Genetics: Chromosomes, Cell Cycle, and Sex Determination
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
156 Terms
Eukaryotic chromosome
Composed of DNA, RNA, and protein; a thread-like structure of nucleic acid (DNA) around a core of protein.
Telomere
The end part of a chromosome that protects it from deterioration.
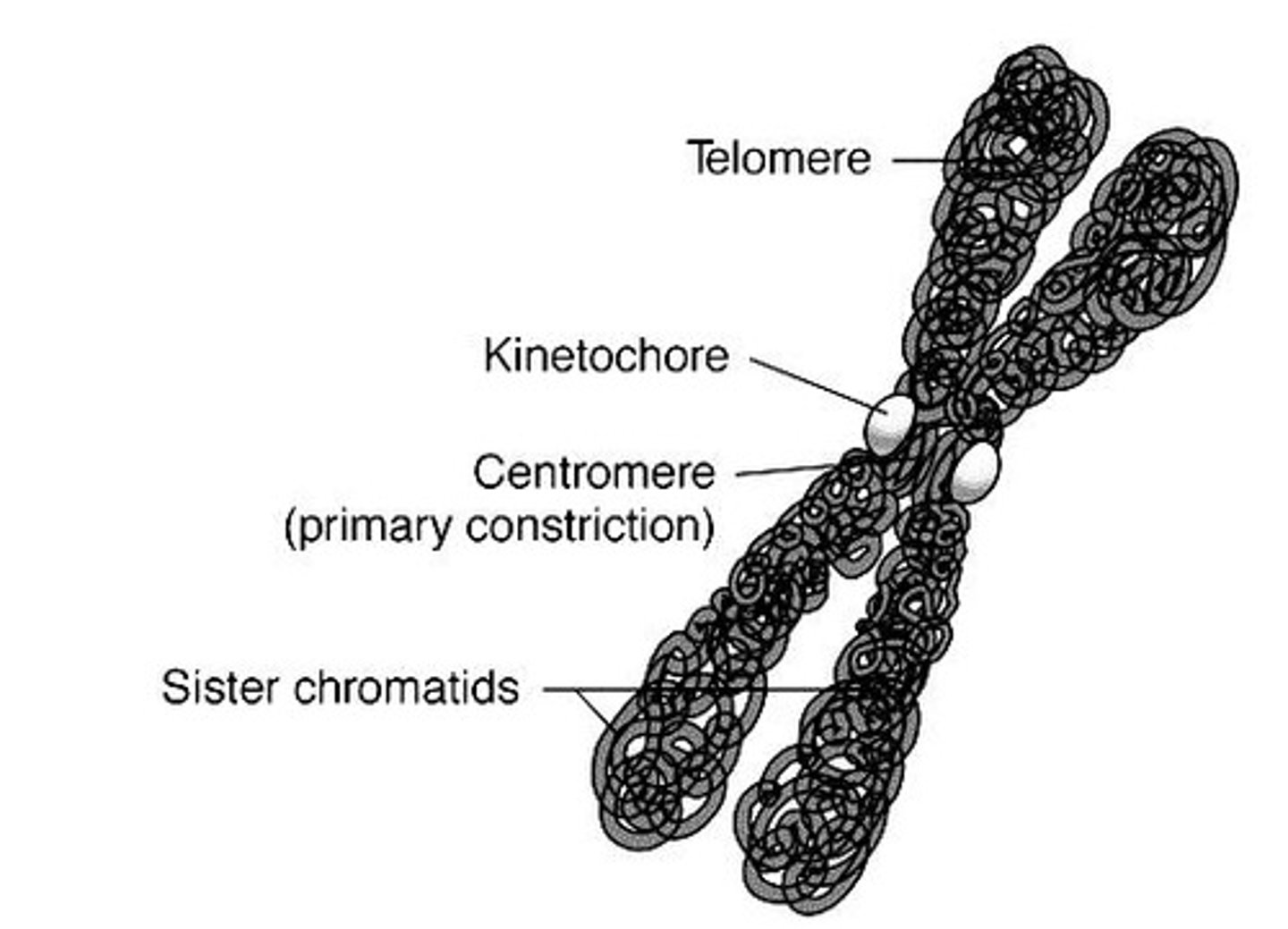
Centromere
Region of constriction in chromosomes where the spindle apparatus attaches.
Kinetochore
A protein structure on the chromosome where the spindle fibers attach during cell division.
Chromatid
One of the two identical halves of a replicated chromosome.
Monad
One chromatid; not typically visible, before replication.
Dyad
Two chromatids; visible after replication.
Diploid
Organisms that have a pair of chromosomes, called homologs or homologous chromosomes.
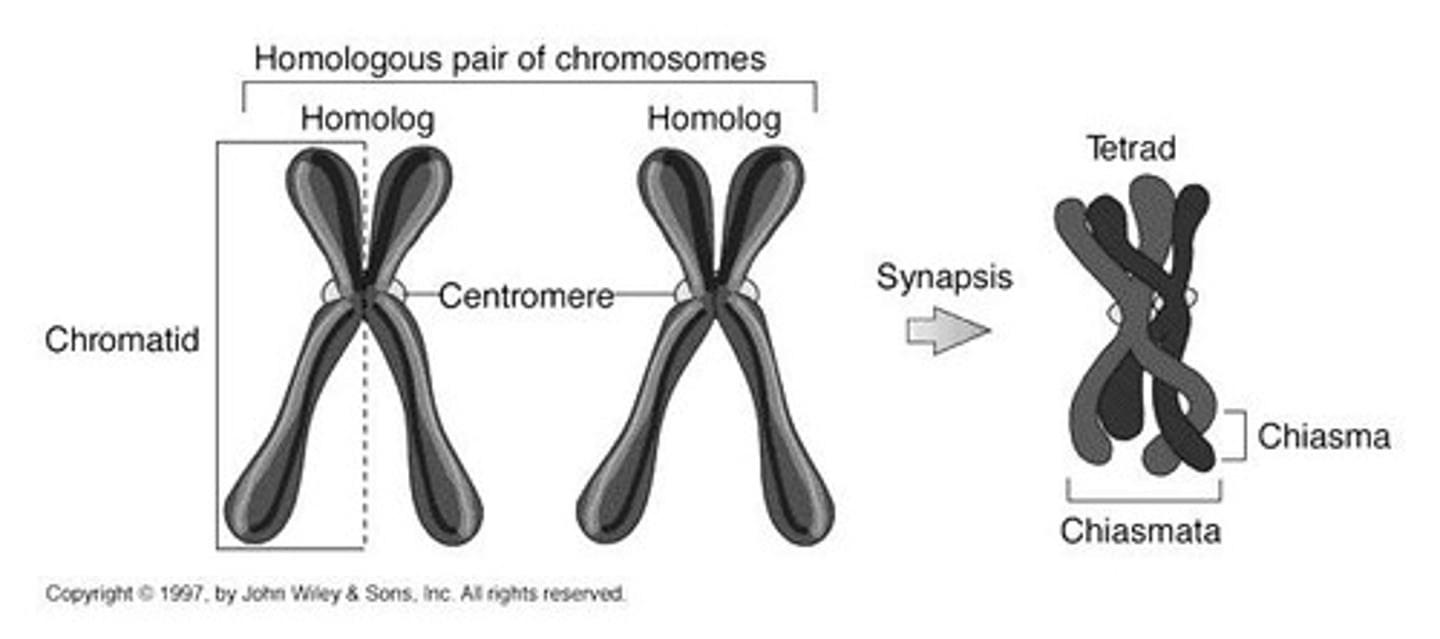
Tetrad
Formed from paired homologs during prophase I of Meiosis I and consists of 4 chromatids intertwined.
Chromatin
DNA and histone proteins in the nucleus which condense to form chromosomes.
Chromosome condensation
Coiling and packing of DNA into distinct packages which are easier to separate during nuclear division.
Sister chromatids
The two components of the same chromosome after DNA has been replicated; they share a common centromere and are exact copies of each other.
Homologous chromosomes
Same type of chromosome (one from each parent) that have the same length, same genes at the same loci, same banding pattern, and same centromere position, but may have different alleles for the genes.
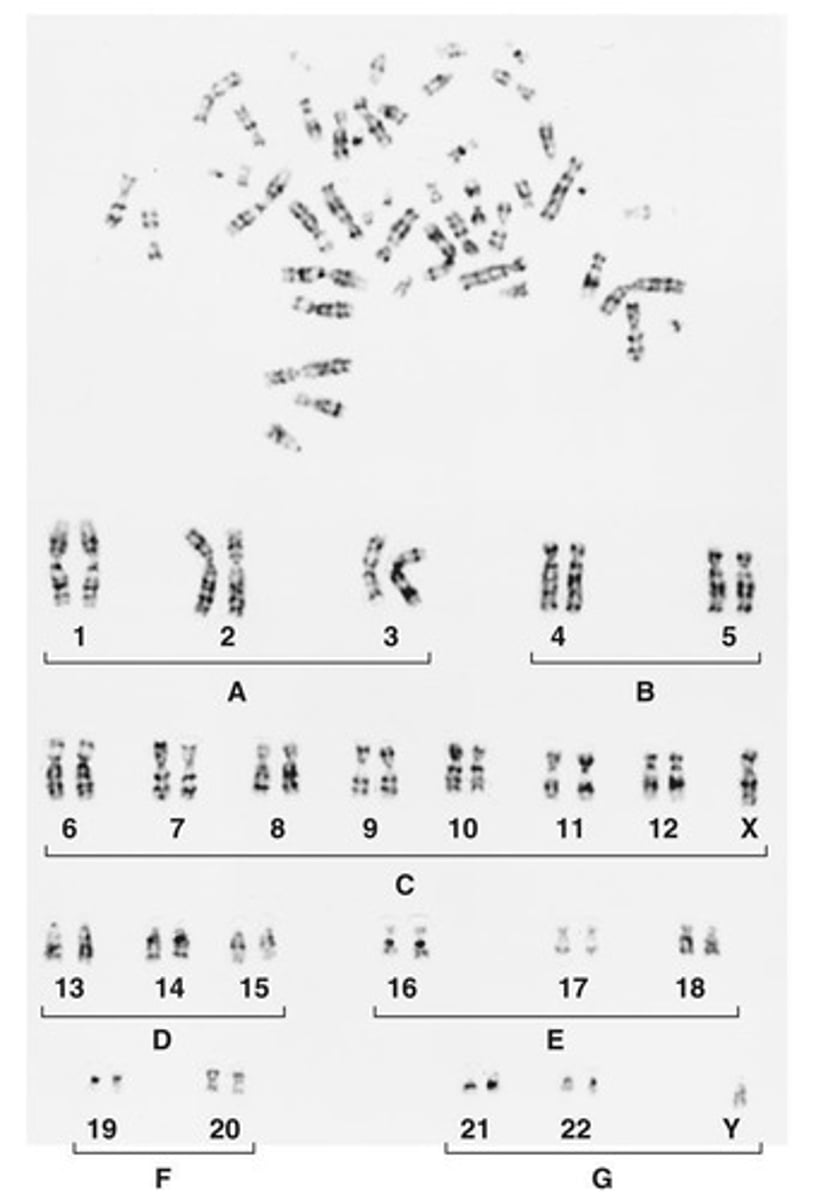
Karyotype
The number and appearance of chromosomes in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
Cell cycle
The process of cell growth and division, represented as G1→S→G2→M→C (24 hr cycle).
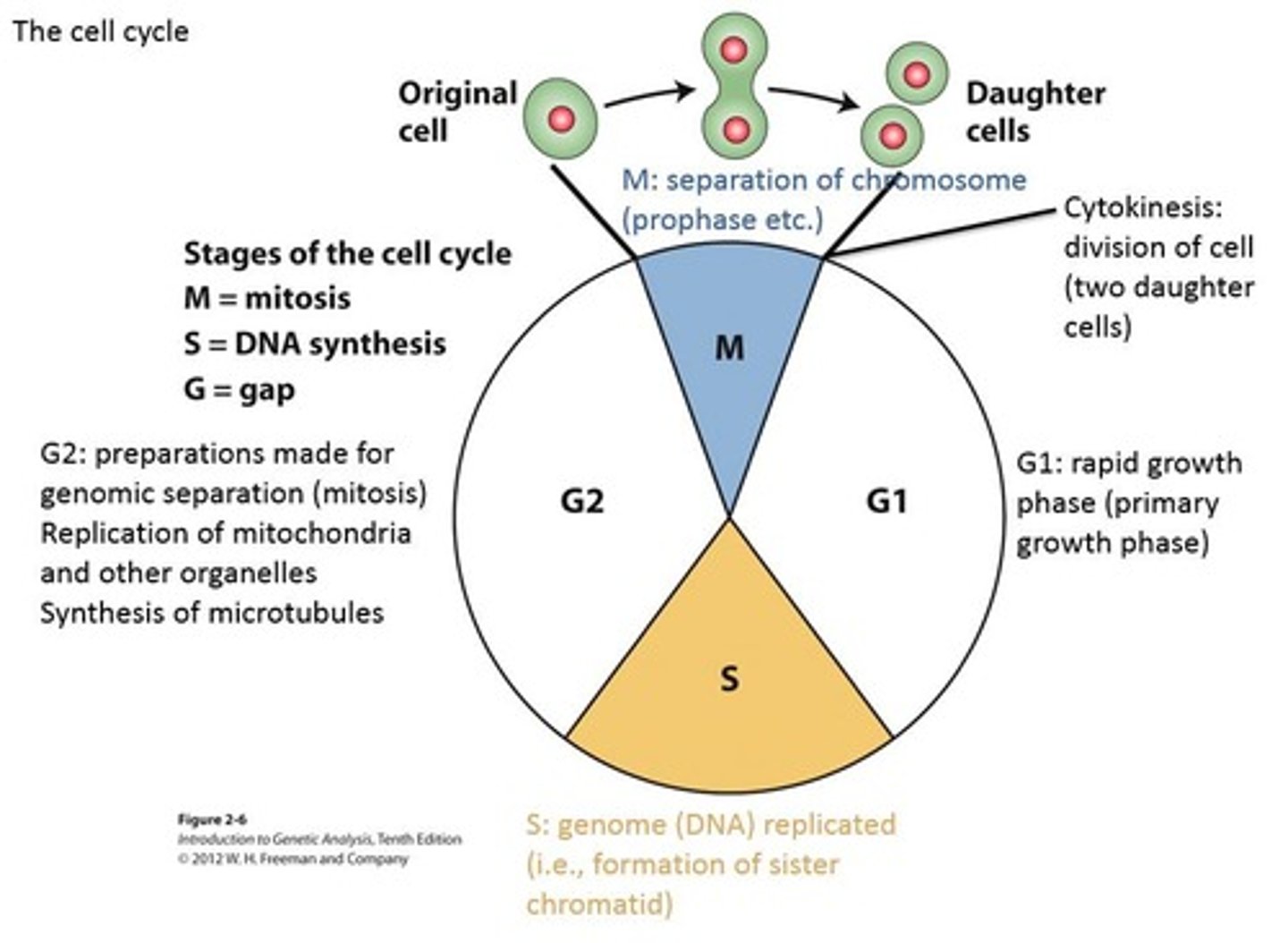
G1 phase
(5-10 hrs) Rapid growth phase, primary growth phase.
S phase
(7-9 hrs) Genome (DNA) replicated, formation of sister chromatids.
G2 phase
(3-4 hrs) Preparations made for genomic separation (mitosis), including replication of mitochondria and other organelles.
Mitosis
(1 hour) Separation of chromosomes during cell division.
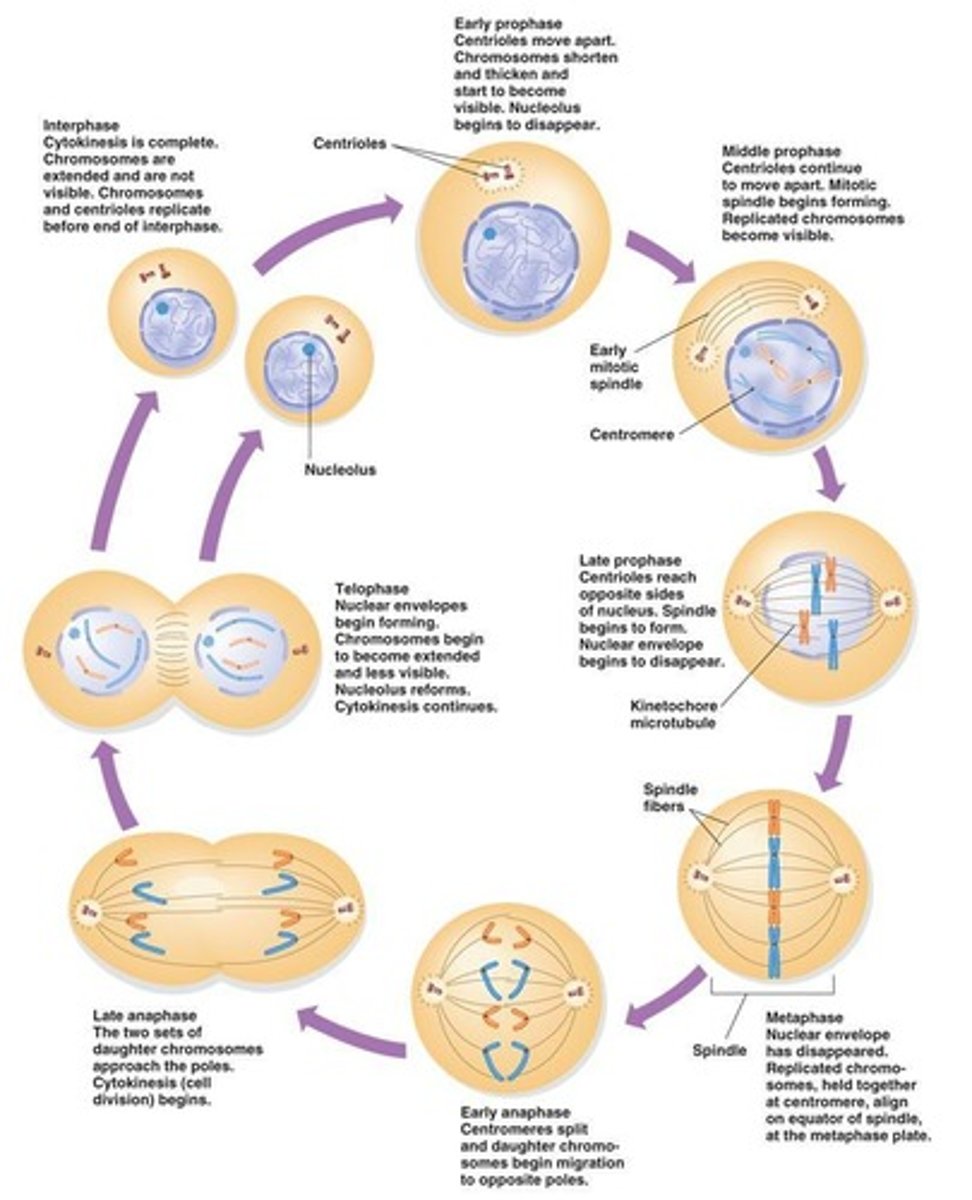
Cytokinesis
Physical division of the cell into two daughter cells.
S-phase
DNA molecules replicate to form identical chromatids.
Mitosis (nuclear division)
Process where 2n → 2n + 2N or 1N → 1N + 1N.
Stages of Mitosis
Prophase (early) → metaphase (middle) → anaphase (toward) → telophase (end).
Prophase
Mitotic apparatus forms & condensed chromosomes become visible.
Metaphase
Centromeres align, chromosomes (pairs of sister chromatids) align along the metaphase or equatorial plate.
Anaphase
Separation of sister chromatids which move toward poles.
Telophase
Chromosomes arrive and nuclei reform; spindle apparatus is disassembled.
Animal cytokinesis
Involves 'pinching' with furrow.
Plant cytokinesis
Rigid cell wall and cell plate forms.
Products of Mitosis and Cytokinesis
One 2n cell → two 2n daughter cells; One 1n cell → two 1n daughter cells.
Daughter Cells of Mitosis
~ ½ the size of the parent cell, but nucleus has the same DNA content as the parent cell.
Equational division
One (2N) cell gives rise to two (2N) daughter cells.
Sexual Life Cycle
Life cycle that exhibits alternation of haploid and diploid chromosome number.
Meiosis
Reduction division: 2N → N + N + N + N.
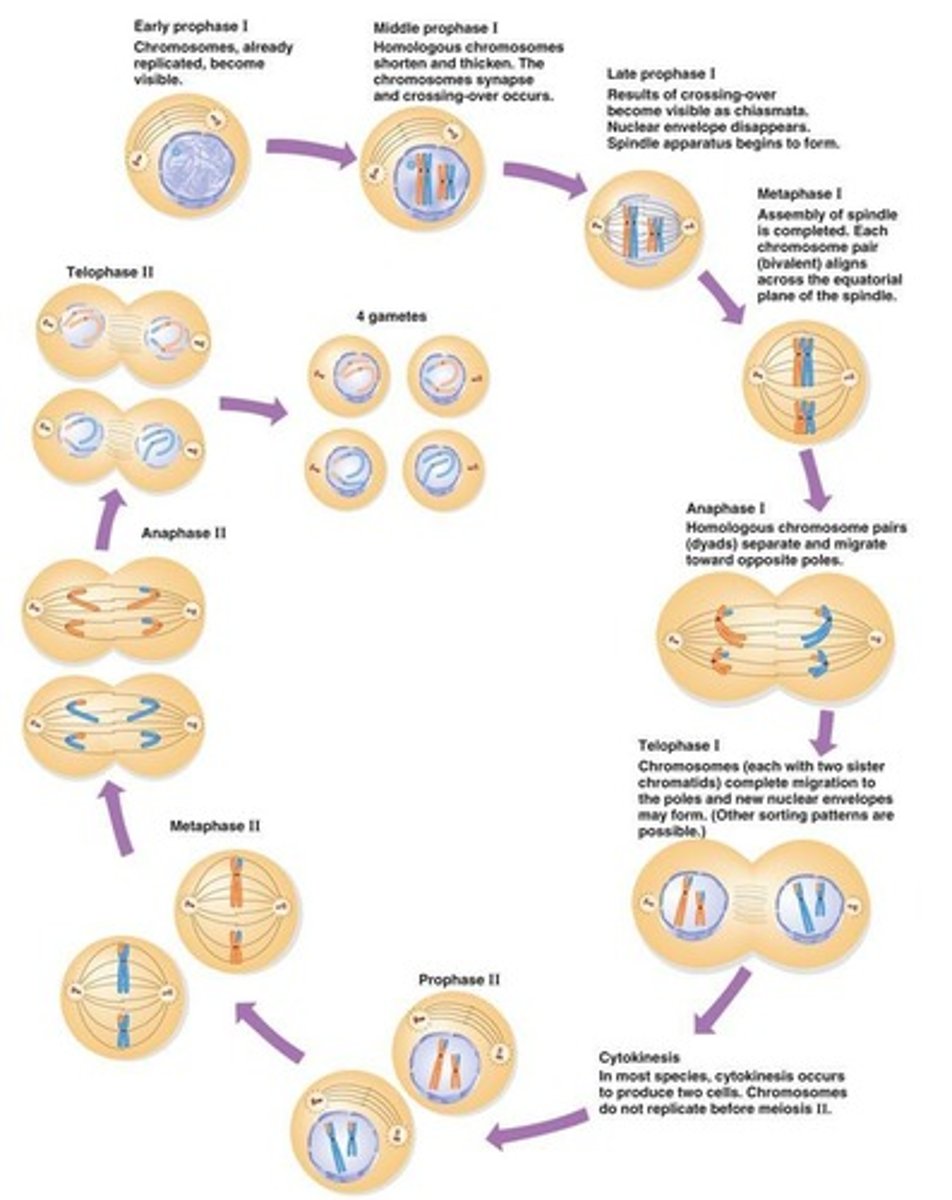
Meiosis I
First round of chromosome separation (separation of homologues).
Meiosis II
Second round of chromosome separation (separation of sister chromatids).
Prophase 1
Homologs pair and exchange information.
Leptonema
2 copies of condensed chromosomes appear as a single thread.
Zygonema
Homologs pair and form tetrad (4-stranded structure), also called bivalent.
Pachynema
You can see four chromatids; crossing over occurs between homologs.
Chiasmata
Site of crossover; formation of ladder-like synaptonemal complex.
Diplonema
Homologs unpair & pull away from each other; crossing over is seen.
Diakinesis
Homologs thicken and move to center of nucleus; nuclear membrane disperses.
Metaphase 1
Paired homologs align in the middle.
Anaphase 1
Paired homologs separate & are pulled toward poles randomly.
Telophase 1
Homologs (sister chromatids intact) arrive at poles.
Leptotene
The first stage of prophase I where chromosomes condense into visible strands.
Homologous chromosome
Chromosomes that are similar in size, shape, and nature of inherited characters, with one chromosome from each parent.
Bouquet stage
A term coined by Darlington to describe the stage in which chromosomes touch the undersurface of the nuclear envelope by their telomeres pointing towards the centrioles.
Zygotene
The stage where chromosomes line up with each other into homologous chromosome pairs, also known as zygonema.
Synapsis
The pairing or coming together of homologous chromosomes during the zygotene stage.
Bivalent chromosome
Paired chromosomes during the zygotene stage that are equal in length and position of centromere.
Pachytene
The stage where chromosomal crossover occurs, involving the exchange of segments between nonsister chromatids of homologous chromosomes.
Diplotene
The stage where homologous chromosomes separate slightly, allowing some transcription of DNA, while remaining tightly bound at chiasmata.
Dictyotene stage
The suspended state of developing oocytes in human fetal oogenesis that occurs during diplotene and remains until puberty.
Synaptonemal complex
The structure that facilitates the pairing of homologous chromosomes during the zygotene stage.
Nonsister chromatids
Chromatids from homologous chromosomes that are involved in the crossing over process.
Crossing over
The process during pachytene where segments of homologous chromosomes are exchanged.
Procentric
A term describing the start of pairing at the centromere during zygotene.
Proterminal
A term describing the start of pairing at the chromosome ends during zygotene.
Intermediate
A term describing the start of pairing at any other portion of the chromosome during zygotene.
Tetrad chromosome
Another term for bivalent chromosomes, referring to the paired structure of homologous chromosomes.
Meiotic spindle
The structure that begins to form during diakinesis, similar to the spindle formed during mitosis.
Nuclear membrane
The membrane that disintegrates into vesicles during diakinesis.
Telomeres
The ends of chromosomes that cluster at one end of the nucleus during the zygotene stage.
Prophase II
Chromosomes condense.
Metaphase II
Haploid number of chromosomes (dyad) align in the middle.
Anaphase II
Separation of dyad to monad (1n to 1n).
Telophase II
2 daughter cells from each of the two previous cells.
Products of Meiosis
4 haploid cells and unduplicated (monad).
Nondisjunction
Failure of sister chromatids or homologs to separate properly in meiosis I or II.
Disjunction
The normal separation of chromosomes in meiosis I or sister chromatids in meiosis II.
Trisomy
A condition resulting from nondisjunction, leading to gametes with too many chromosomes.
Monosomy
A condition resulting from nondisjunction, leading to gametes with too few chromosomes.
Down Syndrome
Trisomy of chromosome 21.
Patau Syndrome
Trisomy of chromosome 13.
Edward Syndrome
Trisomy of chromosome 18.
Klinefelter Syndrome
Extra X chromosomes in males (i.e., XXY, XXXY, XXXXY, etc.).
Turner Syndrome
Lacking one X chromosome in females (i.e., X0).
Triple X Syndrome
An extra X chromosome in females.
XYY Syndrome
An extra Y chromosome in males.
Risk of Down Syndrome
Increases after age 35; a woman aged 44 has a 40 times higher risk of conceiving a baby with Down Syndrome compared to younger women.
Reduction of ploidy
A key aspect of meiosis.
Mixing of chromosomes
Occurs on sides of metaphase in metaphase I; number of possible combinations in nuclei is 2^n where n=number of chromosome pairs.
Metaphase I
Chromosomes line up in pairs.
Daughter cell chromosomes in Meiosis I
Remain duplicated, containing sister chromatids.
Daughter cell chromosomes in Meiosis II
Are no longer duplicated (sister chromatids have separated from each other).
Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance
Genes are part of the chromosomes and that they deal with heredity.
Euchromatin
A lightly packed form of chromatin that is rich in gene concentration and is often under active transcription.
Heterochromatin
Tightly packed DNA that is transcriptionally inactive.
Centromeres
Regions of a chromosome that are heterochromatic.
Barr body
The inactivated X-chromosome in mammalian females.
Friedrich Miescher
A Swiss physician and biologist who first isolated nucleic acid from the nuclei of white blood cells.
Haploid
The basic chromosome number; 1 complete set of chromosomes.
Polyploidy
Multiple sets of chromosomes.
Tetraploid
4n; a type of polyploid with four sets of chromosomes.
Hexaploid
6n; a type of polyploid with six sets of chromosomes.
Octaploid
8n; a type of polyploid with eight sets of chromosomes.
N chromosome number
The number of chromosomes in a haploid set.
C amount of DNA
The amount of DNA (weight) in an N nucleus.