Toxicology Unit 1
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
173 Terms
4 Steps to the Mechanism of Toxicology
Delivery
Reaction
Dysfunction
Repair/Disrepair
[all/some] endogenous compounds are potential targets for toxicants
All
all ______ ______ are potential targets for toxicants
endogenous compounds
Most prevalent and toxicologically relevant endogenous compounds are _________ ________ and ________
nucleic acids and membranes
2 types of reactions
covalent and noncovalent
Noncovalent reactions are:
typically reversible
include hydrogen and ionic bonds
covalent reactions are:
typically irreversible (permanent!)
Common with electrophiles and radical cations
Hydrogen abstraction reaction:
What abstracts H atoms? What does it form?
neutral free radicals abstract H atoms from endogenous compounds. Forms cross links with DNA.
Electron transfer reaction:
Exchange of electrons to oxidize or reduce other molecules
Enzymatic Reactions
Toxics act enzymatically on target proteins
Dysfunction of target molecule
toxicant inhibits/blocks functions of the target molecule
Destruction of target molecule
toxicant alters the primary structure of an endogenous molecule by cross-linking or fragmentation
Neoantigen formation
covalent binding to xenobiotics or their metabolites to a protein may invoke an immune response
Dysregulation of gene expression occurs at elements that are responsible for
Transcription
intracellular Signal Transduction components
Synthesis, storage, or release of extracellular signaling molecules
Dysregulation of transcription involves
altering the activation of TFs (No DNA —> RNA)
Dysregulation of signal transduction involves
altering protein phossphorylation or interfering with GTPase activity of G Proteins (GPCR)
Dysregulation of extracellular signal production involves
altering hormone circuits
Dysregulation of ongoing cell function involves
disruption of steps in signal coupling in specialized cells
Dysregulation of excitable cells is an example of
dysregulation of ongoing cell function
An example of ysregulation of excitable cells is
disruption of neutrotransmitters
3 ways cell death is inflicted
ATP Depletion
Sustained rise in intracellular Ca+2
Overproduction of ROS/RNS (Free radicals)
Necrosis
Unorganized cell death caused by MPT (mitochondrial inner membrane permeability) where the cell swells and lyses.
Apoptosis
Organizes cell death where the cell shrinks and breaks into fragments to be phagocytosed.
Key in cell death mechanisms is the release of
cytochrome C
Molecular repair can involve
Chemical alterations being reversed
Removal and reinsertion of new units
Total degradation aod re-synthesis
Chemically altered DNA
Types of molecular repair
Repair of proteins, lipids, and DNA (includes direct repair, excision repair, and recombinational repair)
Molecular repair
Proteins
Lipids
DNA
Tissue Repair involves
regeneration of tissue by proliferation
Types of tissue repair
Replacement of lost cells by mitosis
Replacement of ECM
Side reactions of tissue repair
Inflammation: cytokines secreted and produce free radicals
Altered protein synthesis: cytokines can inc or dec gene transcription
Generalized Reactions: cytokines can trigger fever
If repair fails
Tissue necrosis: happens if repair mechanisms are insufficient or molecular damage is not readily reversible
Fibrosis: Excessive depostion of ECM of abnormal composition (scarring. Dangerous in organs but not skin). ECM production is not turned off.
Carcinogenesis: insufficient function of various repair mechanisms
Failure of DNA repair
Mutation, the initiation event
Damaged DNA can cause adduct formation
Mutation passed to daughter
Altered genes produce mutant protein, reprogramming cells for multiplication
Creates a rapidly proliferation tumor)
Fill in the Blanks
Exposure site: injection/bite site, skin, GI tract, Respiratory tract, placenta
↑ Absorption
↑ Distribution to target organ
↑ Reabsorption
↑ Toxication
X Presystemic elimination
X Distribuution away from target organ
X Excretion
X Detoxication
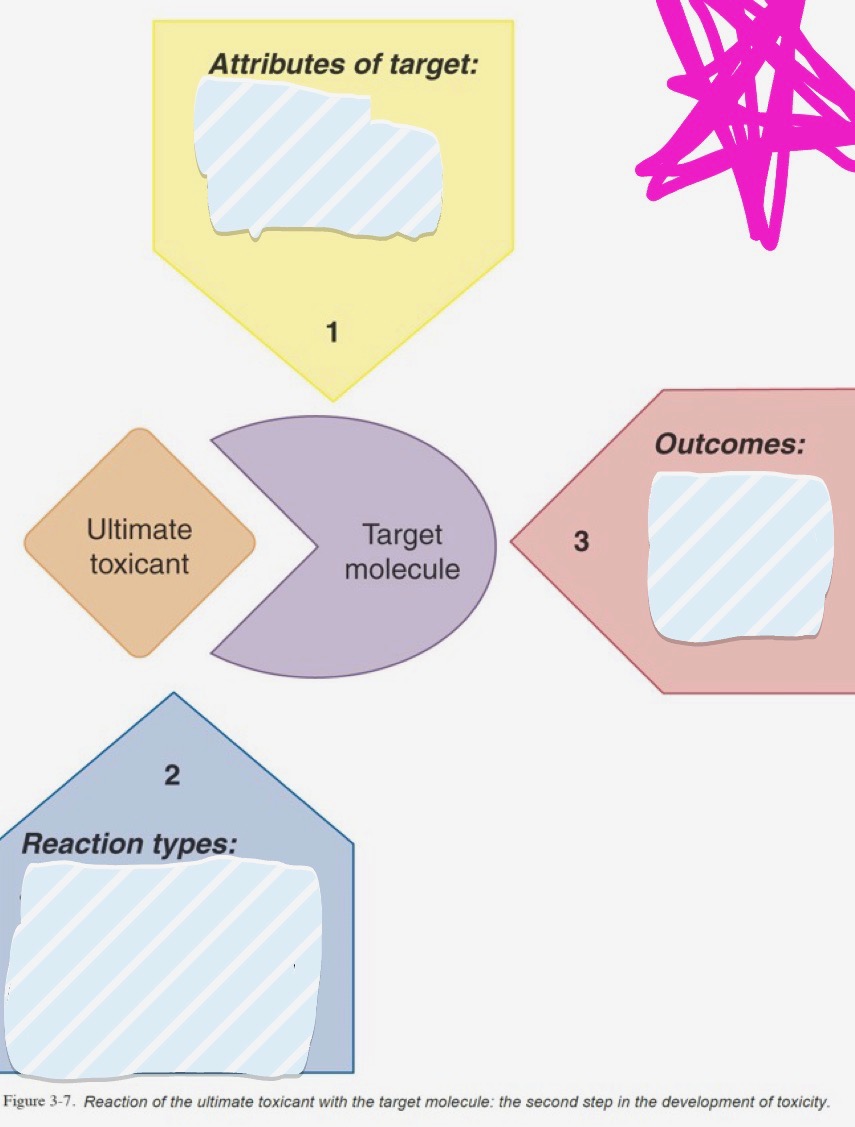
Ultimate toxicant
Target molecule
Target location
Attributes of Target
Reaction types
Outcomes
Reactivity, Accessibility, Critical function
Noncovalent binding, covalent binding, hydrogen abstraction, electron transfer, enzymatic reaction
Dysfunction, destruction, neoantigen formation
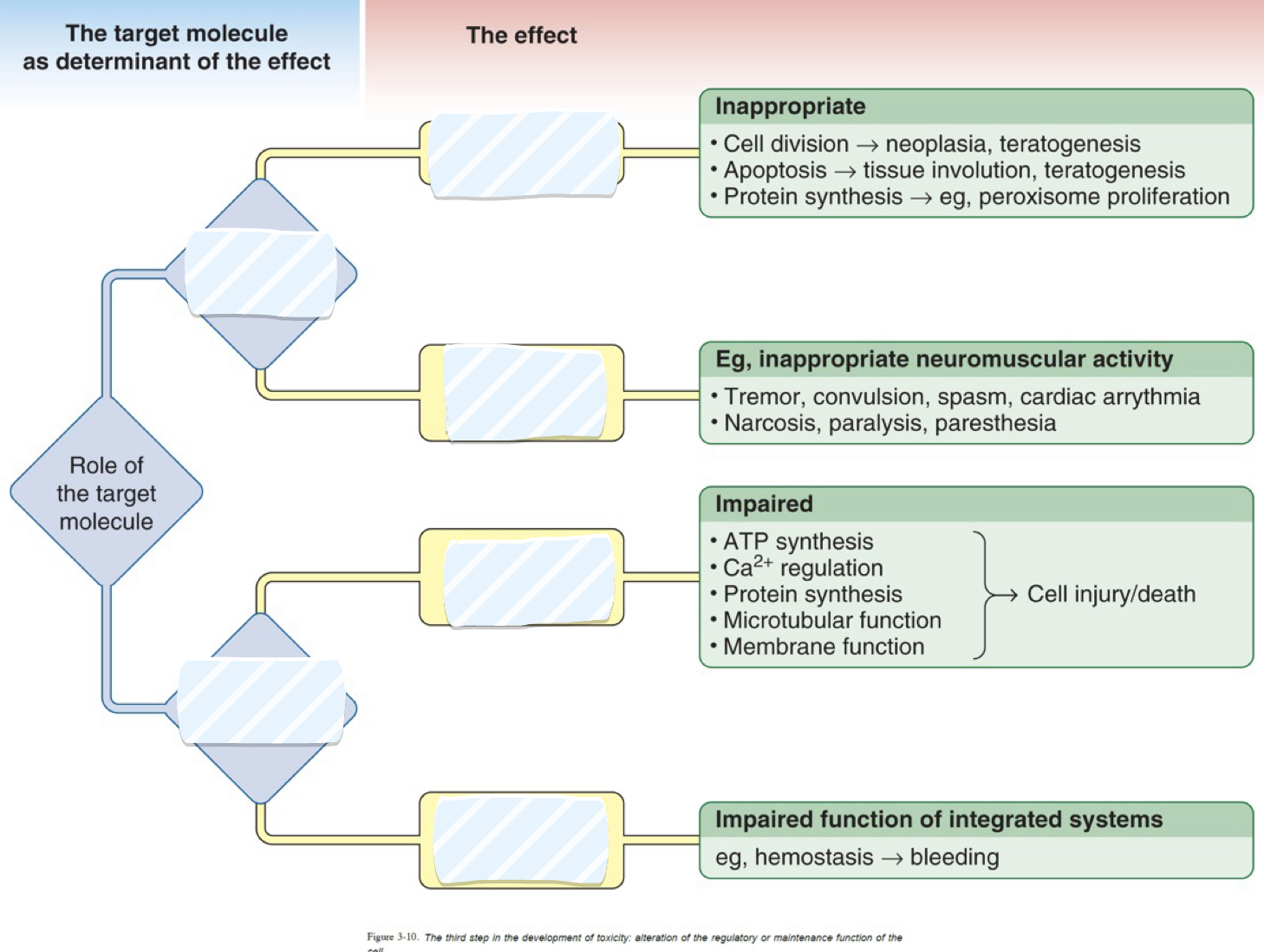
Fill in the blanks
Role of target molecule: Cell regulation (signalling), Cell maintenance
Cell Regulation: Dysregulation of gene expression, Dysregulation of ongoing function
Cell maintenance: Impaired internal maintenance, impaired external maintenance.
Fill in the blanks
Molecular: Proteins, lipids, DNA
Cellular: Autophagy of damaged cell organelles, Regeneration of damaged axons
Tissue: Apoptosis, cell reproduction, ECM production
Definition of Volatile organics (BP and VP)
BP below 250C at atm
WHO: below 260C
European Union: VP ~ 0.01kPa (~1/11,000atm)
Volatiles may…
be significant contributors to air and groundwater pollution
Definition of Semivolatile organics
USEPA: BP above 240-260C, below 400C
VP range 10^-14 to 10^-4 atm.
PAH stands for
Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons
PCB
Polychlorinated biphenyls
Varying degrees of solubility, VP, Kow, Toxicity because of varying Cl content
NPL
Carcinogenic
Impacts immune and reproductive sys. and intellectual development
PCDDs
polychlorodibenzodioxins
bioaccumulative
Organophosphorus insecticides
AKA anticholinesterase agents
Neurotoxin
can cause paralytic condition and muscle weakness
Organochlorine pesticide
Low VP and solubility
High Kow (very fat soluble, accumulates in fat)
Bioaccumulates
Associated with suppression of immune system and cancer
Slow biotransformation, does not excrete well (gets stored in fat)
Carbamate insecticide
2ndary amine
Dissapates quickly (shorter half life than OP, but f(x) similarly)
Perfluroinated compounds
PFOS (stain resistant), PFOA (non-stick coating)
Sillanes and Silyl ethers
lubricants and cosmetics
Polybrominated compounds
flame retardants
N-nitro and nitroso compounds
explosives, tobacco smoke, industrial chemicals.
carcinogenic
Heavy metals
Specific gravity exceeds the specific gravity of water by 5+ times
Arsenic
Carcinogenic (bladder, liver, kidney, skin,lung), peripheral vascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, adverse pregnancy.
In pesticides, wood preservatives; byproduct of gold refinement.
Can be ingested or inhaled
Cadmium
Osteroperosis in women, height loss in men, kidney damage, elevated BP, CVD, Itai-Itai
Chromium
III- Essential
VI- Toxic carcinogen
Lead
Naturall occurring toxic metal
Mercury
Bioaccumulates, especiall in water and fish (aquatic invertebrates)
“Dose makes the poison”
Paracelsus
What is a poison
Any agent capable of producing a deleterious response in a biological system
Toxicity
Degree to which something is poisonous
Toxicant or Xenobiotic
Toxic substance man-made or resulting from human activity
Toxin
Toxic substance made by living organism
Additive
2+2=4
Synergistic
2 + 4 =10
Potentiation
0+2=4
Antagonism
2+4=3A
Acute
Exposure <24 hours
Subacute
Exposure < 1 month
Subchronic
Exposure 1-3 months
Chronic
Exposure longer than 3 months
In vivo
Alive organism exposed purposefully or accidentally
In vitro
cells derives from organisms
in silico
computer modeling or simulation predictions
Factors affecting disposition
Absorption, distribution, metabolism/biotransformation, excretion
Barriers to absorption
skin or cellular membranes
Passive transport means
no energy is used
Types of passive transport
facilitated diffusion (carrier-mediated but not moved against a gradient)
simple diffusion
filtration
Filtration
Water in bulk flowing across porous membrane. small solute may pass with water. filters by size.
Active transport
Uses energy
Moves against gradient
Can become saturated at high substrate []; exhibits a transport maximum (Tm)
Potentially competitively inhibited
Selective for certain structures
If it says “anion” or “cation” (oat, oct, oatp), it is probably _____ transport
active
Kinds of special tansport
Endocytosis (pino and phago)
Absorption definition
Process by which toxicants cross body membranes and enter the bloodstream
Main sites of absorption
GI tract, lungs, skin
Enteral administration
Oral to rectal system
Parenteral Administration
all routes not enteral. administered other than mouth or alimentary canal
Absorption takes place where in the GI tract?
ANYWHERE. The whole thing, mouth to rectum.
First-Pass effect
Not all of the ingested material is absorbed because the liver extracts some into the bile.
Gas solubility ratio
[] in blood / [] in gas
Gases with low solubility ratio are ____ limited
perfusion. Will exist in gas more than blood.
Depends on blood flow. if there is more flow, the compound will be able to leave.
Gases with high solubility ratio are ____ limited
ventilation. Will exist in blood more than gas.
Depends on how much of the compound is inhaled.
Particles > 5um
deposited in nasophayngeal region. Removed by blowing, sneezing, wiping.
Particles 2-5um
Desposited in tracheo-bonchiolar region. cleared by movement of mucus.
Particles <= 1um
Penetrate alveolar regions of lung and may be absorbed into the blood
Rate-determining layer of skin absorption is the
stratum cornium
Parenteral administration routes
Intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, intramuscular, intravenous
Intraperitoneal
into body cavity
subcutaneous
into layer of skin below dermis and epidermis
intramuscular
into the muscle
intravenous
directly into the bloodstream
Final distribution depends on…
affinity of a xenobiotic for various tissues.
First pass effect, AKA…
Enteropathic circulation
Rate of distribution determined primarily by
blood flow
Rate of diffusion out of capillary bed and into cells and tissues