9.2 cardiac output
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
how to vary stroke volume
vary the force of contraction, which will thus vary how much blood is pumped out
how to vary force of contraction
amt of blood pumped out is proportional to how much blood returns to the heart
as more blood comes back to the heart, the blood that is coming back stretches the heart muscle to a greater extent than normal (preload)
this increases the force of contraction and increases the stroke volume, the volume of blood pumped per beat
thus: increasing the stretch increases the force of contraction
preload
degree of increased stretch in the ventricular walls
Frank-Starling mechanism
increased stretch → increased force
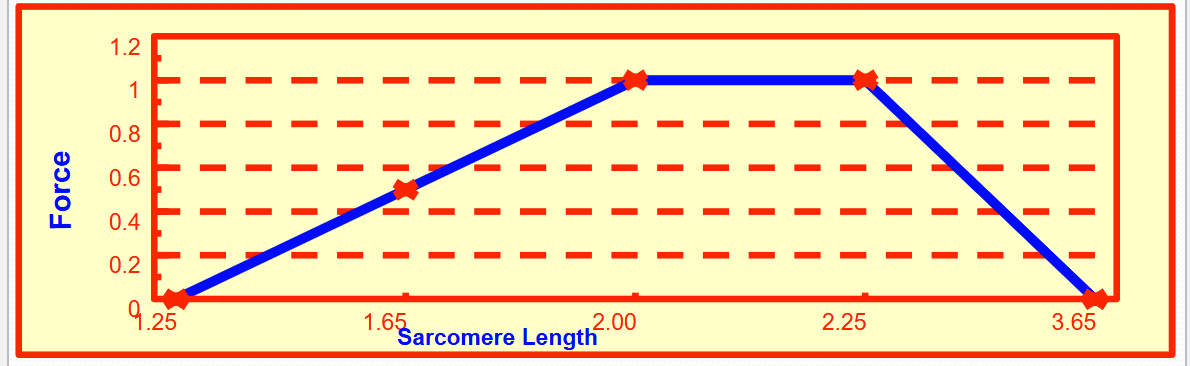
describe skeletal muscle’s optimal length
optimal length has maximal cross bridge activity and maximal pulling and maximal force
in the heart at rest you (are/aren’t) at the optimal length
aren’t
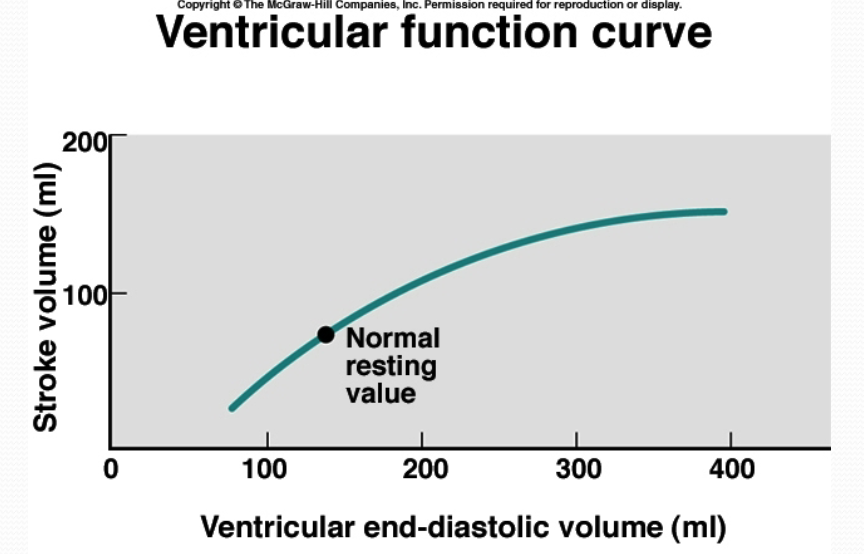
increasing the force of contraction will (increase/decrease) the volume of blood leaving per beat
increase (black dot is the normal resting volume that you pump out at every beat)
two types of activity that can affect the force of contraction
sympathetic activity, parasympathetic activity
how do parasympathetic and sympathetic nerve fibers affect the heart?
influence the pumping action of the heart by affecting both the heart rate and stroke volume, keeping the blood pressure, blood O2 and CO2 levels, and blood pH in the appropriate range (homeostasis)
parasympathetic activity
vagus nerve carries parasympathetic nerve fibers to the heart (primarily)
vagus nerve innervates the SA node (cluster of cells in the right atria that generate electrical impulses that initiate the heart beat. is the heart’s pacemaker)
parasympathetic nerve stimulation has an inhibitory effect → decreases heart rate
mechanism for parasympathetic nerves to decrease heart rate
parasympathetic neurons produce the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine (ACh)
ACh binds to ligand gated channels on cardiac cell membrane which causes K+ to go out → hyperpolarizes the cell + decreases permeability of Na+ and Ca2+
hyperpolarized membrane takes longer to depolarize (and thereby causes an AP) → heart rate decreases
ionotropic receptors
form an ion channel pore
metabotropic receptors
indirectly linked w ion-channels on the plasma membrane of the cell thru signal transduction mechanisms (e.g., G proteins, neurotransmitters are ligands)
what is the acetylcholine receptor in the heart?
M2
the M2 muscarinic receptors are located in the heart, where they act to slow the heart rate down to normal sinus rhythm after stimulatory actions of the sympathetic nervous system by slowing the speed of depolarization
nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChR)
ionotropic acetylcholine receptors, responsive to nicotine, Na+ and K+ ion channel
muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChR)
metabotropic acetylcholine receptors, responsive to muscarine
sympathetic activity
sympathetic nerves from the thoracic region of spinal cord project to heart as cardiac nerves
sympathetic nerves innervate the SA and AV nodes, the coronary vessels, and the atrial and ventricular myocardium (heart muscle)
sympathetic stimulation increases heart rate and force of muscular contraction
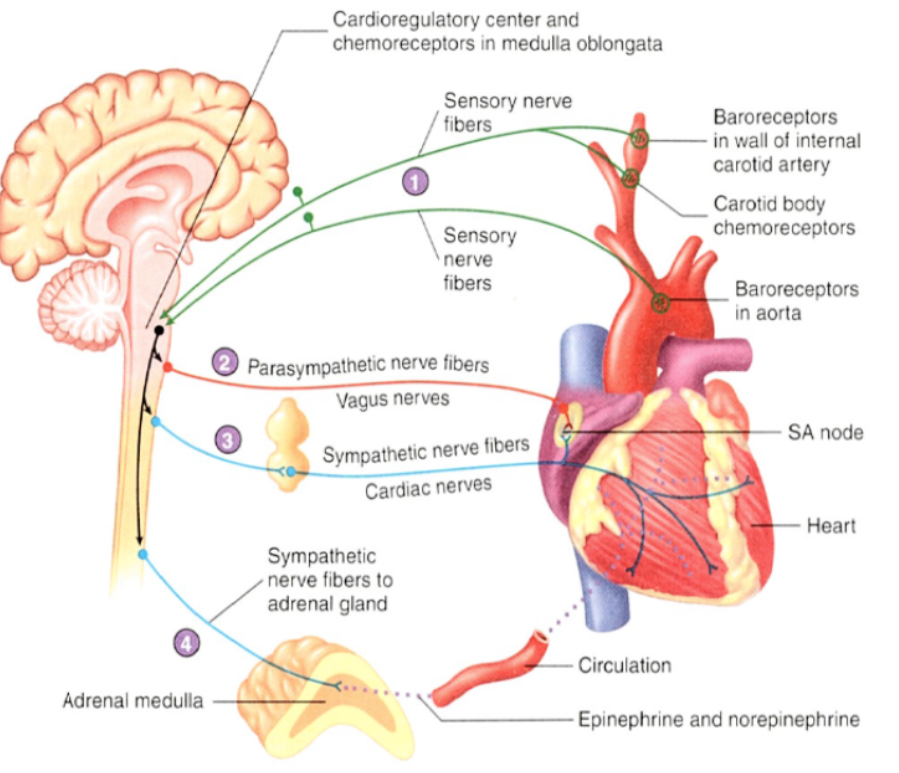
nervous system regulation of the heart
sensory (green) neurons carry APs from baroreceptors to the cardioregulatory center. chemoreceptors in the medulla oblongata influence the cardioregulatory center
the cardioregulatory center controls the frequency of APs in the parasympathetic (red) neurons extending to the heart through the vcagus nerves. the parasympathetic neurons decrease the heart rate
the cardioregulatory center controls the frequency of APs in the sympathetic (blue) neurons. the sympathetic neurons extend thru the cardiac nerves and increase the heart rate and stroke volume
the cardioregulatory center influences the frequency of APs in the sympathetic (blue) neurons extending to the adrenal medulla. the sympathetic neurons increase the secretion of epinephrine and some norepinephrine into the general circulation. epinephrine and norepinephrine increase the heart rate and stroke volume
catecholamines + which effect does it carry out?
an amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine
act as hormones or neurotransmitters (norepinephrine and epinephrine)
carries out sympathetic effect on heart function
bind to 2 different classes of receptors termed the alpha and beta adrenergic receptors
also known as adrenergic neurotransmitters; neurons that secrete them are adrenergic neurons
epinephrine is __ from norepinephrine
derived/synthesized
norepinephrine-secreting neurons are
noradrenergic
norepinephrine
a neurotransmitter from sympathetic neurons (specifically, the postganglionic sympathetic neurons)
increases the rate and degree of cardiac muscle depolarization, which causes an increase in the frequency of the AP and the force and velocity of the contraction
agonist for cell surface beta adrenergic receptors
causes G-protein mediated synthesis and accumulation of cAMP in cardiac cells
opens Ca2+ slow channels, increases cell’s ability to depolarize, also helps open Na+ channels
epinephrine (aka adrenaline)
a hormone released from the adrenal medulla
similar in structure to norepinephrine
has essentially the same effect on the heart as norepinephrine
nerve signals to the adrenal gland activate the conversion of stores of norepinephrine to epinephrine and cause its release into the bloodstream
increases cardiac output and blood glucose levels
epinephrine and norepinephrine stimulation together
increased physical activity, emotional excitement, or stressful situations cause sympathetic stimulation of the cardioregulatory center in the brainstem (medulla)
this causes the sympathetic stimulation to the heart and causes the adrenal gland to secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine into the bloodstream
epi and norepi are transported thru the blood to the cardiac muscle cells where they bind beta adrenergic receptors
effects of norepinephrine and epinephrine
prep the body for fight or flight
increase blood pressure, heart rate, upregulate the blood and oxygen supply to muscle tissue
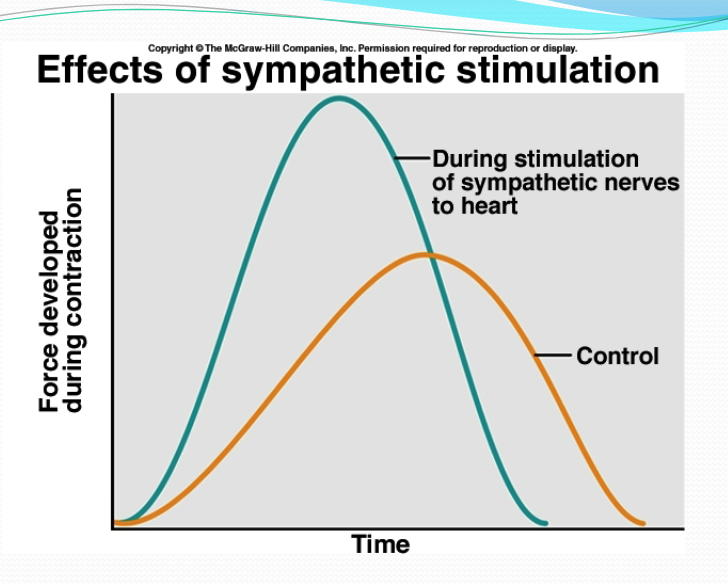
what does a faster rise and fall indicate, and how does this occur?
indicates a shorter, stronger heartbeat. caused by increased rate of calcium release/entry + increased rate of calcium uptake
what parts of the cell do norepinephrine and epinephrine affect?
the channels that bring calcium into the cell
the channels that allow calcium to leave the sarcoplasmic reticulum
the calcium troponin interaction
the reuptake of calcium into the sarcoplasmic reticulum
if the interaction btwn the troponin and the calcium is __, heart contracts __. if calcium is taken up by the sarcoplasmic reticulum __, heart relaxes __.
faster, faster, faster, faster
sympathetic effect on contractility
for the same volume, there is a stronger contraction bc the sympathetic stimulation enables the heart to pump out more of whatever is there. you more completely empty the heart
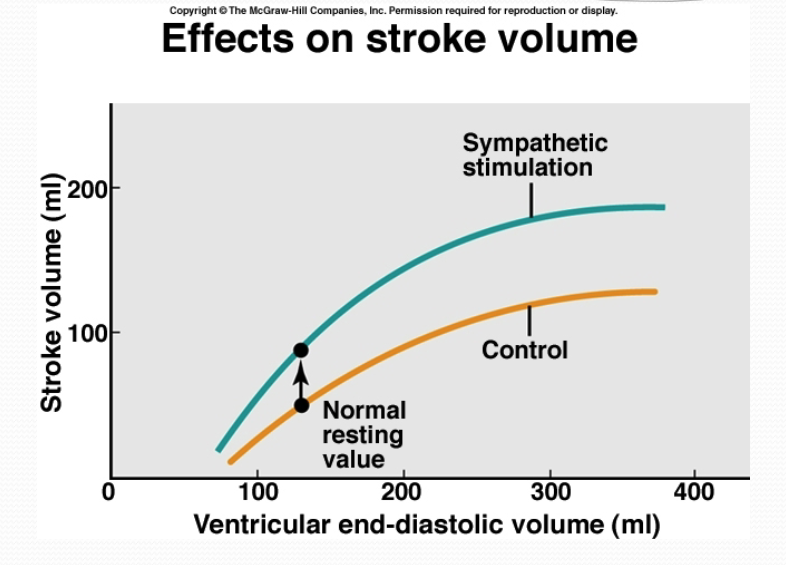
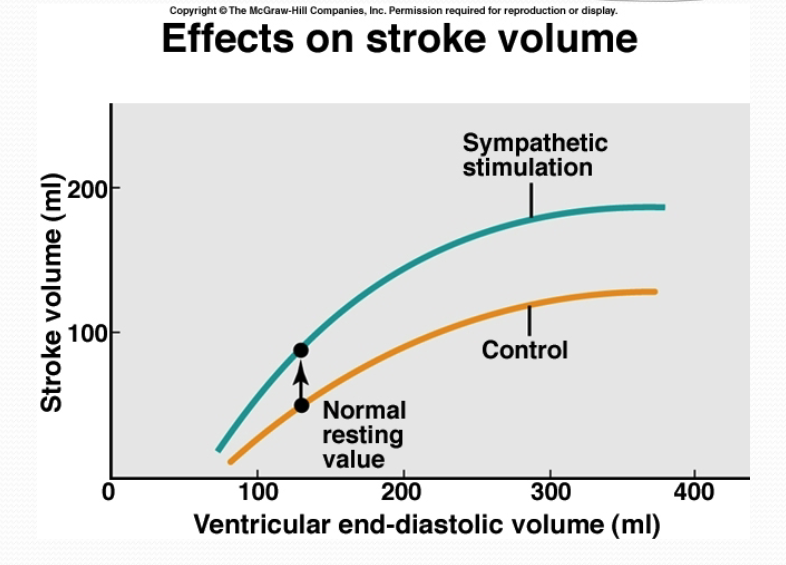
interpret this graph
greater contraction for same end diastolic volume
for any amount of blood coming back as shown by the yellow line, you pump out more, as shown by the green line
effects of autonomic nerves on SA node
sympathetic nerves (norepinephrine on beta-adrenergic receptors): increased heart rate
parasympathetic nerves (ACh on muscarinic receptors): decreased heart rate
effects of autonomic nerves on AV node
sympathetic nerves (norepinephrine on beta-adrenergic receptors): increased conduction rate
parasympathetic nerves (ACh on muscarinic receptors): decreased conduction rate
effects of autonomic nerves on atrial muscle
sympathetic nerves (norepinephrine on beta-adrenergic receptors): increased contractility
parasympathetic nerves (ACh on muscarinic receptors): decreased contractility
effects of autonomic nerves on ventricular muscle
sympathetic nerves (norepinephrine on beta-adrenergic receptors): increased contractility
parasympathetic nerves (ACh on muscarinic receptors): no significant effect
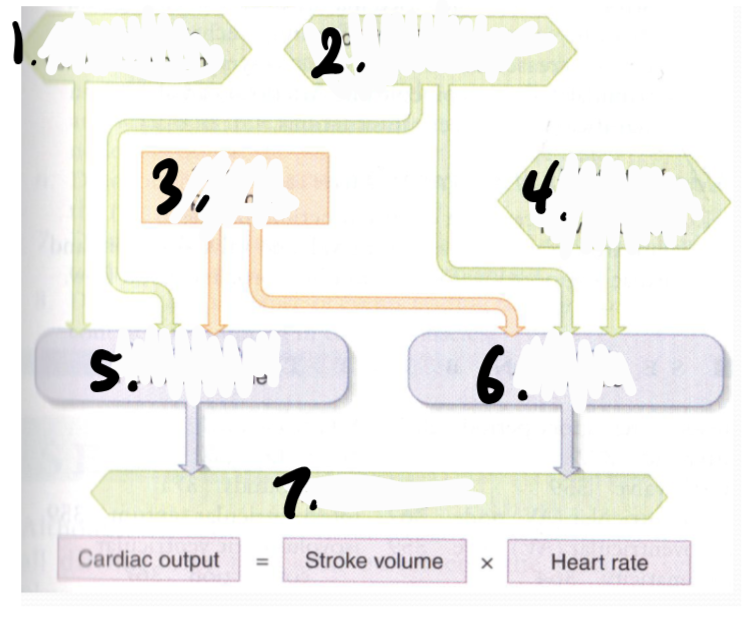
higher end-diastolic ventricular volume, higher activity of sympathetic nerves to heart, high plasma epinephrine, lower activity of parasympathetic nerves to heart, higher stroke volume in cardiac muscle, higher heart rate in SA node, higher cardiac output