AP exam 3
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
two methods of long istance signaling
Hormonal signaling
neuronal signaling
CNS
Comprises the brain and spinal cord
PNS
extends from the spina cord to the rest of the body
Somatic nervous system
Controls voluntary movements
e.g. wlking and talking
Autonomic nervous system
Regulates involuntary movements; innervatees visceral organs and glands
e.g. breathing, digestion, heart rate
Afferent nerves
Sensory information Into the CNS
Efferent nerves
information away from the CNS
enteric Nervous system
controls motility/ activity in the digestive tract
Neuroglial cells
support the neurons ( non-transmitting cells)
Schwann cells, oligodendrocytes, migroglia etc.
neurondss become activated when graded potentil raises to the ?
threshold potential
which division of the PNS is responsible for the fight or flight response
sympathetic
excitable cells
cells that use movement of electrolytes in/ out of the cell to generate an electrical current
initial part of the axon that transforms the grade potential into action potential
Axon hillock
terminal buttons
store/ relesse vessicles containing neurotransmitters
neurotransmitter
chemical messenger molecules that act on target cells
types of synapse junctions
neuron to neuron
neuro-muscular
neuro-glandular
Main inhibitory neurotransmitter of the CNS
GABA
Main excitatory NT in the CNS
Glutamate
Major NTs
Catecholamines
Norepinephirine
epinephiring
DA ( dopamine)
Serotonin
Acetylchoine
endorphins
Norepinephrine function
NT for fight or flight
epinephrine function
circulating hormone for fight or flight
dopamine main function
award/ pleasure
muscle control parkinsons
serotonin function
mood hormone
muscle control, digestive tract control
Acetylcholine function
PNS: control of afferent and efferent nerves
CNS: involved in memory and thinking pathways
Endorphins
Natural agonists of opiod receptors
inhibits pain signaling, can also cause euphoria
three classes of neurons
afferent neurons
efferent neurons
interneurons

interneurons
connect one neuron to another
all wihin the CNS
99% of neurons in humans
membrane potential (mV)
sepertion og electrical charges across a cell membrane
resting membrane potential
the membane potential when the cell is at est
no ions flow in/ out of cell
T or F: Action potentials must be started by a graded potentia in the neuronal cell body
True
Axtion potentials begin at
the axon hillock
T or F: Action potentials are conducted segment by segment along the axon
true
two types of axon conduction
contigous conduction ( unmyelinated)
Saltatory conduction ( myelinated)
why do signals move in only one ditection
the ions only open the front door of each voltage channel allowing it to only move forward
how do local anesthetics work
by bonding and inhibiting voltage gated Na+ channels
no Na+ → no AP → no spreding depolarization
myelin
lipid rich insulator of conduction
nodes of Ranvier
unmyelinated gaps
unmyelinated conduction ( contigous)
afferent c-type neurons
nociception, temp., itch, gentle touch
move much slower
Type A neurons
Largest,fastest most myelinated
efferent: motor neurons
afferent: proprioception ( muscles), fast pain reveptors, sensitive touch receptors
Type B neurons
medium speed
Afferent: visceral senses
efferent: autonomic within the spina cord
NT function ends when
they are removed from the synaptic clet
three mechanisms NT use to terminate signas
transported back into the axon terminal by reuptake carriers
inactivation/ destruction by an enzyme
diffusion away from the synaptic cleft
two classes of cells in the CNS
neurons: transmitting cells
Neuroglial cells: non-transmitting/ supporting cells
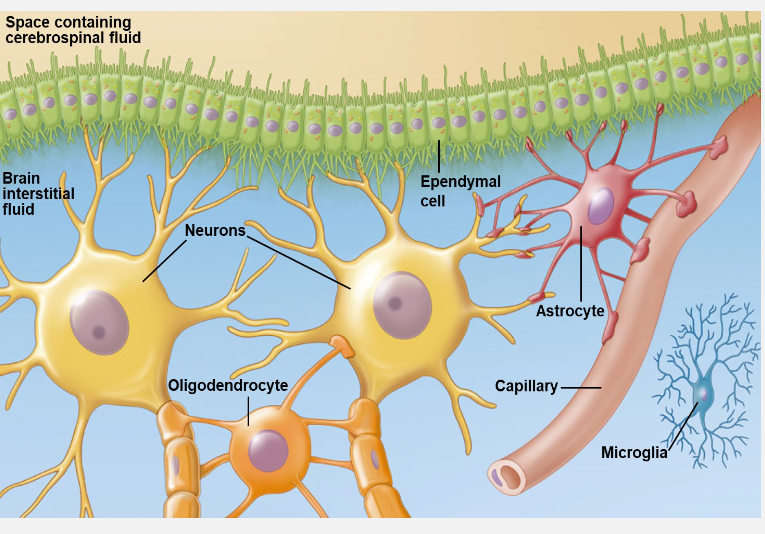
Astrocytes
support neuron structure and alignment
support blood brain barrier
most abundant neuroglial
facilitates glucose absorption
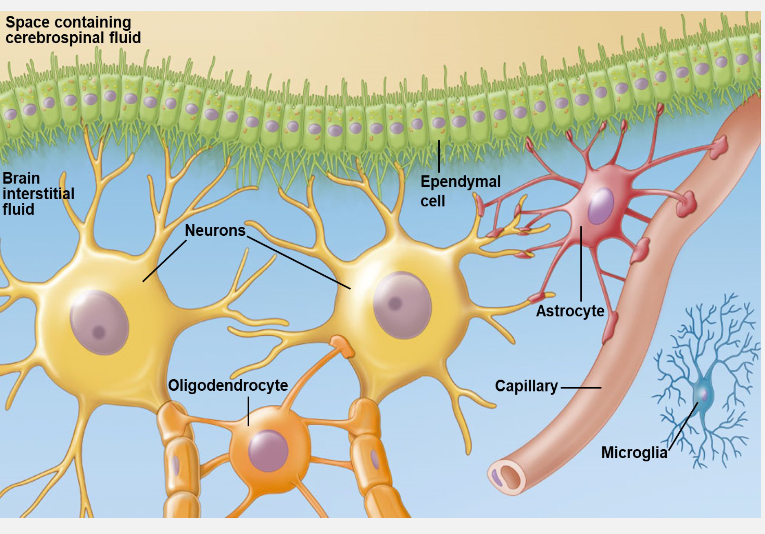
Oligodendrocytes
creates myelin sheaths in CNS
one olig. myelinates multiople axons
increases speed of action potential; reduces ATP usage
Ependymal cells
line spces sin the brain and spina cord
forms cerebrospinal fluid
Microglia
immune defense cells in CNS
phagocytic cells
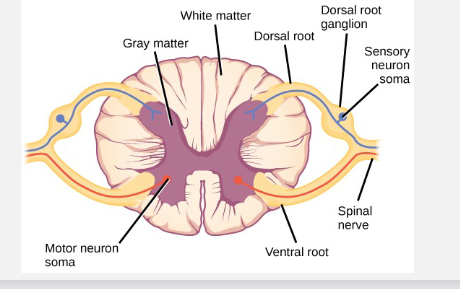
what is grey matter comprised of
cell bodies and glial cells
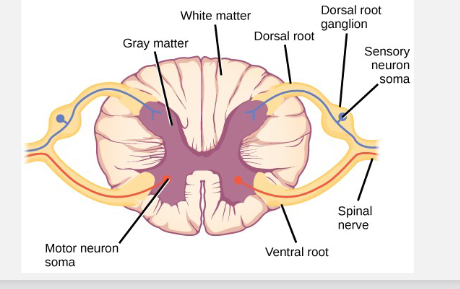
what is white matter comprised of
myelinated axons
where do efferent spinal neurons begin?
in the ventral horn of the spinal cord
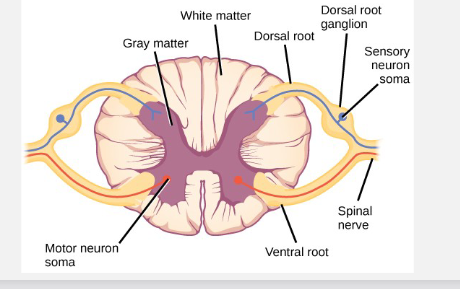
where do sensory affernt neurons end
the dorsal horns of the spinal cord
Brainstem
connects brain to spinal cord
controls breathing, heart rate swallowing
medulla oblongota, pons, midbrain
MAOI drugs increase__?
the amount of DA, serotonin and norepinephrine stores in the neurons
DA, serotonin and norepinephrinf are metabolized by__?
monoamine oxidase
(MAO-A and MAO-B)
Diencephalon
thalamus- inputs/outputs
hypothalmus- integrates CNS woth endocrine system
cerebellum function
conrols balance and coordination of movements
involved oin motor learning
receives info from visua land auditory senses
Medulla oblongota
contains cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers
swallowing, coughing, sneezing
autonomic nervous system control
Pons- middle part
cranial nerves connect here for respiration, eye movement, facial sensations, and facial movements
urination control, breathing aids
pain receptor processing from the neck down
Midbrain
coordinates reflex responses to sight and sound
sleep/ wakefulness paterns
thermoregulation
damage to cerebellum
abstract reasining/ planning difficulties
speech issues
changes in personality
the hypothalamus is responsible for what four F’s?
feeding
fighting
fleeing
fornicating
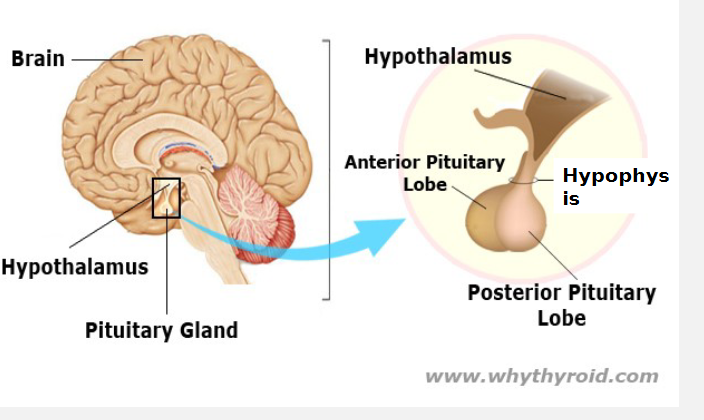
hypothalamus
contol center for homeostasis in the body
sends hormones to APG and PPG
hormones sent to anteriior pituitary gland (APG)
sex hormones
thyroid hormones
stress hormones
growth hormones
hormones sent to the posterior ptuitary gland (PPG)
vasopressin
oxytocin
Thalamus
relay all sensory inputs ( except smell)
contra-lateral pathways ( dessucation in brain)
memory recall
relays outgoing motor instructions
functional area of cerebral cortex
Primary cortices- direct input/ control
Association cortices- complex planning, self-awarness, language, personality
Fiber tracs(White matter)- transmmit signals from one area to another
__ connects the two cerebral hemispheres
corpus callosum