Chapter 10: Calvin Cycle and C4/CAM
Where does the Calvin Cycle occur?
stroma of the plant; it is light-independent
How many cycles for one glucose molecule?
6 cycles per one glucose
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Where does the Calvin Cycle occur?
stroma of the plant; it is light-independent
How many cycles for one glucose molecule?
6 cycles per one glucose
How many G3P molecules per one glucose
2 G3P molecules per one glucose
How many Calvin Cycle turns for one G3P molecule?
3 turns per one G3P molecule
Requirements for the Calvin Cycle
18 ATP, 12 NADPH, 6 CO2
How many molecules of CO2 to input?
each cycle = 1 CO2 molecule per
(easier to do 3 CO2 at a time)
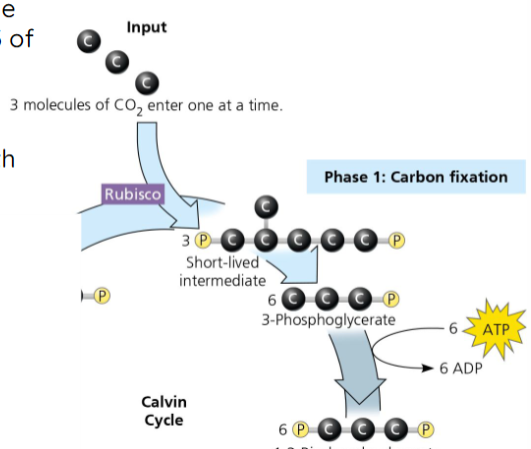
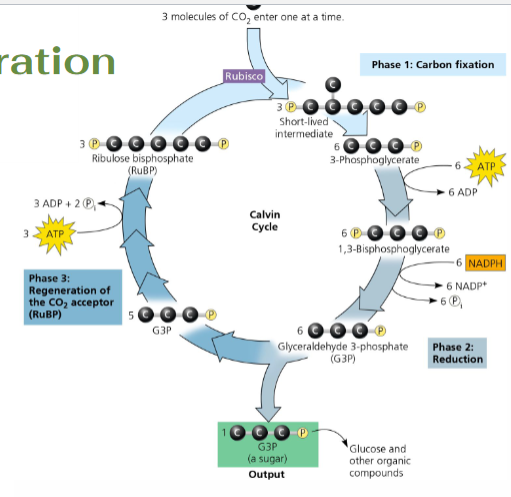
Three stages of the Calvin Cycle
Carbon Fixation
Reduction
Regeneration
Rubisco function
the key enzyme responsible for capturing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and incorporating it into organic molecules
most common protein on Earth (alledgedly)
Carbon Fixation: molecules output
3 CO2 + 3 RuBP (5-carbon) → Short-Lived Intermediate
Short-Lived Intermediate → 6 3-PGA
Reduction: ATP inputs/outputs
needs: 6 ATP → 6 ADP; P added to each 3-PGA
turns into: 6 3-PGA → 6 1,3-BisPGA
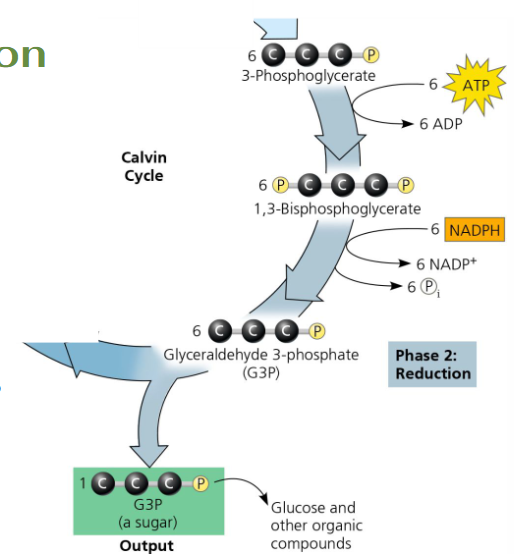
Reduction: NADPH inputs/outputs
needs: 6 NADPH → 6 NADP+
donates/loses: pair of e- and the one phosphate
turns into: 6 1,3-BisPGA → 6 G3P
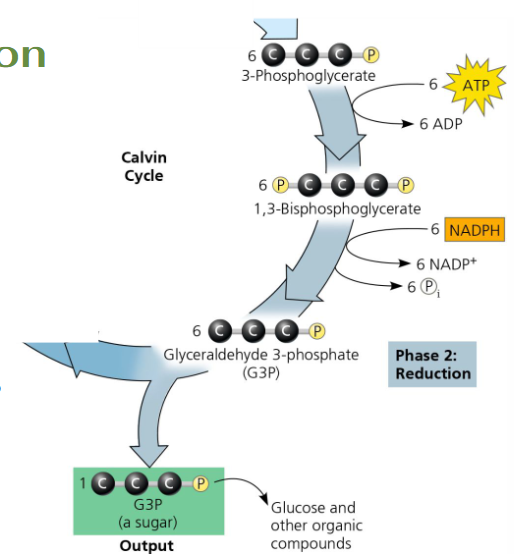
Where does the 6 G3P go?
1 G3P leaves the cycle as an output; the 5 other G3P cycles until all 6 are output
Regeneration: inputs/outputs
needs: 3 ATP → 3 ADP + 2 P
regeneration of RuBP
turns into: 5 G3P → 3 RuBP
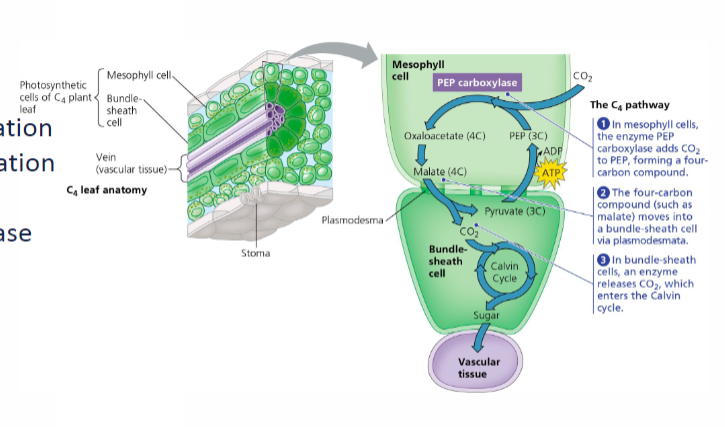
C4 Plants
physical separation of Carbon Fixation (CO2 fixation → PEP)
PEP Carboxylase
Costs 1 ATP
better in hot conditions
ex: corn (maize), sugarcane, sorghum, millet, switchgrass, crabgrass, and amaranth
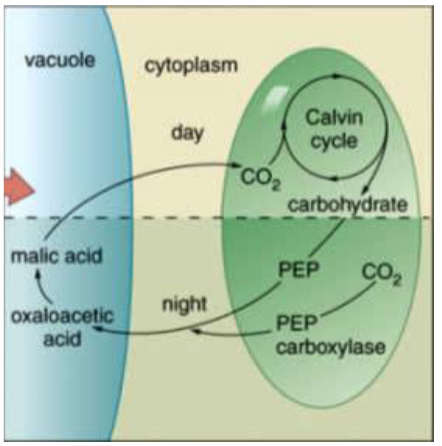
CAM Plants
temporarily/temporal separation of Carbon Fixation
Crassulacean Acid Metabolism
Store Malate in Vacuoles during Night, Calvin Cycle during day
better in dry conditions
ex: cacti, pineapple, agave, Opuntia (prickly pear), Kalanchoe (florist kalanchoe), and common iceplant