BU288 Final
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
What is conflict?
A process that occurs when one person, group or organizational subunit frustrates the goal attainment of another. Relevant to motivation, decision making, negotiation.
What are the 5 causes and predictors of conflict?
Group identification/Intergroup Bias
Interdependence (sometimes, can depend on presence of other conditions)
Power, Status, Culture
Ambiguity
Scarce resources (resulting in power jockeying)
What are the 3 types of conflict?
Relationship
Task
Process
What are the responses to conflict within groups (there are 6)?
desire to win
concealing information
stereotypes and self-image exacerbated
increased group cohesiveness
reduced between group interaction
aggressive people may emerge as leaders
What is constructive conflict and how can it occur?
Conflict that promotes good decisions, and organizational change; benefits outweigh the costs.
It occurs with elevated task conflict low/minor levels of relationship conflict and process conflict has to have open-minded conversations of differences.
What is destructive conflict?
Comes from frequent use of assertive style damaging function and performance
How can managers use conflict to their advantage?
Managers can use conflict stimulation to foster change: increasing conflict, used when conflict is suppressed and people are withdrawn (avoidant style), peaceful relationships take precedence.
What are the 5 conflict management styles on the assertive/cooperative dimensions?
Avoiding → “hiding head in the sand,” doesn’t change the situation, works in trivial issues where information is lacking/people need to cool off
Accommodating → doesn’t work well if it is viewed as a sign of weakness, works if you are wrong, issues is more important to other
Competing → holding power, sure of your fact, truly win-lose situation and no future interactions
Compromise → can be trigger for procedural conflict, doesn’t create the most creative response, not useful with power asymmetry, good if else fails
Collaborating → not intense conflict with information on both sides, enhances productivity/achievement
What is stress, stressors and stress reactions?
Stress: psychological reaction to demands inherent in a stressor potentially making person feel tense
Stressors: environment condition or events that can potentially induce stress.
Stress Reactions: behavioural, psychological and physiological reactions
What are the 3 main stress reactions?
Physiological changes (blood pressure, muscle tension, etc.)
Psychological changes
affective (unstable mood, easily irritated)
cognitive (lower concentration, confidence)
Behavioural (eating, violence)
avoiding (task related or relationship related)
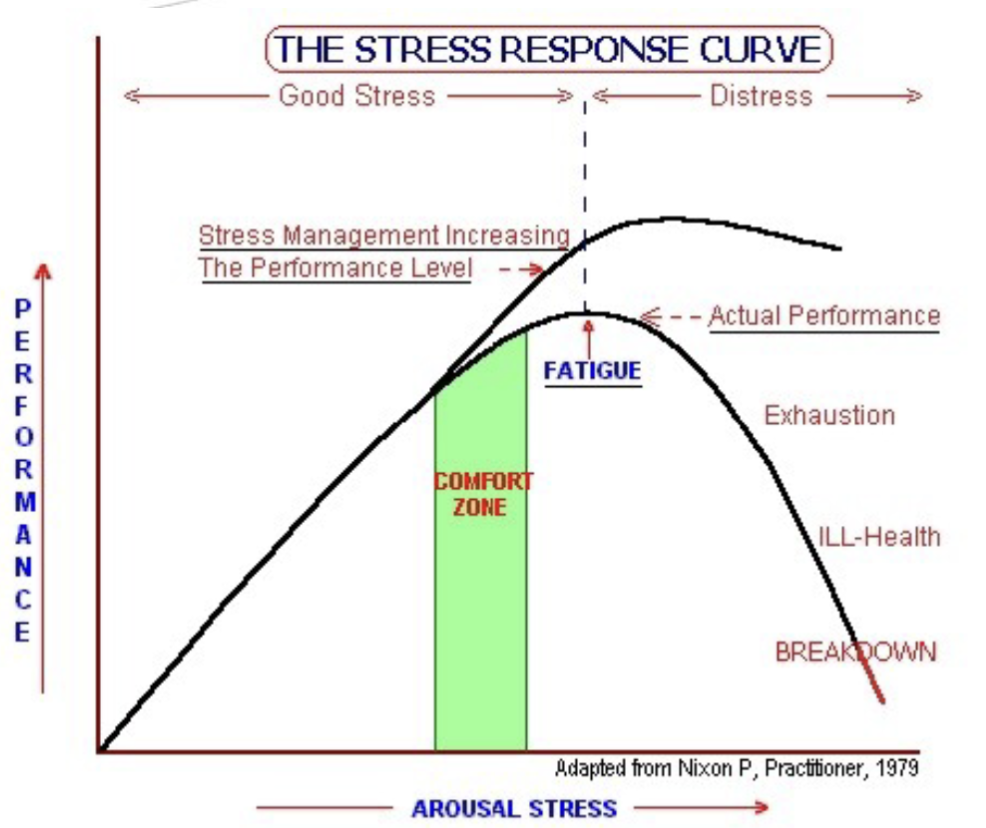
How does the stress response curve work?
Basically stress is good up to a point, where it starts to be counter productive. Your stress threshold can increase over time.
What are the 3 personality traits that influence stress reaction?
Locus of control → internal has a better reaction
Type A → don’t handle as well
Negative affectivity → high don’t handle as well
What are the 3 types of organizational stressors?
Executive and Managerial → Role Overload and heavy Responsibility
Operative Level → Job design, poor physical conditions
Boundary Role (interacting with public), burnout and emotional labour
What is emotional labour and the 2 reactions to it?
“Surface with a smile” associated to burnout.
Surface acting
Deep acting
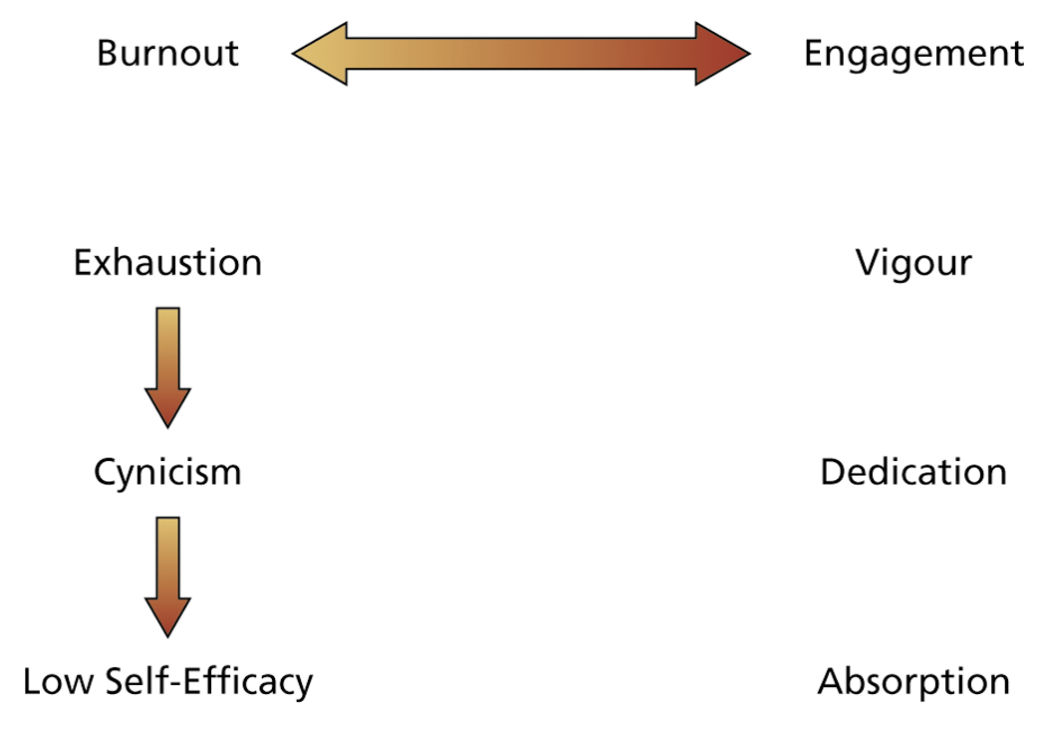
How does the burnout-engagement continuum work?
Related to job demands resources model:
So basically engagement and burnout are connected in the sense that burnout is caused by exhaustion, these feelings of exhaustion lead to cynicism and low self-efficacy. Therefore people who have lower self esteem are more prone to burnout.
What is the job-demands resources model and how does it work?
Determines how employees tend towards engagement vs. burnout.
Basically describes that as long as job demands aren’t extreme, job resources can help to buffer negative effects of demands but demands are more negative than positive effects of resources.
What can organizations do to manage stress (there are 6)?
Job resources, family friendly practices, stress management programs, work-life balance, fitness and wellness programs, changing job design.
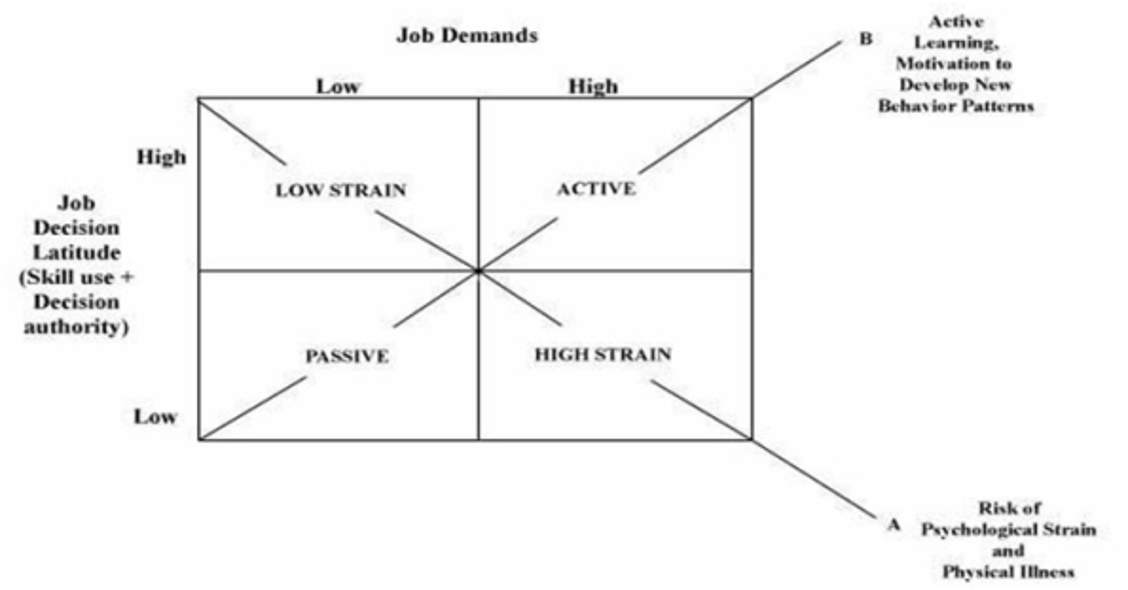
How does the control-demand support model work?
Explains how job characteristics influence employees’ psychological well-being and shows how job demands can cause stress for employees, but depending on your level of job decision latitude, you can manage these stressors through utilizing job skills to gain autonomy and control over their work.
What is leadership?
when individuals exert influence on the goal achievement of others in an organizational context.
What are the 3 broad leadership types?
1. Strategic leadership → ability to act efficiently to initiate changes that will create a viable future for organization
2. Emergent leadership →informal leadership, rely on being well liked or highly skilled
3. Shared leadership → emergent, leadership roles and influence are distributed among team members
What is the difference between Management vs Leadership?
Leaders → create, originate, develop, inspire trust, set a direction, challenge the status quo
Managers → implement, copy, maintain, control, accept the status quo
What are the 4 Different Leadership Theories?
1. Trait theories: characteristics of the person, WHO becomes a leader
2. Situational/contingency theories: situations affect leadership, WHEN leadership is effective
3. Behavioural theories: ways the leader acts, HOW leaders can lead
4. Exchange based theories, transformational and transactional leadership
What is Leadership Trait Theory?
Leadership depends on personal qualities or traits of the leader, personality, social, physical, intellectual traits. Assumes you can’t learn to be leader
What are the 5 traits related to Leadership Trait Theory?
$MONIE$
OCEAN → all especially agreeableness, extraversion, openness to experience
Intelligence → somewhat related
Emotional intelligence → some effective leaders are high
Narcissism → associated to leader behaviours and effectiveness in extreme variations
Motivation to lead → desire to attain leadership roles linked to leadership emergence and effectiveness
What are the 5 problems with Leadership Trait Theory?
better at predicting leader emergence than leader effectiveness
NO universal traits found that predict leadership in all situations
leadership categorization theory which leads to: bias and discrimination of promoting people, historical gender biases related to masculine traits
What is Leadership Categorization Theory?
people are more likely to view somebody as a leader when they posses prototypical characteristics of leadership
What are situational theories of leadership?
Relationship between leadership orientation and group effectiveness is contingent on the extent to which situation is favourable for exerting influence.
What are the 2 Situational Leadership Theories?
1. Fiedler’s Contingency theory (LPC and situation preferability)
2. House’s Path-goal theory
What is Fielder’s Contingency Theory?
Contingency theory: association between leadership orientation and effectiveness depends on what the situation is
Leadership orientation is measured by having leaders describe their least-preferred co-worker (LPC).
In Fielder’s Contingency Theory, what is situational favourableness and what focus is better in each type?
situational favourableness is the contingency, tells us which orientation is more effective in what situation
favourable: good leader-member relations, structured task and strong position power
weak: opposite
Task focus most effective (LOW LPC)→ when situational favourableness is very high or very low
Relationship focus most effective (HIGH LPC) → when situational favourableness is medium
What is House’s Path-Goal Theory?
Concerned with the situations under which each of the 4 various leader behaviours are effective, leader’s job to assist followers in attaining their goals.
What are the 4 kinds of leader behaviour in House’s Path-Goal Theory?
1. Directive → informs subordinates of expectations, guidance and shows how to do tasks (initiating structure)
2. Achievement → set challenging goals, expects performance at highest level, continuously seeks improvement in performance
3. Participative → consults, takes suggestions into consideration
4. Supportive → friendly and approachable, show concern for status and well being
When do you use each behaviour in House’s Path-Goal Theory?
Directive: when individuals have difficulty doing task or the task is ambiguous
Achievement: when individuals like challenges and are highly motivated
Participative: when they need to buy into decisions or have a high need for empowerment, not useful when task is clear
Supportive: when individuals are under stress or otherwise show that they need to be supported
What are the different situational features that determine when to use each behaviour in path-goal theory?
Employee characteristics and environmental factors to influence job satisfaction, acceptance of leader and effort (theory predicts these factors rather than performance)
What are Behavioural Theories, and the 2 theories?
What different behaviours to leaders engage in and what are the outcomes? Relates to leadership styles
Initiating/consideration structure
Punishment and Reward
What is Leadership Consideration and initiating Structure theory and their influences?
Either high, low or average on one or both dimensions.
Consideration → approachability and showing personal concern/respect, related to follower satisfaction, motivation and effectiveness
Initiating → leader concentrates on group goal attainment, clearly defined the roles, standardized procedures, etc, related to job and group performance
What is Leader rewards and Punishment behaviour theory and it’s influences?
Both must be contingent and related to behaviour
Leader reward → compliments, tangible benefits, special treatment. Related to employee perceptions, attitudes and behaviour
Punishment → using punishments, related to preventing unfavourable outcomes
What are the 2 types of Leader Behaviours and when do they work well?
1. Participative/democratic leaders → involve employees in making decisions, works well in increasing motivation
2. Autocratic/directive leaders → provide directions, act as sole expert, do not seek input, do not encourage suggestions, works well in urgent situations
What is Participative Leadership?
Involve employees in making decisions, no participation is boss-centred leadership. Minimal includes employees decision before making a decision, maximal, allows employees to make their own decisions.
What are the Pros and Cons of Participative Leadership (3 of each)?
Pros: motivation (from job enrichment), quality (decisions), acceptance of decisions
Cons: time and energy, loss of power, lack of receptivity (some employees might not care, feeling they’re doing work of management)
What is the Situational Model of Participation of Participative Leadership?
specifies when leaders should use participation and to what extent
A (autocratic), C (consultation), G (group), I (individual), II (group) describe the situations
either: AI, AII, CI, CII, GII
Which type to use depends on quality requirement, commitment requirement and problem structure.
What are the 3 Exchange Relationship-Based Theories of Leadership?
1. Leader-Member Exchange Theory
2. Transactional
3. Transformational
What is Leader-Member Exchange Theory?
Leaders develop relationships with their employees at different qualities. Effective leadership processes result when leaders and employees have high-quality relationships.
Based on social exchange theory, people who are treated favourable feel a sense of obligation to reciprocate and returning that treatment
Higher quality relationships reciprocate extra effort, commitment and performance
What is Transactional Leadership and its 3 types?
Based on a straightforward exchange relationship between leader and followers. Leaders set goals, provide support, are participative.
3 Forms of Transactional Leadership:
Contingent reward (technically all transactional leadership has this aspect)
Management by exception (can be active or passive)
Laissez-faire (non-leadership or absentee)
What is Management by exception?
leader monitors follower behaviour, anticipates problems, and takes corrective actions before the behaviour creates serious problems, done by:
Noticing an exceptional situation
Identifying the root cause
Taking corrective action
What is a Laissez-Faire Leader?
provide limited instructions, limited contact with members, no feedback, “let people do their job.” Only works if you can trust team.
What is Transformational Leadership and its 4-is?
Leader provides followers with a new vision creating true commitment, broadening goals/increasing followers’ confidence
1. Idealized influence (charisma) → strong, confident, powerful role model
2. Inspirational motivation → articulate appealing vision
3. Intellectual stimulation → encouraging critical thought and creativity
4. Individualized consideration → know and has genuine concern for followers
What is Charisma?
originally viewed as divinely inspired or possessing a gift from God, capable of having profound and extraordinary effects on followers
What are the pros and cons of Charismatic leaders?
Pros: strong loyalty, enthusiastic dedication, emotional identification
Cons: only seeking self-glorifying projects, ignoring info that doesn’t fit vision, inflexible, blinded by excessive confidence, inhibit criticism by followers
What are the 4 Positive Leadership Theories?
EASE
1. Empowering leadership
2. Ethical leadership
3. Authentic leadership
4. Servant leadership (genuine concern to serve others and a motivation to lead)
What are the difference in Leadership in Men vs Women?
Women: democratic leadership style
Encourage participation
Share power and information
attempt to enhance followers’ self-worth
prefer to lead through inclusion
Men: directive command-and-control style
rely on formal authority
What is the Difference Between Leadership vs Power?
Leadership: focuses on goal achievement, requires goal compatibility with followers
Power: influence those who are dependent, used as a means for achieving goals, requires follower dependency
What is communication?
Interpersonal communication is a process in which information is exchanged between sender and receiver
How does the communication process work?
The Communication Process:
The sender → thinks, encodes information, transmits message
The receiver → has to perceive that there is a message to receive, decode message, understand
Feedback → both ways, sender and receiver give to show message is understood and taken
What is effective communication?
Right people receive right information in a timely manner
What are the 3 types of communication through the chain of command?
Downward communication
Upward communication
Horizontal communication
What are the 3 problems in formal organizational communication?
Informal communication between members
Filtering (water down message from fear of perception, increases with more links in the chain)
Slowness (decrease with cross-functional teams and employee empowerment)
What factors do manager-employee communication effectiveness rely on (there’s 6)?
Manager leadership style (most important)
How employees allocate time
How long it takes to learn a job
Importance to pay
Authority of an employee
Skills, abilities, performance and obstacles to performance
What is the mum effect?
Minimizing Unpleasant Messaging
form of filtering, avoiding negative messages, especially when responsible
How do conflicting role demands contribute to withholding information?
Needing to balance task and relationship, possibly resulting from unclear priorities?
What kind of employees/organizational features encourage more communication?
Employees: more satisfied, stronger job identification
Organization: psychological safety
People who speak up experience less stress
How does the communication “grapevine” work?
Informal communication network, cuts across formal lines: can actually contribute to effective communication
What are the pros of informal communication?
keep employees informed about important matters
can substitute formal communication
informal recruiting source
test of employee reactions to proposed changes without formal commitments
What are the cons of informal communication?
can be a pipeline for rumours, spread fastest when: information is ambiguous, content is important to those involved, recipient is anxious, rumour seems credible
orgs. should avoid being mum about giving bad news
What are the verbal languages of work?
Jargon (can be a barrier to those on the outside)
Humour (relationship needs to be established first for it to be good)
How does body language serve as non-verbal communication?
Sender’s bodily motions, facial expressions or physical location in relation to receiver
→ reveals: liking, interest, status, power
→ liking shown by: closeness of physical position, physical touch, eye contact, leaning forward, torso directed to receiver
How do props, artifacts and costumes act as non-verbal communication?
Use of various objects, office decor, clothing, etc, can reveal the same information as body language.
What are the differences between male and female communication?
Women focus on making connections and put themselves in a “one-down” position.
Men are concerned with establishing status and put themselves in a “one-up” position.
How does language influence cross-cultural communication?
communication better between those who have similar cultural values
same language ≠ perfect communication but can help
How do context cues influence cross-cultural communication?
Context is the cultural information that surrounds a communication episode. High context means more information taken from context rather than words.
People from high context cultures want to know details
Getting to the point quickly is not favourable in high context cultures
Age, seniority and status give credibility to messages in high context cultures
People from low-context cultures favour very detailed business contracts
High context cultures place less emphasis on length in a contract and more on context in which deal was made
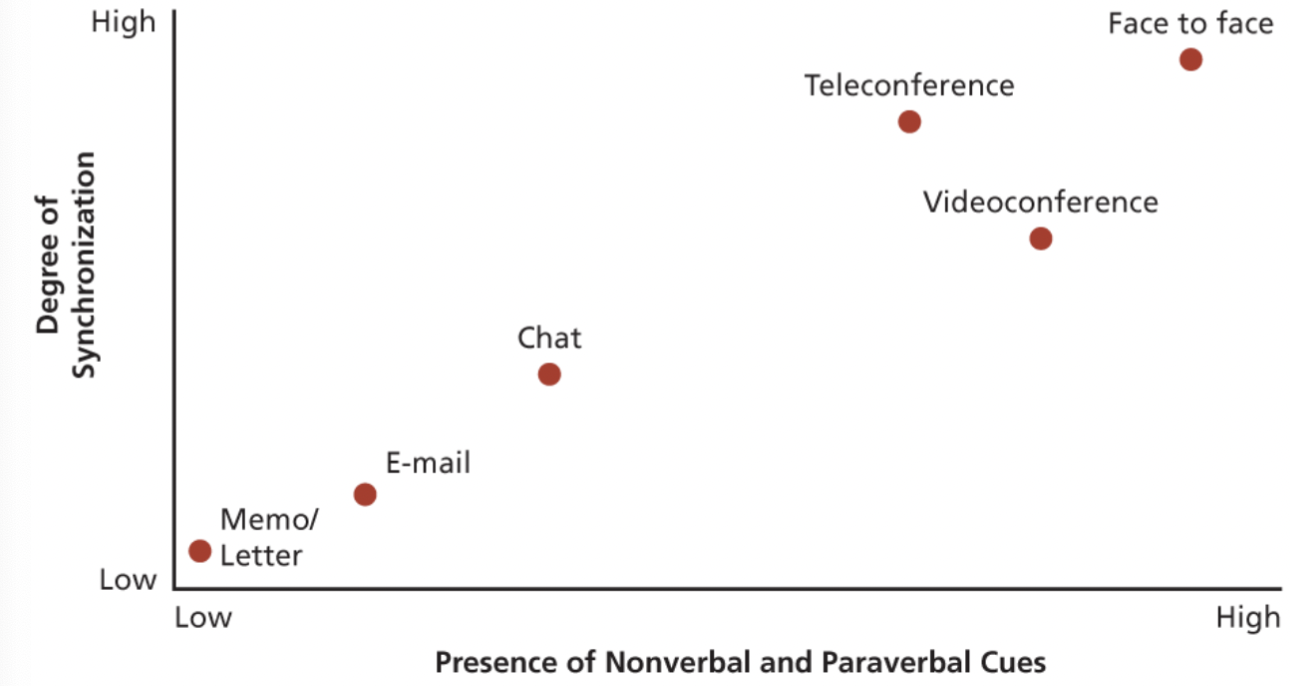
What are the impacts of using different communication mediums?
Information richness: potential information-carrying capacity of a communication medium - degree that information is synchronous (two-way, in real time) and that both parties can receive non-verbal cues.
e.x. face-to-face is highly rich because channels are synchronous and all forms of cues are occurring, feedback is ongoing and immediate
What are the 6 basic principles of improving communication?
Take the time
Be accepting of the other person
Do not confuse the person with the problem
Say what you feel - words, thoughts feelings, and actions contain the same message
Listen actively - watching body language, empathy, questions, etc.
Timely and specific feedback
How can you improve communication across cultures (3 ways)?
Assume differences until you know otherwise
Recognize differences within cultures
Watch your and their language
What are 5 ways organizations can improve communication?
Employer branding - clear and consistent image of positive features of organization as an employer
Provision of explanations
360-degree feedback (when employee appraisals are based on feedback from coworkers, higher ups, customers, etc.)
Employee surveys and survey feedback
Suggestion systems
What is organizational culture?
shared beliefs, values and assumptions that exist which determine the norms (viewed as an iceberg.) Culture determines norms which can determine behaviour. Organizations can have many subcultures.
What are the 4 characteristics of organizational culture?
represents a “way of life” for members
fairly stable overtime, can persist despite turnover
content of culture involves matters internal (e.x. innovation or risk taking) to organization or external (e.x. putting the customer first)
strong impact on performance and satisfaction
What are the 4 types of organizational culture?
The 2 dimensions are external vs. internal focus and flexible vs. stable.
Consistency → internal and stable, e.x. governments
Mission → stable and external, e.x. charities
Adaptability → meeting needs of external environment and responding to change, e.x. tech companies
Involvement → good at changing focused on operations and internal processes, members participate
What is Power and the 5 characteristics?
The capacity to influence others who are in a state of dependence or interdependence.
1. A capacity
2. Doesn’t imply a negative relationship
3. Can flow in any direction, and doesn’t require a hierarchy
4. Dependence or interdependence
5. Between individuals and groups
What are the 5 bases of power? (and 6th)
1. Legitimate power → power from person’s position of job, based on authority and hierarchy, people have been socialized to accept its influenced
2. Reward power → ability to provide positive outcomes and prevent negative, any member can attempt to exert this
3. Coercive power → derived from the use of punishments and threat, generally ineffective, provoking resistance
4. Referent power → being well liked, the identification with the power holder
5. Expert power → having special information valued by organization, difficulty of replacement (most associated with employee effectiveness)
6. Connection → based on networking
What bases of power are positional?
Legitimate, reward, coercive
What bases of power are personal?
Referent, expert, connection
What are the 3 reactions to power and which kinds of power lead to each reaction?
1. Resistance → person is opposed to request and tries to avoid it: coercive
2. Compliance → person goes along with the request at minimal effort: reward and legitimate
3. Commitment → person is enthusiastic about request and carries out: referent and expert
How do people gain power?
Doing the Right Things:
1. Extraordinary activities
2. High visibility
3. Relevant activities
Cultivating the Right People:
1. Outsiders
2. Subordinates
3. Peers
4. Superiors
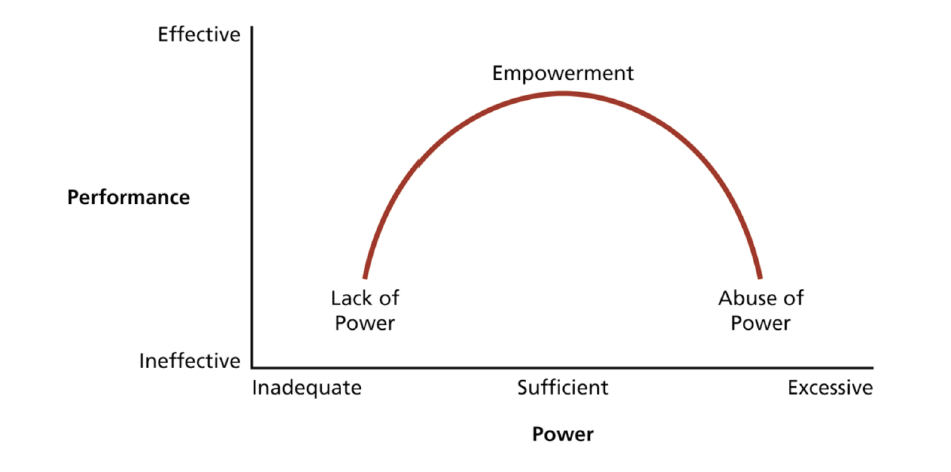
What is Empowerment and what does it lead to?
Giving people authority, opportunity and motivation to take initiative to solve organizational problems
job satisfaction and self-efficacy
organizational commitment
OCB
high performance
What are the 7 Influence Tactics?
tactic you use depends on the type of power you have, and who you’re trying to influence
1. assertiveness
2. ingratiation (flattery, friendliness, etc.)
3. self-promotion (image enhancement, name dropping)
4. rationality (planning, compromise)
5. exchange
6. upward appeals (formal or informal appeals to superiors for intervention)
7. coalition formation (seeking united support)
What are the 2 tactics to Convert Power to Influence?
Soft tactics → personal sources of power to appeal to attitudes and needs, resulting in commitment and compliance
Hard tactics → force behaviour change through positional power, resulting in resistance and compliance
What are the 3 power motive profiles (related to McClelland’s theory)?
1. Affiliative managers → concerned with being liked, less effective
2. Personal power managers→ motivated by self-interest, more effective than affiliative but less than institutional
3. Institutional managers (most effective managers) → have high n Pow, use their power for institution than self aggrandizement, participative leadership style, unconcerned with how people like them
What are the 4 reasons power is necessary in organizations/how subunits obtain power?
scarcity
uncertainty (those who can make more certainty get more power)
centrality (those most connected with most immediate impact)
substitutability (ability to substitute)
What are Organizational Politics?
The pursuit of self-interest in an organization, whether or not this self-interest corresponds to organizational goals.
What is the impact of organizational politics?
High political climates result in lowered job satisfaction, commitment and OCB, increased stress and turnover, may affect performance
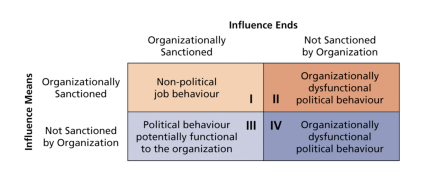
How do influence means and influence ends work?
Impact of politics depends on link between influence means (from organization or not from organization) and influence ends (organizational goals or personal goals)
Using any kind of means for personal ends is dysfunctional political behaviour.
What is political skill and the 4 facets?
The ability to understand others at work and to use that knowledge to influence others to act in ways that enhance one’s personal or organizational objectives.
→ positively related to performance
1. Social astuteness (reading others)
2. interpersonal influence
3. sincerity (apparent)
4. networking ability
What is networking and the 4 components?
Involves establishing good relations with key organizational members or outsiders to accomplish one’s goals.
1. Maintaining contacts
2. Socializing
3. Engaging in professional activities
4. Increasing internal visibility
What is the power of authority, why do we obey it and what is the impact?
Power of Authority principle: people defer to experts or those in positions of authority
Why we obey authority: authorities possess high levels of knowledge, wisdom and power
It can be used to exploit people: people faking it, clothing and titles can influence
What is Abusive Supervision?
sustained display of hostile verbal and nonverbal behaviours, excluding physical contact
What is Machiavellianism?
Doing whatever it takes to get what you want: stable set of cynical beliefs about human nature, morality, and the permissibility of using various tactics to achieve one’s ends.
What is knowledge hiding?
politically motivated behavior to intentionally conceal requested relevant information
→ playing dumb, evasive hiding, rationalized hiding
→ high Machs, distrustful, competitive and over-politicized work
What are Defensive Reactive Politics and the 2 types?
political behaviour in self-defence
1. Avoiding
stalling
over conforming
buck passing (having someone else act, letting someone else take the risk to prevent failure)
2. Blame
buffing (carefully documenting information showing that an appropriate course of action was followed)
scapegoating (blaming others when things go wrong)
What are Ethics?
Systematic thinking about the moral consequences of decisions, set standards as to what is good or bad in conduct and decision making