8. Radiographic INterpretation Part 2
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
what are the six relevant nasal structures?
Nasal septum
Nasal fossa
Floor of the nose
Soft tissue of nose
Inferior conchae
Anterior nasal spine
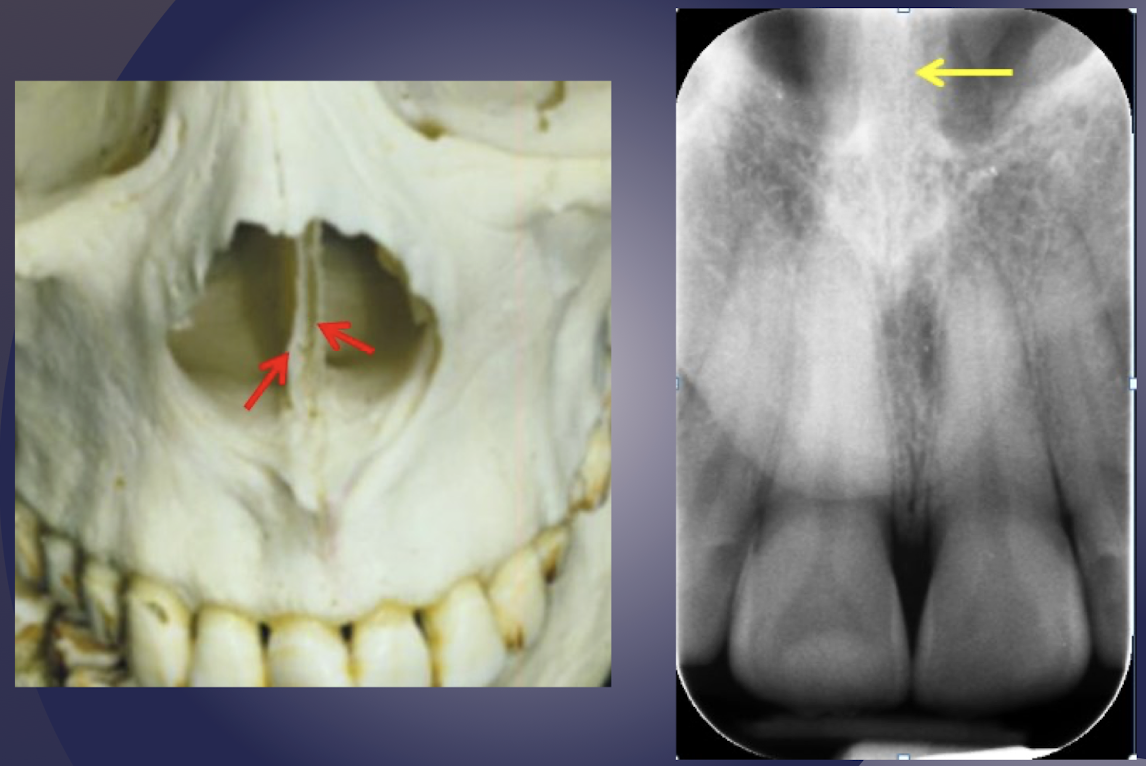
nasal septum
which nasal structure?
radiopaque shadow midline of nasal cavity
appears wide and not sharply defined; superimposition of septal cartilage and vomer bone
nasal septum
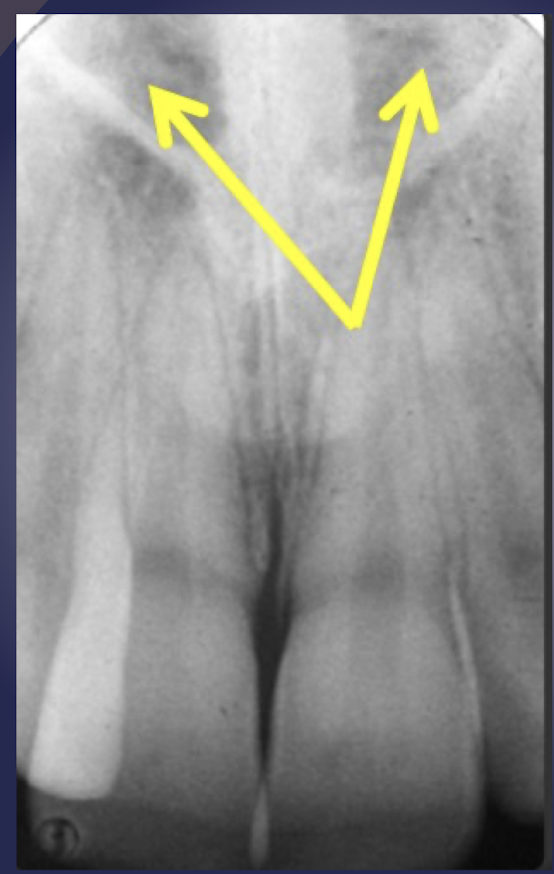
nasal fossa
which nasal structure?
Air filled cavity above the roots of maxillary central incisors
Limited by the nasal septum medially and floor of nasal fossa inferiorly
nasal fossa
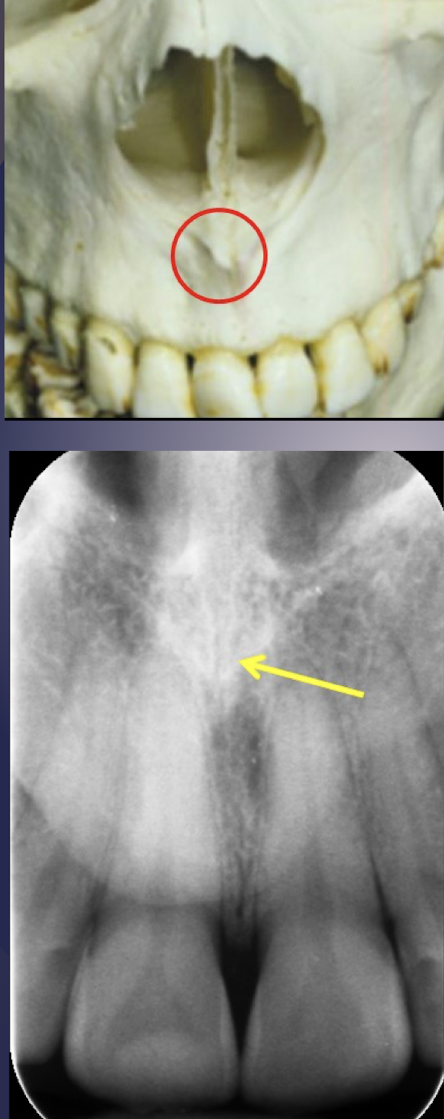
anterior nasal spine
which nasal structure?
Radiopaque V-shaped projection at the base of the nasal septum
Periapical radiograph of maxillary central incisors
anterior nasal spine
floor of nasal fossa/hard palate
which nasal structure?
radiopaque line extending bilaterally away from base of anterior nasal spine
floor of nasal fossa/hard palate
floor of nasal fossa/hard palate extends anteriorly/posteriorly
posteriorly, superimposed over maxillary sinus
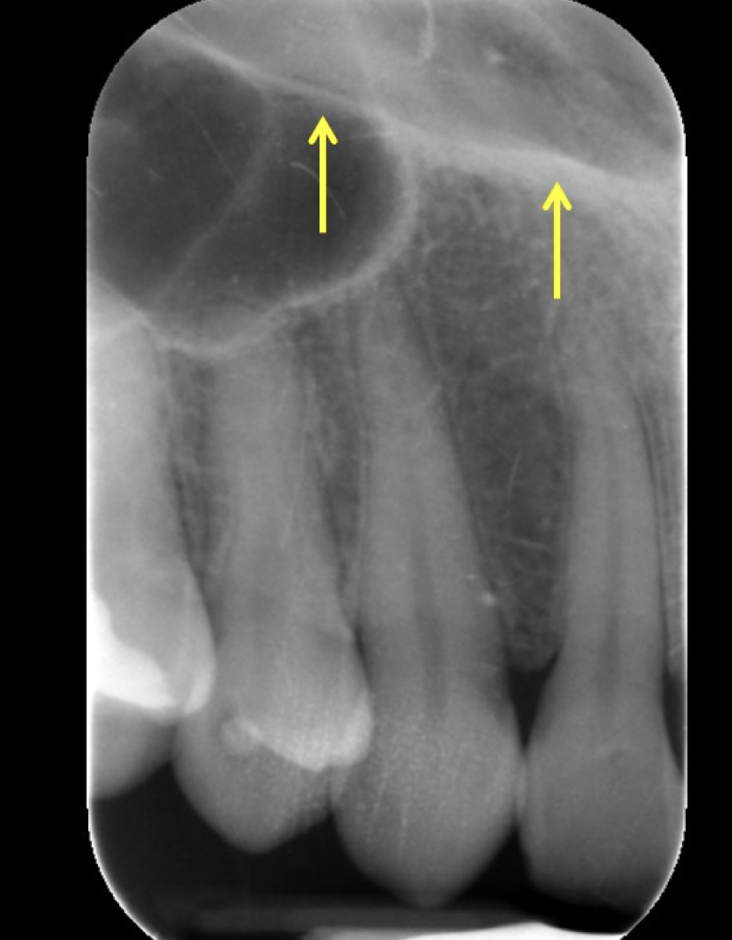
floor of nasal fossa/hard palate
floor of nasal fossa/hard palate
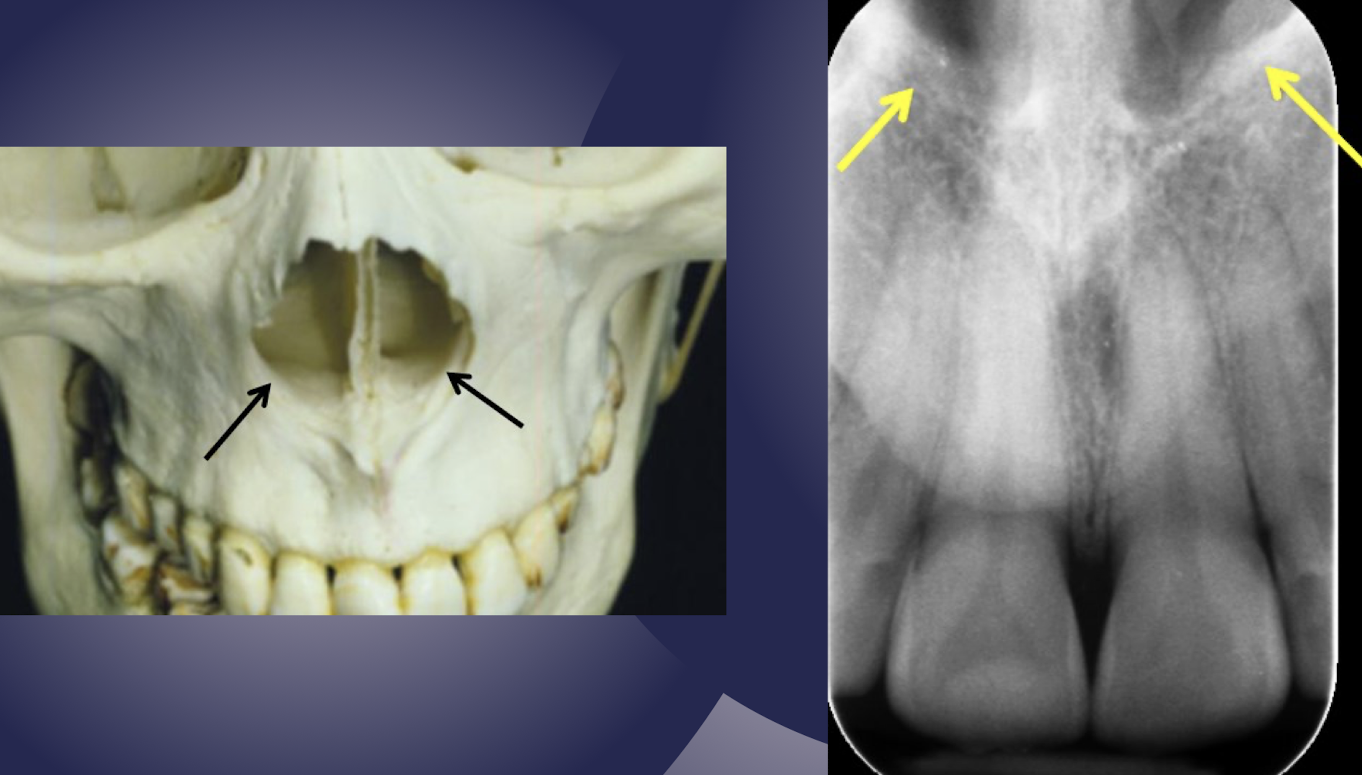
inferior concha/inferior turbinate
which nasal structure?
radiopaque shadow on lateral walls of nasal fossa
inferior concha/inferior turbinate
soft tissue tip of nose
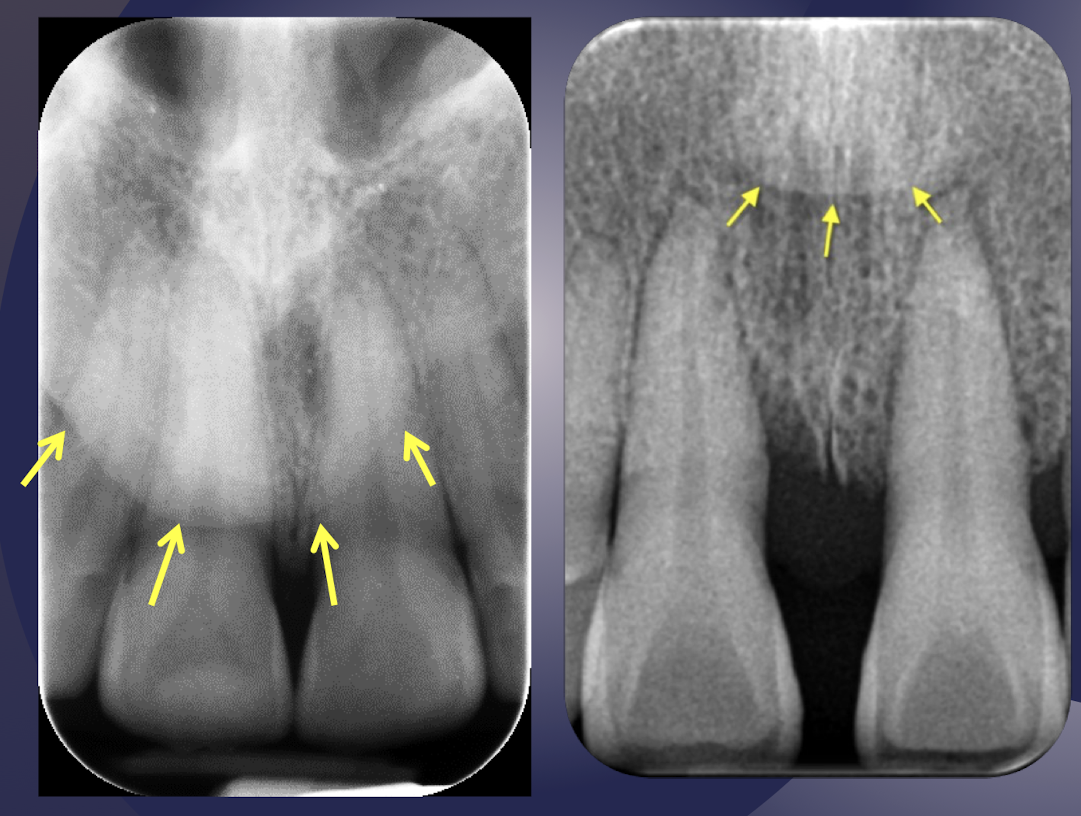
which soft tissue structure of nose?
Maxillary central-lateral incisor area
Slightly opaque shadow with sharp border
Location may be coronal or apical to root apex based on x-ray projection geometry
tip of nose
soft tissue nasolabial fold
which soft tissue structure of the nose?
Oblique line in maxillary premolar area
slight opacity (Thick cheek tissue) posterior to the line
soft tissue nasolabial fold
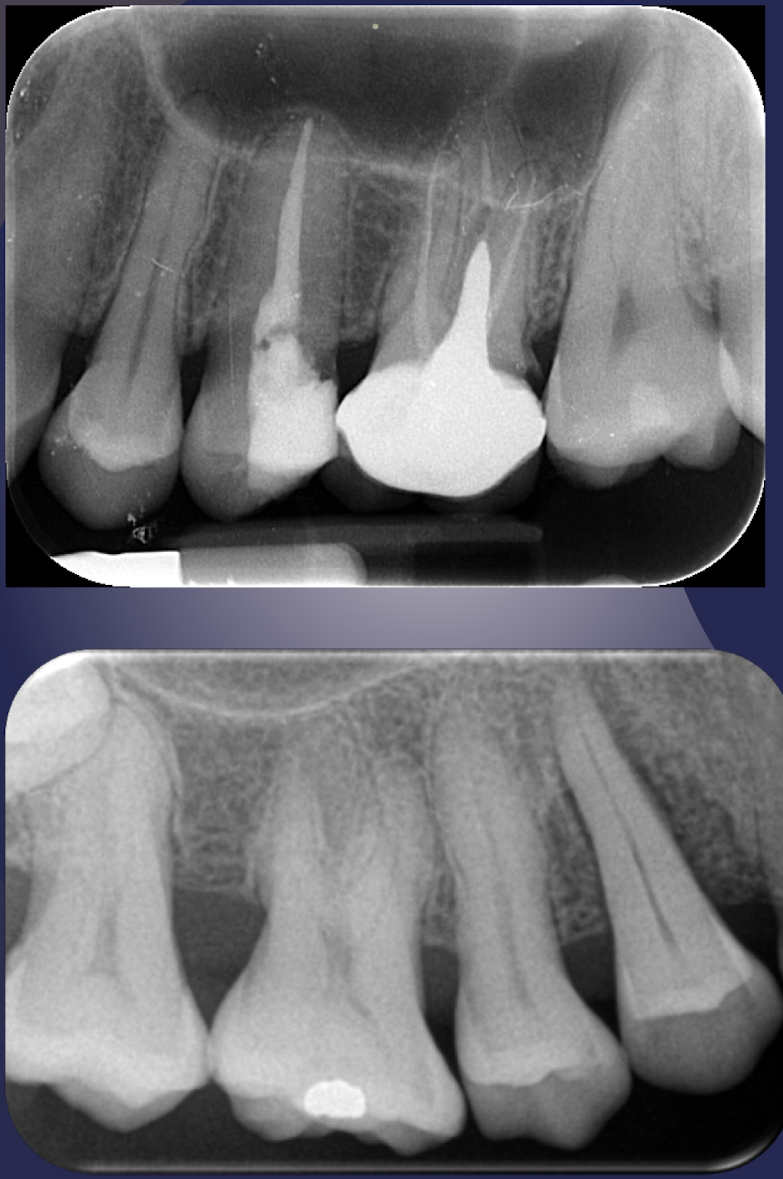
definition: air containing cavity lined w mucus membrane
maxillary sinus/antrum
maxillary sinus
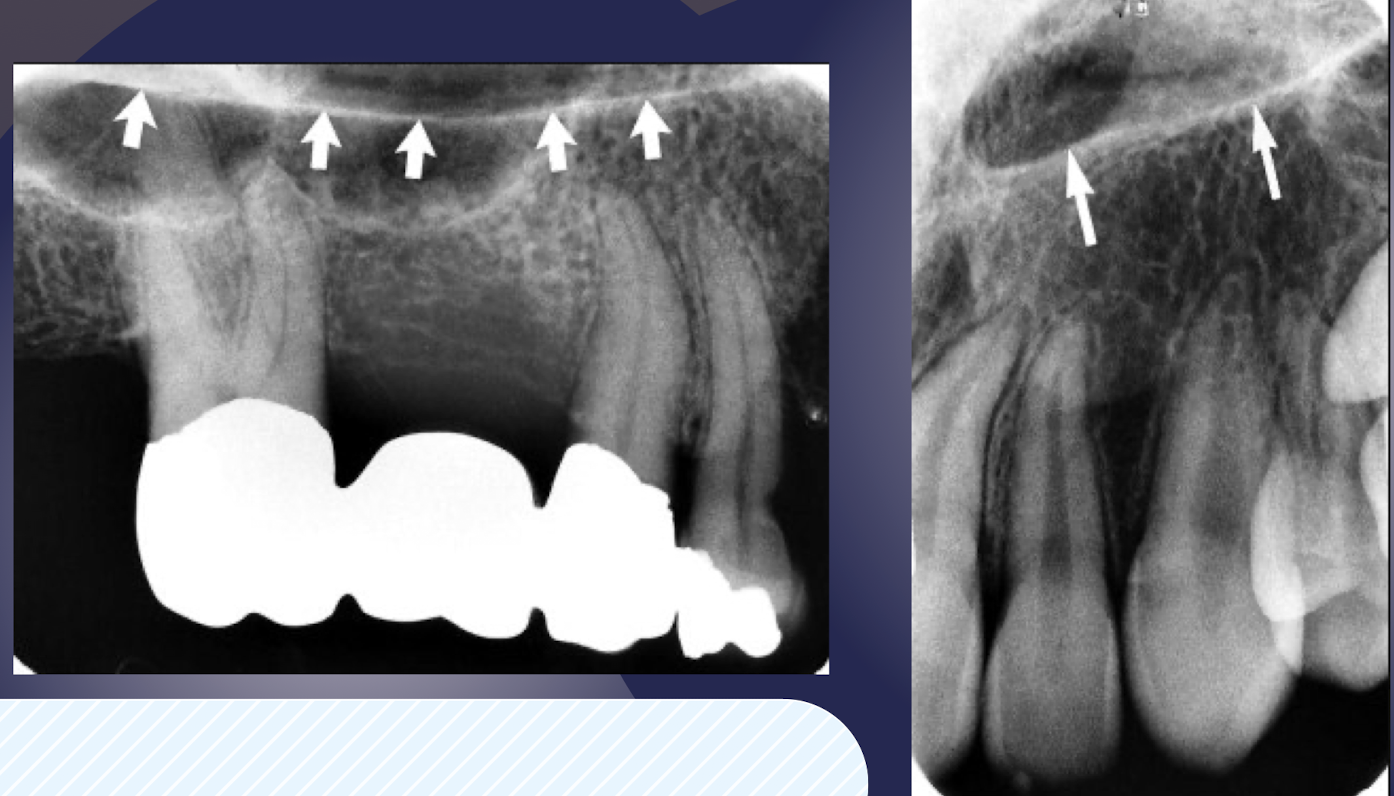
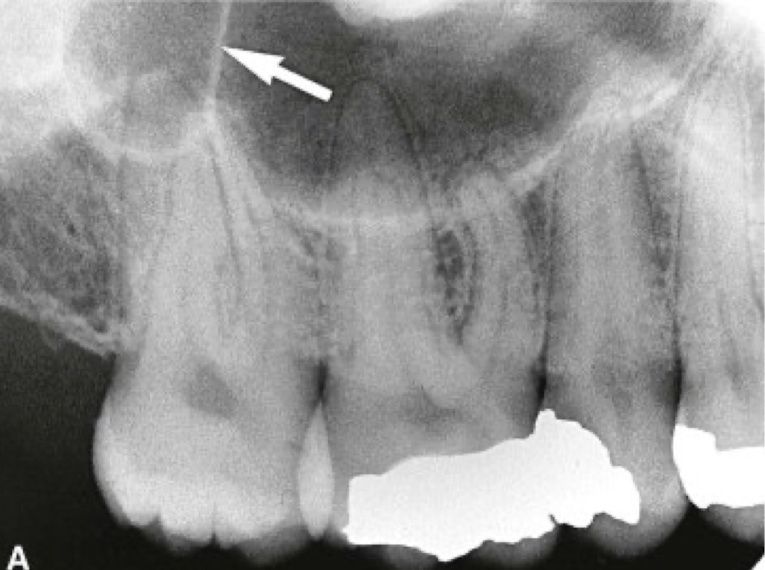
what structure of maxilla?
Thin, delicate, tenuous radiopaque line
Thin layer of cortical bone
Appears continuous in absence of disease
Close relationship to roots of maxillary posterior teeth
Roots may appear to project into the sinus however a thin layer of bone covering the root is seen as a fusion of lamina dura and sinus floor
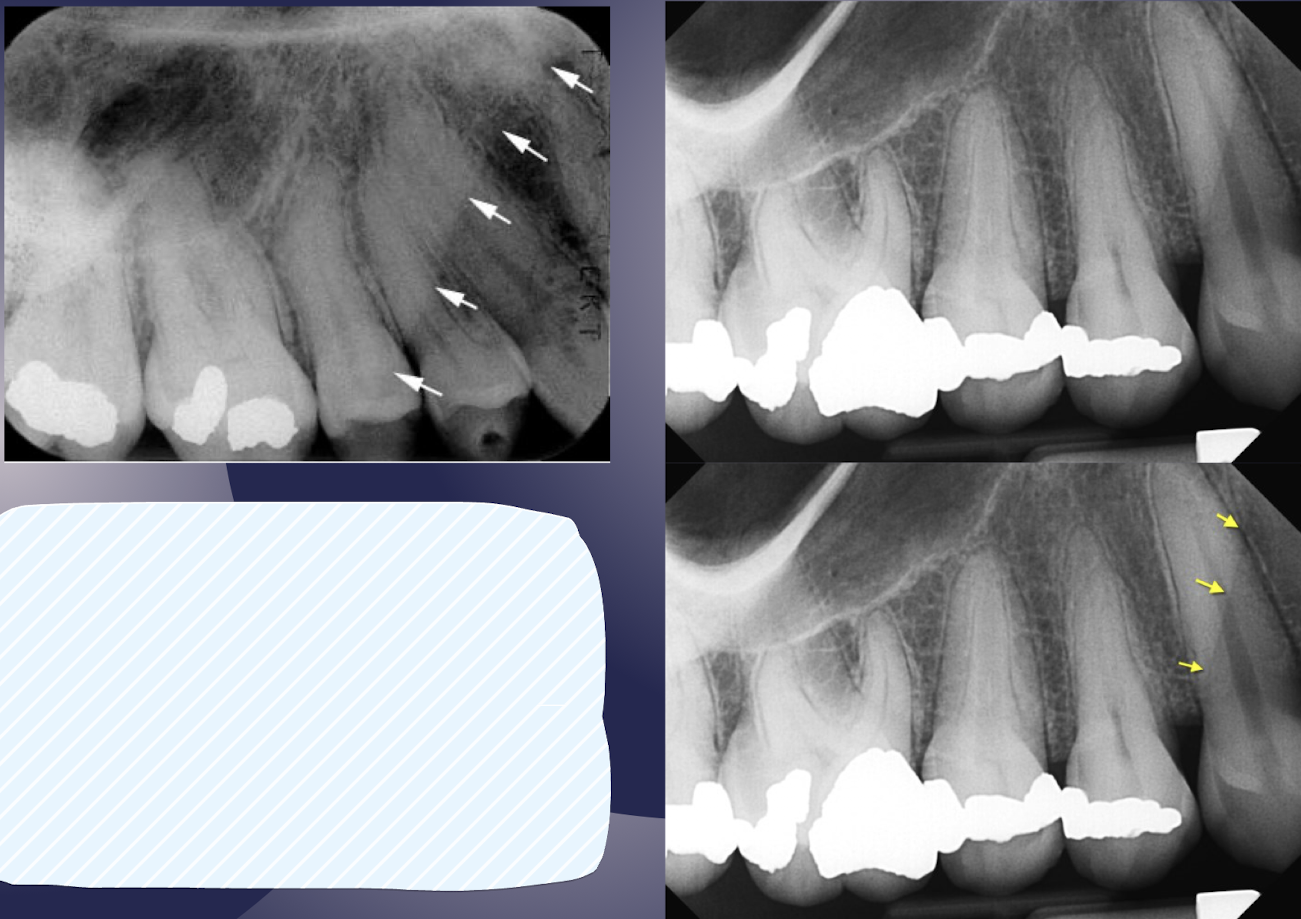
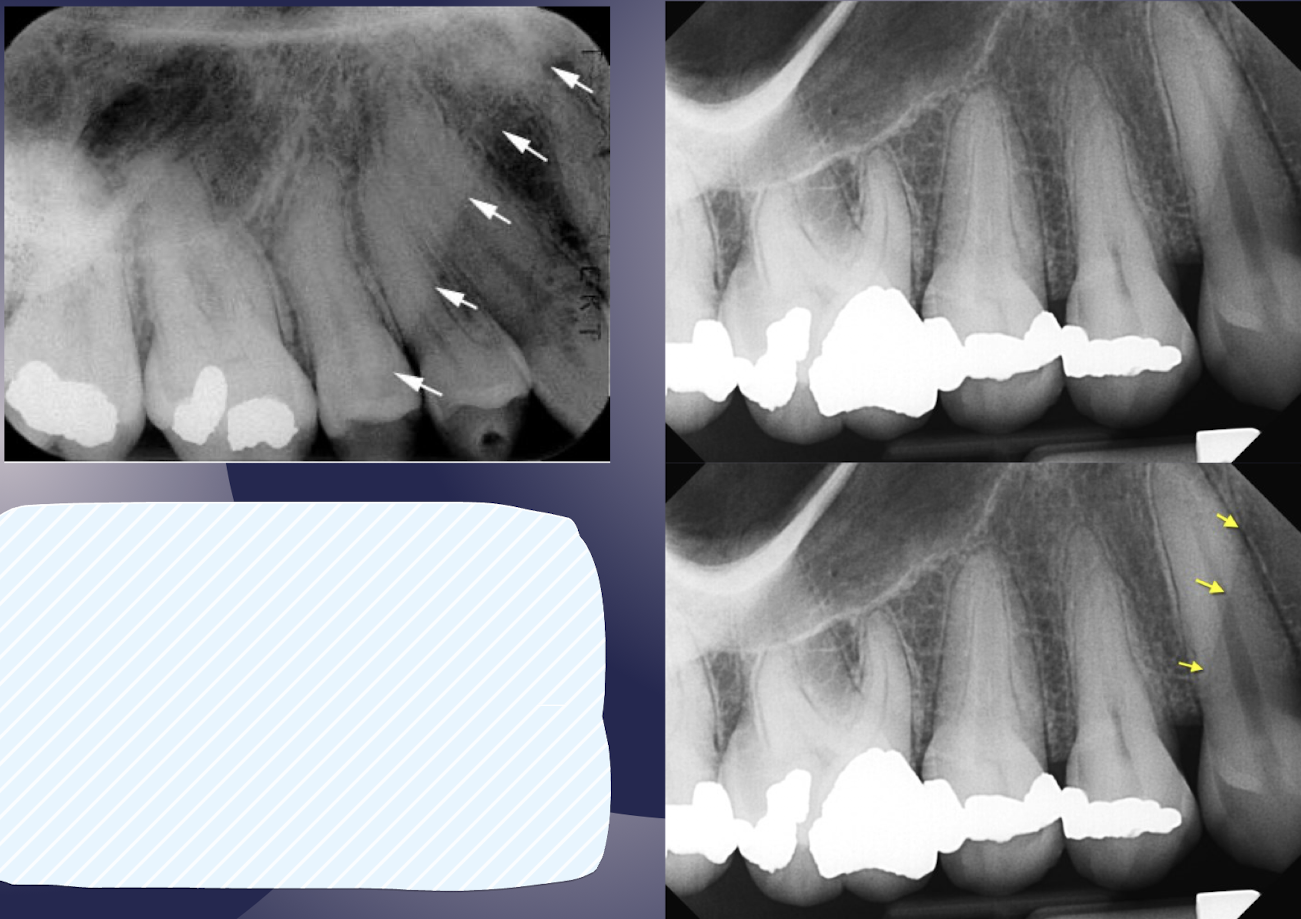
floor of the maxillary sinus
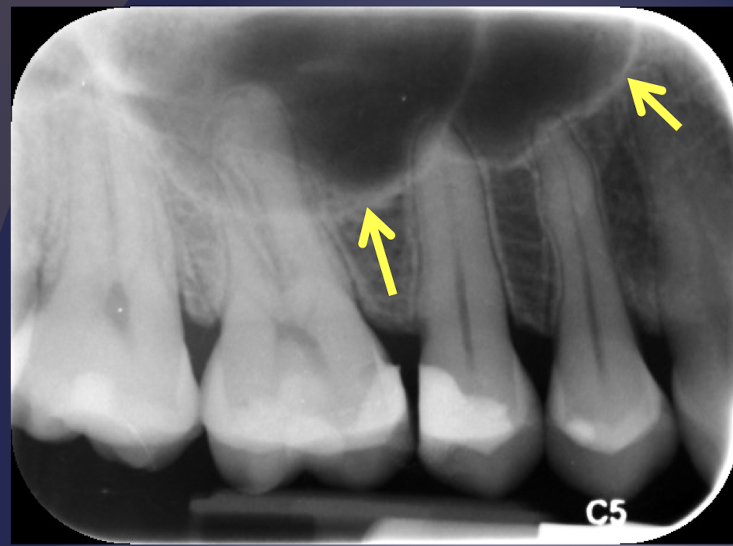
floor of the maxillary sinus
intimate relationship btwn teeth and sinus; periapical infection due to thin layer of cortical bone
T or F: floor of maxillary sinus may extend beyond apices and toward alveolar ridge
true
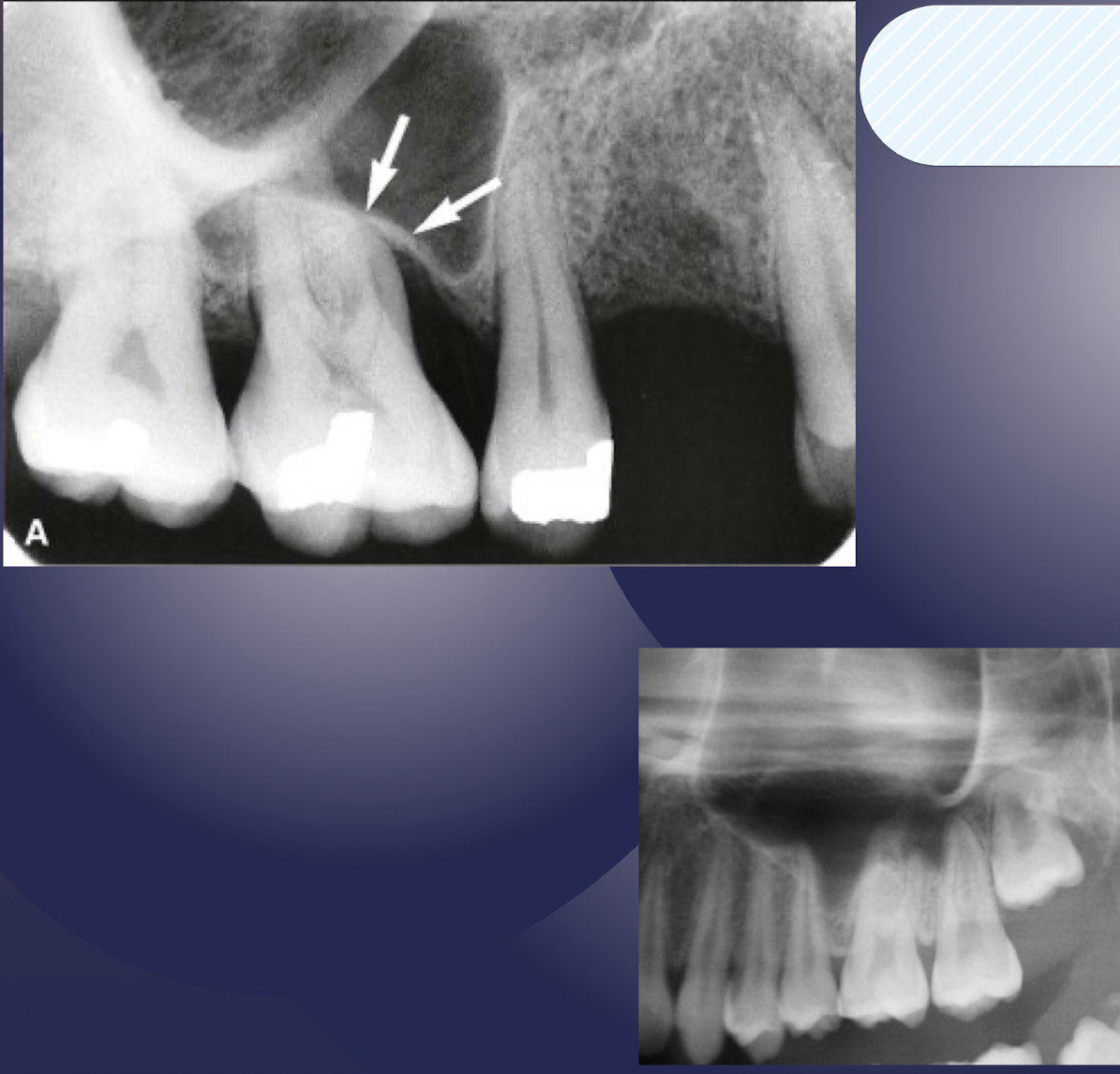
definition: floor of maxillary sinus extends toward crest of alveolar ridge in response to missing teeth
pneumatization of maxillary sinus
definition: in response to loss of function (tooth loss) sinus may expand farther into alveolar bone
pneumatization of maxillary sinus
pneumatization of maxillary sinus
pneumatization of maxillary sinus
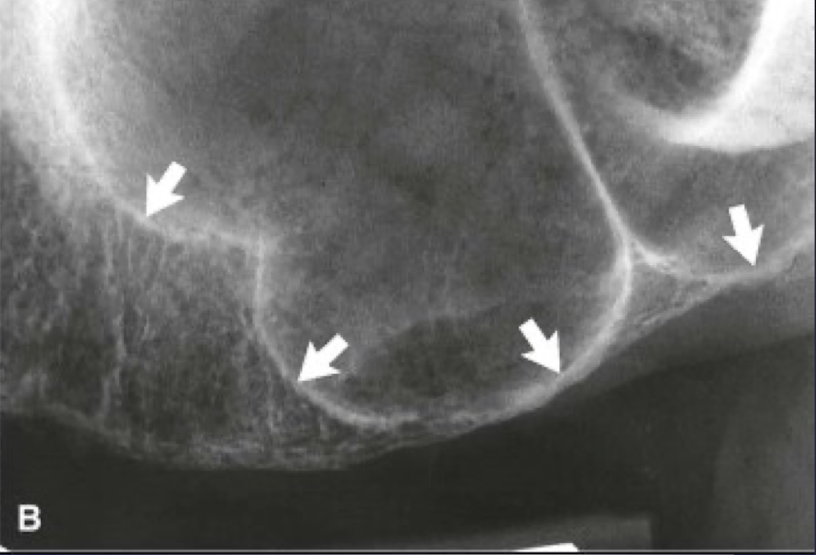
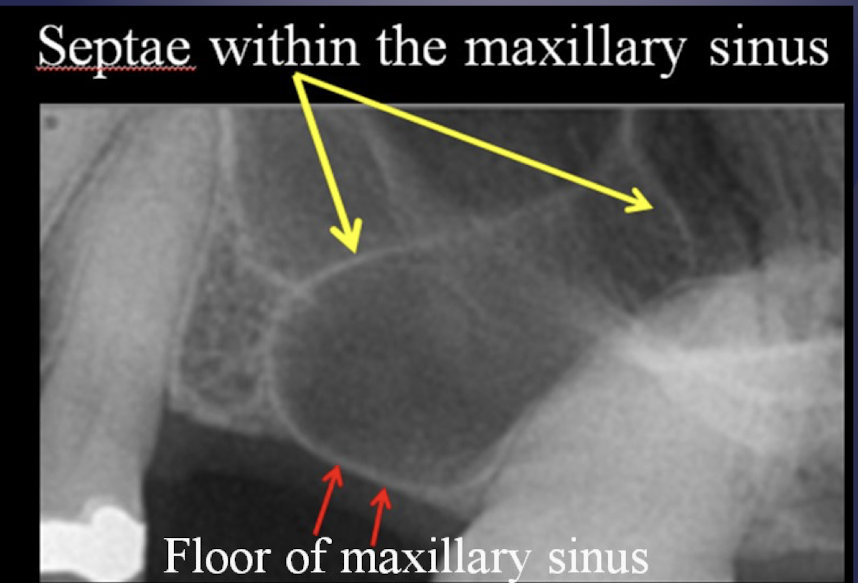
definition: thin folds of cortical bone projecting from sinus floor and wall into the sinus
septae
maxillary septae
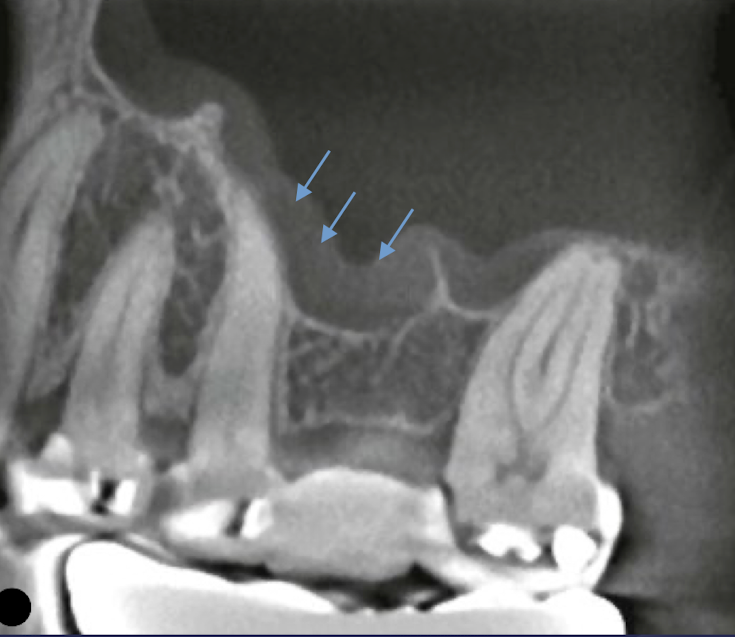
Thickening of sinus mucus membrane
CBCT sagittal
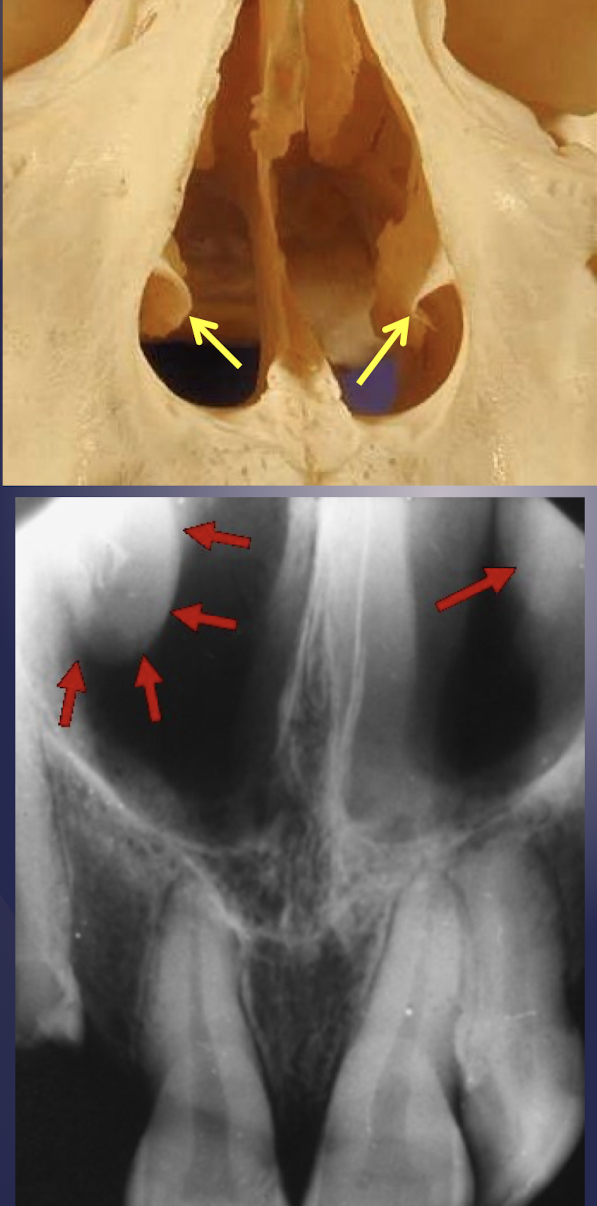
what is the Y-line of Ennis?
formed by nasal fossa floor and antero-medial wall of maxillary sinus
In periapical radiograph of Canine: The floor of sinus and nasal cavity are superimposed and seen crossing one another forming an inverted Y
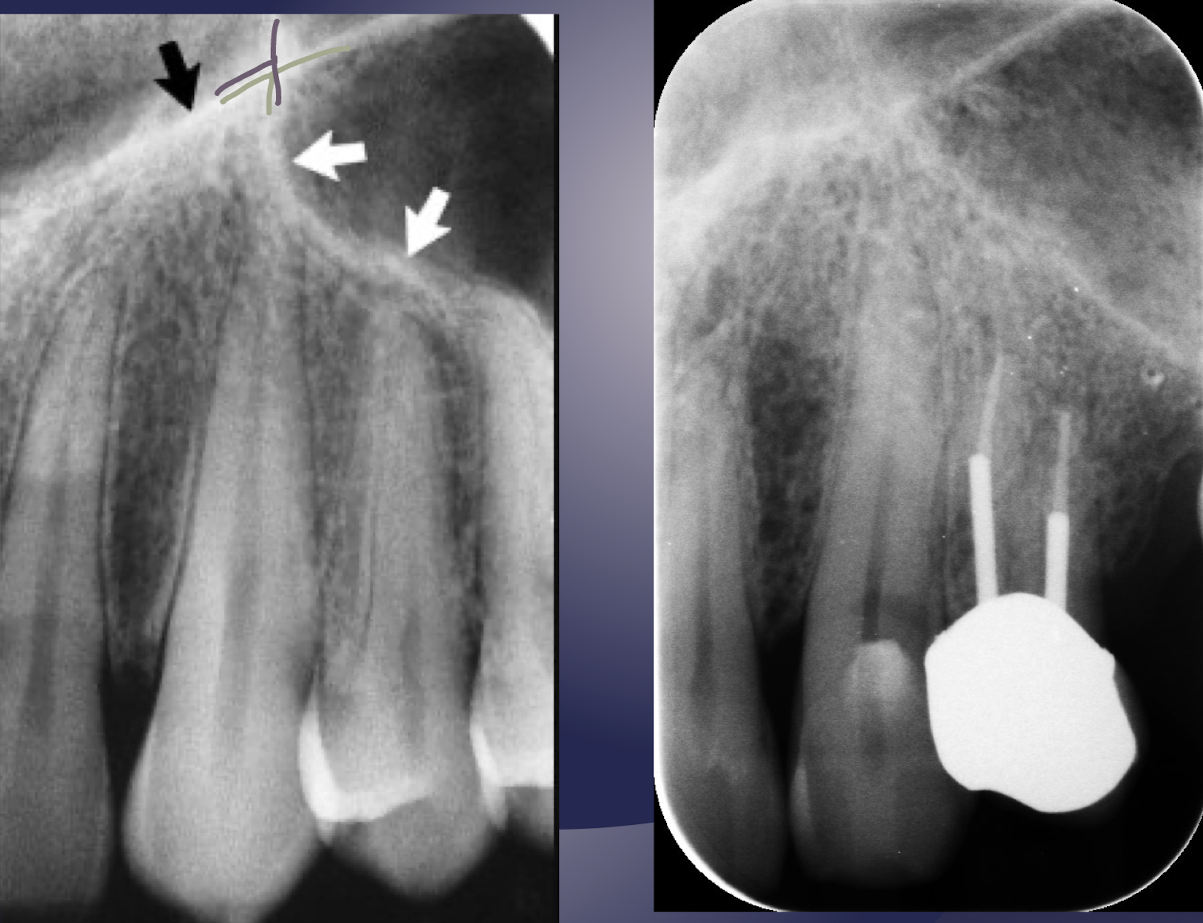
Y-line of Ennis =green line
black arrow: nasal fossa
white arrow: anterior border of maxillary sinus
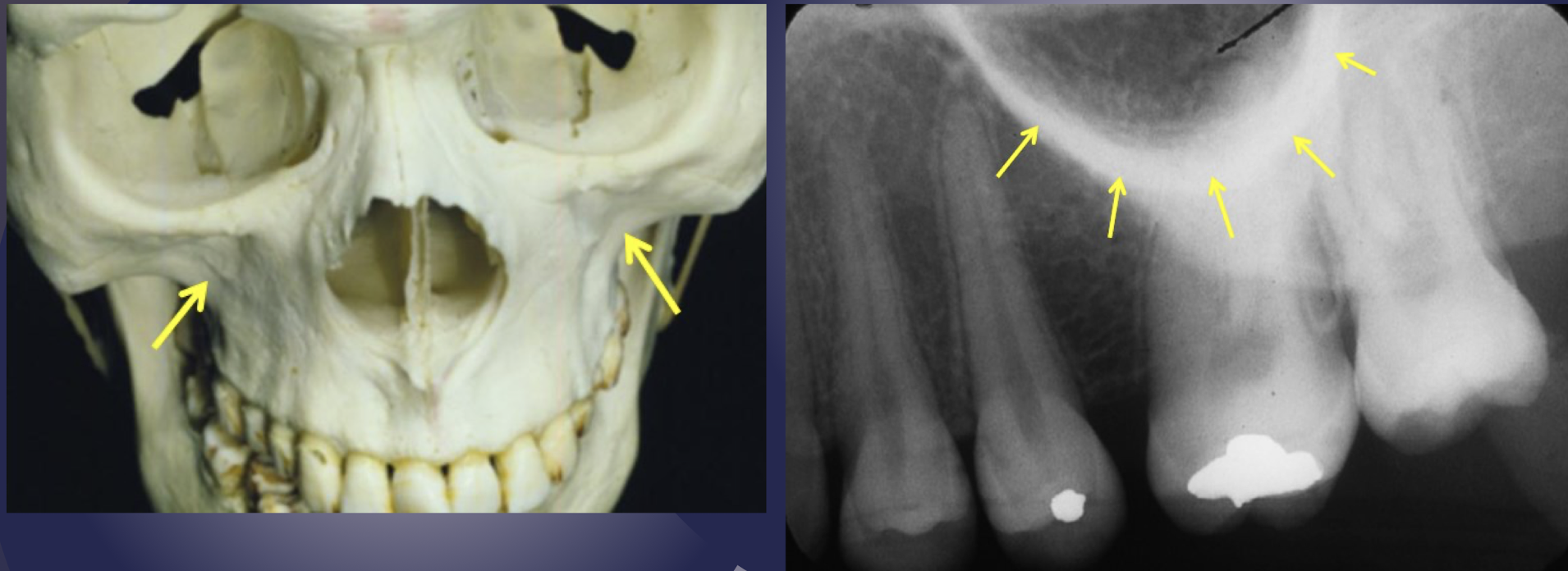
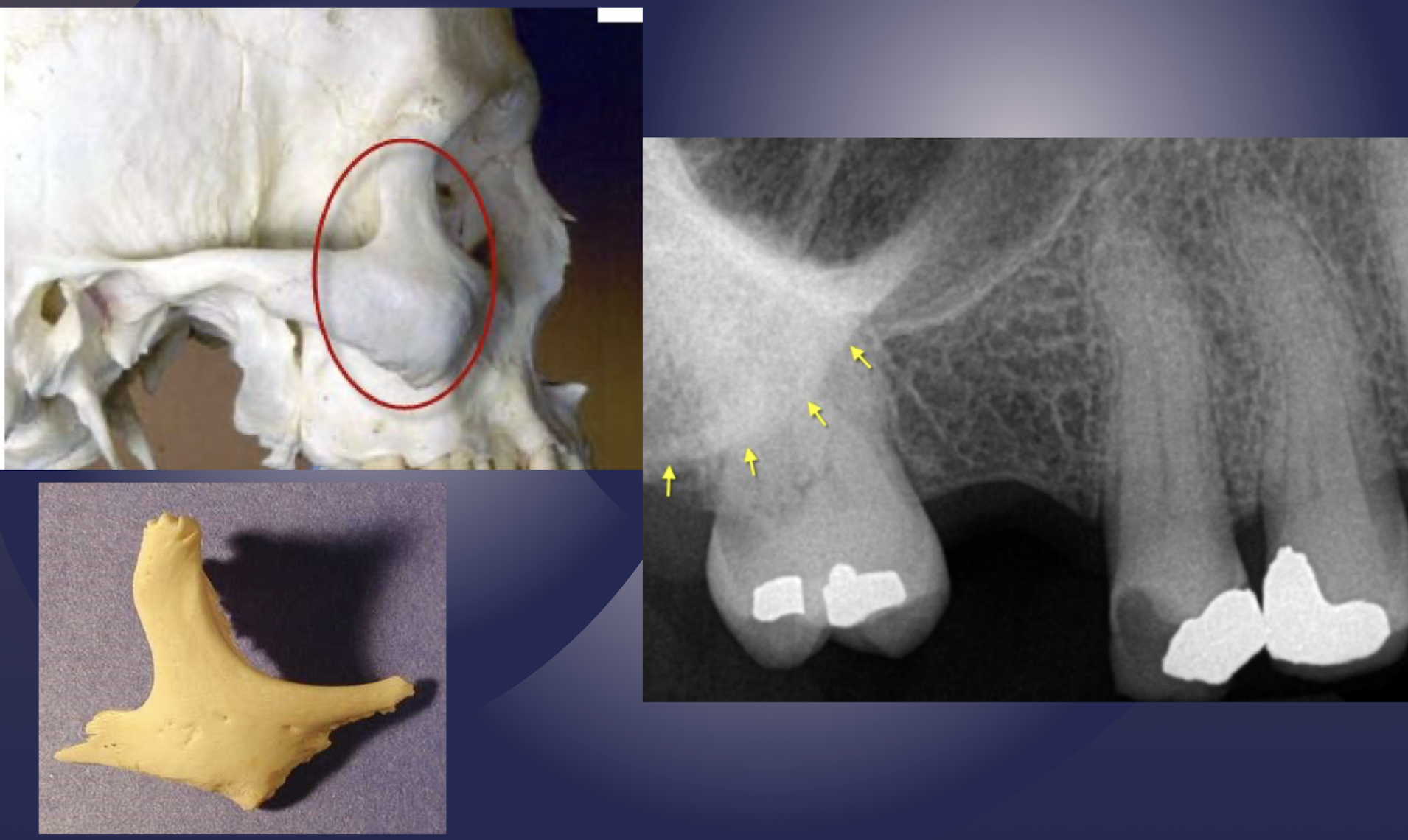
zygomatic process of maxilla
which part of maxilla?
Extension of lateral maxillary surface
Serves as articulation for zygomatic bone
Seen in the apical region of maxillary first and second molars
U or V shaped thick radiopaque structure
zygomatic process
zygomatic process
zygomatic bone
zygomatic bone
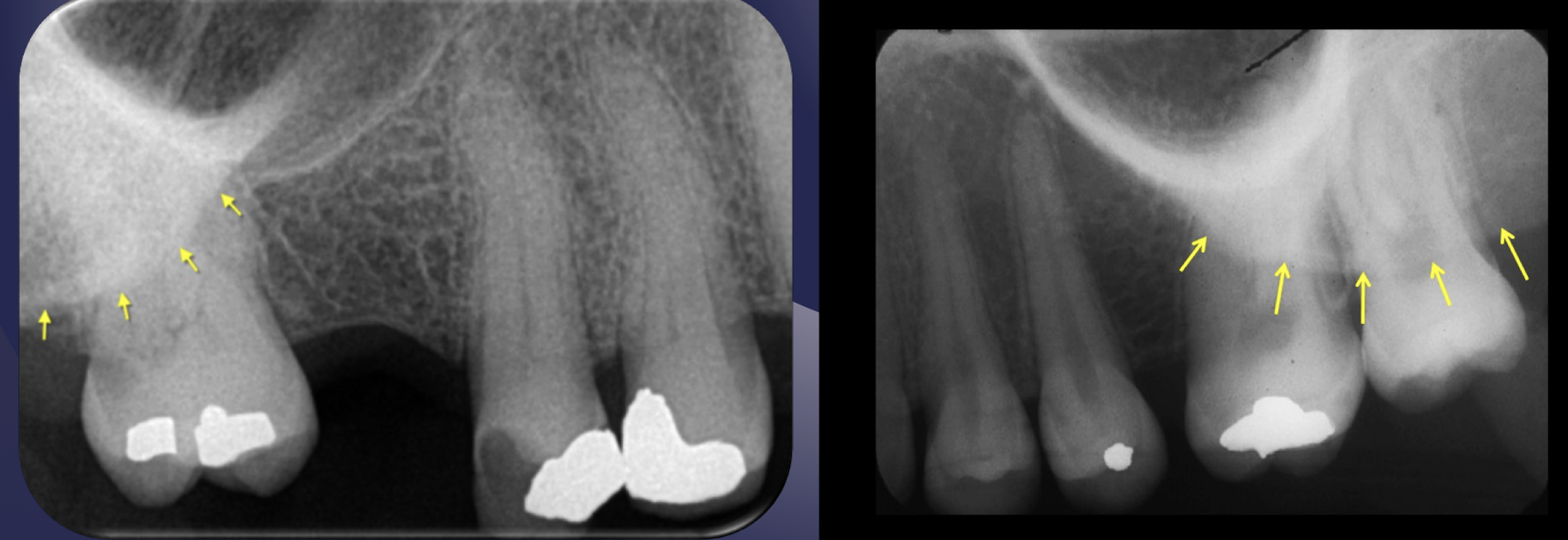
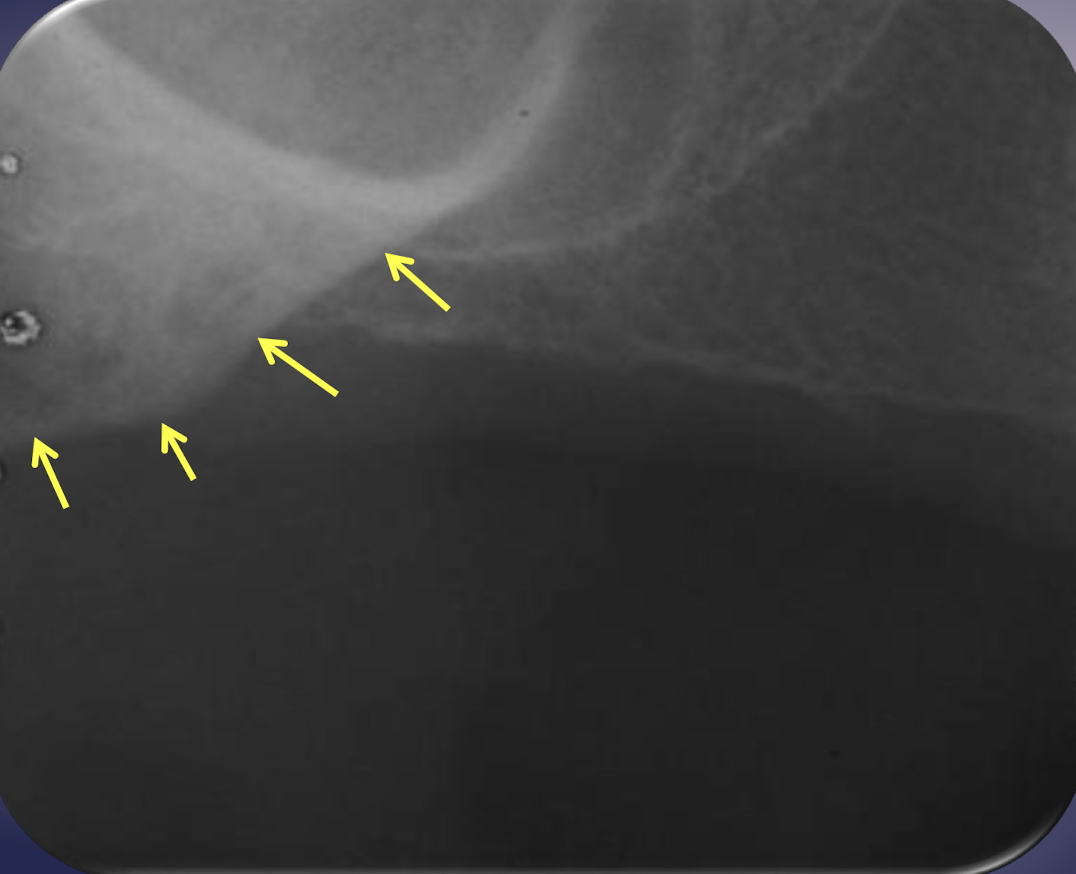
which part of the maxilla has homogenous radiopacity over apices of maxillary molars?
zygomatic bone
side, site, type of radiograph
side: right
site: zygomatic process
type of radiograph:
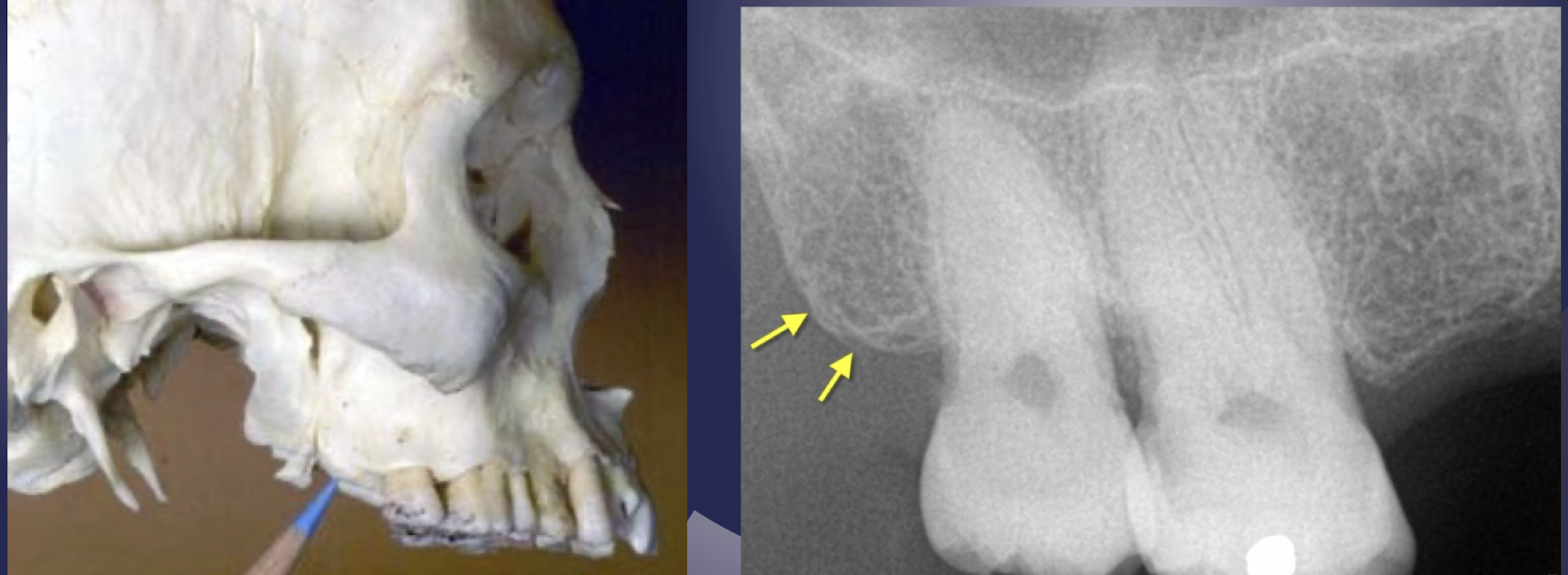
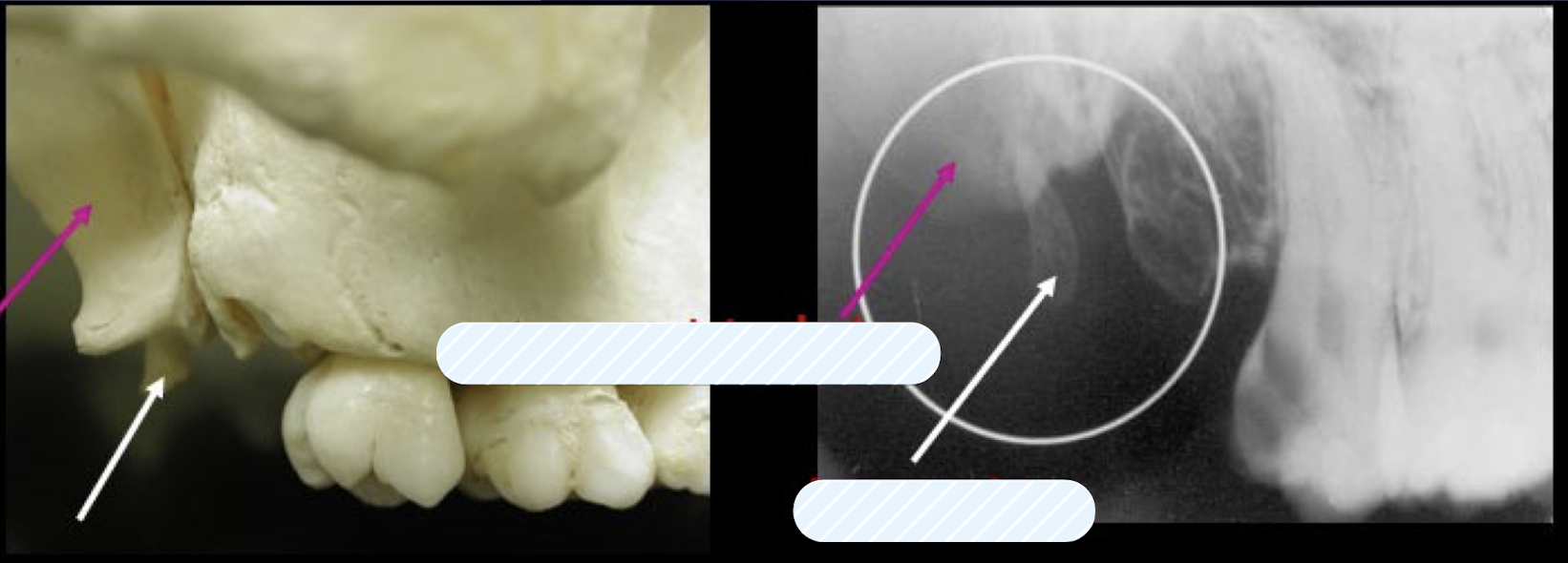
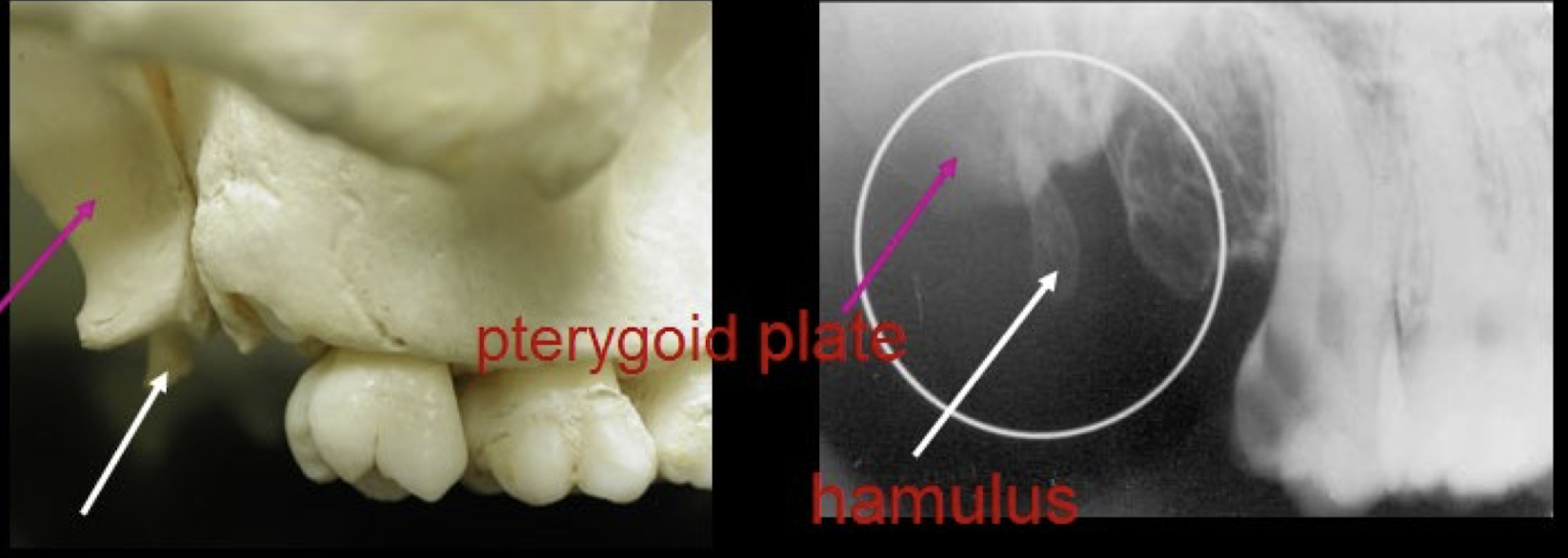
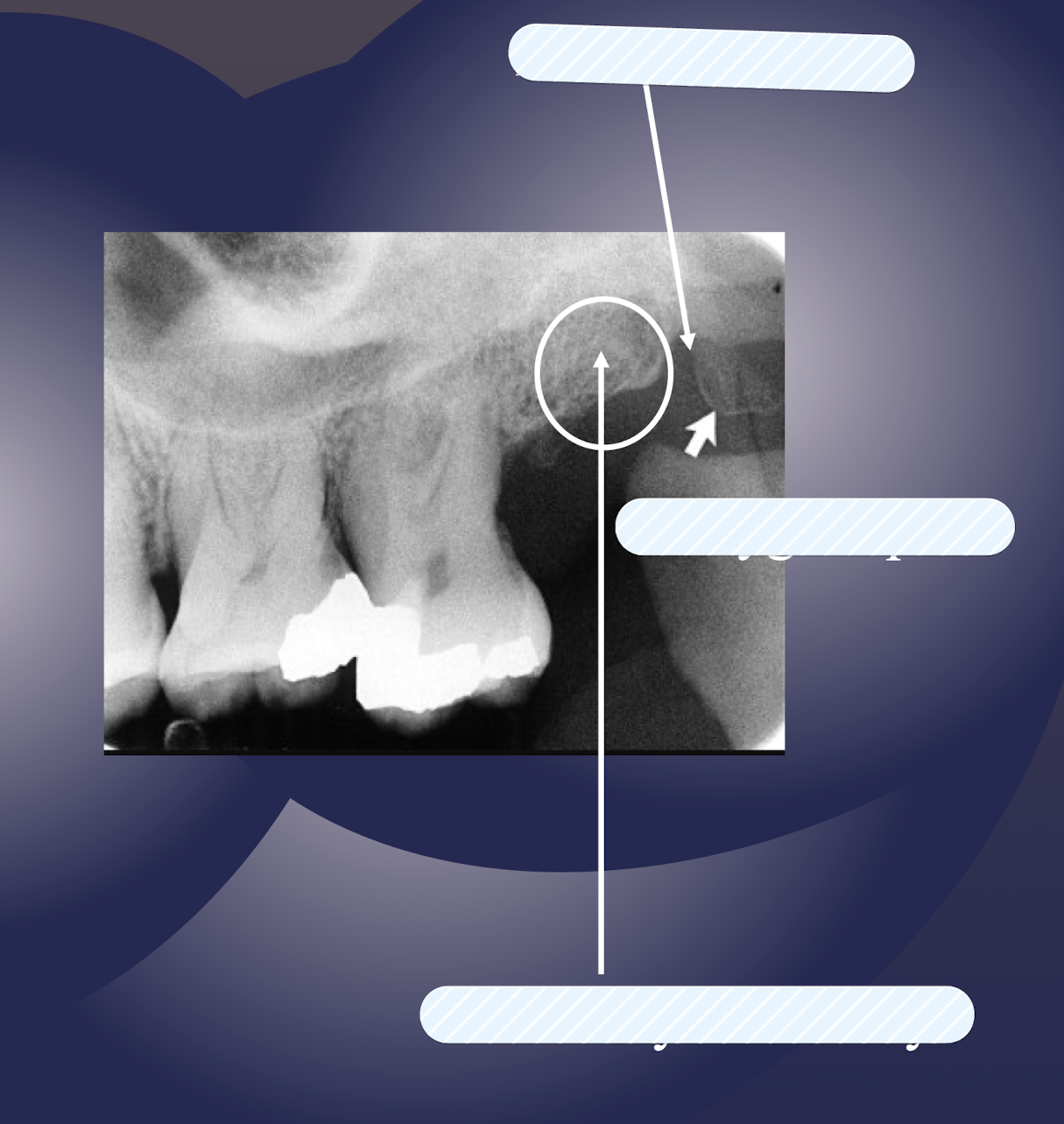
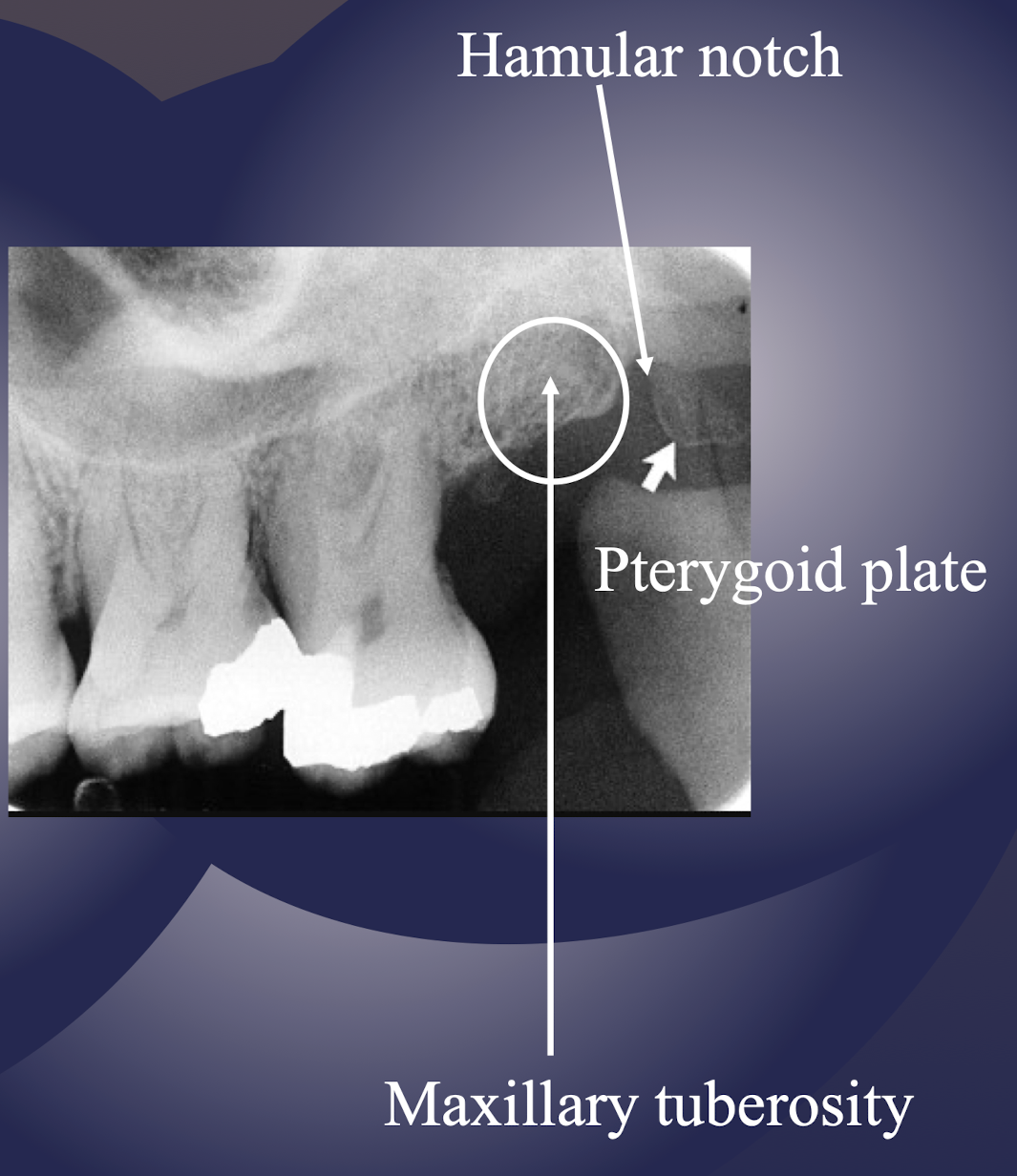
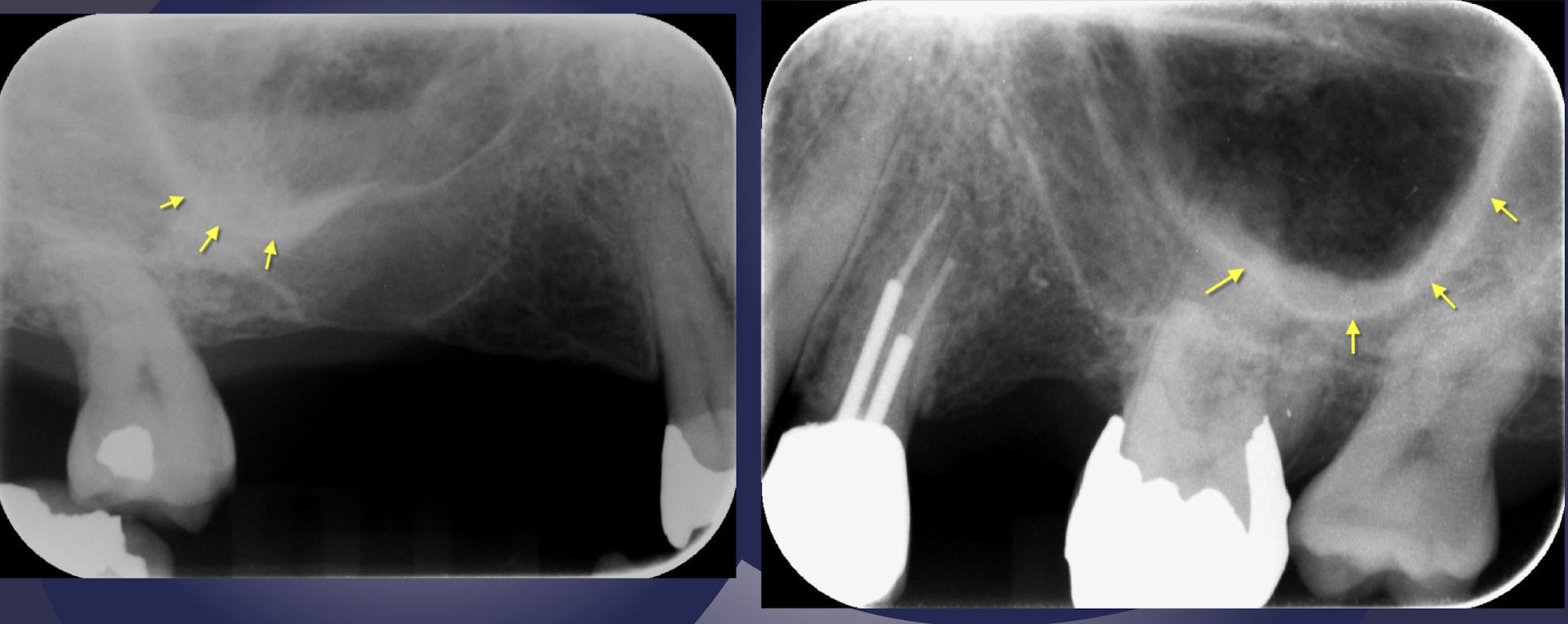
maxillary tuberosity
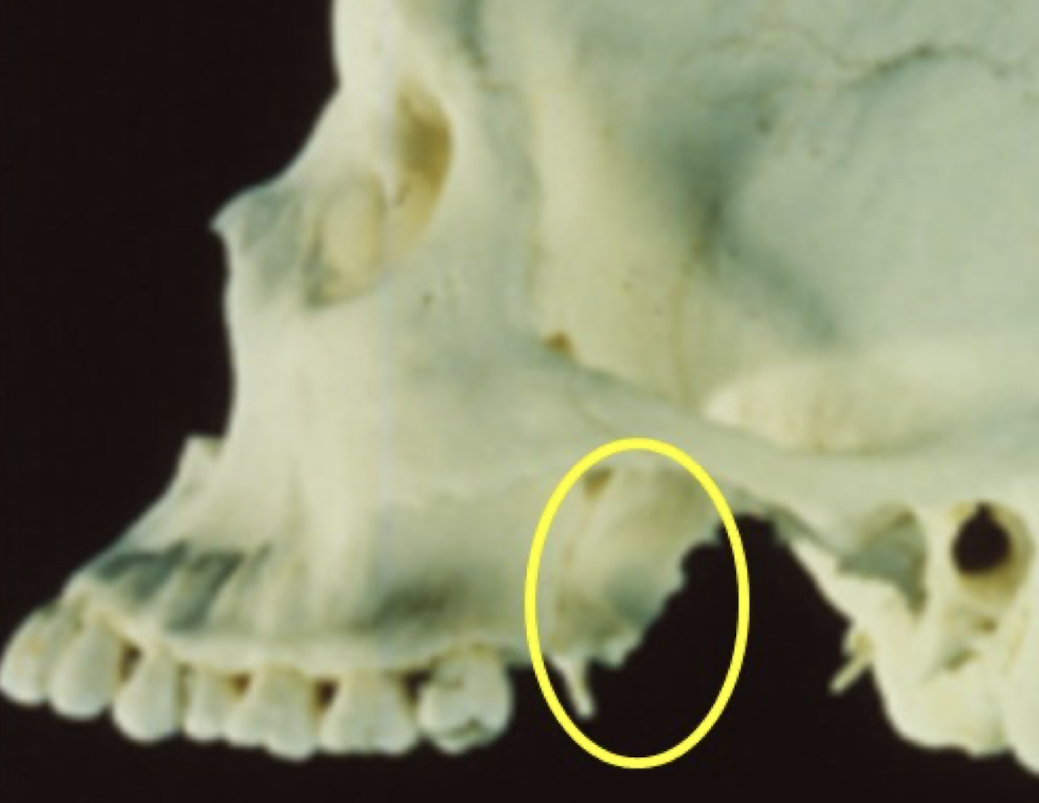
pterygoid plates
T or F: Lateral and medial pterygoid plates cast a single radiopaque shadow posterior to tuberosity
true
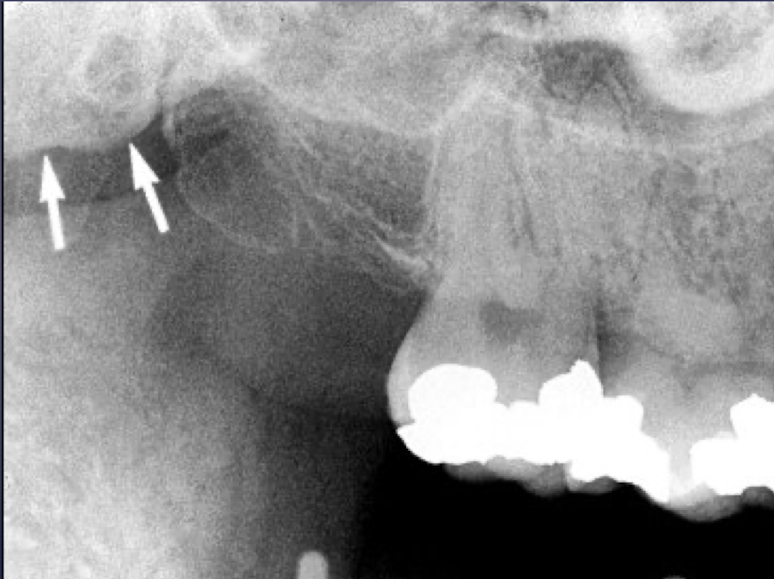
Lateral and medial pterygoid plates cast a single radiopaque shadow posterior to tuberosity