Metabolic Pathways pt 1; Catabolic Pathways
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Catabolic Pathways
Release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simpler compounds
Aerobic Respiration
Oxygen is consumed as a reactant along with organic fuel
Anaerobic Respiration
Organic fuel is broken down without oxygen
Fermentation
Partial breakdown of organic fuel (sugars) without oxygen
Cellular Respiration
Aerobic (and anaerobic) respiration
exergonic
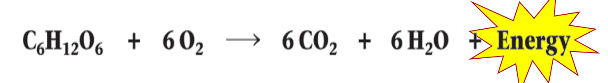
Redox
The transfer of electrons from one molecules to another. Always coupled!
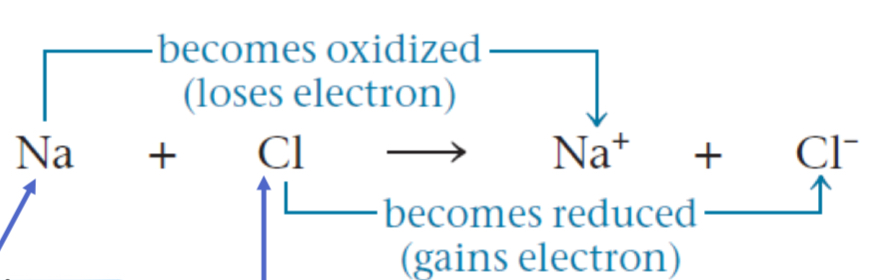
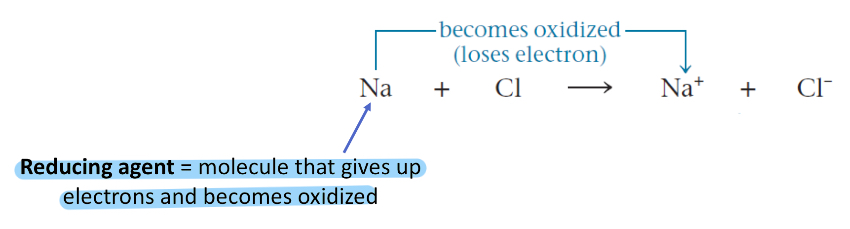
Reducing Agent
Molecules that gives up electrons and becomes oxidized
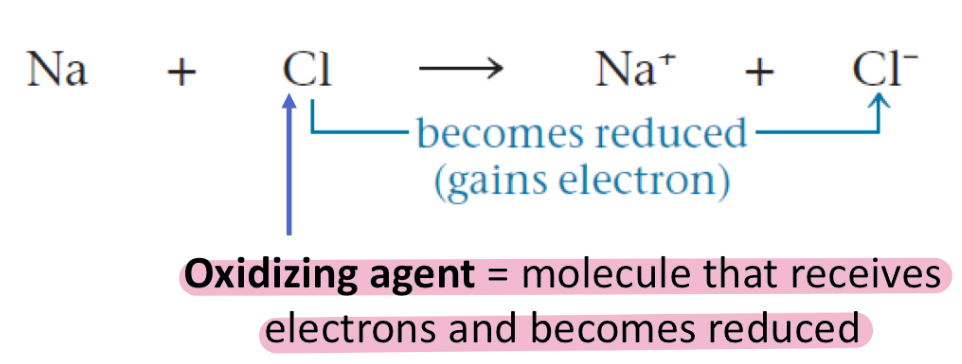
Oxidizing agent
Molecule that receives electrons and becomes reduced
Combustion of Methane
C-H and O-O bonds:
e- shared equally
Higher potential energy reactants
Less energy to break
H+ and e- get transferred from CH4 to O2
C=O and O-H bonds:
e- shared unequally
C is oxidized
Unequal e- sharing makes bonds more stable
More energy is released when formed, more energy is required to break bonds (photosynthesis)

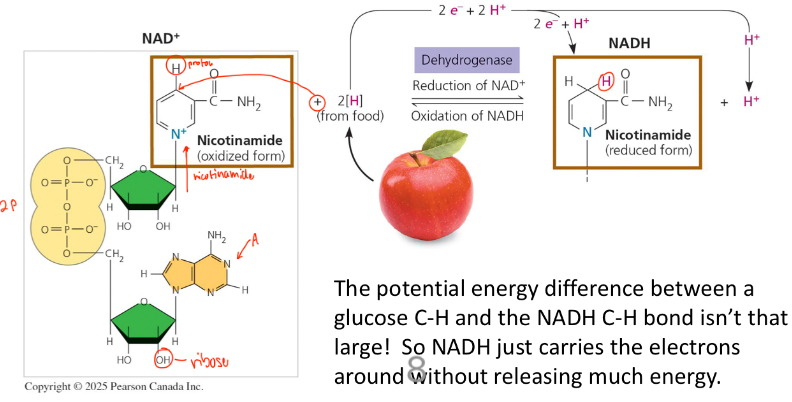
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)
Is an electron transporter (“shuttle”)
Facilitates the electron transfer over multiple steps in the breakdown of glucose
It’s a coenzyme and oxidizing agent
It can cycle between an oxidized (NAD+) and reduced (NADH) form
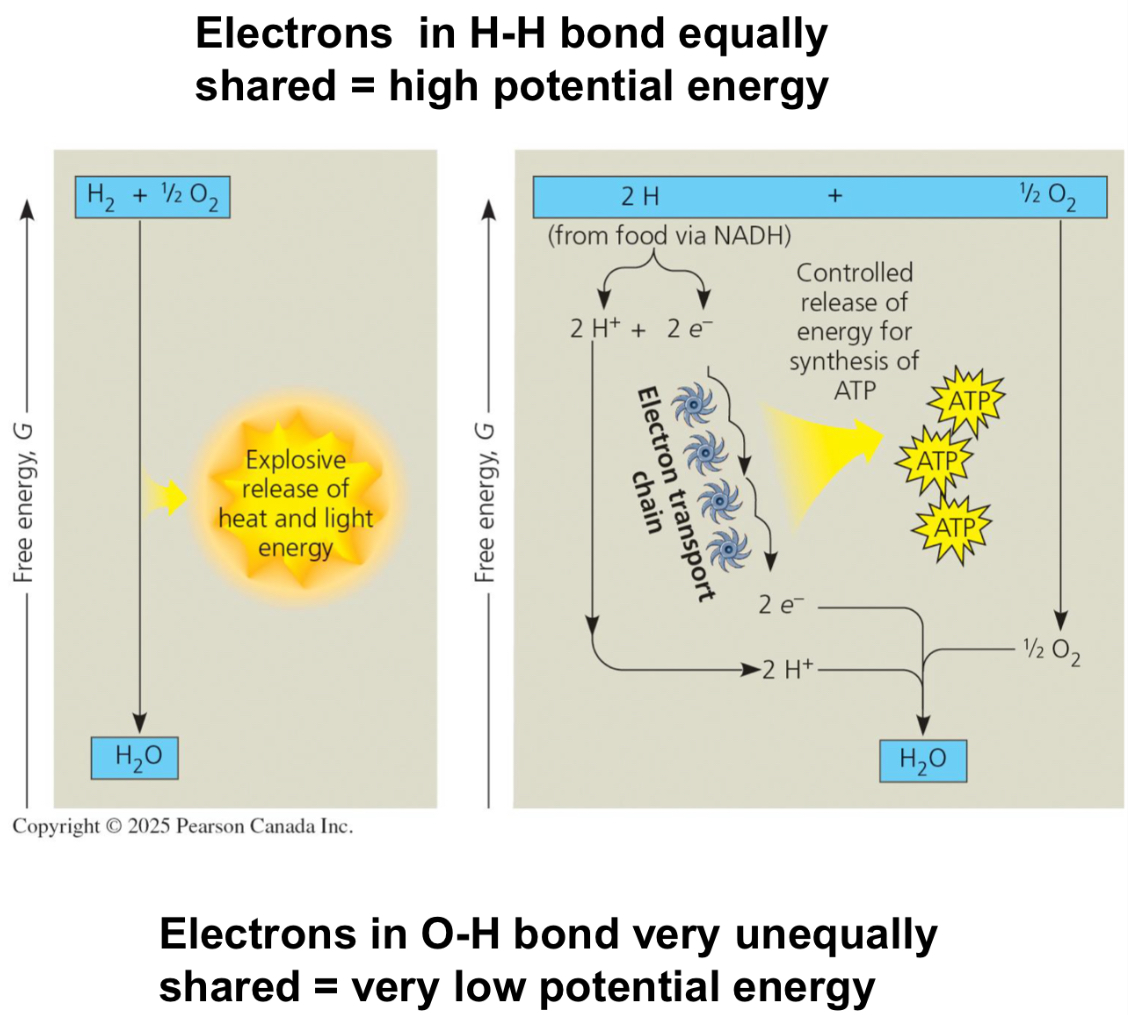
Electron Transport Chain
IF the transfer of electrons was uncontrolled
One big release of energy, with LOTS of heat loss
IF controlled by the cell
Small releases of energy at each step, which can be used to make more ATP
e- get removed from glucose and are transferred to the ETC
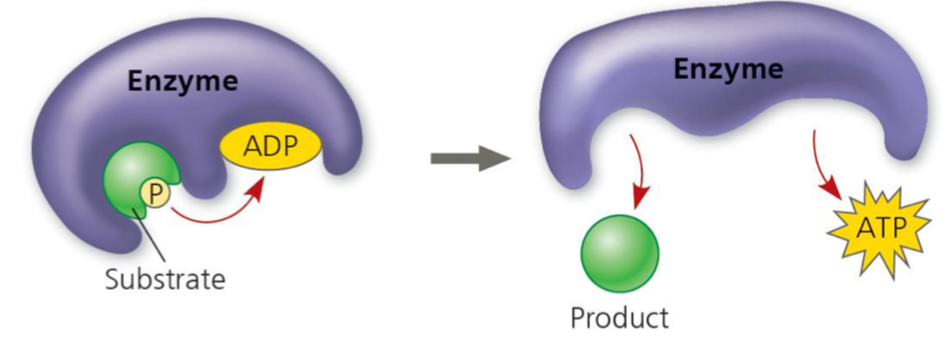
Substrate-level phosphorylation
An enzyme catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from a substrate to ADP, forming ATP
The substrate is generated as an intermediate in the breakdown of glucose
Direct transfer of energy to ATP
Accounts for about 10% of ATP generation during cellular respiration
Occurs in the cytosol and mitochondria
Oxidative phosphorylation
Energy is released from electrons in the ETC makes a H+ gradient
This gradient is used to drive a protein complex called ATP synthase
Indirect transfer of energy to ATP
Makes approx. 90% of ATP during cellular respiration
Mitochondria only
Overview of Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis (SLP ATP) → Pyruvate Oxidation → Citric Acid Cycle (SLP ATP) → Oxidative Phosphorylation (OP ATP)
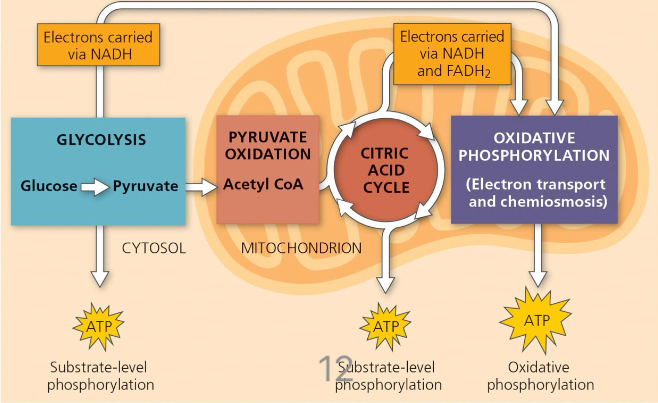
Glycolysis
Means “sugar-splitting”
Glucose (6-carbon sugar) is split into two 3-carbon sugars
No loss of carbon
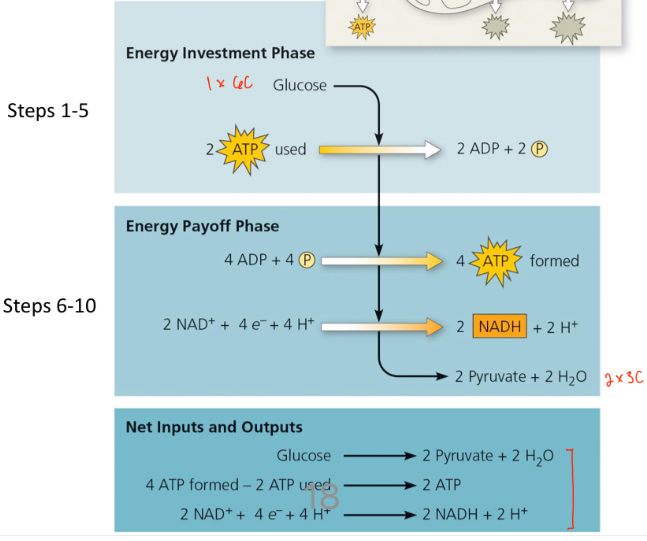
Pyruvate
Actively transported to the mitochondrion after glycolysis which is then converted to acetyl CoA.
Pyruvate —> acetyl CoA
Oxidized carboxyl group is removed
The 2-carbon molecule is oxidized forming acetate (CH3COO-)
Coenzyme A (S-CoA) attaches by its sulphur group
The Citric Acid Cycle (AKA Krebs Cycle, Tricarboxylic Acid cycle (TCA))
Generates 1 ATP molecule per cycle via substrate-level phosphorylation
Most energy is transferred to NAD+ and FAD which shuttle electrons to the ETC where most of the energy will be produced
Total Yield per glucose
Since each glucose at the start of glycolysis yield 2 acetylene CoA, the total yield per glucose is:
6NADH’s , 2FADH2’s, 2ATP’s
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
A collection of protein complexes within the inner membrane of the mitochondrion
Sequential redox rx
Every component becomes reduced when it accepts electrons from its uphill neighbour, since the electronegativity (ability to attract electrons) is less than downhill
ETC complex I
Electrons acquired from glycolysis and the citric acid cycle via NAD+ are transferred from NADH to the ETC complex I.
The first molecule in complex I is a flavoprotein (flavin mononucleotide (FMN)) which gets reduced as NADH give up its electrons
FMN returns to its oxidized form as it passes the electrons to iron-sulfur protein in complex I
Electron then moves to ubiquinone (Q) — not a protein (AKA coenzyme Q)
Next, electrons are transferred to the cytochromes
Proteins consisting of an iron group the accepts/donates electrons
Complexes III and IV both have cytochromes
The cytochromes then pass the electron to molecular oxygen which picks up 2e and 2 protons (Hydrogen) to form water
ETC complex II
Electrons acquired from the citric acid cycle via FADH2 undergo a similar process
KEY difference: it joins the ETC via complex II
Lower E level than complex I and NADH
Both donate the same number of electrons at the end for oxygen reduction but FADH2 converts about 1/3 less energy than NADH.
NADH > FADH2
ATP synthase
A protein complex that is found throughout the inner membrane of the mitochondrion
Makes ATP from ADP + inorganic P
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Works like an iron pump but reverse
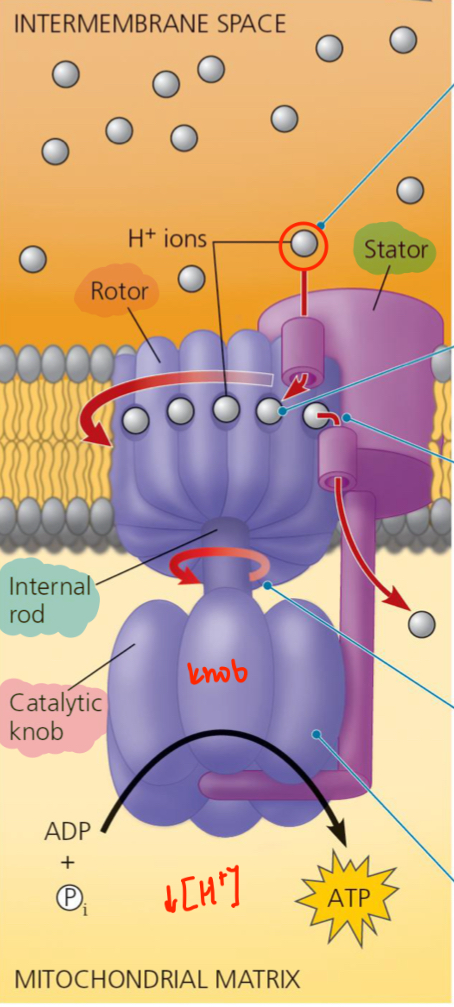
Stator
A channel anchored in the membrane, which H+ ion can flow down their concentration gradient. (High → Low)
Entrance, Step 1
Rotor
H+ ions enter binding sites in the rotor changing the shape of the protein subunit so that it spins (like a centrifuge).
Constant influx of H+ atoms
Each H+ ion must make ONE COMPLETE turn before going through a second channel in the stator and into the mitochondrial matrix
Rod and Knob
Rotor causes the rod to spin, which extends into a knob held stationary by the stator.
Turning off the rod activates catalytic sites that produce ATP from ADP in he knob
ETC effect on the H+ gradient
Since ETC is exergonic, energy is used to pump H+ ions from the mitochondrial matrix to the inter-membrane space (space between the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes).
H+ ions then diffuse back into the mitochondrial matrix via the ATP synthase which produces a proton-motive force
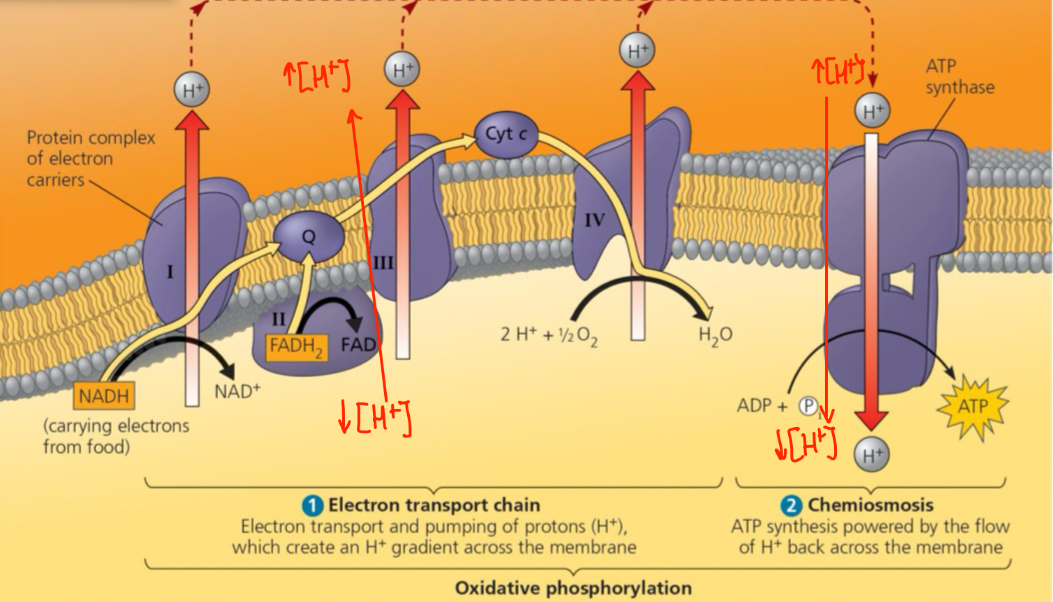
Chemiosmosis
ATP synthesis powered by the flow of H+ back across the membrane
an energy coupling mechanism
Uses energy stored from H+ gradient across the membrane to drive cellular work
Anaerobic respiration
Respiration in which the final e- acceptor is not oxygen
Still contains an ETC but the final e- acceptor is different
Species specific → some sulphate-reducing bacteria use SO4^(-2)
Produced hydrogen sulphide as a byproduct instead of water
Fermentation
Does not have an ETC or oxygen as the final e- acceptor
NOT cellular respiration
Alcohol fermentation
Pyruvate is converted to ethanol
CO2 is released from Pyruvate, converting it into 2 molecules of acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde is reduced by NADH to ethanol
This regenerates the NAD+ needed in glycolysis
Many bacteria do this
Also yeast
Sourdough or beer
Lactic acid fermentation
Pyruvate is reduced directly by NADH to form lactic acid
No release of carbon dioxide
Fungi
Bacteria → cheese and yogurt
Obligate Anaerobes
Organisms that only carry out fermentation or anaerobic respiration
HAVE to be in O2 free environment
Only fermentation
Facultative Anaerobes
Organisms can utilize both fermentation and cellular respiration to make enough ATP.
Prefer cellular respiration but can fermentation