AP GOV Unit 4: American Political Ideologies and Beliefs
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Demographics
statistical data relating to the population and particular groups within it (ex. age, race, gender)
Political Culture
-a set of attitudes and practices held by a people that shapes their political behavior. It includes moral judgments, political myths, beliefs, and ideas about what makes for a good society
-commonly shared attitudes, beliefs, and core values about how government should operate
Political Socialization
a lifelong process by which people form their ideas about politics and acquire political values. The family, educational system, peer groups, and the mass media all play a role.
Core Values
the fundamental beliefs of a person or organization
Individualism
a social theory favoring freedom of action for individuals over collective or state control
Equality of opportunity
-giving people an equal chance to succeed
-a widely shared American ideal that all people should have the freedom to use whatever talents and wealth they have to reach their fullest potential
Free enterprise
Economic system in which individuals and businesses are allowed to compete for profit with minimum government interference
Rule of Law
principle that the law applies to everyone, even those who govern
Globalization
-Actions or processes that involve the entire world and result in making something worldwide in scope
-the process by which businesses or other organizations develop international influence or start operating on an international scale
Scientific Polling
method of polling that provides a fairly precise reading of public opinion by using random sampling
Public Opinion Polls
interviews or surveys with samples of citizens that are used to estimate the feelings and beliefs of the entire population
Opinion Polls
an assessment of public opinion obtained by questioning a representative sample of the populaion
Benchmark Polls
-generally the first poll taken in a campaign. It is often taken before a candidate announces his or her bid for office, but sometimes it occurs immediately following the announcement
-initial poll on a candidate and issues on which campaign strategy is based and against which later polls are compared
Tracking Polls
continuous surveys that enable a campaign or news organization to chart a candidate's daily rise or fall in support
Entrance Polls
Public opinion surveys taken before voters cast their ballots
Exit Polls
Polls conducted as voters leave selected polling places on Election Day asking how they voted
Push Polls
polls that ask for reactions to hypothetical, often false, information in order to manipulate public opinion
Polling Universe
the set of people that a particular poll is meant to represent
Random Sample
method of selecting from a population in which each person has an equal probability of being selected
Representative Sample
A sample that reflects the characteristics of the target population
Mass Survey
a way to measure public opinion by interviewing a large sample of the population
Focus Group
A small group of individuals who are led in discussion by a professional consultant in order to gather opinions on and responses to candidates and issues
Sampling Error
an error that occurs when a sample somehow does not represent the target population
Reliability of data
-a state that exists when data is sufficiently complete and error free to be convincing for its purpose and context
-the extent to which an experiment, test, or measuring procedure yields the same results on repeated trials
Veracity of data
uncertain or imprecise data
Political Ideologies
sets of political values held by individuals regarding the basic goals of government and politics
-Capitalism, communism, socialism, and Marxism are ideologies
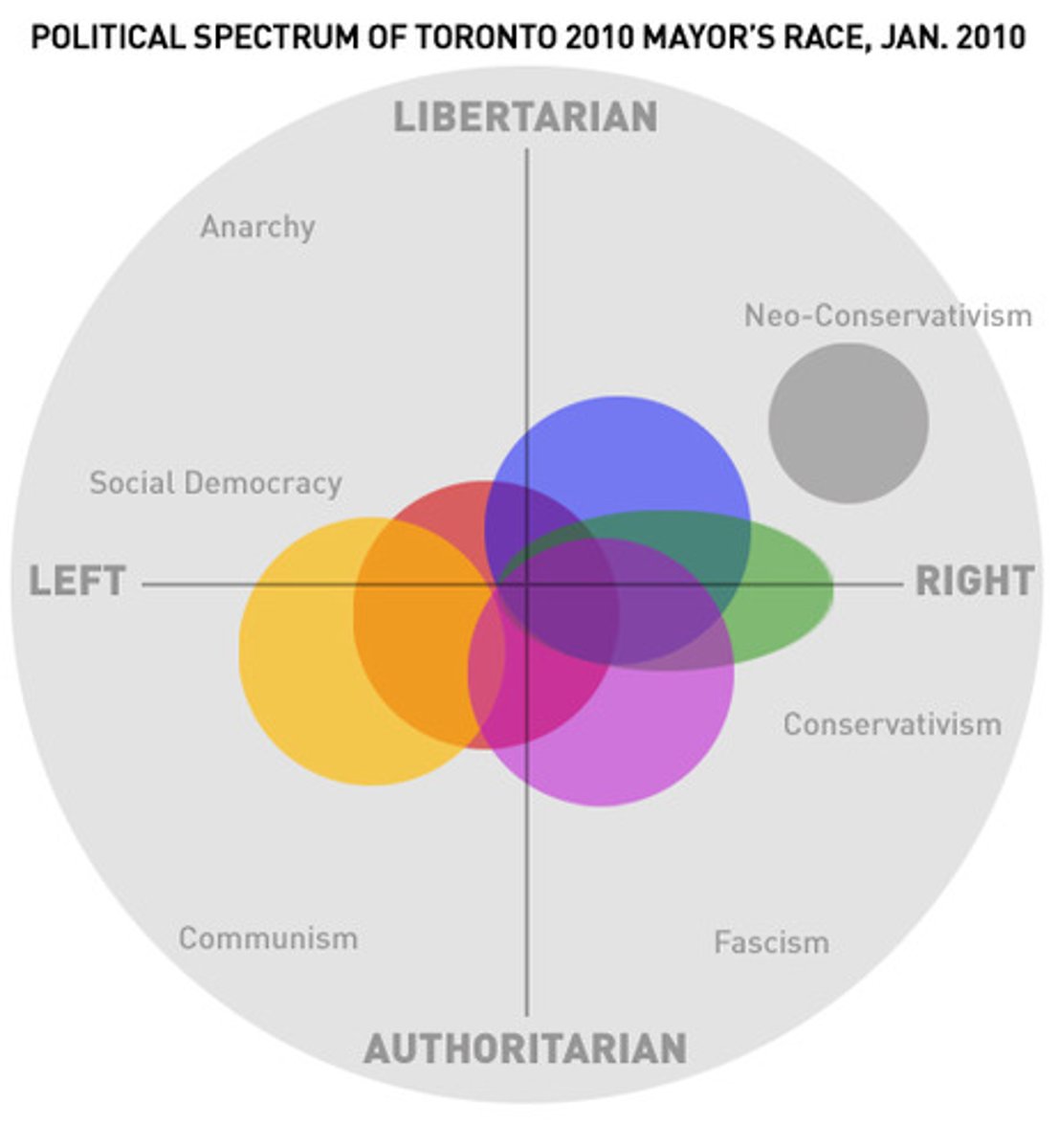
Political Spectrum
The term political spectrum is a concept that models political beliefs and ideologies as a continuum, with left-wing liberalism and right-wing conservatism anchoring the two poles. A radical extreme of the far-left would be anarchism, with fascism its counterpart on the far-right and most people falling somewhere closer to the center on the political spectrum.
Liberal Ideology
Liberalism, political doctrine that takes protecting and enhancing the freedom of the individual to be the central problem of politics. Liberals typically believe that government is necessary to protect individuals from being harmed by others, but they also recognize that government itself can pose a threat to liberty
Conservative Ideologies
any political philosophy that favors tradition (in the sense of various religious, cultural, or nationally-defined beliefs and customs) in the face of external forces for change, and is critical of proposals for radical social change.
Moderate
Voters who describe themselves as centrist often mean that they are moderate in their political views, advocating neither extreme left-wing politics nor right-wing politics
Political Polarization
Political polarization refers to the cases in which an individual's stance on a given issue, policy, or person is more likely to be strictly defined by their identification with a particular political party (e.g., Democrat or Republican) or ideology (e.g., liberal or conservative)
Democratic Party
Democrats are sometimes referred to as "the Party of the People," attracting immigrants, blue-collar workers, women, and minorities. Democrats tend to take a more liberal stand on important issues. They believe that the federal government should take a more active role in people's lives, particularly those who are in need. One of the strongest beliefs of the Democratic Party is that of equality on all fronts. Democrats believe in equal opportunity despite race, religion, gender, or sexual orientation. They also believe in equal educational opportunity for all.
Republican Party
In general, Republicans tend to take a more conservative stand on issues. They believe that the federal government should not play a big role in people's lives. Most Republicans favor lower taxes and less government spending on social programs. They believe in less government intervention in business and the economy.
Regulation of the marketplace
A regulated market (RM) or controlled market is an idealized system where the government controls the forces of supply and demand, such as who is allowed to enter the market and/or what prices may be charged.
Libertarian Ideologies
-Libertarians seek to maximize political freedom and autonomy, emphasizing freedom of choice, voluntary association, and individual judgment.
-"The Party of Principle"
-We seek to substantially reduce the size and intrusiveness of government and cut and eliminate taxes at every opportunity.
-We believe that peaceful, honest people should be able to offer their goods and services to willing consumers without inappropriate interference from government.
-We believe that peaceful, honest people should decide for themselves how to live their lives, without fear of criminal or civil penalties.
-We believe that government's only responsibility, if any, should be protecting people from force and fraud.
Property Rights
The rights of an individual to own, use, rent, invest in, buy, and sell property.
Voluntary Trade
trade in which both partners freely agree to and benefit from the exchange of goods/services
Keynesian economic policies
-increased government expenditures and lower taxes to stimulate demand
-This idea is called "demand-side policy". If people are working, the economy is good. If people are not working, the economy is bad.
-Keynes said when the economy is bad, people want to save their money. That is, they do not spend their money on, or invest in, things they want. As a result, there is less economic activity. Therefore, the government should spend more money when people do not have work. The government can borrow money and give people jobs (work). Then people can spend money again and buy things. This helps other people find work.
Supply-side economic policies
a theory arguing that economic growth can be most effectively created by lowering taxes and decreasing regulation.
Monetary Policy
-Government policy that attempts to manage the economy by controlling the money supply and interest rates.
-Monetary policy consists of the actions of a central bank, currency board or other regulatory committee that determine the size and rate of growth of the money supply, which in turn affects interest rates. Monetary policy is maintained through actions such as modifying the interest rate, buying or selling government bonds, and changing the amount of money banks are required to keep in the vault (bank reserves).
-The Federal Reserve is in charge of monetary policy in the United States.
Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy refers to the use of government spending and tax policies to influence macroeconomic conditions, including controlling demand, employment, inflation and economic growth.
Federal Reserve Board
an independent agency of the federal government established in 1913 to regulate the nation's banking and financial industry
Social equality
Social equality is a state of affairs in which all people within a specific society or isolated group have the same status in certain respects, including civil rights, freedom of speech, property rights and equal access to certain social goods and services.
Economic equality
-the idea that each individual should receive the same amount of material goods, regardless of his or her contribution to society
-A situation in which there are only small differences in wealth among citizens.
a level playing field where everyone has the same access to the same wealth