Neurobiology exam 1
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
which statement accurately describes the expression of genes in the nervous system?
most of the genes in the human genome are expressed in the CNS
compared with projection neurons, axons of local circuit neurons (interneurons)
are shorter
which glial cell type serves as a resident immune cell in the central nervous system?
microglia
The part of a synapse to which the neurotransmitters bind is called the
receptor
which statement best describes the function of a neuron with multiple, highly branched dendrites and one axon?
it integrated information from many neurons
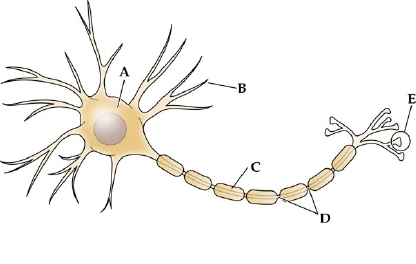
label a
cell body (SOMA)
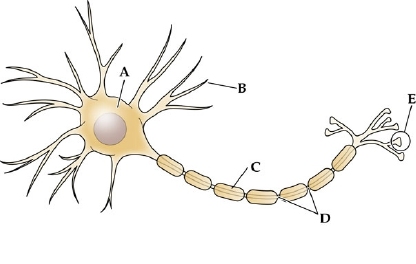
label b
dendrites
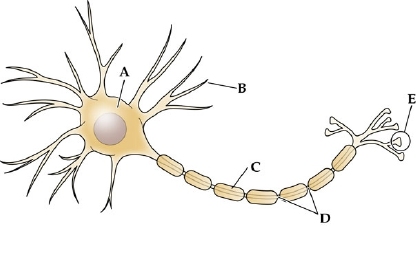
label c
myelin sheath
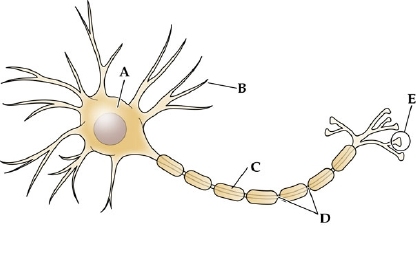
label d
node of ranvier
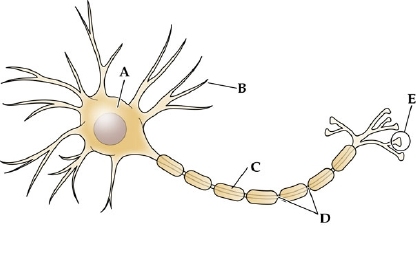
label e
axon terminal
a mouse model is created through Cre/lox technology in which a gene is knocked out of the CNS only. Which region would continue to express the gene?
spinal nerves
cognitive neuroscience is concerned with
perception, emotions, language and memory
the structural brain imaging technique that relies on atoms b ehaving like small magnets is called
MRI
which function is a characteristic primarily of neurons only, and not glia?
transmit action potentials
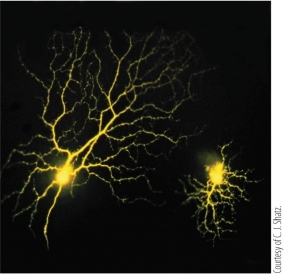
which method was used to visualize the retinal neurons shown?
intracellular injection of a fluorescent dye
which cellular layer of early embryo does entire nervous system come from?
(neuro) ectoderm
the amplitude of the action potential of a given neuron is
always the same
the resting potential of a cell is negative because
at rest there is an excess of K+ inside the cell, and the membrane is permeable chiefly to K+
the resting membrane potential typically ranges from _____ to _____.
-40mV; -90mV
which state of the plasma membrane does not occur during an action potential?
resting phase
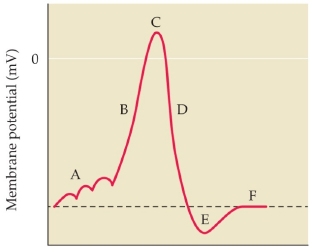
in the phase labeled D, _____ ions are moving ______ the cell.
potassium; out of
which stimulus is most likely to evoke an action potential?
large depolarizing current pulse
During which phase of an action potential foes membrane permeability to Na+ exceed membrane permeability to K+?
rising and overshoot phases
an action potential occurs if current injected into a neuron ____ the neuron to reach _____ potential
depolarizes; threshold
the voltage clamp method controls the _____ at any desired level
membrane potential
a neuron has received enough stimulation to fire an action potential; it also has been treated with TEA, a K+ channel blocker. Which outcome is possible?
the cell will initially depolarize, but repolarization will take much longer because it relied only on ion pumps
when current is injected into an axon, what happens to the current?
the current will decay exponentially with increasing distance from the injection site (if no action potential is present)
which statement about Na+ permeability during an action potential is most accurate?
it is responsible for rising phase of action potential
membrane potential depolarizes, Na+ channels open, Na+ current increases, ______.
K+ channels open
practically speaking, how would you determine that Na+ influx into a cell underlies the early current?
remove Na+ from the extracellular compartment and assess the early current under new conditions
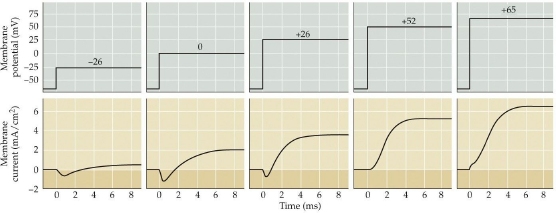
which of the following is the key event at a membrane potential of 52 mV
the early current reverses its polarity
the _____ most directly affects the rate of information processing within the central nervous system
propagation speed of action potentials
which of the following is not integral to the action potential waveform?
an initial decrease in the potassium current
Nodes of Ranvier represent
gaps in the myelin wrapping
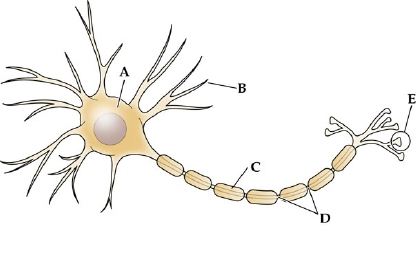
where will voltage-gated Na+ channels be most abundant?
structure D
an action potential travels in only one direction along the axon because of its ______ property
refractory
which statement correctly differentiates between the passive and active current in a myelinated axon?
the active current flows only the in nodes of Ranvier, unlike the passive current