Chapter 5: The Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Know parasym, receptor types, uderstand difference between direct/indirect acting drug, diversions, drug termonaly, effects of para/sym on body, receptor types.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What two systems control the body?
The nervous/endocrine system
What is the endocrine system responisble for?
controlling respiratory drive, influencing lung development. breathing patterns, oxygen consumption, and immune responses within the lungs.
What is the Nervous system resonsible for?
send messages from various parts of your body to your brain, and from your brain back out to your body to tell your body what to do.
What two parts is the nervous system divided into?
The central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
What does the Central nervous system Consist of?
Brain , spinal cord.
What does the autonomic nervous system control?
involuntary, unconcoous control mechaisms of the body. (ex. respiratory rate)
What does the autonomic nervous system regulate?
Heart Rate (HR)
Respiratory Rate (RR)
Pupil Dilation and Contraction
Glandular Secretion (such as salivary glands)
Smooth Muscle Contraction (blood vessels and airway)
What does the Peripheral Nervous system Consist of?
Sensory (afferent) neurons
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
Parasympathetic Branch
Sympathetic Branch
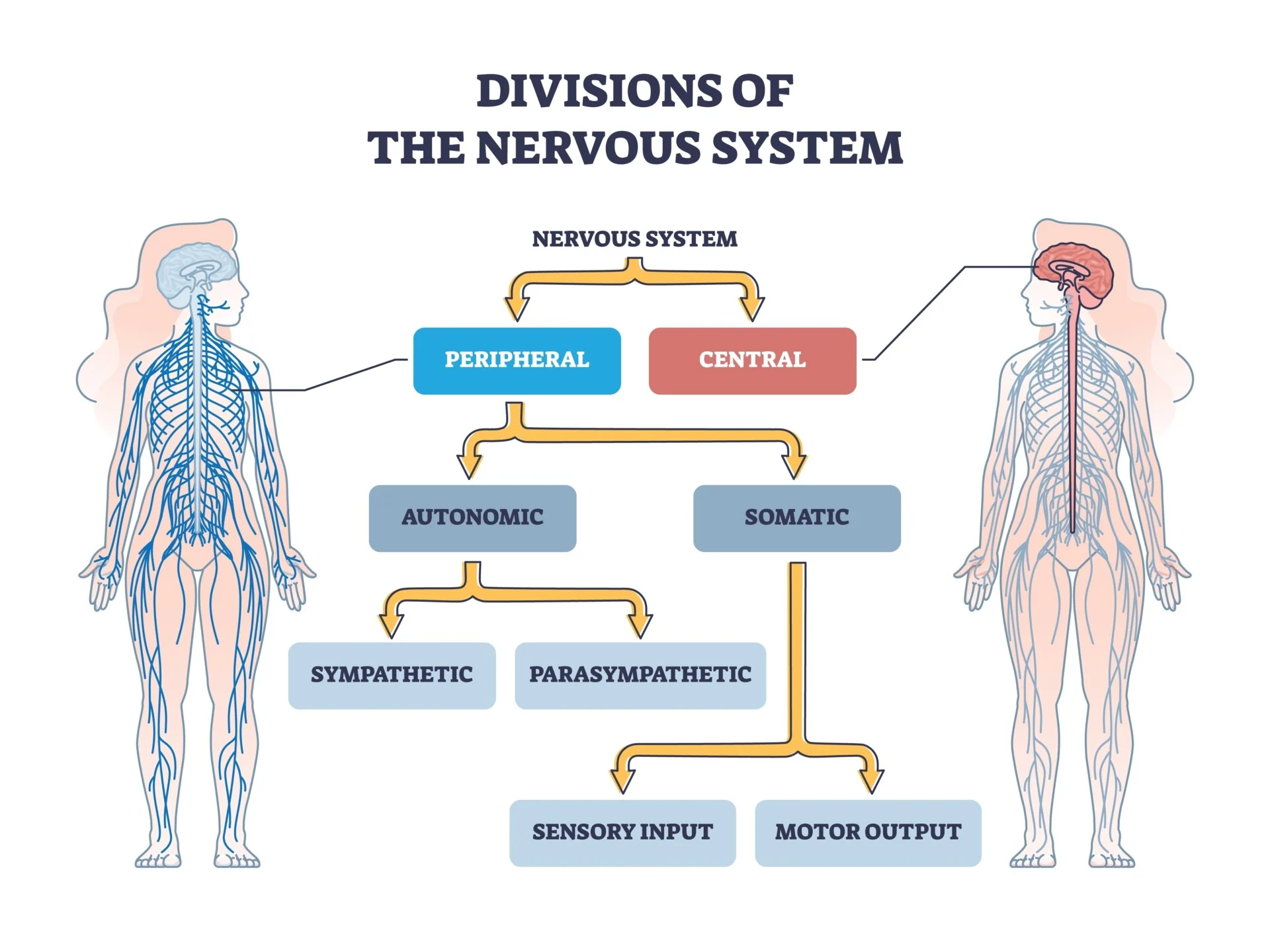
What are the divisions of the nervous system?
Nervous System: Peripheral/Central
Peripheral:Autonomic/Somatic
Autonomic: Sympathetic/Parasympathetic
Somatic: Sensory/Motor Output
What is the difference between the sympathetic vs parasympathetic nervous system?
While your sympathetic nervous system carries signals that put your body's systems on alert, your parasympathetic carries signals that relax those systems.
What happens when the Parasympathetic Nervous System is overstimulated?
SLUD syndrome.
Salivation
Lacrimation
Urnination
Defication
Phrase used to describe the Parasympathetic Nervous System
Rest and Digest
What is the Parasympathetic Nervous System considered?
A more discrete, finely regulated system.
What is Parasympathetic Nervous System resonsible for in day-today body functions?
digestion
bladder/rectal discharge
Bronchial mucas secretion
Is the Parasympathetic Nervous System essential for life?
True
What is the phrase used to describe Sympathetic Nervous System?
Fight or Flight
What can the Sympathetic Nervous System Increse/Shift or dilate? 5 listed.
Heart rate/Blood pressure Increase
Blood flow shifts from periphery to the muscles and heart
Blood sugar increases
Bronchi Dilate
Is Sympathetic Nervous System essential for life?
False
What drug terminology is: -mimetic
Mimics
What drug terminology is: -lytic
“lyses” or cancles out effect
What drug terminology is: Agonist
Stimulates the receptor site
What drug terminology is: Antagonist
Blocks receptor site
What are Parasympathomimetic/ cholinergic /muscarinic drug classes?
a drug that stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system by mimicking/amplifying.
What are Parasympatholytic/anticholinergic/antimuscarinic drug classes?
group of medications that blocks or inhibits the action of the parasympathetic nervous system
What are Sympathomimetic/adrenergic drug classes?
medications that mimic the effects of the sympathetic nervous system's "fight or flight" response by activating adrenergic receptors (alpha and beta receptors) in the body.
What are Sympatholytic/Antiadrenergic drug classes?
drug class inhibits the function of the sympathetic nervous system.
What does Parasympathetic Effect in the Cardiopulmonary System?
Decreases in heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, bronchoconstriction
What does Parasympathetic Effect in the Eye?
Miosis:: constriction of pupil
What does Parasympathetic Effect in the GI tract
Increased motility
What does Parasympathetic Effect in Insulin Secretion?
increased insulin
What do Cholinergic Drugs do?
They enhance the action of acetylcholine. (parasympathetic)
What does Anticholinergic Drugs block? What is that apart of?
Acetylcholine, part of the parasympathetic nervous system
What are the affects of Parasympatholytic (Antimuscarinic) effects.
Bronchodiliation, preoperative drying secretions, antidiarrheal agent, prevention of bed wetting for children, treeatment of bradycardic.
What does a Anticholinergic Dug do to the parasympathtic nervous system?
Anticholinergic Dug blocks the parasympathetic nervous system
What are Sympathetic Effects on the cardiopulmonary system?
Increases hr, bp, rr, bronchodilation
What are Sympathetic Effects on the eye
Mydriasis (dilation of pupil)
What are Sympathetic Effects on the Insulin secretion?
Decreased
What are Sympathetic Effects on the GI tract
decreased motility
What are the three receptor subcatagories?
alpha 1, beta 1, beta 2
What happens when you stimulate Alpha 1 (a1)?
Vasoconstriction
What happens when you stimulate Beta 1?
Increases the rate and force of cardiac constriction
What happens when you stimulate B2
Relaxes bronchial smooth muscle and vasculer beds of skeletal muscle?
How much innervation does the Sympathetic effect have in the lungs?
little to no innervation
Where are B2 receptors found?
Trachea to termincal bronchioles
What if you give a Alpha 1 in the lungs?
Causes vasocontriction of blood vessles. (Active bleediing in airway)
What if you give Beta 2 in the lungs?
elaxation of airway smooth muscle and increase in mucus clearance
What does the Parasympathetic cause in the lungs?
Bronchonsitriction, increases airway secretions, vasodilation
What is direct-acting?
Mechanism of action: Drug binds directly to a receptor to activate it
What is indirect-acting?
Mechanism of action: Produce their effects not by directly binding to and activating receptor.