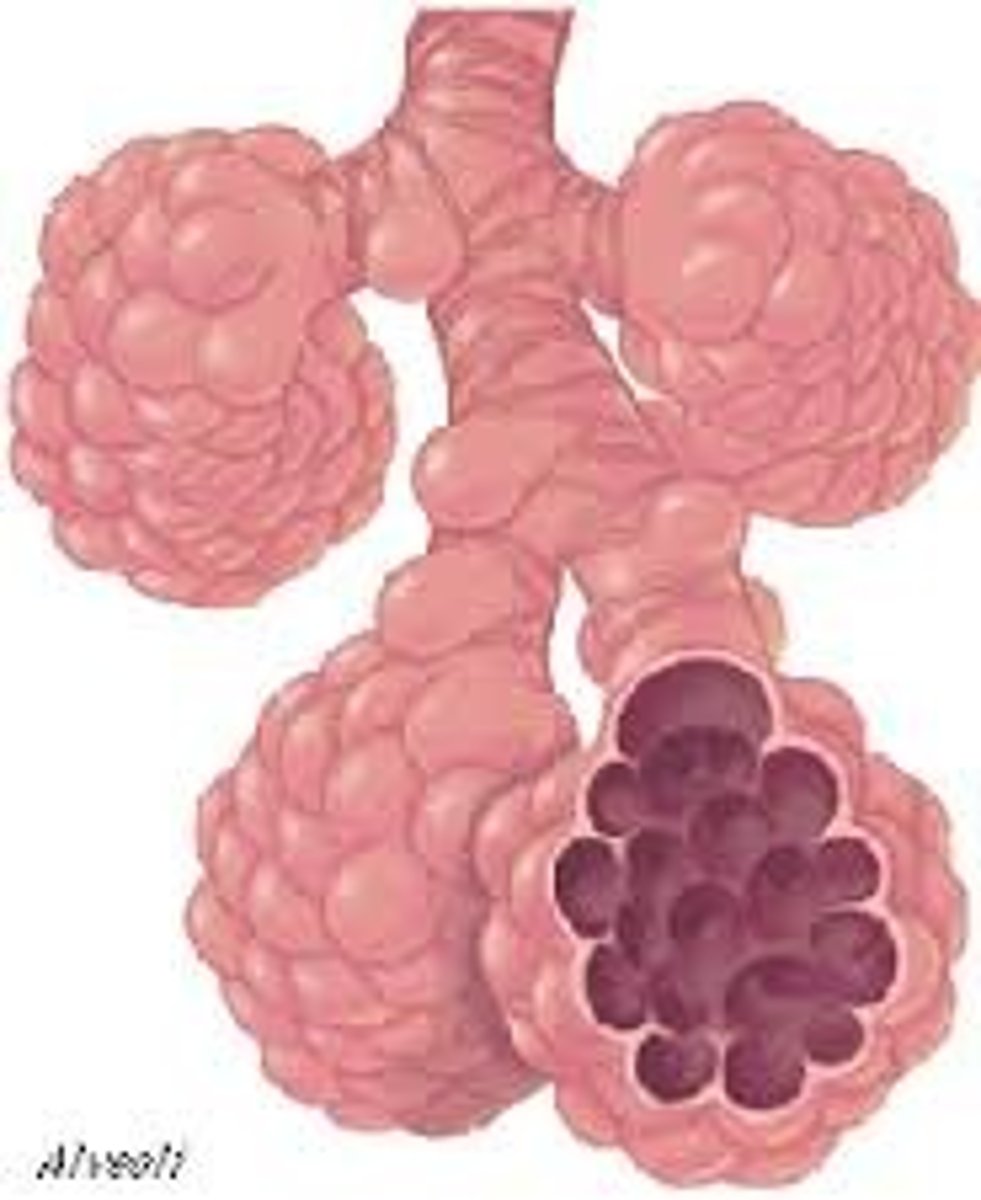
alveoli
tiny sacs of lung tissue specialized for the movement of gases between air and blood
capillaries
Smallest blood vessels on alveoli (diffuses air into and out of lungs)
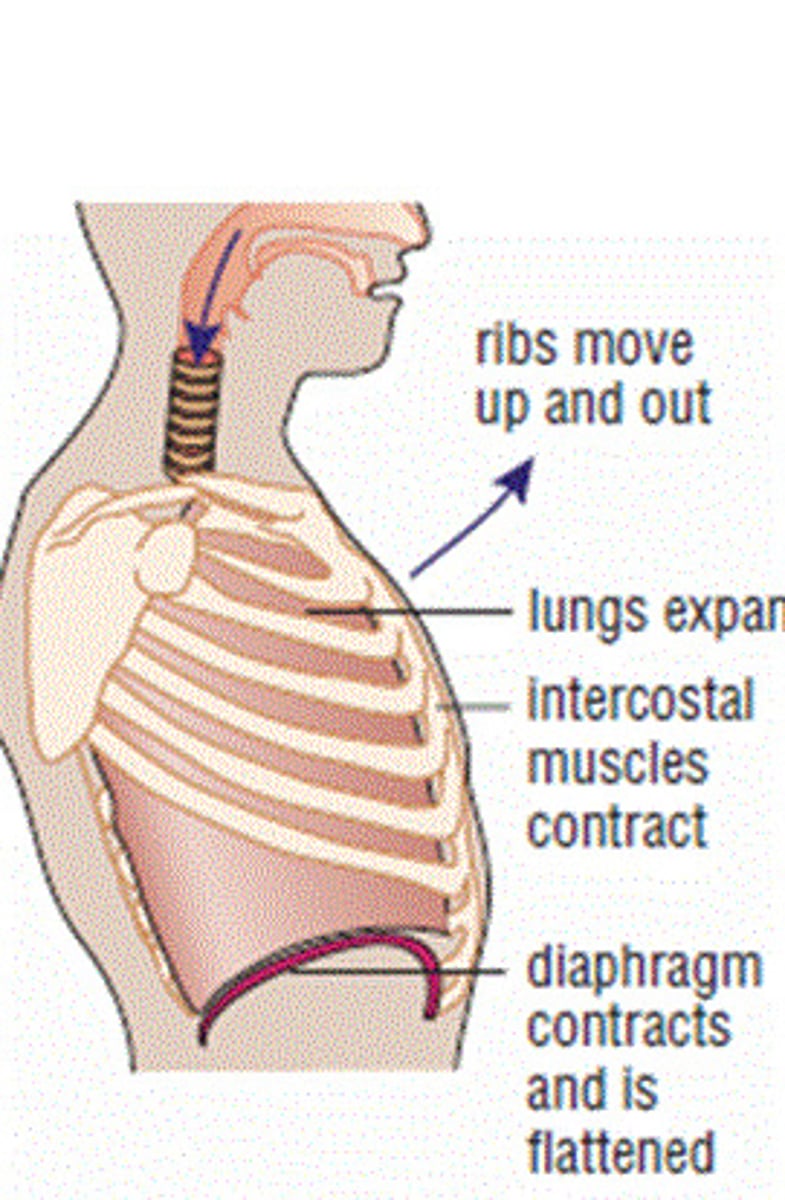
inhalation
air into
rib cage and diaphraghm contract
pressure inside lungs
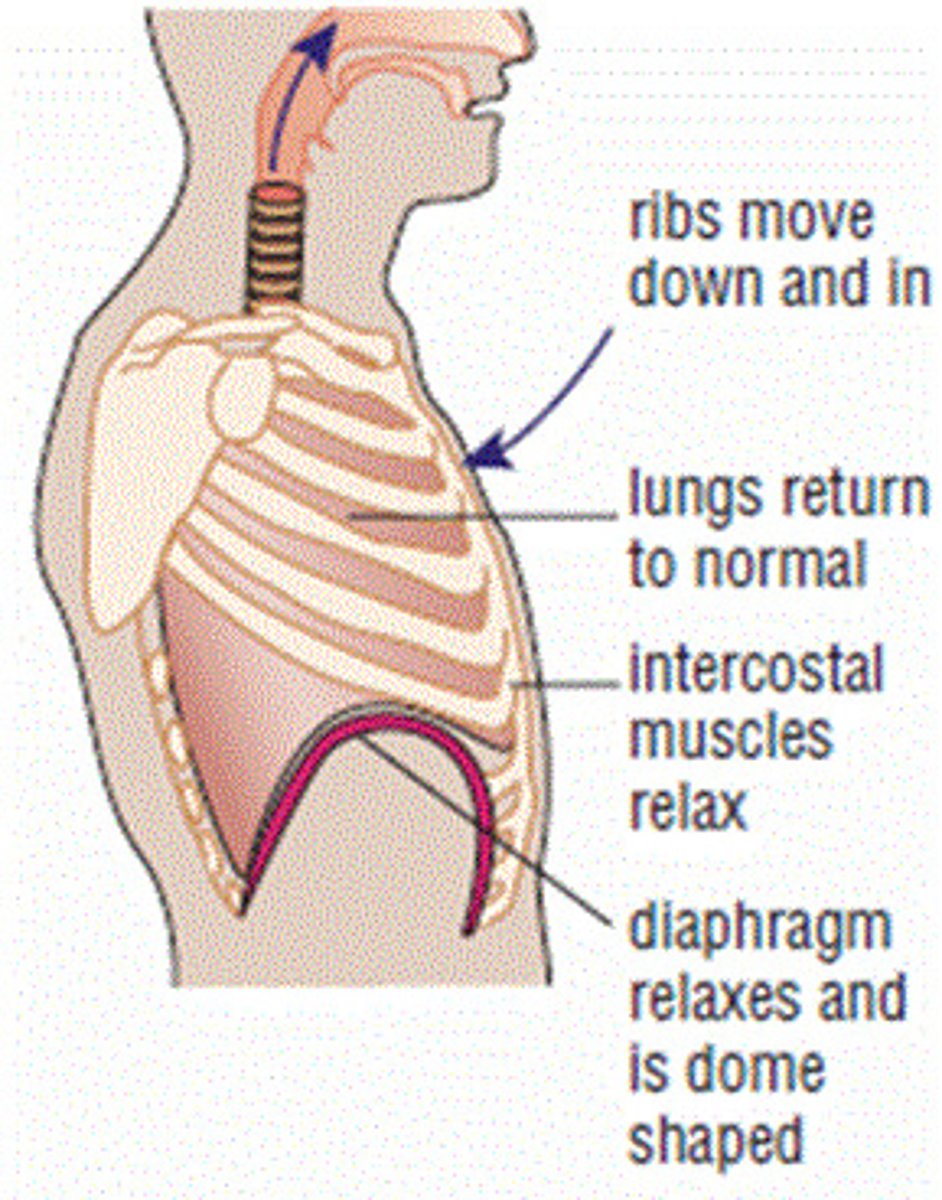
exhalation
breathing out
diaphraghm n rib cage relax
diaphraghm moves up
rib cage down and in
volume in chesr cavity decreases
gas exchange
by diffusion: oxygen moves into capillaries from alveoli and carbon dioxide moves into alveoli through capillaries
features of alveoli for gas exchange
-large surface area
-moist surface
-thin lining
-dense capillary network
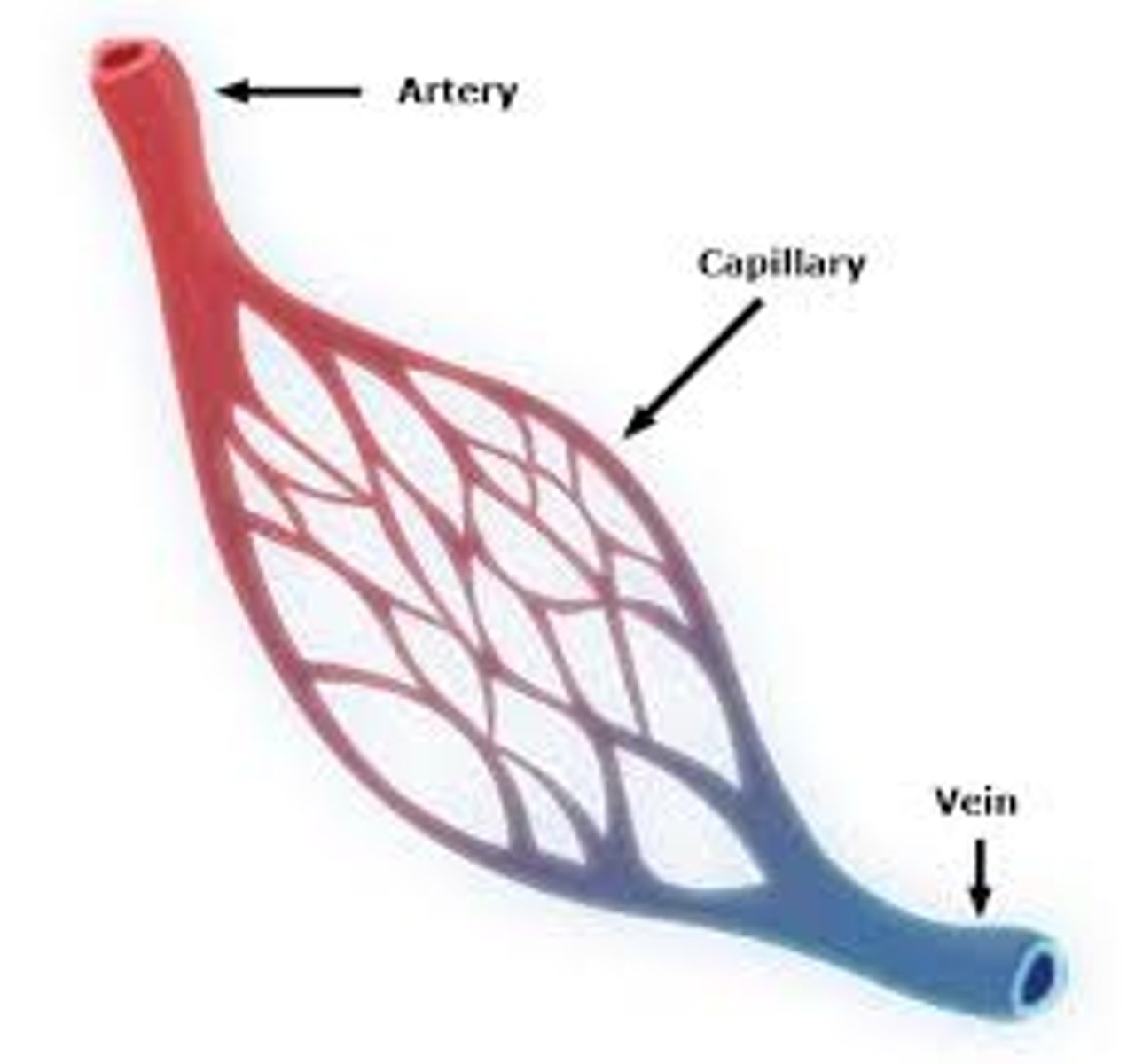
features of capillaries for gas exchange
-dense network
-large surface area
-one cell thick lining easy diffusion
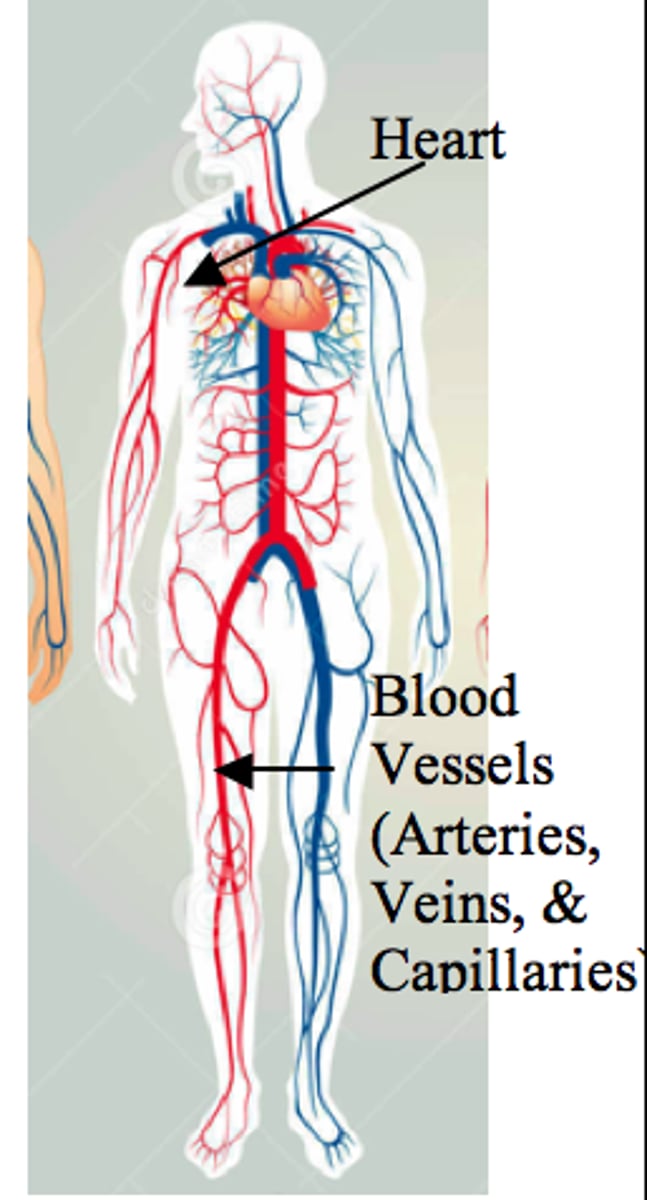
circulatory system
Transports oxygen, waste, nutrients, hormones, heat, etc... around the body
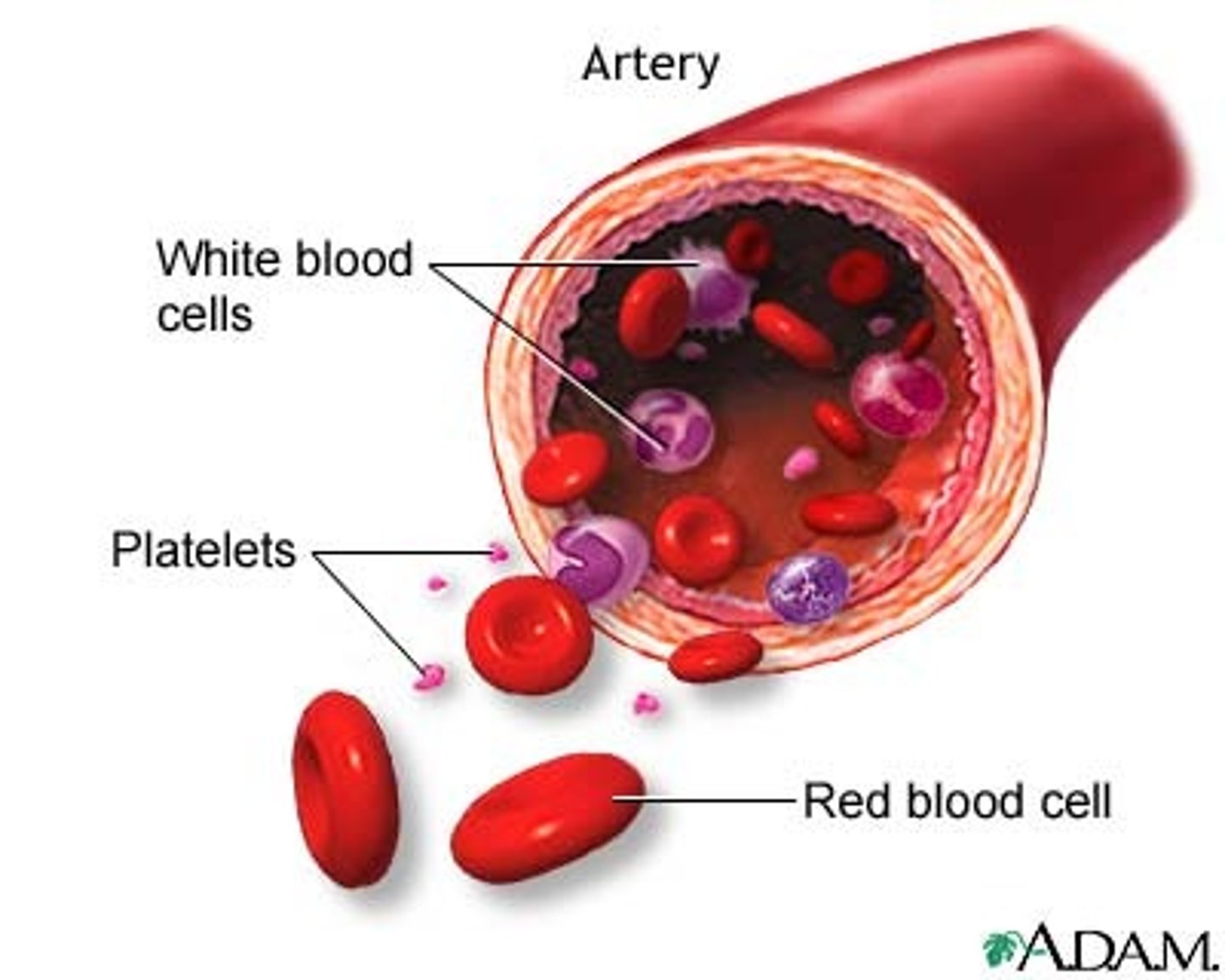
what is blood?
-connective tissue
-plasma (90% water, 10% dissolved substances)
n solid (red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets)
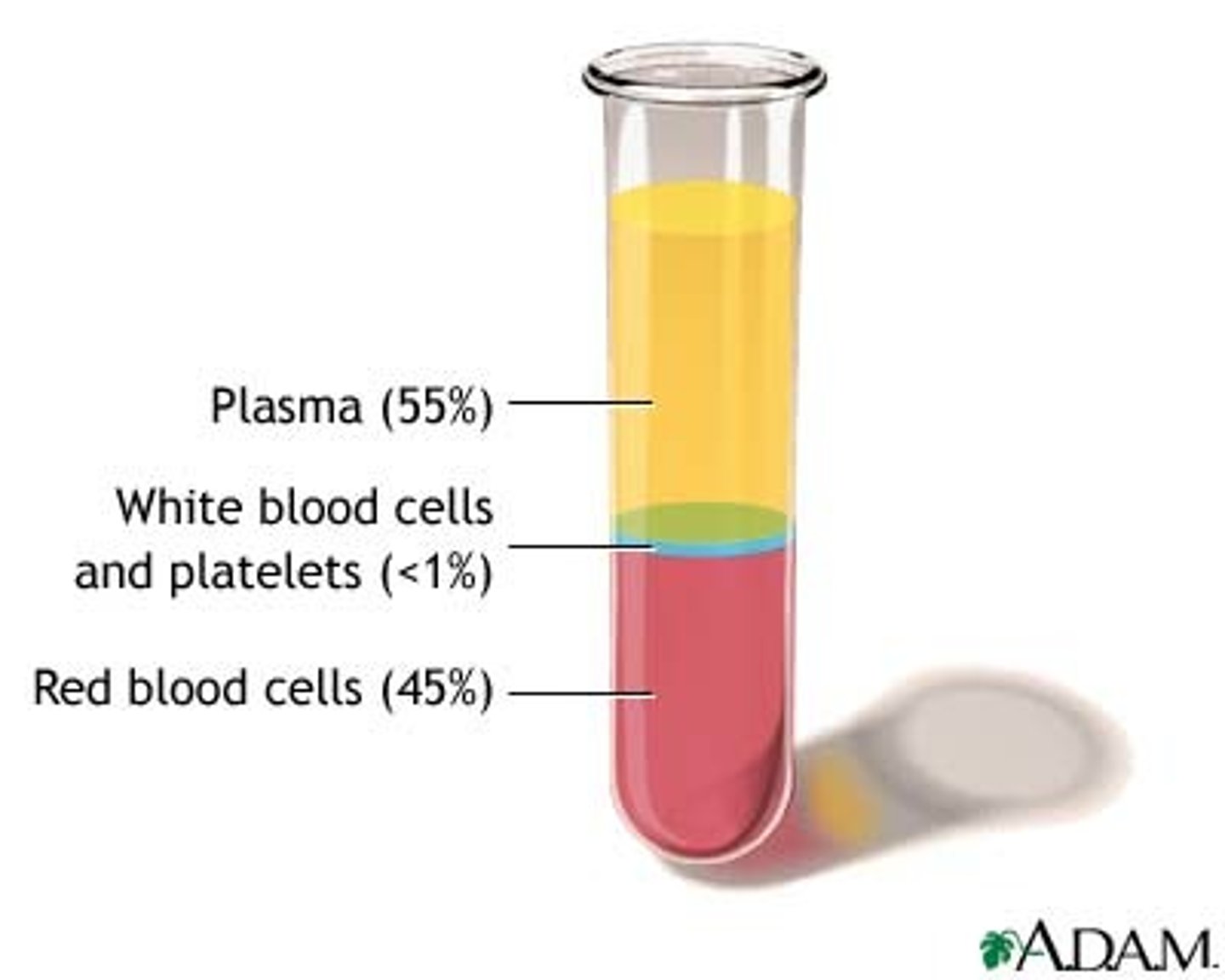
RBC, WBC, platelets
rbc: transports oxygen through hemoglobin
wbc: fights infection
platelets: blood clotting
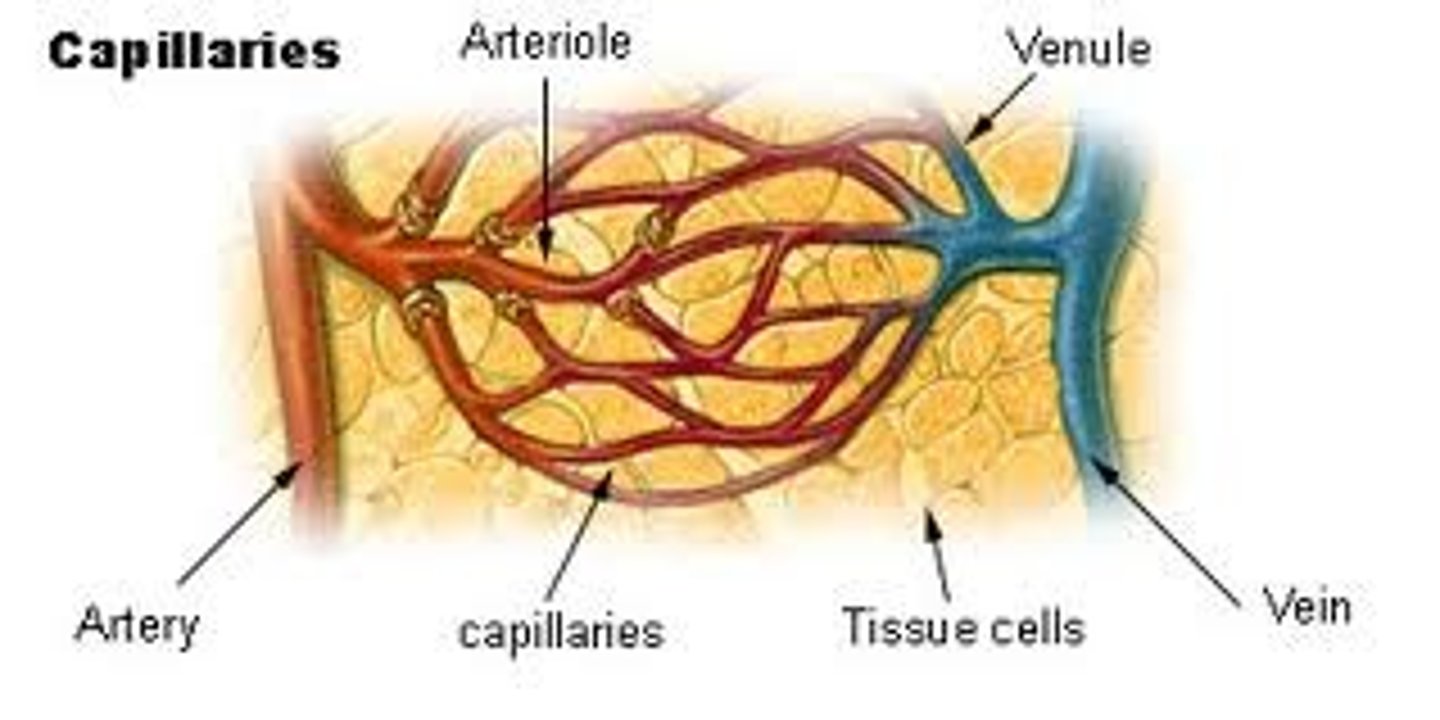
3 types of blood vessels
arteries, veins, capillaries
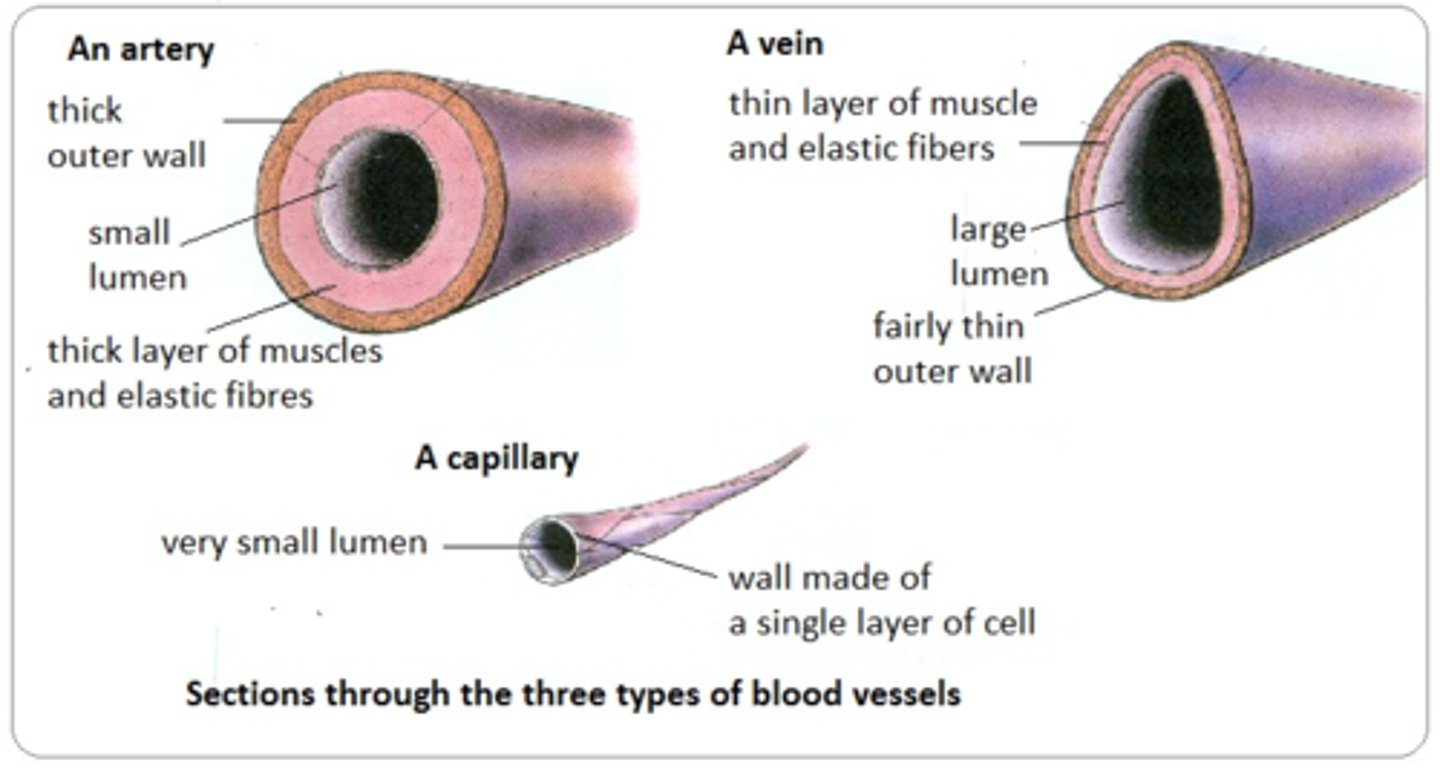
arteries
carry blood away from the heart, thick n elastic walls, smaller artery=arteriole
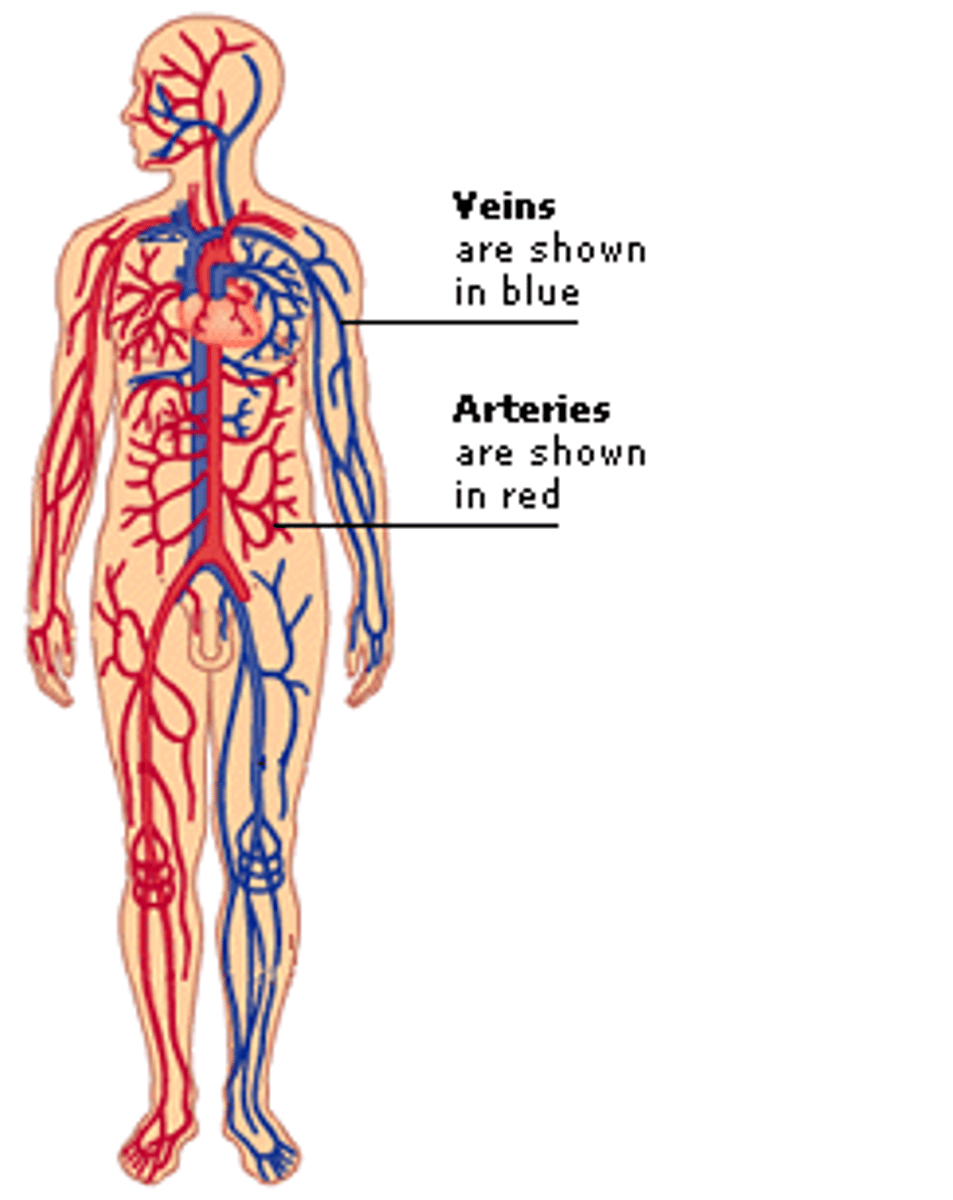
veins
carry blood toward the heart, thin walls, valves (prevent backflow), small vains=venuoles
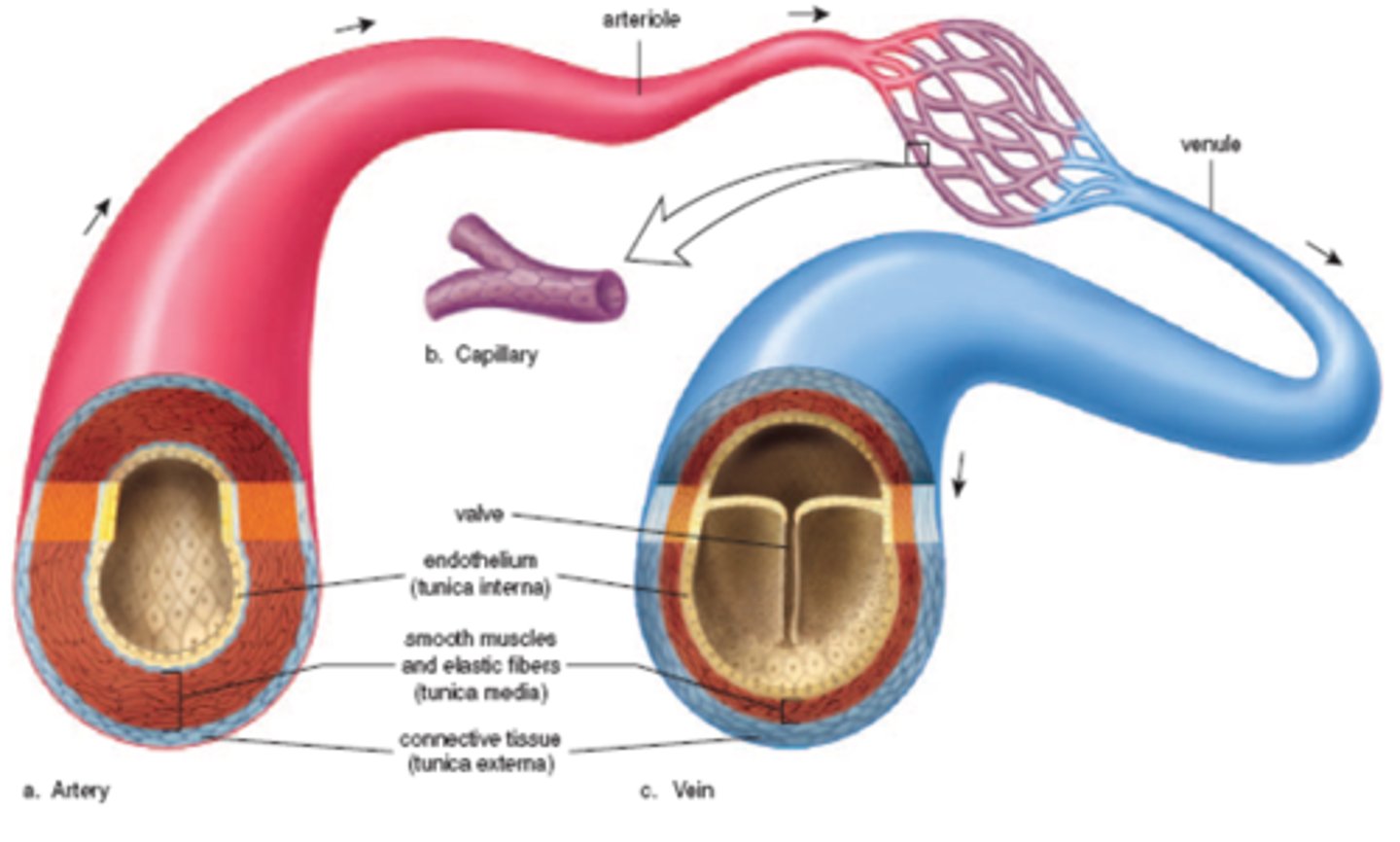
capillaries
carry blood from arteries to vains (not elastic, thin)
heart
four-chambered double pump that is responsible for the flow of blood in the body
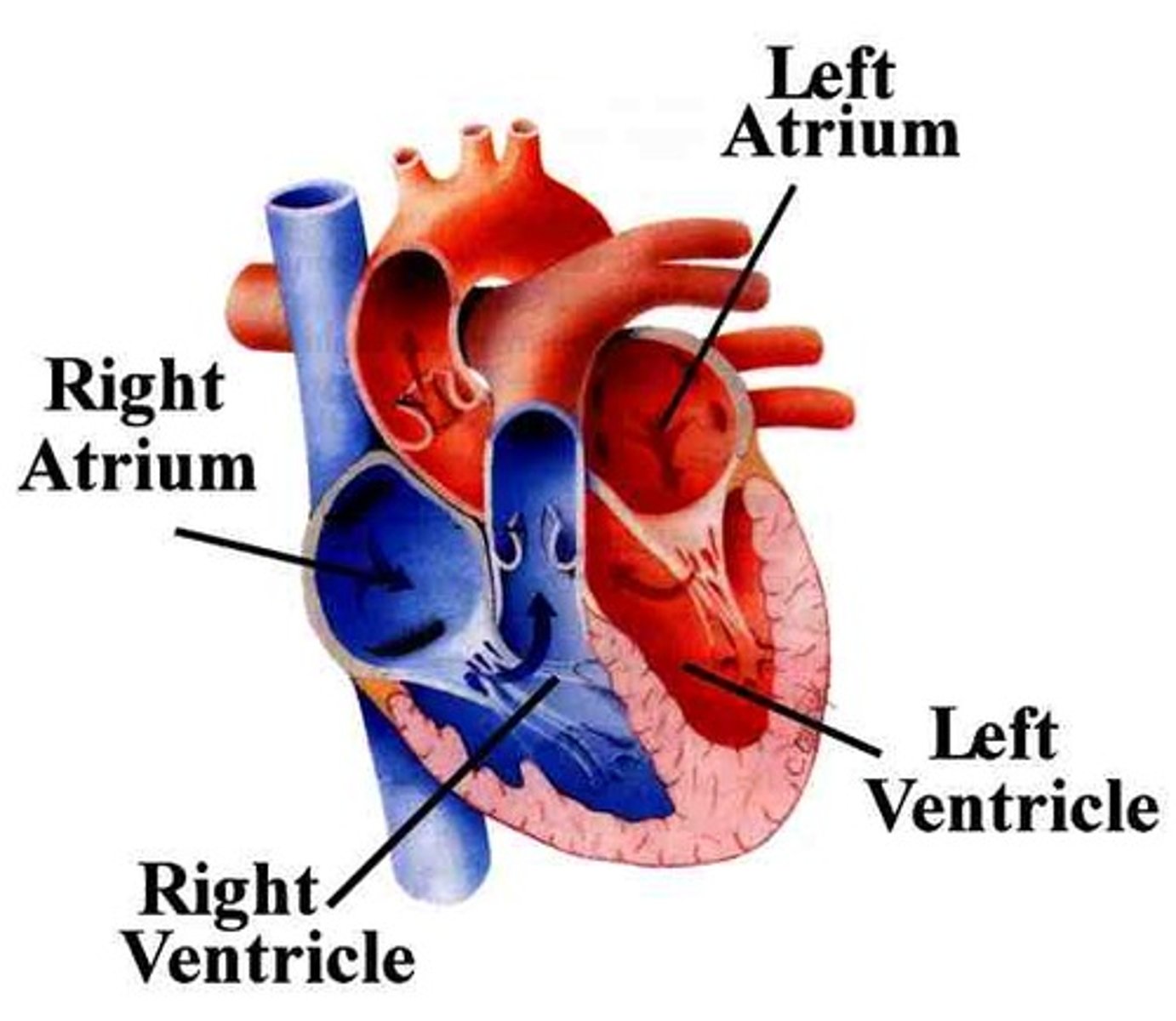
left side of heart
deals with oxygenated blood
right side of the heart
deoxygenated blood (right n left divided by septum)
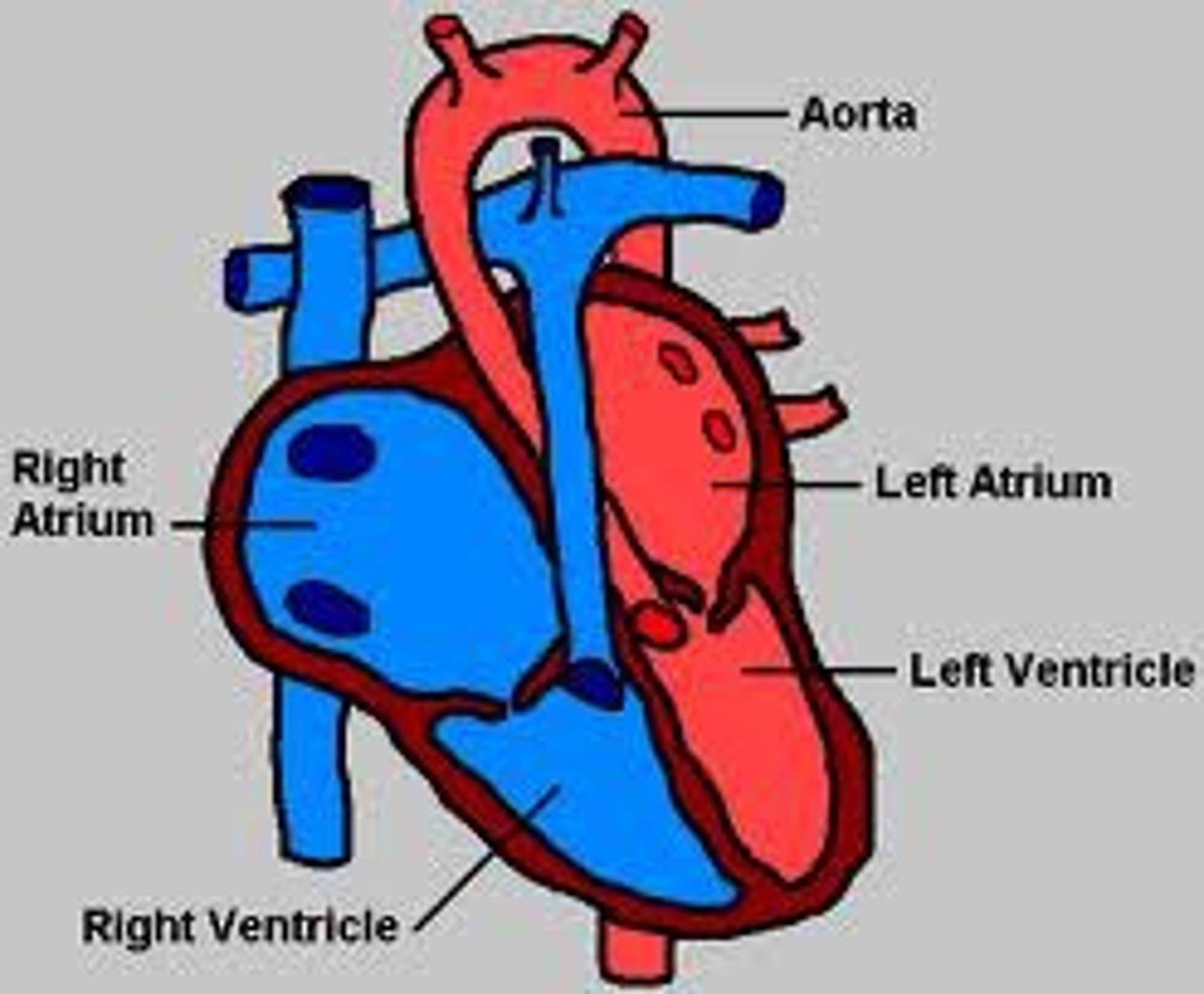
blood flow in the heart (to lungs)
-capillaries, venuoles, veins(superior/inferior vena cava), right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, left pulmonary artery, lungs
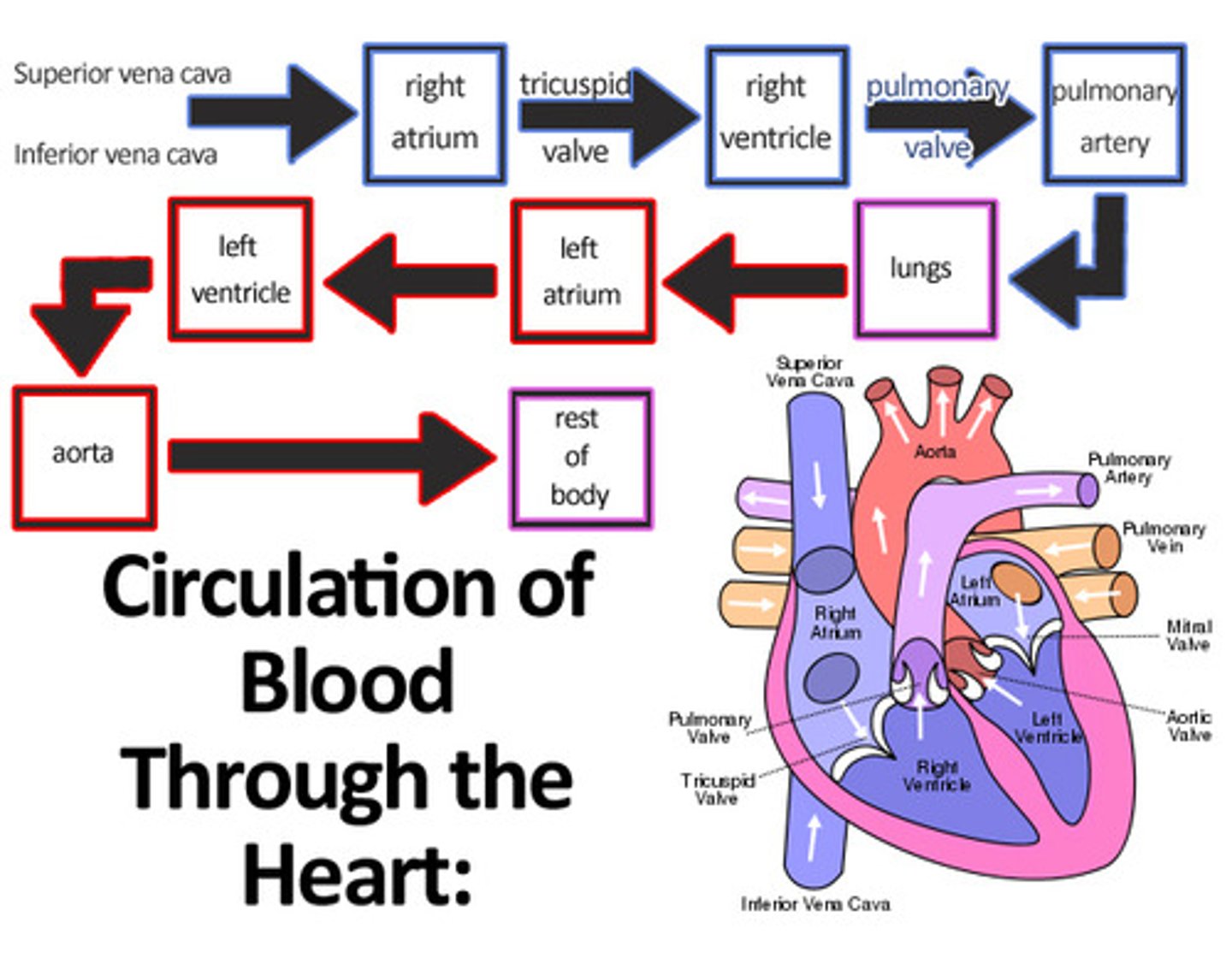
blood flow in the heart (from lungs)
-lungs, pulmonary veins (four 2 from each lung), left atrium, bicuspid valve, left ventricle, aorta, arteries, arterioles, capillaries
nervous system
central (brain n spinal)
peripheral (nerves)
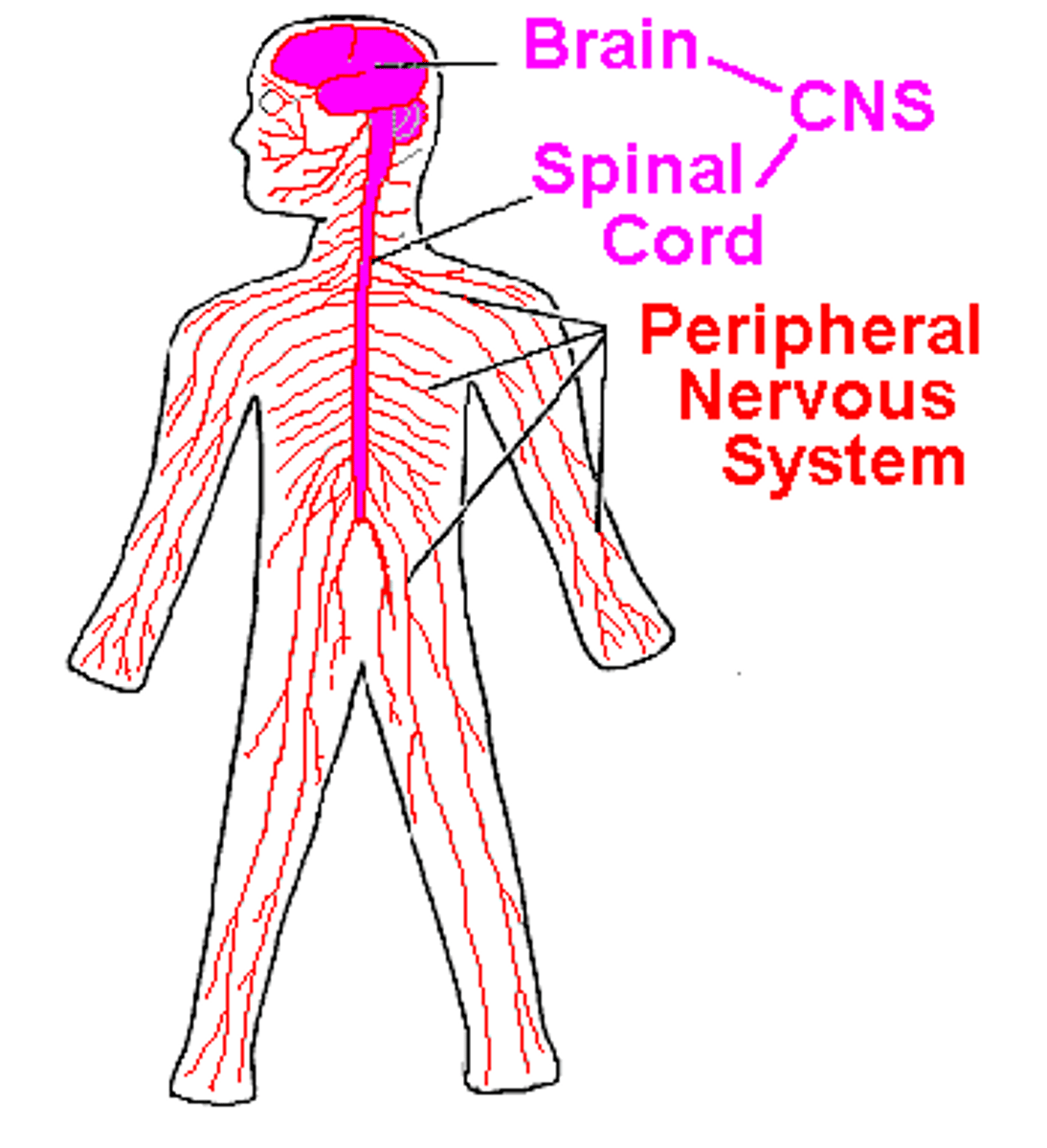
peripheral nervous system
1) nerves that control voluntary muscles
2) nerves that carry information from sensory organs
3) nerves that regulate involuntary functions
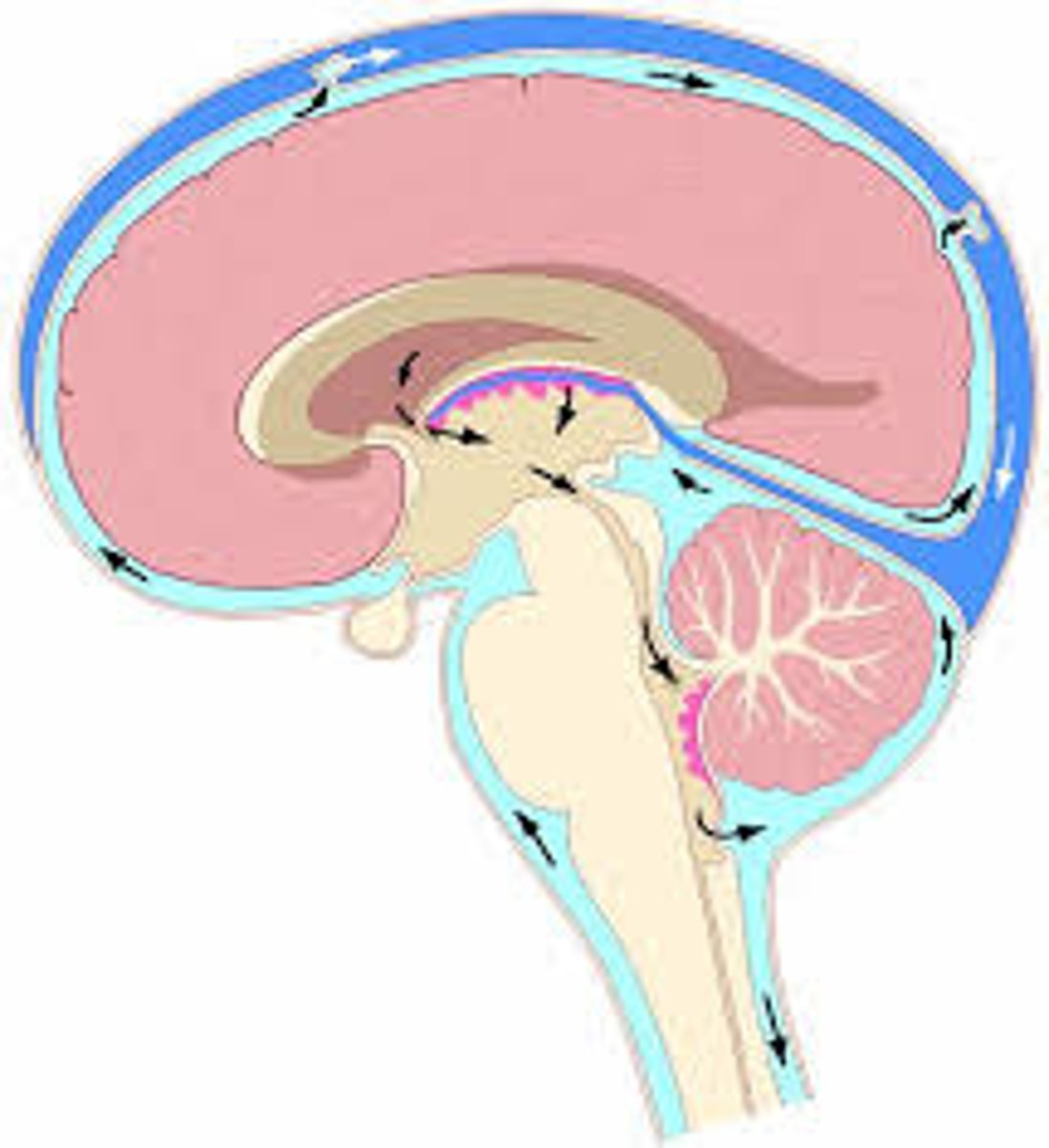
2 structures protecting CNS
-skull and celebrospinal fluid
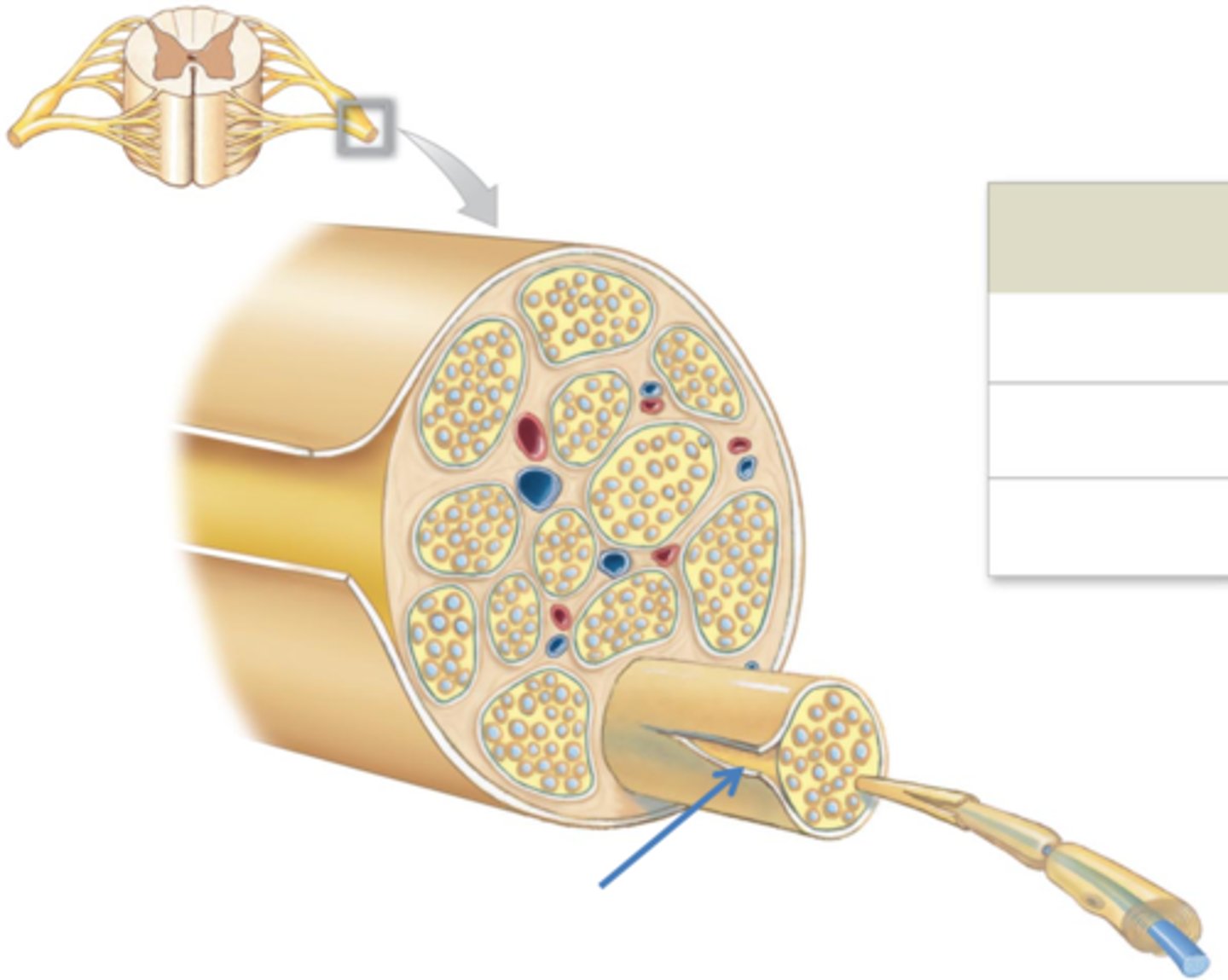
what are nerves?
bundles of neurons wrapped in connective tissue
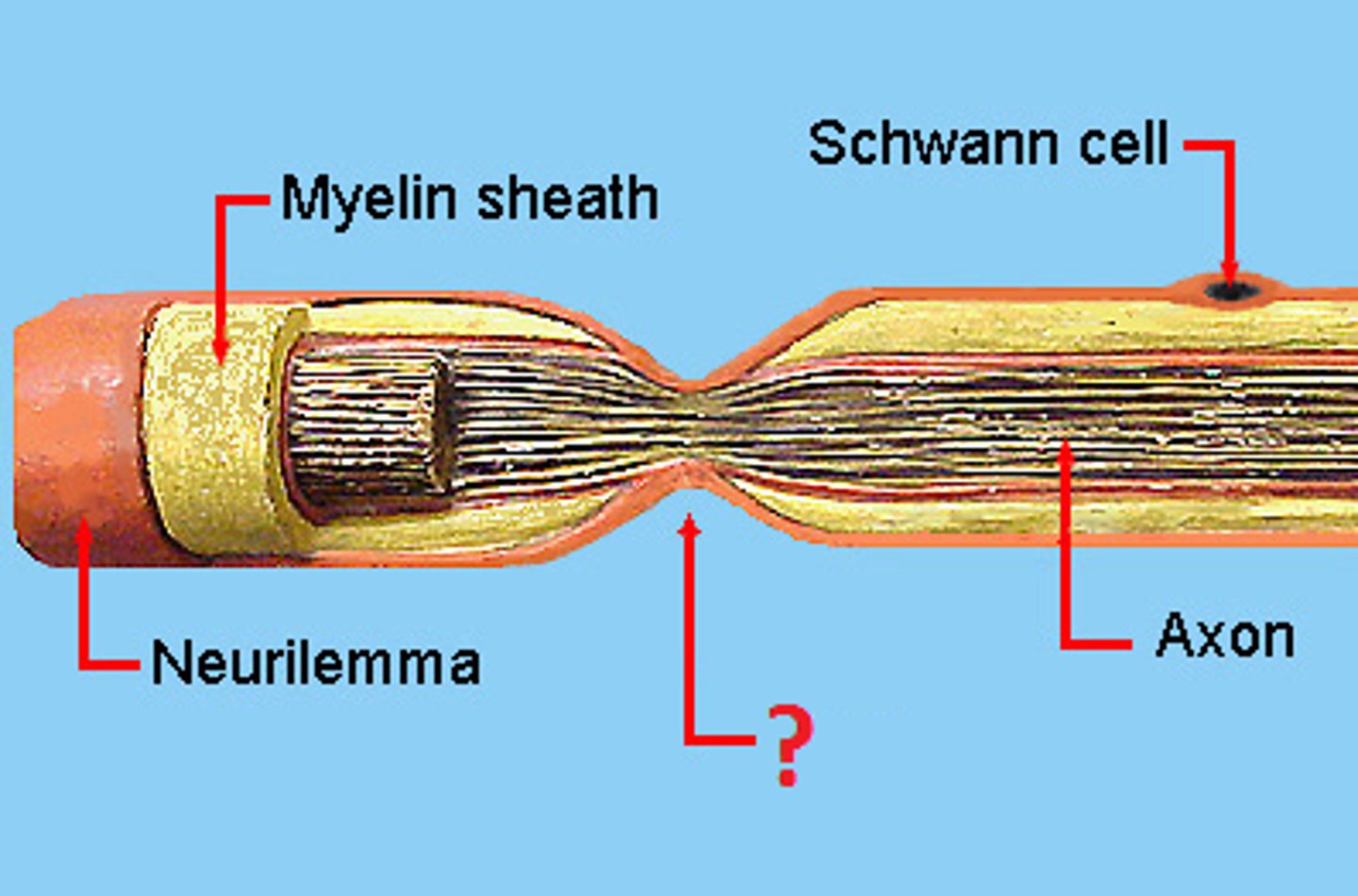
what is myelin sheath
-insulation preventing electrical impulses from passing to the wrong person
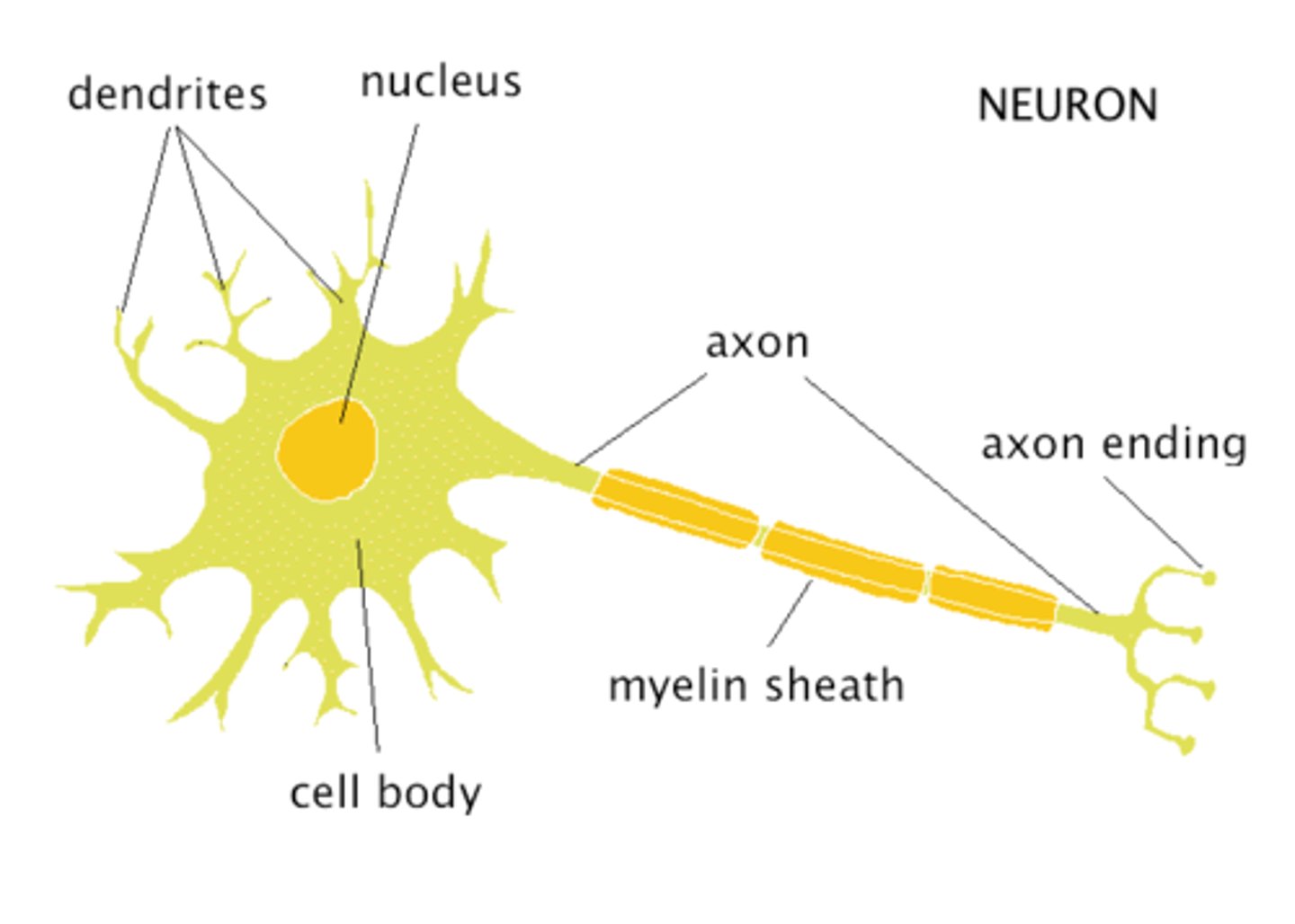
label the nerves
sensory receptors
Specialized cells unique to each sense organ that respond to a particular form of sensory stimulation.
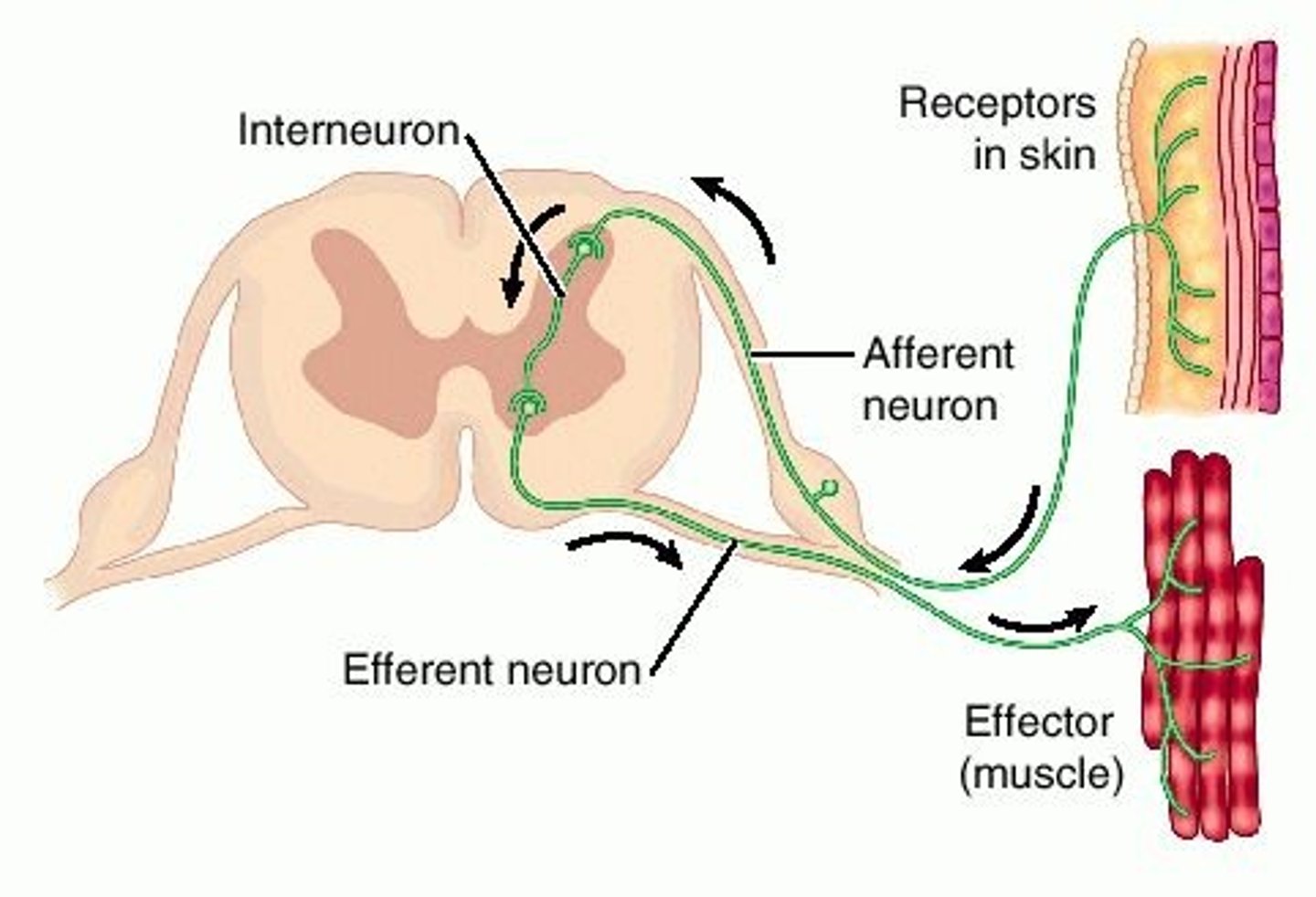
what types of information do sensory recepors detect?
-temperature, pain, nalance, position, motion, pressure
what is diabetes?
a disease in which the pancreas produces too little insulin
what is plaque? what is it caused by?
buildup of calcium and cholestrol
-inherited genetic information, poor lifestyle, high saturated fat diet, smoking, lack of exercise
what are symptoms of coronary artery disease?
tiredness, dizziness, pain, or a burning sensation in chest or arms (angina)
when coronary arteries are blocked what happens?
heart muscle cells dont get oxygen and nutrients n heart tissue dies
symptoms of heart attack
-chest pain, shortness of breath dizziness, anxiety
2 tests to check for attack
-blood test (certain proteins that occur 4-6 hours aftter heart muscle tissue is damaged)
-electrocardiogram (ECG)--> measures electrical signals of the heart (diff when damaged)
what causes tuberculosis? where can it spread?
airborne bacteria
spreads to nervous system n bones
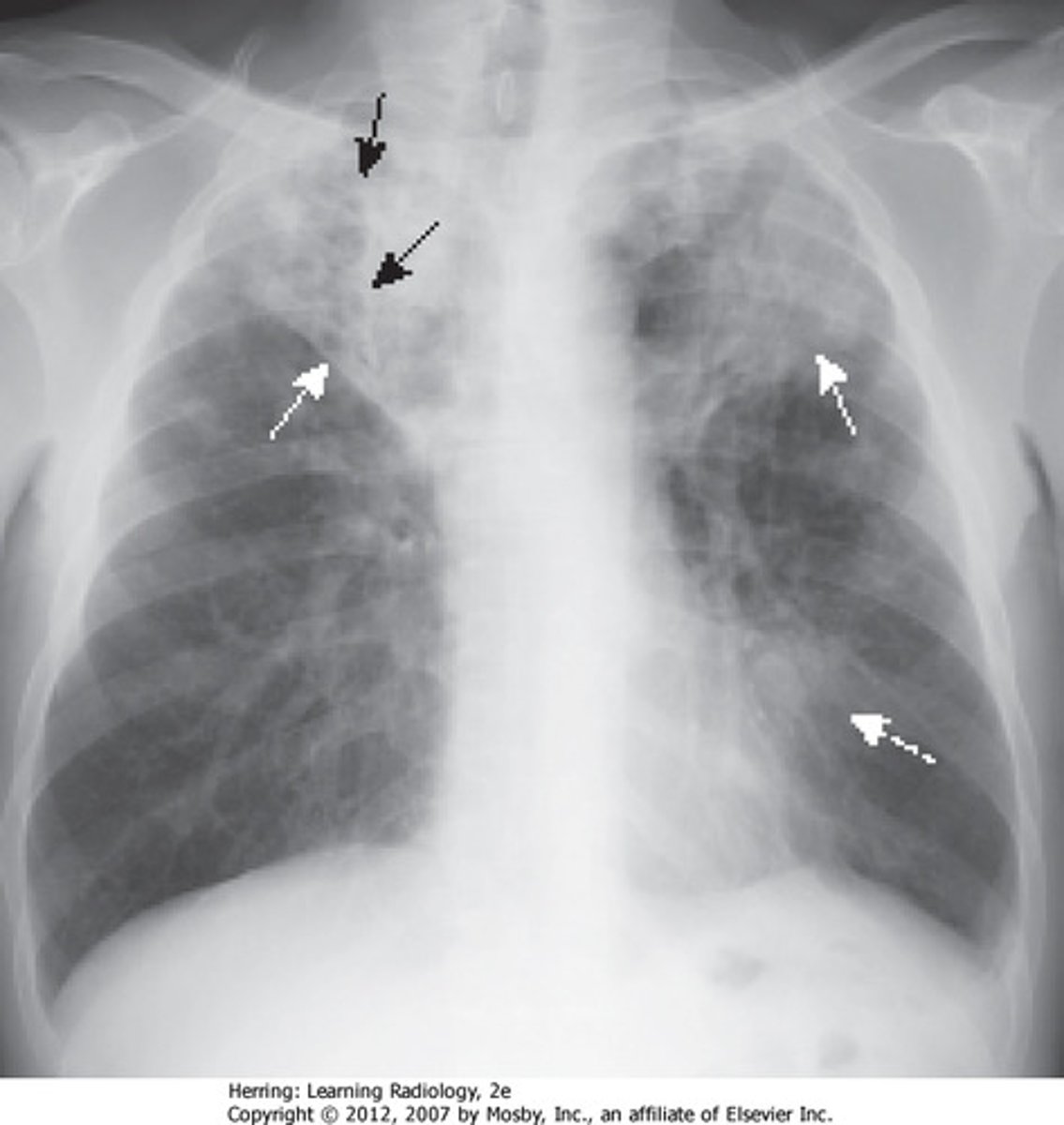
symptoms and problems of TB?
fever cough, weight loss, tiredness, chest pain
can be fatal, pneumonia shows similar results on xray
bacteria may remain dormant in the body for decades
cancers that happen from smoking
lung, bladder, esophagus, mouth
what are symptoms of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)
-high fever, shortness of breath, dry cough, sore throat, headache, muscle pain, exhaustion
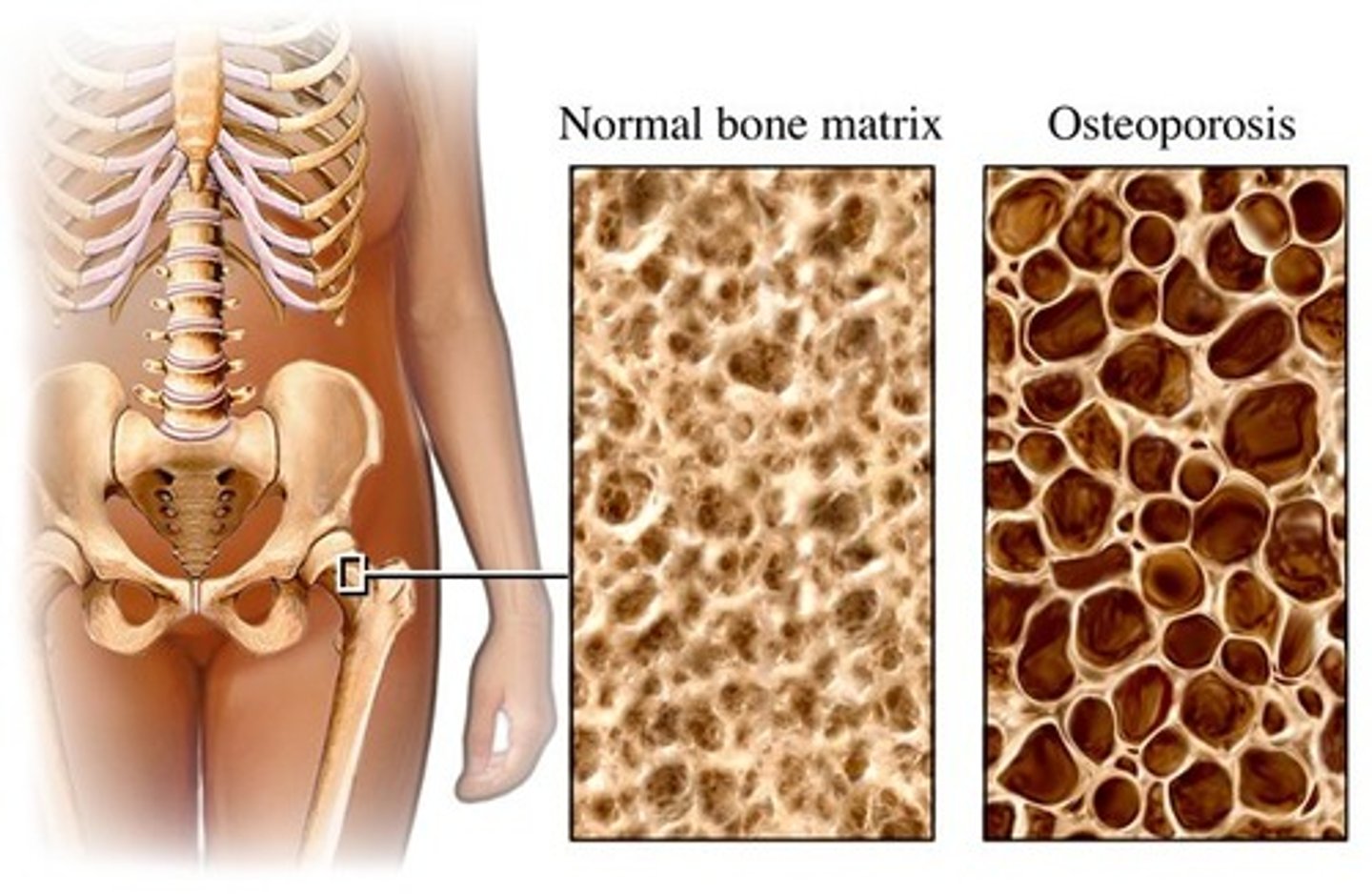
what is osteoporosis? what is it caused by?
-loss of bone tissue making them weak n brittlle
-caused by calcium deficit
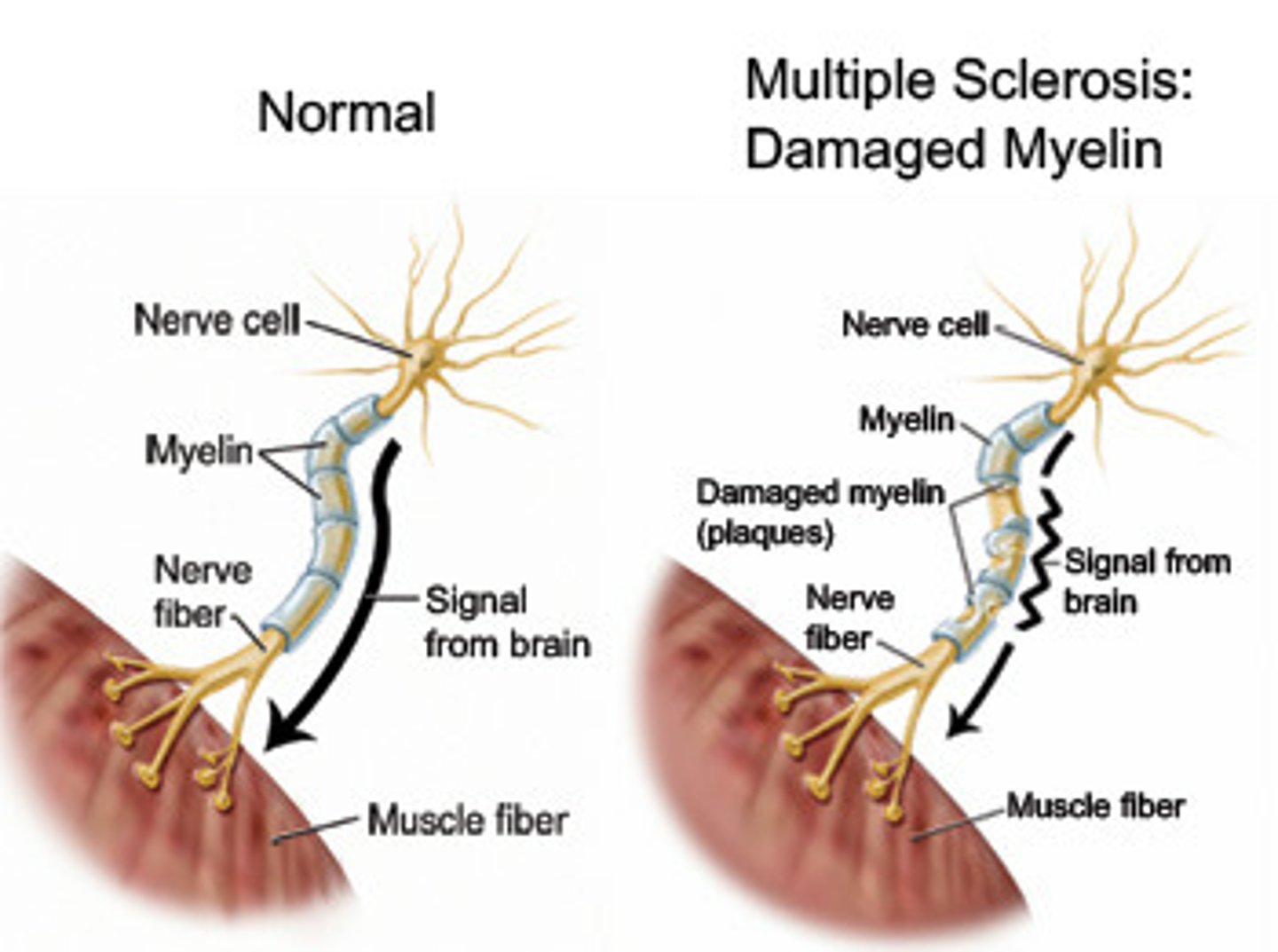
what is multiple sclerosis? what are symptoms and diagnostic methods?
-malfunction of the immune system (attacks n destroys myelin sheath)
-muscle weakness, slurred speech, difficulty walking
-use MRI
what are 4 organs that can be transplanted?
-skin, heart, lungs, kidneys, intestines
what are 4 transplantable tissues?
cornea, skin, bones, tendons, blood vessels
what is the downfall of transplant and what can be done to reduce it?
-rejection of organs and immune system fighting it
-take drugs to reduce immunity and similar genetic makeup organs
what are living donor organs?
-kidney, lung lobe, part of liver
deceased donor organs?
heart, lungs, intestines, face
what are advantages of using relatives to transplant organs
-better genetic match n less waiting time
what is xenotransplantation?
-transplanting animal organs into human bodies
-pig heart valve --> human heart valve
plants have 2 systems
root system and shoot system
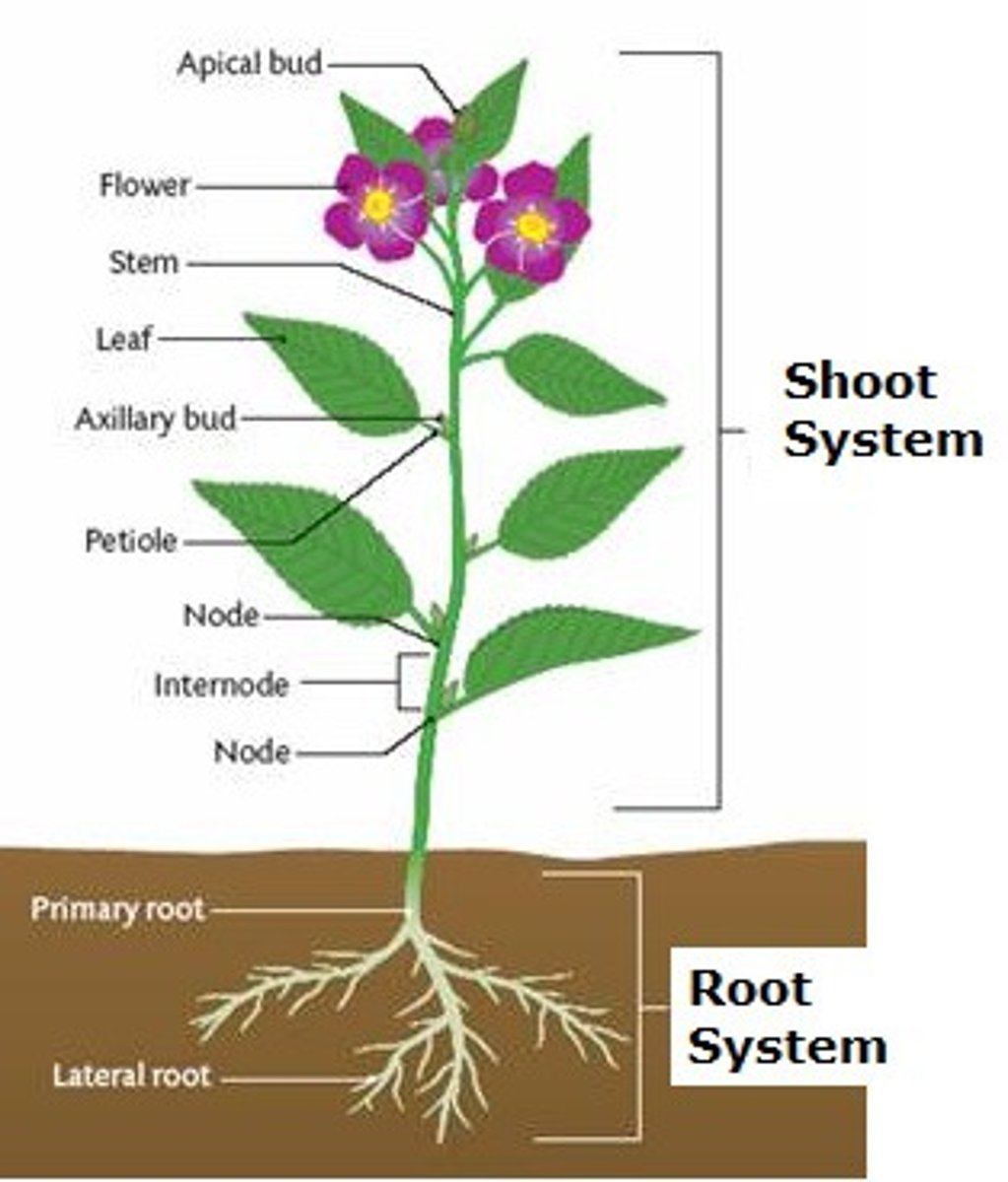
root system
anchors, absorbs and stores
shoot system
leaf: photosynthesis
flower: sexual reproduction
stem: supports and transports
plant stem cells (both types)
meristematic cells
(apical in tips of roots and shoots) (elongation)
(lateral in roots and stems of woody plants) (widening)
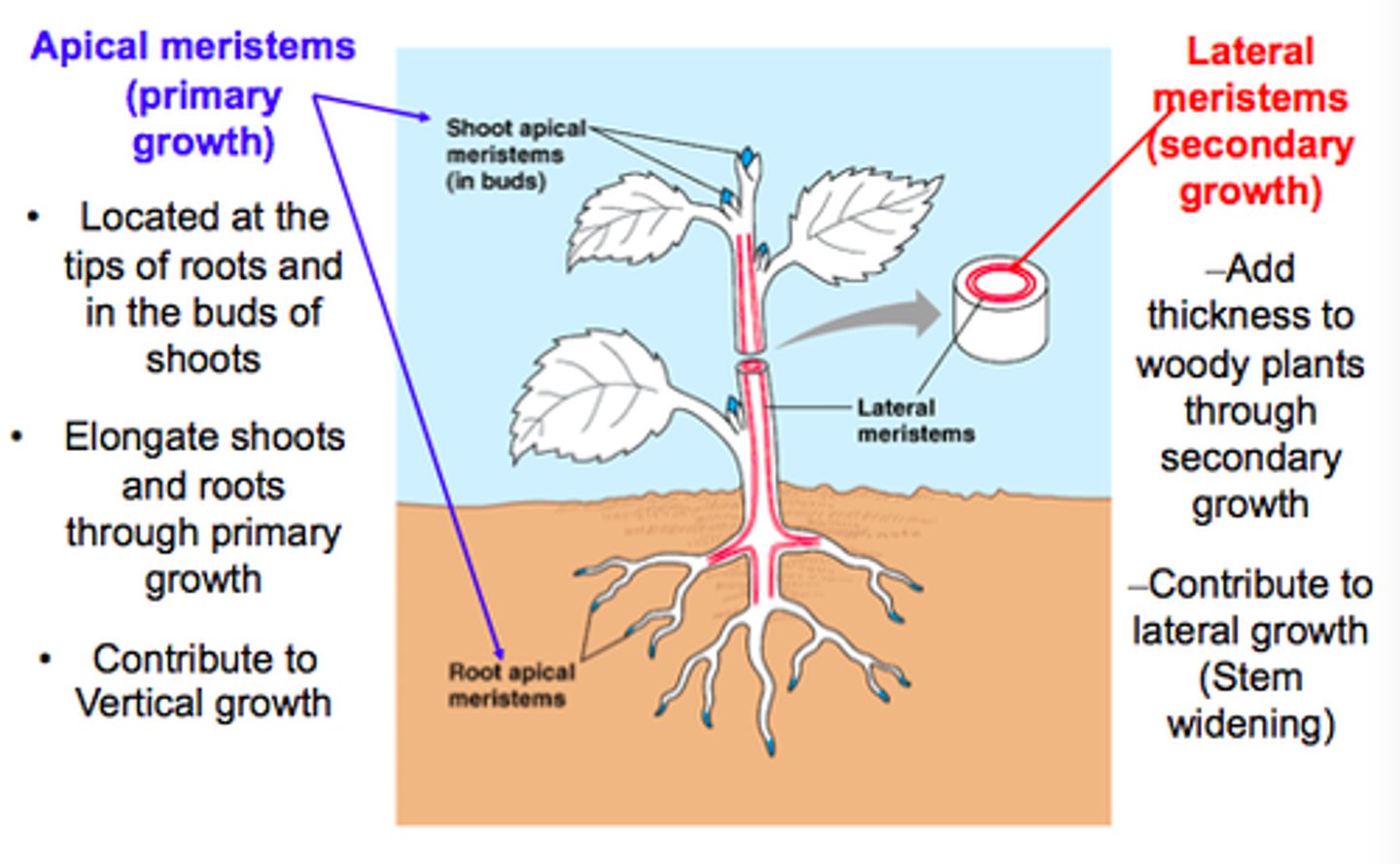
3 main types of tissue for plants
-dermal vascular and ground (all specialized)
dermal tissue
outermost
epidermal: leaf produces wax (cuticle) to help waterproof, root has hairs to absorb water n minerals
peridermal: forms on bark, stems roots
vascular tissue
-transportation
-xylem and phloem
-xylem is dead and upwards (water n minerals)
-ploem is living goes up n down (sugar, minerals, hormones, nutrients)
ground tissue
filler tissue
-green parts is where photosynthesis occurs
-roots store carbs
-stem has support and storage
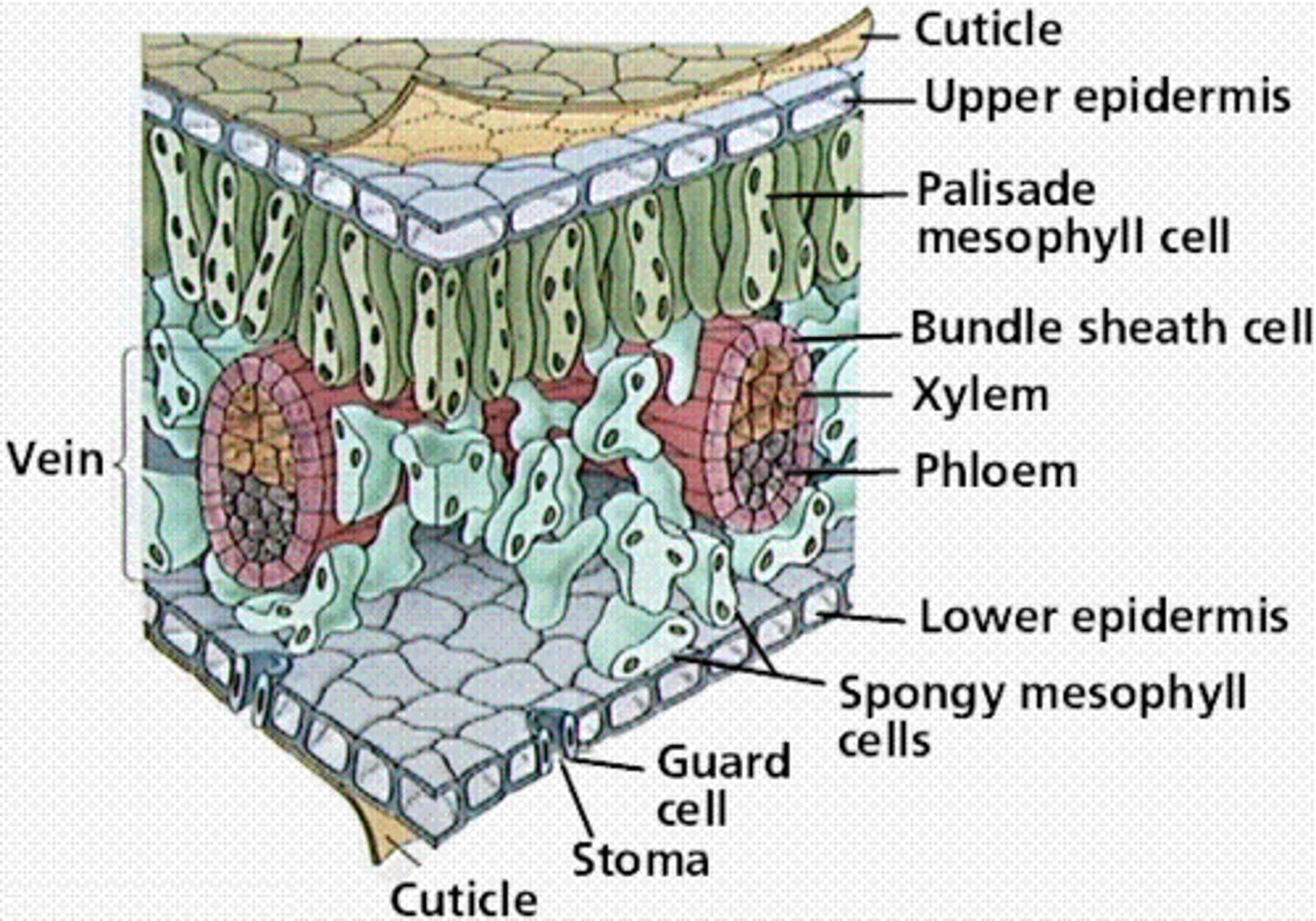
where are chloroplasts located in a typical leaf?
-pallisade mesophyll (tall and closely packed)
-spongy mesophyll (loose and larger spaces)
what are the openings in a leaf?
stomata (stomate, stoma)
guard cells control opening and closing of the stomata (located in upper and lower epidermis)
expand during the day to allow co2 and o2 to diffuse in and out
if dry, stomata closes
cross section of a leaf
composed of cuticle, upper epidermis, lower epidermis, palisade, xylem, phloem, spongy cells, guard cells, veins and cutin