DPT II Exam 6
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
ion movement produced currents that form
action potential
what do voltage gated/ion gated channels prevent
free diffusion
phase 4 SA Node
the cell undergoes spontaneous depolarization (pacemaker potential) which triggers an action potential once the membrane reaches between -40 and -30mV
hypocalcemia
prolongs the QT interval
hypercalcemia
shortens the QT interval
channelopathies
inherited arrythmogenic disease, autoimmune or inflammatory K channelopathies or long QT syndrome or short QT syndrome
catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia
involve multiple genes and ion channels
disturbance in impulse formation
increases automaticity and causes afterdeoplarizations
disturbance in impulse conduction
blocks in conduction, unilateral blocks
a phase of myocytes action potential characterized by slow inward calcium current
phase 2
abnormal impulse conduction tachyarrhytmia
reentrant
torsades de pointes is an example of
afterdepolarizations
abnormal impulses generation tacchyarthmias
automatic
an ECG wave that represents signal travels through venticrles
QRS
activates acetylcholine-sensitive potassium current in atrium
adenosine
phase of SA node action potential characterized by potassium moving out of the cells
repolarization.
block the repolarizing K current and prolong AP duration
dofetilide
an ECG wave that represents ventricle contraction
RST
a phase of myocytes action potential characterized by slow Na influx and slowing of K outflow
phase 4
phase 0 SA node
this is depolarization phase where action potential is initiated
phase 3 SA node
cell repolarizes and once it reaches around -60mV, the cycle starts again
t type
pacemaker ca channel (in SA node)
Phase 0 (myocytes)
rapid depolarization (inflow of Na)
phase 1 (myocytes)
partial (early) repolarization. (inward Na current deactivated, outflow of K)
phase 2 (myocytes)
plateau (slow inward calcium current) triggers contraction
phase 3 (myocytes)
repolarization (ca current inactivates, k outflow)
phase 4 (myocytes)
resting membrane potential
L type
non pacemaker ca channel in myocytes
ECC
process where an action potential triggers a myocyte to contract followed by a subsequent relaxation
p wave
atrial depolarization
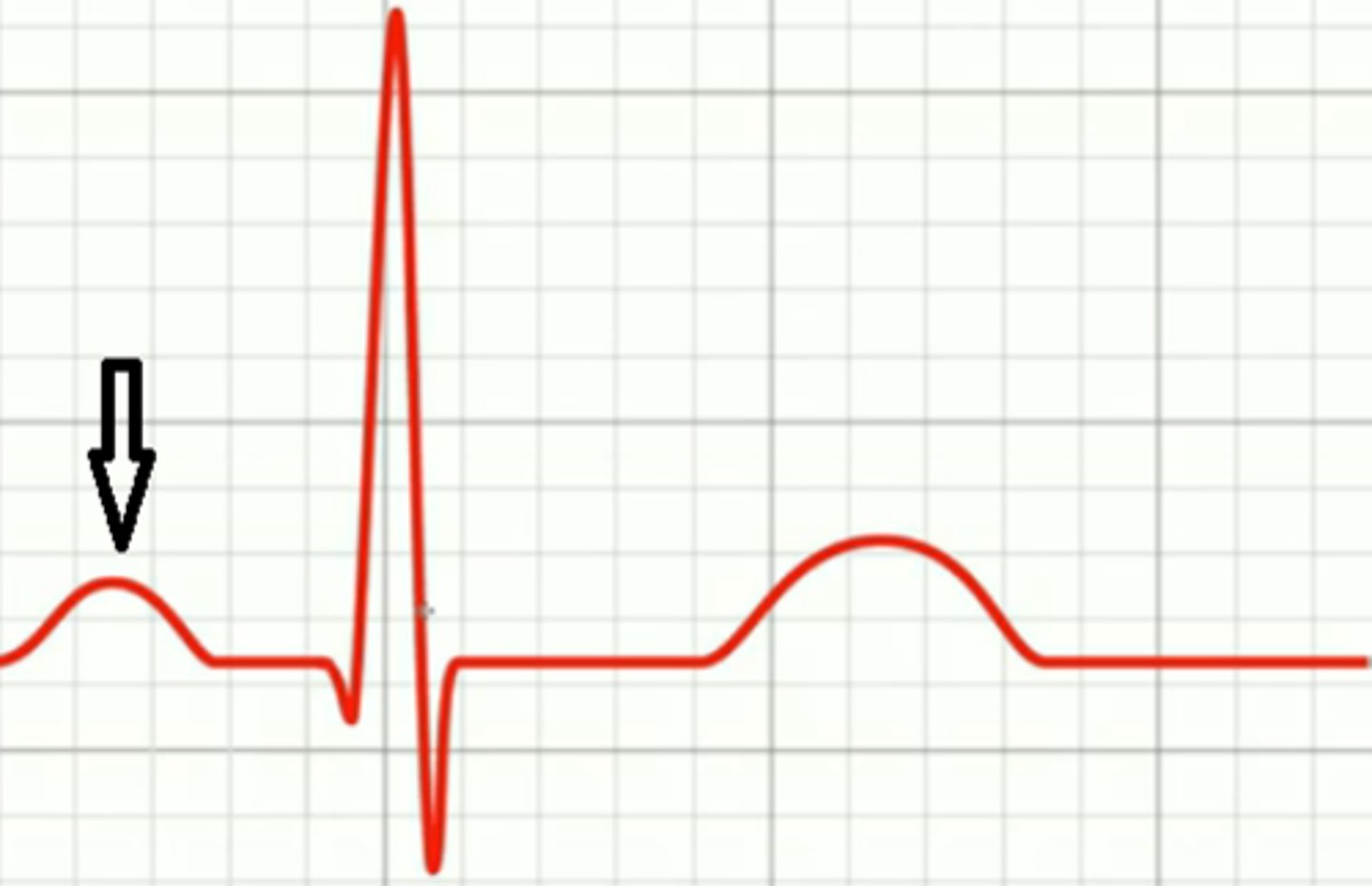
PR interval
wave and segment, current moves from SA node to AV node (atrial contract)

QRS complex
signal travels through ventricles ventricular muscle depolarization
RST interval
ventricles contract
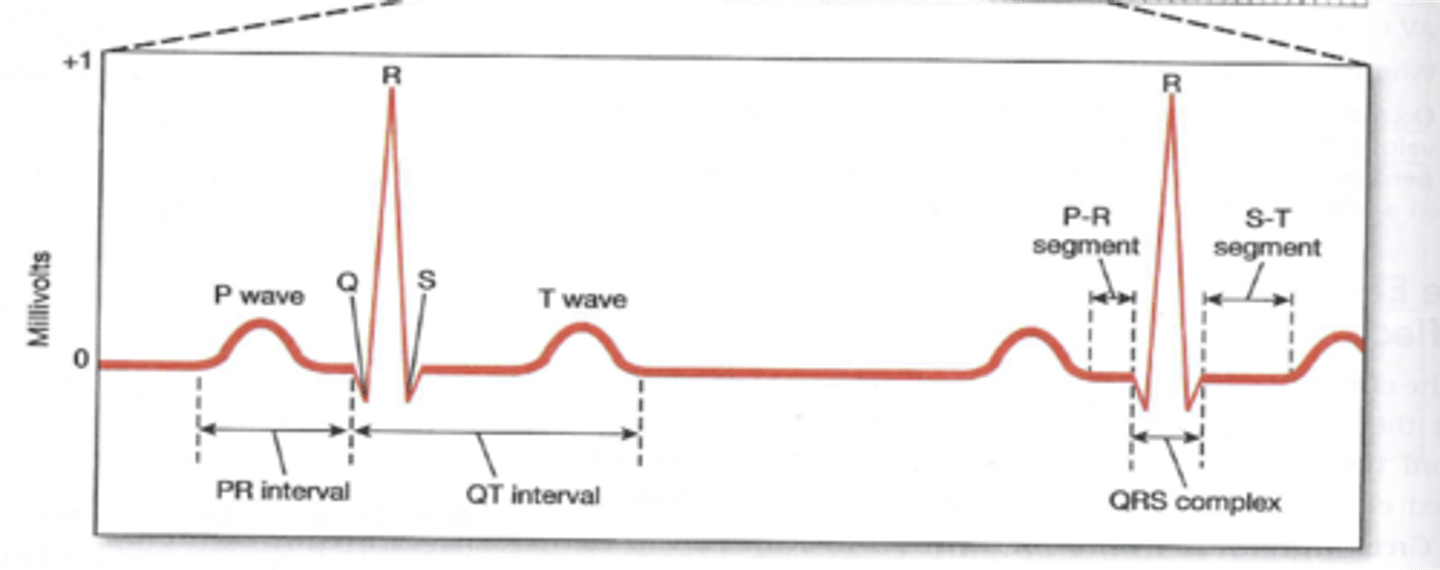
t wave
repolarization of ventricles
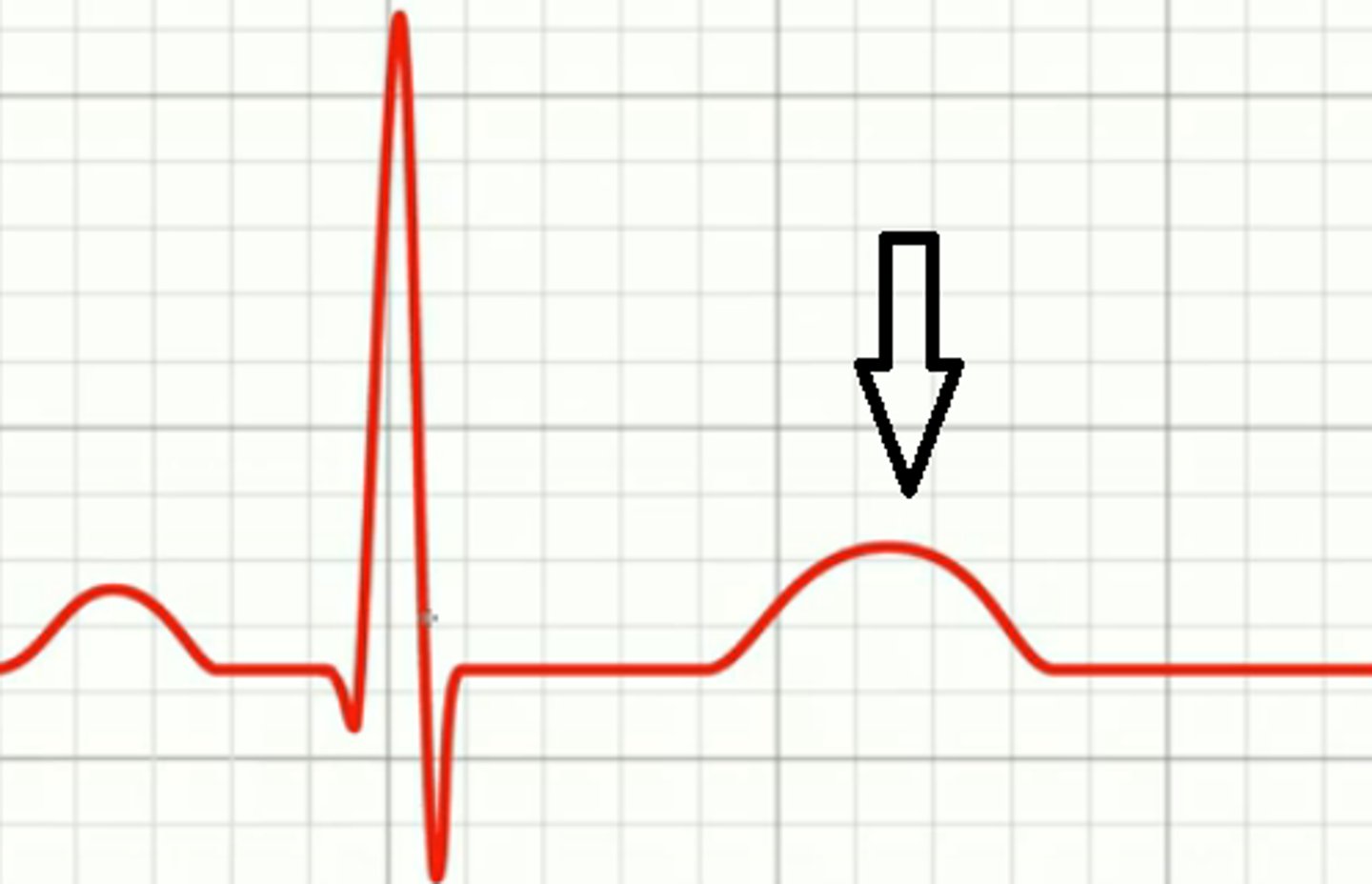
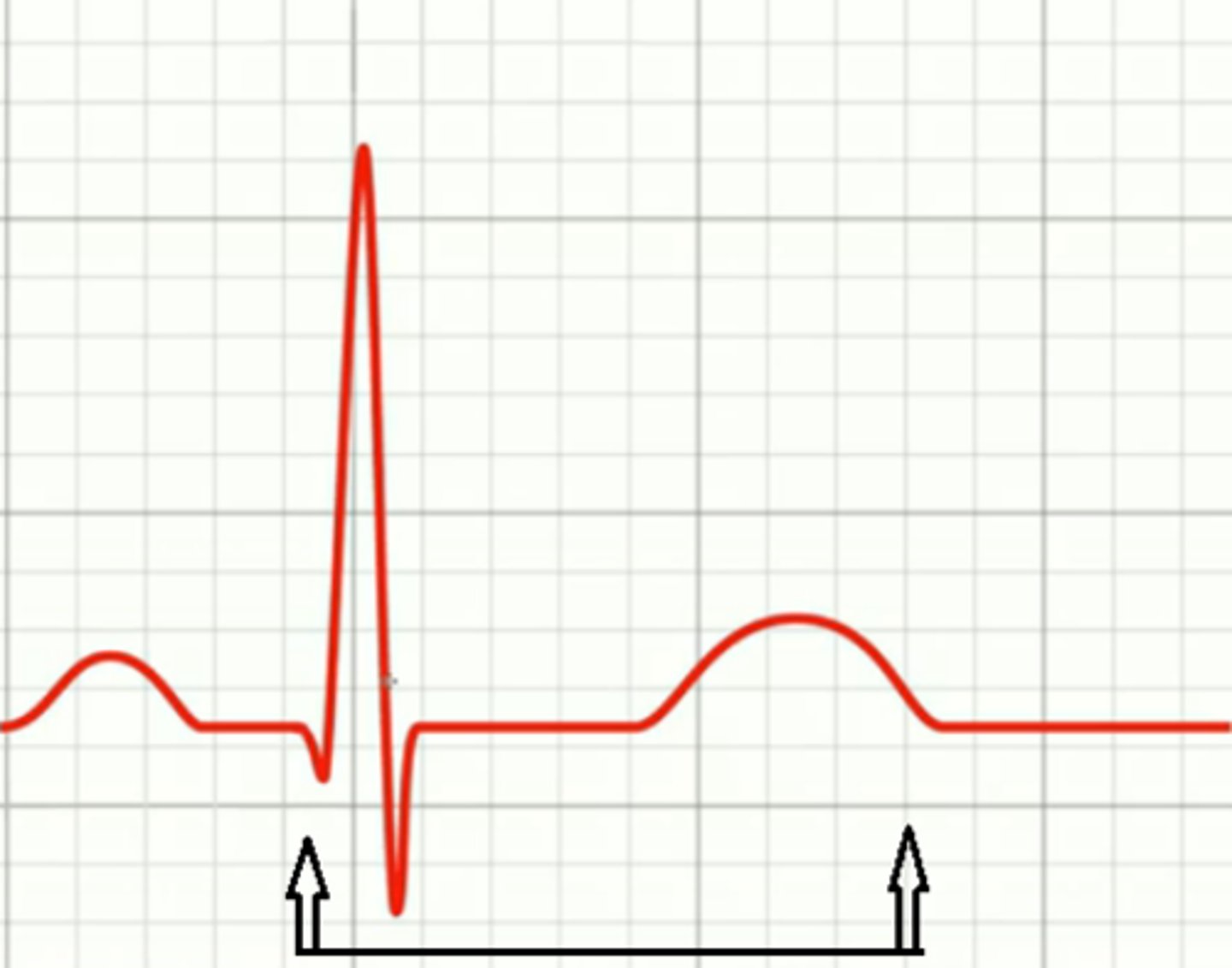
QT interval
reflects the duration of the ventricular action potential
what is flecanide C/E in
MI
what drugs do we use for class IV HF rhythm maintenance
amiodoorone or dofenilide
what do we do as a first line therapy in acute SVT
adenosine or vagal maneuvers
if the adenosine is unresponsive, what do we give next in SVT
diltiazem, verapamil, BB
catheter ablation is used in
rhythm control (afib) / recurrent fib
how do we tx sustained VT with pulse
amiodorne, procanimde, lidocaine
how do we tx non sustained VT with symptoms
BB
how do we tx symptomatic PVC
B blockers and reduce catecholamines
how to tx 2nd and 3rd degree AV block
atropine, dobutamine, dopamine, pacemaker
mobitz 1
PR gets increasingly longer until depolarization
mobitz 2
consistent PR with occasional non conducted depolarization
sinus bradycardia tx
atropine, pacemaker, B agonist
effect of quinidine that has tinnitus, blurred vision, flushed skin
cinchonism
which classes are used for ease control of supra ventricular arrhythmia
class II and IV
which class of antiarrythmics has the greatest effect on QTc interval
class III
most efficacious atiarrythmic
amiodorne
atropine MOA
antimuscaranic, comp antagonist of acetylcholine, direct vagolysis (decreases PR)
ivabradine MOA
sinus node inhibitor, blocks HCN channel responsible for the if current
adenosine moa
binds puringeric G protein receptors (flat line tx)
digoxin MOA
vagal stimulation, blockade of Na/K ATPase pump, increases PR
dofretilide drug interactions
HPCVTMKZ
HCTZ
Prochloprerazine
cimetidine
verapamil
TMP
Megestrol
ketoconazole
zoprasidone
rate controlling drugs
control the ventricular rate in pts with supraventricular tachyarrythmias
rhythm controlling drugs
to convert or maintain normal sinus rhythm
if you decrease PR
you increase HR
EAD
phase 3 (Na opens)
DAD
phase 4 (ca release= digoxin tox)
class Ia act on
supra ventricular and ventricular
class Ib acts on
only ventricular
class Ic acts on
supra ventricular and ventricular
class II
supraventicular
Class IV
supraventricular